
Android is now the world’s most commonly used smartphone platform and is used by many different phone manufacturers. iOS is only used on Apple devices, such as the iPhone.
- Introduction to Android vs IOS
- Interface
- Exclusive features
- Features specific to Android include:
- Software Upgrades
- Apps Available on iOS vs. Android
- Voice Commands on Android vs. iOS
- Building and Publishing Apps for iOS vs. Android
- UI Design for Android vs. iOS 7
- The Bottomline: Choosing between iOS and Android
- Conclusion
Introduction to Android vs IOS:
Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS are operating systems primarily used in mobile technology, such as smartphones and tablets. Android, which is Linux-based and partially open source, is more PC-like than iOS, in that its interface and basic features are generally more customizable from top to bottom. However, the design elements similar to iOS are sometimes seen as being more user-friendly.
You should choose your smartphone and tablet system carefully, as switching from iOS to Android or vice versa will require you to repurchase apps in Google Play or the Apple App Store. Android is now the most widely used smartphone platform in the world and is used by many different phone manufacturers. iOS is only used on Apple devices such as the iPhone.

- Priority conversation
- Integrated device control and payment
- One time permission
- Native screen recording
- Better media control
- Better support for foldable devices
- custom widget stack
- picture in Picture
- compact phone call
- third-party default apps
- search in apps
- emoji search
- exposure lock
- QuickTake Videos
- Pinned chats in Messages
Interface:
Both iOS and Android use touch interfaces that have a lot in common – swiping, tapping, and pinch-and-zoom. Both operating systems boot to a home screen, which is similar to a computer desktop. While the iOS home screen only consists of rows of app icons, Android allows the use of widgets, which display auto-updating information such as weather and email. The iOS user interface consists of a dock where users can pin their most used applications.
A status bar runs across the top on both iOS and Android, providing information such as time, WiFi or cell signal, and battery life; The status bar on Android also shows the number of newly received emails, messages and reminders.
Here’s a comparison of some of the features of Android 11 and iOS 14. Android 11 highlights include:
iOS 14 highlights include:
To see how the current versions are – Android Marshmallow and iOS 143 -Many different manufacturers make Android phones and they often include some customization over the vanilla Android experience. Like HTC Sense or Samsung TouchWiz. Depending on your device and carrier, the apps bundled with your Android device may come pre-installed.
Exclusive features:
Features exclusive to iOS include:
iMessage: Perhaps the most popular iOS app, iMessage handles both SMS messages (when the other party is on a non-Apple platform) as well as Apple-support chat (when all participants use iMessage). Its integration with Apple Pay makes sending and receiving money via iMessage extremely easy.
Airdrop: AirDrop uses Bluetooth to share files, pictures, videos and links from iPhone to any Apple device. It is very easy to use.
Share WiFi Password: Sharing WiFi password between two iOS devices is a breeze. Just put them close together and a pop-up will pop up asking if you want to share your password.
App Offloading: iOS automatically identifies the apps you don’t use and removes them from the device. Data from apps is retained and they are reinstalled when you want to use them.
Breezy setup of new devices: Apple makes it very easy to switch from old iPhone to new iPhone. When setting up a new iPhone, importing apps, data, passwords, and settings is a breeze.
Features specific to Android include:
Customizing the Home Screen: Android offers a lot of flexibility to add widgets and customize the layout of the home screen. It also supports other apps that handle the management of the home screen.
File Management: Allows Android users to choose a file manager, and also provides access to the file system. Plugging an Android device into a PC exposes the phone’s file system as just another drive, allowing drag and drop access to transfer files between the phone and the PC.
Expandable Storage: Most Android phones come with expandable storage. While the phone may only have 32 or 64GB of storage, you can add a microSD card to expand it up to 1TB.
Multiple Users and Guest Accounts: While iOS is a single-user operating system, Android has added support for multiple users and even a guest account. This is especially useful for sharing your phone with kids or with a friend who may need it temporarily.
Split Screen: iOS only supports split screen for the iPad. Android phones also support this feature
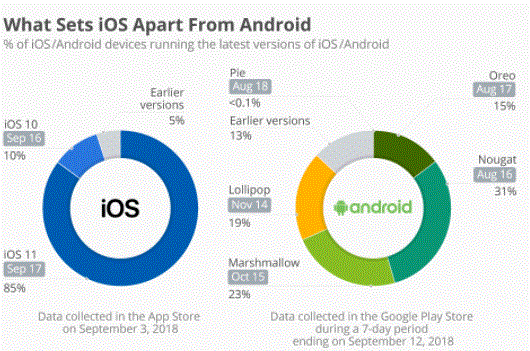
- This is one area where iOS users benefit enormously. iOS upgrades are generally available for all iOS devices. When Apple released iOS 14 in the fall of 2020, it was made available for iPhone models as old as the iPhone 6S, which was released in September 2015. Apple cites hardware capability as some older devices may not get all the new features in one go. upgrade.
- Although Google updates Android frequently, some users may find that they don’t receive updates on their phones, or even buy phones with older software. Phone manufacturers decide when and how to offer software upgrades. They may not offer an upgrade to the latest version of Android for all phones and tablets in their product range. Even when an upgrade is offered, it is usually several months after a new version of Android is released.
- Speed- With the A-series chips, which Apple designs in-house, the company has a nearly two-year lead over the best Android phones, which typically run Qualcomm’s Snapdragon series chips. The iPhone 12 easily beats both the Samsung Galaxy 20 and Google’s Pixel 5 on Geekbench 5 and 3DMark’s Wildlife Stress Test.
Software Upgrades:
- Android gets apps from Google Play, with 600,000 apps currently available, most of which will run on tablets. However, some Android devices, such as the Kindle Fire, use a separate app store with a smaller selection of apps available. Several originally iOS-only apps are now available for Android, including Instagram and Pinterest, and Google’s more open app-store means there are other specialized apps available as well, including Adobe Flash Player and BitTorrent. Android also provides access to Google-based apps, such as Youtube and Google Docs.
- The Apple App Store currently offers over 1 million apps, about 30% of which are available for the iPad. Most developers prefer to develop games for iOS before developing for Android. The list of iOS-only games is put here on Wikipedia.
- The most important thing to consider when comparing Google and Apple’s app stores are the most popular apps available for both platforms. But for tablets, there are more apps designed specifically for the iPad while Android tablet apps are often extended versions of Android smartphone apps. Developers at startups often focus on one platform (usually iOS) when they first launch their smartphone app because they don’t have the resources to serve multiple platforms from the start.
Apps Available on iOS vs. Android:

Voice Commands on Android vs. iOS:
iOS uses Siri, a voice-based virtual assistant, to understand and respond to both dictation and spoken commands. Siri includes a number of features, such as reading game scores and standings, making restaurant reservations, and finding movie times at local theaters. You can also dictate text and email, schedule calendar events, and interface with car audio and navigation.
The video below gives a quick demo of Google Now vs. Siri:
Maps
Apps like Google Maps, Waze and Bing are available for both iOS and Android. When Google released its Maps app for iOS in December 2012, the iOS version outperformed the version available for Android in terms of features, design, and ease of use. Don’t expect the Android version to lag behind. Apple’s own mapping app, which is bundled with every iOS device, was widely panned when it launched with iOS 6.
Web browsing
Android uses Google Chrome as its web-browser, while iOS uses Safari. Both the internet browsers are similar in quality and capabilities and Google Chrome is also available for iOS. Safari is not available for Android.
Facebook integration
Android is integrated with Facebook, allowing users to update their statuses or upload photos from multiple apps and pull contact data from their Facebook friends. iOS is also fully integrated with Facebook, allowing users to update their status and upload images from various apps, sync their contacts with Facebook, and automate their Facebook events to their iOS calendar. can be added. iOS now offers much deeper integration with Facebook and Twitter because of how tightly woven it is into the core apps on iOS.
Mobile payment
Android uses Google Wallet, an app that allows mobile payments. Some Android phones are equipped with an NFC chip (near-field communication) that is used to make wireless payments by tapping the phone at the checkout counter. The service is integrated with Google Wallet but not available on all Android phones or wireless carriers. Mobile payments are supported on devices that have an NFC chip (such as Samsung’s Galaxy S4 and S5), as long as they are running a version of Android newer than 4.4 KitKat.
The protection
Android’s applications are isolated from the rest of the system’s resources, unless a user specifically allows application access to other features. This makes the system less vulnerable to bugs, but developer confusion means that many apps ask for unnecessary permissions. The most widespread malware on Android is where text messages are sent to premium rate numbers without the user’s knowledge, and personal information is sent to unauthorized third parties. Since it is the more popular smartphone operating system, it is more likely to be the focus of attacks.
Building and Publishing Apps for iOS vs. Android:
Android apps are programmed using C, C++ and Java. This is an open forum; Anyone can download the Android source code and Android SDK for free. Anyone can build and distribute Android apps for free; Users are free to download apps from outside the official Google Play store. However, there is a one-time $25 registration fee for developers who wish to publish their apps (whether free or paid apps) on the official Google Play store. Apps published on Google Play are reviewed by Google. Android SDK is available for all platforms – Mac, PC and Linux.
Developers must pay $99 each year for access to the iOS SDK and the right to publish in Apple’s App Store. The iOS SDK is only available for the Mac platform.
Some app development platforms – such as Titanium Appcelerator and PhoneGap – provide a way to code once (say in JavaScript and/or HTML) and have the platform convert it into “native” code for both Android and iOS platforms.
UI Design for Android vs. iOS 7:
In Beyond Flat, SeatGeek founder Jack Groetzinger outlines a lot of the differences in how Android and iOS view their design aesthetic and what that means for app developers. for example,
Buttons: Android buttons are usually monochromatic, with a tendency to use iconography when possible. The standard iOS 7 button is plain monochromatic text with no background or border. When iOS 7 uses button borders, they are quite simple.
Navigation bar action bar: The nav bar in iOS is usually the back button linking to the previous screen. In Android, the navigation bar usually consists of several action buttons.
Intent: Intent on Android allows applications to flexibly interoperate with each other. For example, apps may “register” themselves as capable of sharing which allows a user to share using this app from another app.

The Bottomline: Choosing between iOS and Android:
To summarize the major pros and cons of Android and iOS:
iOS pros and cons
Huge app ecosystem: Distinctive advantages for tablet apps over smartphones Popular apps are generally available for both platforms.
Deeper integration with Facebook and Twitter: It is easier to post and share updates on social networks using iOS than Android because of how deeply these platforms are integrated with iOS.
Interface is closed: limited customization options for the home screen; Only rows of app icons are allowed. No third-party applications pre-installed by the wireless carrier. Users can only install apps from the App Store
Software upgrade: Apple offers software upgrades for all devices that have hardware capable of handling the new software. This means that the devices remain operational with software features for at least two to three years.
Improved Privacy Controls: iOS provides better control over which apps have access to users’ private information such as contacts and location.
Android pros and cons:
Extensive Hardware Selection: There are a huge number of Android devices available at different price points with different hardware capabilities, screen sizes and features.
Highly Customizable User Experience: The home screen can be customized with not only app icons but widgets that allow the user to stay connected or stay informed. Other examples include SwiftKey, which modifies your Android smartphone’s keyboard, and apps that emulate older gaming consoles. Google has fewer restrictions than Apple on what types of apps it allows in its Play Store. In addition, you can choose to install Android apps from places other than the Google Play store.

Conclusion:
iOS is a mobile operating system provided by Apple Corporation. It is primarily designed for Apple mobile devices such as the iPhone and iPod Touch. It was earlier known as iPhone OS. It is a Unix-like operating system based on the Darwin (BSD) operating system. It is the second most used mobile operating system in the world after Android. It is mainly written in C, C++, Objective-C, Assembly Language and Swift. The first version of iOS was launched in 2007.
Android is a mobile operating system provided by Google LLC. It is based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open source software. It is specifically designed for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. It was developed using C, Java, C++ and other languages. The first version of Android was launched by Google in 2008. The latest stable version of Android is Android 10. It is provided completely free of cost. It is the most commonly used operating system overall.


