
- India’s EV Revolution Accelerates
- Tata Motors
- Mahindra Electric
- Ather Energy
- Ola Electric
- Hero Electric
- Ashok Leyland EVs
- MG Motors India
- Hyundai and Kia EVs
- Startups in EV Sector
- Government Support
- Future Projections
India’s EV Revolution Accelerates
India’s electric vehicle (EV) revolution is gaining momentum, supported by evolving technologies, government incentives, and a growing demand for cleaner transportation. With increasing concerns about air pollution, fuel dependency, and sustainability, both established automotive giants and agile startups are investing heavily in EVs. The Indian EV ecosystem, supported by Artificial Intelligence Training is no longer limited to a few experimental models; it now spans electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, passenger cars, buses, and commercial vehicles. This transformation is being spearheaded by a mix of traditional manufacturers, new-age innovators, and active policy support from the government. The electric vehicle (EV) revolution in India is speeding up at a never-before-seen rate because to developing technologies, encouraging government regulations, and growing consumer demand for greener, more sustainable modes of transportation. Both well-established automakers and creative entrepreneurs have made significant investments in the EV industry because to growing worries about air pollution, reliance on fossil fuels, and climate change.
Tata Motors
Tata Motors has emerged as a frontrunner in the Indian EV segment. Its portfolio includes models like the Nexon EV, Tigor EV, and the recently launched Punch EV, while also drawing insights from innovations in Tesla Battery Technology . Tata’s success lies in its strategic integration of in-house battery technology, a growing network of charging infrastructure, and strong brand trust.
- Key Highlights:
- Tata Nexon EV is India’s best-selling electric SUV.
- Launched the Gen-2 Ziptron technology platform for improved range and efficiency.
- Plans to introduce 10 new electric models by 2025.
- Partnering with Tata Power to develop EV charging networks across cities and highways.
Tata’s investments in battery packs and power electronics manufacturing are enabling it to scale efficiently and meet domestic demand.
Mahindra Electric
In India, Mahindra Electric, a division of the Mahindra Group, has led the way in the development of electric vehicles. The XUV400 and other more recent models were made possible by the company’s early models, such as the e2o and eVerito. In addition to focusing heavily on electric three-wheelers and last-mile transportation solutions, Hacking from Scratch techniques are being explored to optimize system efficiency and innovation. Mahindra Electric has formed strategic alliances with major international players such as Volkswagen to create cutting-edge EV platforms.
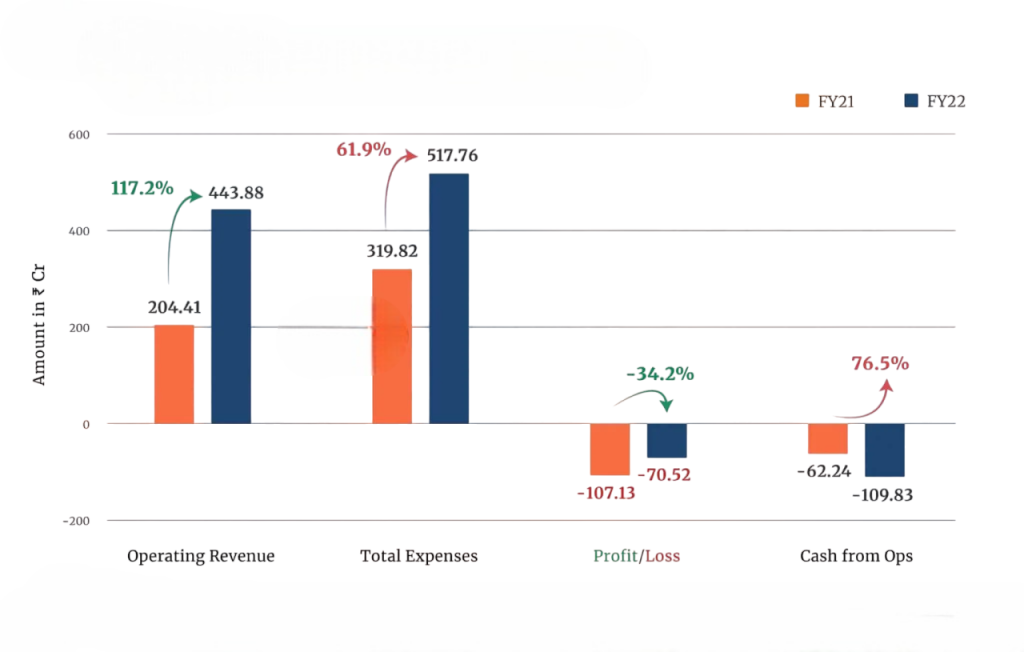
In keeping with its long-term commitment to sustainable mobility, the corporation intends to invest more than ₹10,000 crores in its EV business. Mahindra is also working on the Born Electric platform, which will serve as the foundation for its upcoming SUV models. Mahindra Electric has established itself as a diverse and significant participant in India’s EV ecosystem by concentrating on both personal mobility and fleet applications.
Ready to Get Certified in Artificial Intelligence ? Explore the Program Now Artificial Intelligence Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Ather Energy
Bengaluru-based Ather Energy has revolutionized the electric two-wheeler space in India. Its flagship models, Ather 450X and 450S, are known for advanced features, connectivity, and performance.
- Notable Achievements:
- Ather Grid: A fast-growing public charging network with over 1,500 charging points.
- Proprietary software stack with OTA (Over-The-Air) updates.
- Backed by major investors like Hero MotoCorp.
- Expanding manufacturing capacity to 420,000 units annually.
With a focus on premium user experience and ecosystem building, Ather continues to be a trendsetter in urban electric mobility, leveraging EV Battery Technology to enhance performance and reliability.
Ola Electric
Ola Electric, a subsidiary of the ride-hailing giant Ola, has rapidly scaled to become a dominant player in the electric scooter segment. It launched the S1 and S1 Pro models to great market enthusiasm.
- Key Moves:
- Built the world’s largest two-wheeler factory (FutureFactory) in Tamil Nadu.
- Vertical integration of battery cells, motor, and software.
- Plans to launch electric motorcycles and cars, along with expanding Electric Vehicle Charging infrastructure to support them.
- Introducing fast-charging networks through ‘Hypercharger’ stations.
- Over 1 million electric scooters sold to date.
- Partnered with multiple startups to boost battery swapping infrastructure.
- Focus on localization to bring down manufacturing costs.
- Nationwide dealer and service network presence.
- Deployed electric buses in multiple Indian cities.
- Developed modular EV platforms for buses and last-mile delivery, integrated with EV Charging Stations and Hubs in India.
- Manufacturing hubs in India and the UK.
- Targeting both domestic and export markets for electric commercial vehicles.
- MG ZS EV is among the top-selling electric cars in India.
- Planning to launch a mass-market EV below ₹15 lakhs.
- Collaborating with Tata Power and other partners for charging infrastructure, including advanced Controller in EV systems.
- Introducing AI-based connected features and smart energy solutions.
- Hyundai Ioniq 5 won accolades for design and performance.
- Investing ₹4000 crores to localize EV manufacturing in India as part of initiatives in EV Projects and Systems .
- Developing India-specific EVs for mass-market adoption.
- Kia aims to launch affordable EVs under ₹20 lakhs by 2025.
Ola’s aggressive expansion strategy and focus on affordability and innovation are driving massive adoption, especially among urban youth.
To Explore Artificial Intelligence in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Hero Electric
Hero Electric, one of India’s oldest EV manufacturers, has a vast lineup of electric scooters aimed at affordability and practicality. Unlike premium-focused brands, Hero Electric targets middle-income users and rural mobility.
- Major Highlights:
Its strategy of being a mass-market EV player, supported by Artificial Intelligence Training positions it uniquely in tier 2 and tier 3 cities where cost sensitivity is higher.
Ashok Leyland EVs
Ashok Leyland, a commercial vehicle giant, is playing a significant role in electrifying public transport and logistics. Through its subsidiary Switch Mobility, it is developing electric buses and light commercial vehicles.
- Initiatives and Progress:
Ashok Leyland’s entry into electric mobility aligns with government efforts to electrify public transportation.
MG Motors India
MG Motors, though relatively new to the Indian market, has gained attention with its electric SUV the MG ZS EV. The company brings global expertise and premium features into its EV offerings.
- Progress Report:
MG’s focus is on premium, tech-savvy customers who demand comfort and innovation in electric mobility.
Hyundai and Kia EVs
Hyundai was one of the first international automakers to bring electric cars to India, with its Kona Electric. Kia, its sister brand, has also entered the segment with the EV6 and future plans for budget EVs.
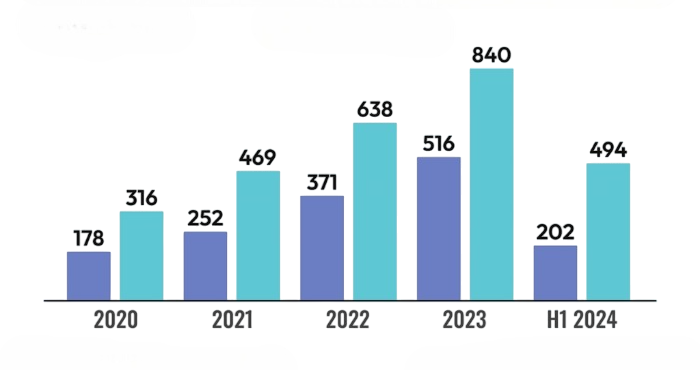
- Updates and Vision:
Their long-term goal is to capture a significant market share through a mix of global technology and localized solutions.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Artificial Intelligence Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Startups in EV Sector
India’s electric car industry is growing and innovating thanks to a number of startups as well as well-known OEMs. While Yulu provides electric bike-sharing services in cities to address last-mile mobility issues, Revolt Motors is concentrating on AI-enabled electric motorcycles in the context of EV vs Fuel Vehicle comparisons. Euler Motors is producing electric three-wheelers for commercial and transport uses, while Simple Energy is creating high-range electric scooters. In addition to developing cutting-edge car designs, these businesses are investigating solutions like shared mobility, fleet management, and battery swapping. They frequently focus on particular issues like urban congestion and effective last-mile deliveries.
Preparing for Artificial Intelligence Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Government Support
Through a number of laws and incentives, the Indian government has significantly accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles. While the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) programme offers financial assistance to battery and vehicle producers, The FAME II programme offers subsidies for electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and buses, highlighting the Electric Vehicle Working Principle . EVs also enjoy a lower GST rate of only 5%, as opposed to 28% for cars with traditional internal combustion engines. Delhi, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu are just a few of the states that have implemented their own EV laws, including incentives such as free registration and subsidies. By encouraging the construction of the required charging infrastructure and lowering the overall cost of ownership for EVs, these government-backed programmes are fostering an environment that is conducive to India’s aspirations for electric mobility.
Future Projections
India’s electric vehicle market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 40% in the coming decade. By 2030, EVs could make up as much as 70% of all new two-wheeler sales, 30% of private car sales, 40% of buses, and 80% of three-wheelers. This rapid growth will be driven by rising fuel costs, increasing environmental concerns, technological advancements in batteries and drivetrains, improved charging infrastructure, and the availability of more affordable Electric Vehicle Parts and EV models. With continued investment from both the public and private sectors, along with supportive government policies, India is well-positioned to emerge as a global hub for electric mobility.
Summary
The Indian EV landscape is vibrant and rapidly evolving. From legacy automakers like Tata and Mahindra to agile startups and international giants, every stakeholder is playing a crucial role in this transition. Government support, consumer awareness, continuous innovation, and Artificial Intelligence Training are propelling India toward an electric future. As the ecosystem matures, India could not only meet its domestic clean mobility goals but also emerge as a significant exporter of EV technology and products.




