
Information Security Management (ISM) ensures confidentiality, authenticity, non-repudiation, integrity, and availability of organization data and IT services. It also ensures reasonable use of organization’s information resources and appropriate management of information security risks.
The Information Security Manager is the process owner of this process.
Information security is considered to be met when −
- Information is observed or disclosed on only authorized persons
- Information is complete, accurate and protected against unauthorized access (integrity)
- Information is available and usable when required, and the systems providing the information resist attack and recover from or prevent failures (availability)
- Business transaction as well information exchanges between enterprises, or with partners, can be trusted (authenticity and non-repudiation)
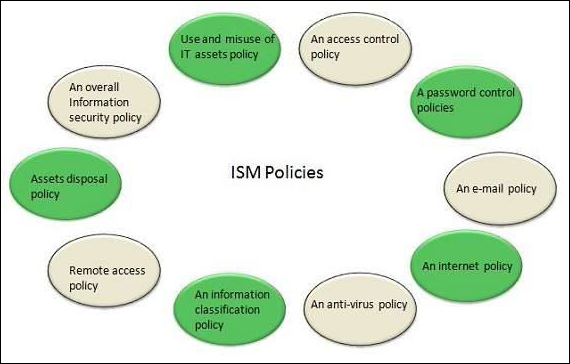
ISM Security Policy
It is required for ISM security policies cover all areas of security, be appropriate, meet the needs of business and should include the policies shown in the following diagram −
ISM Framework
ISM Process
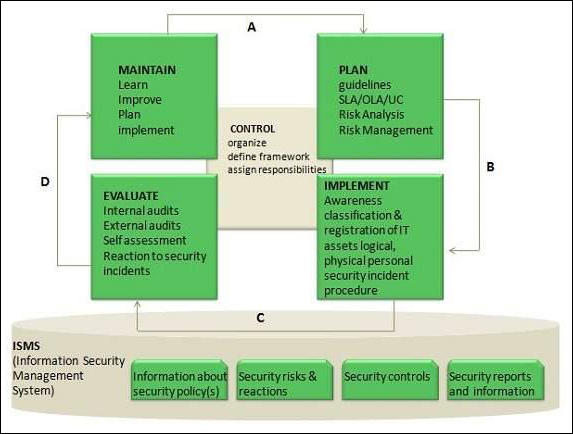
The following diagram shows the entire process of Information Security Management (ISM) −
Key elements in ISM Framework
ISM framework involves the following key elements −
Control
The objective of Control element is to −
- Establish an organization structure to prepare, approve and implement the information security policy
- Allocate responsibilities
- Establish and control documentation
Plan
The purpose of this element is to devise and recommend the appropriate security measures, based on an understanding of the requirements of the organization.
Implement
This key element ensures that appropriate procedures, tools and controls are in place to underpin the security policy.
Evaluation
The objective of Evaluation element is to −
- Carry out regular audits of the technical security of IT systems
- Supervise and check compliance with security policy and security requirements in SLAs and OLAs
Maintain
The objective of Maintain element is to −
- Improve on security agreements as specified in, for example, SLAs and OLAs
- Improve the implementation of security measures and controls
Preventive
This key element ensures prevention from security incidents to occur. Measures such as control of access rights, authorization, identification, and authentication and access control are required for this preventive security measures to be effective.
Reductive
It deals with minimizing any possible damage that may occur.
Detective
It is important to detect any security incident as soon as possible.
Repressive
This measure is used to counteract any repetition of security incident.
Corrective
This measure ensures damage is repaired as far as possible.
What is the need of information security?
We need information security to reduce the risk of unauthorized information disclosure, modification, and destruction. We need information security to reduce risk to a level that is acceptable to the business (management). We need information security to improve the way we do business.
Advantages of Information Security:
- Information security is extremely easy to utilize. For protection of less sensitive material users can simply password protect files. For the more sensitive material users can install biometric scanners, firewalls, or detection systems.
- As technology increases so will the crimes associated with it. Making the use of information security very worth while.
- It keeps vital private information out of the wrong hands.
- For the government it keeps top secret information and cabalities out of terrorist and enemy nation’s hands.
- Information security protects users valuable information both while in use and while it is being stored.
Disadvantages of Information Security:
- Technology is always changing so users must always purchase upgraded information security.
- Since technology is always changing nothing will ever be completely secure.
- If a user misses one single area that should be protected the whole system could be compromised.
- It can be extremely complicated and users might not totally understand what they are dealing with.
- It can slow down productivity if a user is constantly having to enter passwords.
Installing and Configuring Security Controls when Performing Account Management

Let’s recall the basic concept covered in the previous lesson, where we discussed the need to reveal the users’ identity along with the proof for authentication to access a network as well as authorization to access the desired resources.
The important question that we should consider is whether these measures are sufficient to ensure complete security? Let’s examine a few situations where a security breach can occur.
- A user cannot log in because he or she has forgotten the password. The security will be breached if the solution to this issue is to write down passwords on paper. Even if you give forgot password option, it is possible for the users to try one of the previously used passwords or some very easy to remember secret phrase such as birth date or name.
- A user sticks to only a single password for months, which increases the risk of password cracking.
- An intruder tries to log in by entering a genuine user’s username and password repeatedly and succeeds in doing so.
- An administrator performs both administrative and reviewing tasks using just a single set of credentials, which can lead to security compromise.
- Two or more users share a single guest account for accessing common resources such as a network printer.
- Credentials of a user who has left the company is still being accepted for logging onto the internal network. Examining the above scenarios, it is evident that the authentication and authorization are not enough to ensure 100% security. As a system administrator, you will have to take more actions by managing user accounts or credentials. This is perhaps in the form of user account policies for dictating credential or account usage rules or best practices. The access levels of users have a direct impact on the level of network protection. Although it may sound a bit odd that the network needs protection from its own users, it is also a fact that these internal users have maximum rights and privileges, sufficient to disrupt deliberately or misuse its resources even accidentally. Upon logon, by revealing a rule or statement that the access is granted to users if a few conditions are fulfilled or that their activities are monitored will help in following security policy protocols or policies and obtain legal ramifications for non-compliance. So, let us begin this lesson by exploring the best practices or polices for managing user accounts, which all users must agree upon after a fair discussion and understanding of their benefits.
The following screen explains the objectives covered in this lesson. After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Mitigate issues associated with users who have multiple accounts/roles and/or shared accounts.
- Enforce different account policy settings for securing the systems.
- Apply privileges to groups and individual users for access control monitoring, and
- Describe the significance of reviewing and continuous monitoring of what the user actually accesses through the system.
CONCLUSION:
All the information required by ISM should be contained within the SMIS (Security Management Information System). This should include all security controls, risks, breaches, processes and reports necessary to support and maintain the Information Security Policy and the ISMS. This information should cover all IT services and components and needs to be integrated and maintained in alignment with all other IT information management systems, particularly the Service Portfolio and the CMS. The SMIS will also provide the input to security audits and reviews and to the continual improvement activities so important to all ISMSs. The SMIS will also provide invaluable input to the design of new systems and services.





