
A blockchain, originally block chain, is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. … By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way”.
1. What is the principle on which blockchain technology is based on?
Ans: It enables the information to be distributed among the users without being copied.
2. Why is Blockchain a trusted approach?
Ans:
- Blockchain can be trusted due to so many reasons.
- Its compatibility with other business applications due to its open-source nature.
- Its security. As it was meant for online transactions, the developers have paid special attention to keeping up the pace when it comes to its security.
- It really doesn’t matter what type of business one owns, Blockchain can easily be considered.
3. Name the two types of records that are present in the blockchain database?
Ans: These records are block records and transactional records. Both these records can easily be accessed, and the best thing is, it is possible to integrate them with each other without following the complex algorithms.
4. In Blockchain, blocks are linked in what series?
Ans: In Blockchain Blocks are arranged within the Backward to the previous block series.
5. How does a block is recognized in the Blockchain approach?
Ans: Every block in this online ledger basically consists of a hash pointer which acts as a link to the block which is prior to it, transaction data and in fact a stamp of time.
6. Is it possible to modify the data once it is written in a block?
Ans: No, it’s not possible to do so. In case any modification is required, the organization simply has to erase the information from all other blocks too. It is because of no other reason than this, data must be given the extreme care of while using this approach.
7. What are Block Identifiers?
Ans: In Blockchain, blocks can be identified by the block header hash and the block height.
8. Is it possible in Blockchain to remove one or more block from the networks?
Ans: Yes, it can be done. There are times when only a specific portion of this online ledger is to be considered. With the help of default options and filters, this can easily be done without making a lot of efforts.
9. What exactly do you know about the security of a block?
Ans: Well, a block or the entire blockchain is protected by a strong cryptographic hash algorithm. Each block has a unique hash pointer. Any modification in the block constituents will result in the change in the hash identifier of the block. Therefore, it offers an excellent level of security. Thus, one needs not to worry about the safety as well as the security of data that is present in a block.
10. What is a ledger? Is Blockchain an incorruptible ledger?
Ans: Blockchain is considered incorruptible. Any ill-intentioned individual acting alone is powerless. “To take over the network, an attacker would have to control more than 50 percent of its total computing power,” Augier explains. “We hope that’s a theoretical scenario, but we can’t be sure. Should it happen, the individual would take every precaution to avoid being noticed.” Not to mention the energy required to power the computers needed for the blockchain system to work.
11. How is a blockchain ledger different from an ordinary one?
Ans: The first and in fact the prime difference is Blockchain is a digital ledger that can be decentralized very easily. The chances of error in this approach are far less than that in an ordinary ledger. An ordinary ledger is what that is prepared by hands or by human efforts while the Blockchain performs all its tasks automatically. You just need to configure it in a proper manner and by following all the guidelines.
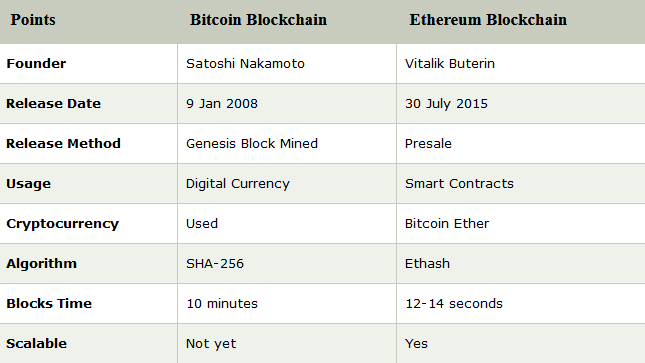
12. What is the difference between Bitcoin blockchain and Ethereum blockchain?
Ans: We can see the basic differences between Bitcoin blockchain and Ethereum blockchain in the below table.
13. A distributed digital ledger is used for recording transaction in Blockchain. What does the system rely on?
Ans: The system relies on the network servicing protocol and the nodes of the network.
14. Name some popular platforms for developing blockchain applications
Ans: After the development of bitcoin, various blockchain platforms started coming up. Ethereum came right after the evolution of Bitcoins, and is one of the popular public platforms for building Blockchain based applications.
Then there is a Hyperledger community for building enterprise-based solutions. Also, Qtum, IOTA, EOS are some of the widely used platforms for building Blockchain.
15. What is Double Spending? Is it possible to double spend in a Blockchain system?
Ans: It’s a condition when one digital token is spent multiple times because the token generally consists of a digital file that can easily be cloned. It simply leads to inflation and organizations must bear a huge loss. One of the primary aims of Blockchain technology is to eliminate this approach up to the possible extent.
Blockchain prevents double spending by confirming a transaction by multiple parties before the actual transaction is written to the ledger. It’s no exaggeration to say that the entirety of bitcoin’s system of Blockchain, mining, proof of work, difficulty etc, exist to produce this history of transactions that is computationally impractical to modify.
16. Each block of a Blockchain consists of which of the following?
A hash pointer to the previous block
Timestamp
List of transactions
Ans: All of the above
17. Which of the following is the first distributed blockchain implementation?
Ans: Bitcoin
Ethereum
18. Bitcoin is based on ________ blockchain?
Private
Ans: Public
Public Permissioned
Permissioned
19. Blockchain can be stored as which of the following?
A flat file
A Database
Ans: Both of the above
None of the above
19. In blockchain, blocks are linked ________?
Ans: Backward to the previous block
Forward to next block
Not linked with each other
20. The primary benefit of immutability is…
Scalability
Improved Security
Tamper Proof
Ans: Increased Efficiency
21. Hash identifying each block in the Blockchain is generated using which of the following cryptographic algorithms?
SHA128
Ans: SHA256
22. A block in the blockchain can never have more than one parent block?
Ans: True
False
23. Blockchain forks can result in which of the following?
Multiple parent blocks
Ans: Multiple children blocks
24. Which of the following is an asymmetric encryption Algorithm?
Blowfish
Twofish
Ans: RSA
Triple DEA
25. Explain the significance of blind signature and how it is useful?
Ans: It is a form of digital signature in which the content of a message is disguised (blinded) before it is signed. The resulting blind signature can be publicly verified against the original, unblinded message in the manner of a regular digital signature.
Blind signatures are typically employed in privacy-related protocols where the signer and message author are different parties. Examples include cryptographic election systems and digital cash schemes.
26. What is Secret Sharing? Does it have any benefit in Blockchain technology?
Ans: It is a well-known fact that security matters a lot in digital transactions. Secret sharing is an approach meant for the same. In Blockchain technology it is an approach that divides secret or personal information into different units and sent them to the users on the network.
The original information can only be combined when a participant to whom a share of the secret is allocated agrees to combine them together with others. There are several security-related benefits it can offer in Blockchain technology.
27. Can you explain what are off-chain transactions?
Ans: An off-chain transaction is the movement of value outside of the blockchain. While an on-chain transaction – usually referred to as simply ‘a transaction’ – modifies the blockchain and depends on the blockchain to determine its validity an off-chain transaction relies on other methods to record and validate the transaction.
28. What exactly do you know about executive accounting? Does Blockchain support the same?
Ans: Executive accounting is nothing but a special type of accounting which is designed exclusively for a business that offers services to the people. There is no strict upper limit on services and a business can manage any through the executive accounting. Blockchain has algorithms that are specially meant to handle executive accounting. In fact, it cut down many problems that are associated with the same.
29. What are the threats to the information you are familiar with?
Ans: There are lots of threats to information in the present scenario. Due to increase in online transactions over the internet, many hackers have become active and are adopting new approaches to hack information and servers that contain financial information.
The major threat is software attack, identity theft, information extortion, as well as sabotage. In addition to this, Trojan horses, worms, and viruses are other trouble creators.
30. How will you handle the risk management when it comes to securing the transactions records?
Ans: It is basically a process of finding the threats and all the vulnerabilities to the financial records of an organization. The best thing that can be done with this approach is to take the right countermeasures against them immediately.
Another approach is to pay attention to a backup plan. Based on the value of information, more approaches such as buying new risk management software can simply be considered. The prime risk to information is from black-hat hackers.
31. What is 51% attack?
Ans: 51% Attack refers to a situation where a group of miners who hold more than 50% of the Network Hash Rate could manipulate with the New transactions (Stopping the transactions to proceed or gaining conformations) or able to reverse the transactions that were recently confirmed and kind of doing Double spend. It is Highly unlikely to be able to do that today but it is possible.
32. What challenges information leak can impose on an organization?
Ans: An information leak can cut down the reputation of an organization up to an excellent extent. In addition to this, it can be the reason for organizations bearing huge losses. Many organizations who fail to implement security protocols to keep their data secure have already lost the trust of their customers and are struggling very hard to get the same reputation again. The overall profits of any organization can reduce up to 80% if no attention is paid to the online transaction security.
33. What is information processing according to you? What are the key challenges that are associated with it?
Ans: The information is often shared on a network. Before actually transmitting it over a network, it needs to be changed into formats that can fit the standards of the channels (the channel is a link between the sender and a receiver).
The work done to convert the information at both sender and receiver end is generally regarded as information processing. The biggest challenge to information processing is securing it during that time. Another challenge is processing bulk information can impose a limit on performance.
34. Name organizations that can use Blockchain technology?
Ans: There is no strict upper limit on the category of business who can consider this approach. The fact is almost all the businesses are engaged in online or financial transactions that they need to make to run the processes smoothly. Large-scale corporations, financial institutions, private businesses, government departments and even defense organizations can trust this technology very easily.
35. What are the core requirements for a Business Blockchain?
Ans: A business blockchain requires a shared ledger, smart contract functionality, privacy and trust.
36. What are the key principles in Blockchain that are helpful in eliminating the security threats that need to be followed?
Ans: Yes, there are a few principles that need to be followed with respect to time. They are:
1.Auditing
2.Securing applications
3. Securing testing and similar approaches
4. Database security
5. Continuity planning
6. Digital workforce training
All these principles are basic and are easy to implement. They are helpful in making the transactions records useful.
37. What is a security policy?
Ans: A security policy defines what exactly needs to be secured on a system. It bounds a network user under some core protocols that they all must agree and follow to enhance the overall security. When it comes to information or financial records of an organization, multiple security policies are implemented than just one.
38. Is the Blockchain Different from Banking Ledgers?
Ans: Banks and accounting systems use ledgers to track and timestamp transactions. The difference is that the blockchain is completely decentralized and an open source. This means that people do not have to rely on or trust the central bank to keep track of the transactions. The peer-to-peer blockchain technology can keep track of all the transactions without the fear of having them erased or lost.
Furthermore, the blockchain, because of its open-source nature, is more versatile and programmable than central banking ledgers. If programmers need new functionality on the blockchain, they can simply innovate on top of already existing software through consensus. This is difficult for central banks because of all of their regulations and central points of failure.
39. Can you list some of the popular consensus algorithms? Why we need different consensus mechanisms?
Ans: Some of the popular consensus algorithms are:
- PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance)
- Proof-of-work
- Proof-of-stake
- Delegated proof-of-stake
- Proof-of-elapsed time
Now, the possible reasons why we need consensus mechanism more than “proof-of-work” are”
- Different business needs
- Different use cases
- Also:
- Cryptography/Strength of Algorithm
- Regulation requirements
- Implementation
- Performance
- Tokenization
- Security
- Privacy
40. Are there any network specific conditions for using Blockchain technology in an organization?
Ans: There is no specific condition of using it. However, the network must be a peer-to-peer network under the concerned protocols. It validates the new block simply and helps organizations to keep up the pace in this matter without investing in third-party applications.
41. Name the steps that are involved in the Blockchain project implementation?
Ans: Well, there are total six steps involved in this process and they are:
- Requirement identification
- Screen ideas consideration
- Project development for Blockchain
- Feasible study on the security
- Implementation
- Controlling and monitoring the project
42. Where is a blockchain stored?
Ans: The blockchain can be either stored as a flat file or as a database.
43. What are the different types of Blockchains?
Ans: There are mainly three types of Blockchains introduced to the world.
1. Public Blockchain
Ans: A Public blockchain is a kind of blockchain which is “for the people, by the people, and of the people.” There is no in-charge it means anyone can read, write, and audit the blockchain. It is an open-source, distributed, and decentralizes public ledger so anyone can review anything on a public blockchain. They are considered to be Permissionless blockchain.
2. Private Blockchain
Ans: A Private blockchain is a private property of an individual or an organization. It is controlled by a single organization that determines who can read it, submit the transaction to it, and who can participate in the consensus process. They are considered to be permissioned blockchain.
3. Consortium Blockchain or Federated Blockchain
Ans: In this blockchain, the consensus process is controlled by a pre-selected group, i.e., group of companies or representative individuals. This pre-selected group is coming together and making decisions for the best benefit of the whole network. Such groups are also called consortiums or a federation that’s why the name consortium or federated blockchain.
Both the records can easily be accessed and can integrate with each other without following any complex algorithm.
44. List the key features of blockchain?
Ans: The essential properties of a blockchain are:
- Decentralized Systems
- Distributed ledger
- Safer & Secure Ecosystem
- Fast
- Low Transaction Fees
- Fault-Tolerant
- Minting
45. Name some popular platforms for developing blockchain applications.
Ans: Some of the popular platforms for developing blockchain are:
- Ethereum
- Hyperledger Sawtooth
- Quorum
- Ripple
- R3 Corda
- Qtum
- IOTA
- EOS
46. Is it true that a block in the blockchain can never have more than one parent block?
Ans: Yes, it’s true that Blockchain can never have a parent Block. Each and each block is independent in Blockchain
47. What are the main blockchain features?
Ans: Blockchain has a lot of features. The main features are as below.
- Security: Blockchain provides unparalleled security
- Immutability: Data once written cannot be changed or altered.
- Fast: Blockchain offers quick transactions
- Decentralized: Any centralized authority or entity do not control it
- Fault tolerant: Blockchain networks are fault tolerant.
- Low transaction fees: No need for the third party makes it cheaper and more effective
- Minting: Provides coin minting by various methods.
48. What is a block in blockchain technology?
Ans: Blocks are the storage unit of the blockchain. They are fundamental to the network, and the transactions data is stored within them. They can be seen as books with each page equivalent to a transaction. Blocks are immutable. This means if a data is recorded, it can not be changed or deleted. Also, blocks are organized linearly in a blockchain.
A block is mined by a miner which acts as a way to verify the transaction. This means that until a transaction is not mined, it will not be shown on the blockchain and the transaction will be deemed incomplete.
49. What makes blocks unique?
Ans: Each block has its own value attached to it. They can be identified with the help of block height and block header hash value.
50. How does the security of a block work?
Ans: A block is the most secure part of a blockchain. A cryptographic hash algorithm protects it. The block also consists of a distinctive hash pointer which adds more security to the block. If the value within a block is changed, the hash value will also change. This is a security identifier and provides a reasonable level of security to the whole blockchain. Also, hackers need to know the hash key of the previous block even to attempt to make changes to the block information.
51. What are the types of blockchain? Explain the types in short
Ans: There are three types of the blockchain.
- Private: Private blockchain works in a closed ecosystem and is set to permissioned. This means that no outsider can join or know the activities within the private blockchain.
- Public: Public blockchain works in an open ecosystem where anyone can join and do transactions.
- Consortium: Consortium blockchain is semi-decentralized in nature.
52. What is the difference between private and public blockchain?
Ans: The basic difference between private and public blockchain is how they operate. The private blockchain is based on a closed ecosystem and hence is controlled in a certain way. Public blockchain are open to everyone.
53. What’s the difference between blockchain and centralized network?
Ans: The main difference between a centralized network and blockchain is how they are controlled. The blockchain is completely decentralized and doesn’t require a central authority. Inadvertently, it also brings benefits to blockchain such as trust, transparency, immutability and so on.
54. What is a cryptocurrency?
Ans: Cryptocurrency is a digital currency that works without any centralized control. Cryptocurrency powers a lot of blockchain networks out there. They are also known as virtual currencies and differ from the likes of fiat currencies. For example, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin are examples of cryptocurrencies.
55. Discuss the role of encryption in blockchain?
Ans: Encryption is an age-old technique to protect data from third parties or leak. It is the basics of data security in the modern world. Blockchain also utilizes encryption to good effect. The data before it is sent off to the receiver is encrypted. The receiver will only be able to unlock it as it is only meant for him. Once the receiver receives it, it is unencrypted and can be used as liked.
Blockchain also uses encryption in other ways. Also, modern blockchain solutions tend to improve encryption and provide complete privacy based experience for users.
56. How secure is blockchain? Have they even been hacked?
Ans: The blockchain is comparatively secure when compared to other similar technologies right now. However, they are not completely secure as it is vulnerable to a 51% attack. A 51% attack is a way by which a group of miners or organizations gains access to more than 50% of the networking computer power. Once done, they can easily take control and alter transactions in the network which can lead to asset theft and data alteration.
Blockchain platforms are also prone to another form of human errors. The most prominent example is the ETC-ETH fork that happened because a coder deleted some ethereum smart contract code which leads to ETH lock. It became inaccessible which led to a hard fork in the blockchain.
The 51% attack is theoretically possible but is hardly carried out in the real world as it would require huge computational processing power.
57. Why is blockchain more trustworthy?
Ans: The blockchain is trustworthy because of many reasons. The first reason is the security that blockchain offers. It is the most secure technology solution right now. Next, it is entirely decentralized. This removes the need for a centralized entity and the risks associated with it.
The last feature that makes blockchain more trustworthy is immutability. Data once stored cannot be changed.
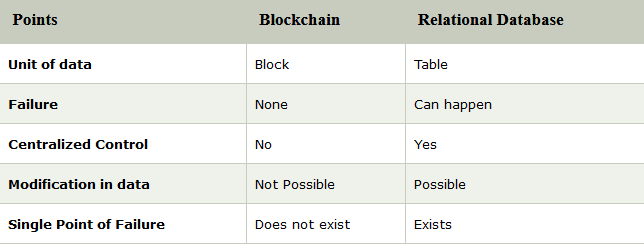
58. How does Blockchain differ from relational databases?
Ans:
The blockchain differs from the relational database in the following ways.
59. What are the Merkle trees? Are they important?
Ans: Merkle trees is a data structure that is used in cryptography. It is also known as the hash tree. Technically, in the tree, every leaf node is designated with the hash of the data block. The non-leaf node on the other hand stores the cryptographic hash of the child nodes. Hash trees are incredibly efficient in terms of performance and can be used to verify large data structure.
For example, it is not required to transfer the whole block to verify a block.
60. What is the difference between the standard ledger and a blockchain ledger?
Ans: The biggest difference between these two types of ledger is the decentralization that they have to offer. Blockchain ledger is decentralized which means that it offers unique capabilities such as trust, immutability, transparency, and security. Standard ledger does carry these features but is limited to certain extent.
As humans create, modify and monitor the standard ledger, there is always a chance of an error creeping in or worse a security breach. Blockchain ledger solves all the problems that standard ledger have by providing a decentralized version.
61. What type of records blockchain supports? Is there any restriction for record keeping?
Ans: The blockchain supports has no parity when it comes to recording data or records of any type. This means that blockchain can have multiple use cases for different industries and verticals. Anyone from startups to industries running supply chain management can use blockchain to store data and utilize the power of blockchain to their advantage.
Some of the examples of blockchain records include the following.
- Medical records
- Supply chain management records
- Employee records
- Transaction/eCommerce records
- Management records
- Documentation
- Music records
And so on.
62. What are the key elements of the blockchain ecosystem? Explain each of them briefly.
Ans: The blockchain has four key elements. They are as follows.
- Shared ledger
- Node application
- Virtual Machine
- Consensus Algorithm
Shared Ledger: Shared ledger is the logical component of a blockchain. It is decentralized in nature.
Node Application: A node application is a software/solution that lets a computer connect with the blockchain. For example, Bitcoin uses a Bitcoin wallet application to identify each node on the network.
Virtual Machine: The virtual machine handles all the tasks that a blockchain undertakes. It is part of the node application and provides an environment where instructions can run.
Consensus Algorithm: The Consensus algorithm is used to set the blockchain rules by which every node can come to a conclusion. There are different consensus algorithms used in the blockchain.
63. What is a Shared ledger? Explain in detail.
Ans: A Shared ledger is the data structure that is stored in a blockchain’s node application. It holds the content of the blockchain and ensures that every node can have access to it. Shared ledger is distributed in nature.
One of the good examples includes the Ethereum client where it has a ledger that interacts with other components such as payments, smart contracts etc. Each blockchain has its own way of managing its shared ledger keeping the basics intact.
64. What is Node Application? Explain in detail
Ans: Node application is a computer application that a computer needs to be part of the ecosystem. Without the node application, it is not possible for a device to participate in blockchain activity.
There are different node applications when it comes to the blockchain. Bitcoin, for example, uses the Bitcoin wallet application to make a computer compatible with the blockchain.
Technically, there is a service overlay network(SON) that interfaces between the blockchain and the computer. The computer needs to use the node application to read and reply in a specific manner,
Not all node applications are free from restriction. Some blockchains are stick when allowing a node to join the application. It needs permission to do so.
65. What is a Virtual Machine? Explain in detail
Ans: Virtual Machine runs as a part of a node computer. It is a virtual state of a machine that mimics a real machine. It is imaginary and provides certain functionalities in a pre-defined state. Virtual machines also work and don’t have to rely on the host computer or machine. The key point here is abstraction which is used to provide an operating environment for an application or service to work.
All the blockchain have their virtual machines. They are designed and work differently. For example, VM used by Bitcoin and Ethereum are different. Ethereum virtual machines are also more advanced than Bitcoin. It can stay on an Ethereum node and interact with smart contracts.
66. What is Consensus Algorithm?
Ans: Consensus algorithm is also a part of node application. It is used to reach a consensus in the ecosystem. There is no single way to achieve consensus, and that’s why different blockchain environments use different consensus methods. Bitcoin, for example, uses Proof-of-Work(PoW) consensus algorithm.
The nodes that participate in the blockchain have to use consensus algorithms.
67. What are the different types of Consensus Algorithm? Explain each of them briefly.
Ans: There are three main types of consensus algorithm.
- Proof-of-Work(PoW)
- Proof of Stake(PoS)
- Delegated Proof of Stake(DPoS)
Proof-of-Work(PoW): Proof-of-Work(PoW) is used by the most popular cryptocurrencies out there. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin use it. It works by solving complex mathematical problems. The hash needs to be solved for the block to be mined. Once it is done, the transaction is validated, and the consensus is made.
Proof-of-Stake(PoS): Proof-of-Stake(PoS) works by staking coins. The nodes need to stake a minimum amount of coins to become part of the consensus network. Once they become part, they actively take part in making decisions on the network. Unlike Proof-of-Work, PoS doesn’t require huge computational power, and hence power.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake(DPoS): Delegated Proof-of-Stake is a centralized approach to a blockchain network. In this consensus method, the stakes choose delegates which in turn validate the transactions.
68. Can you share the names of platforms that are actively developing Blockchain apps?
Ans: There are many organizations or platforms that are actively improving the blockchain ecosystem. Hyperledger community is one of the leading open source platforms that is working towards developing enterprise-grade blockchain solutions.
Ethereum platform is also active in blockchain app development. They do differ in their approach. Ethereum provides developers, organization, and business to create blockchain apps, whereas Hyperledger is creating tools, techniques and other methods to empower the different blockchains.
69. What are the various approaches employed in attacking the RSA algorithm?
Ans: There square measure totally different approaches employed in assaultive the RSA algorithm:
Brute force: It involves all potential secret keys
Mathematical attacks: In mathematical attack, we tend to square measure mistreatment totally different techniques, that is analogous in the effort to issue the merchandise of 2 primes
70. What are the main elements of a block?
Ans: There are three main parts of a block.
- Hash pointer that points to the previous block. Block 0 doesn’t point to other blocks.
- Timestamp
- Transactions list.
71. What cryptographic algorithms are frequently used in blockchain?
Ans: There are many cryptographic algorithms used in the blockchain. They are as follows:
- RSA
- Blowfish
- TripleDES
- AES
72. What makes RSA a secure cryptographic algorithm?
Ans: RSA provides a state of the security algorithm for applications to use. It stands for Riverst, Shamir, and Adelman. They are the developer of this algorithm. RSA offers public-key encryption and hence is applicable in a variety of use-cases including blockchain. It is also the first encryption that is widely used for signing data and encryption. It works by using both private and public keys.
73. Explain blind signature and how it is useful?
Ans: A blind signature is an essential part of cryptography where the information is blinded or encrypted. The information is signed and hence becomes encrypted. The approach is verified and ensures that privacy protocols are maintained in the network.
74. Can RSA be attacked? If so, how?
Ans: Yes, hackers can attack RSA. However, being attacked is not equal to weak protection. It is just the methods that can be used to attack it and take a chance to break it. There are two ways, one can attack RSA, i.e., brutal force and mathematical attacks.
75. What are the benefits of blockchain? Explain it from your viewpoint and understanding.
Ans: Blockchain has many benefits. First of all, it provides instant and secure online transactions. It also uses a decentralized ledger system which provides transparency and verifiability to new heights. It also means that no one can alter the data.
Overall, the use of blockchain further improves the security and ensures that the business doesn’t have to spend too much money in making their security strong. Blockchain also enables business and startups to reach a global audience without worrying about geographical restrictions. Currently, it is breeding innovation in almost every sector out there.
76. What are the key principles that need to be followed to make blockchain secure?
Ans: Even though blockchain is secure, it still needs to be implemented correctly. The following principles need to be followed for proper implementation.
- Auditing
- Security testing
- Securing applications
- Continuity planning
- Database security
- Digital workforce training.
78. Explain a real-time blockchain use case?
Ans: Healthcare can use blockchain to their advantage. Many startups are currently working on a blockchain powered health app that lets patients store their information on the blockchain. The decentralized nature means that they don’t have to carry documents. Healthcare specialists can also take advantage of it as they can access the patient’s data anytime they want. Researchers also benefit from public blockchain where they can access large public data.
79. What is the difference between public and private key?
Ans: A private key is used to encrypt a message or a transaction that is sent on the blockchain. The sender can send a message using the public key of the receiver. The receiver, on the other hand, can decrypt the message or the transaction using his private key. This way the communication or transaction is kept safe from any temper.
- Never give your private key!
80. Will blockchain change the world?
Ans: The blockchain is going to revolutionize our daily life. It has the potential to change how we spend and transact. Also, it is already changing various sectors such as transport, education, business, and so on. As it allows a peer-to-peer network, it will become easier to do business without any geographical restrictions.
Healthcare, for example, will also benefit from it by providing a place to store information for seamless access by authorities and patients.
81. State an example of asymmetric encryption Algorithm?
Ans: The example of asymmetric is RSA
82. What is the principle of Blockchain Technology?
Ans: It allows the information to be distributed among the users while not being traced.
83. Explain the importance of blind signature and the way it’s useful?
Ans: It is a type of digital signature within which the content of a message is disguised (blinded) before it’s signed. The ensuing blind signature may be publically verified against the first, unblinded message within the manner of a daily digital signature.
Blind signatures are generally used in privacy-related protocols where the signer and message author are totally different parties. Examples include cryptographic election systems and digital money schemes.
84. Why is Blockchain a trustworthy approach?
Ans: Blockchain can be trustworthy thanks to such a large amount of reasons.
Its compatibility with different business applications thanks to its open-source nature.
Blockchain security. Because it was meant for online transactions, the developers have paid special attention to maintaining the pace once it involves its security. It extremely doesn’t matter what style of business one owns, Blockchain will simply be thought of.
85. Name the 2 kinds of records that are present within the Blockchain Database?
Ans: These records are block records and transactional records. Each of these records will simply be accessed, and also the neatest thing is, it’s doable to integrate them with one another while not following the complicated algorithms.
86. What do you mean by blocks within Blockchain Technology?
Ans: Blockchain consists of a list of records. Such records are kept in blocks. These blocks are successively linked with different blocks and therefore represent a sequence known as Blockchain.
87. How is a block recognized within the Blockchain approach?
Ans: Every block during this online ledger essentially consists of a hash pointer that acts as a link to the block that is before it, transaction knowledge and in fact a stamp of time.
88. Is it possible to switch the data once it’s written in an exceeding block?
Ans: No, it’s impossible to do so. Just in case any modification is needed, the organization merely has to erase the knowledge from all different blocks too. Because as a result of no different reason than this, knowledge must be given the acute care of while mistreating this approach.
89. What exactly does one comprehend the security of a block?
Ans: Well, a block or the complete blockchain is protected by a powerful cryptographic hash algorithm. Every block includes a distinctive hash pointer. Any modification within the block constituents will lead to the modification within the hash identifier of the block. Therefore, it offers a wonderful level of security. Thus, one needs to not worry regarding the protection additionally because of the security of knowing that’s a gift in an exceedingly block.
90. What are Merkle trees? How vital are Merkle trees in Blockchains?
Ans: Merkle Tree additionally called ‘hash tree’ is a data structure in cryptography during which every leaf node could be a hash of a block of knowledge, and every non-leaf node could be a hash of its kid nodes.
If somebody has to verify the existence of selected dealing in an exceedingly block, then he doesn’t need to transfer the complete block. Downloading a collection of a branch of this tree that contains these dealings is enough. We have a tendency to check the hashes when we are simply raising the branch (relevant to my transaction). If these hashes are considered sensible, then we all know that these specific dealings exist during this block.
91. Name the common sort of ledgers which will be thought of by users in Blockchain?
Ans: These are:
- Centralized Distribution
- Decentralized distribution
- Distributed network
92. How is a blockchain ledger different from a standard one?
Ans: The first and of course the prime distinction is Blockchain is a digital ledger which will be decentralized terribly simply. The probabilities of error during this approach are way under that in a standard ledger. An ordinary ledger is what that’s ready by hands or by human efforts whereas the Blockchain performs all its tasks mechanically. You simply have to be compelled to assemble it in an exceedingly correct manner and by following all the rules.
93. What type of records is kept in a Blockchain? Is there any restriction on the same?
Ans: There is no restriction on keeping records of any sort within the Blockchain approach. Industries are using Blockchain for securing all kinds of records.
The common kinds of records (to name a few) which will be unbroken on the Blockchains are:
- Records of medical transactions
- Identity management
- Transaction process
- Business transactions,
- Management activities
- Documentation
94. Can you explain the elements of the Blockchain Ecosystem?
Ans: There square measure four completely different part of Blockchain system
- Shared Ledger
- Virtual Machine
- Node application
- Consensus Algorithm
95. State difference between proof of stake and proof of work.
Ans: Proof of Work
- The possibility of Mining a Block depends upon the amount of work a miner does
- Takes more energy than proof of stake
Proof of Stake
Stakeholder Validate new block by but utilizing their share of coin on the network
The first example of proof of stake is Peercoin
96. Name some widespread platforms for developing blockchain applications.
Ans: After the event of bitcoin, numerous blockchain platforms started arising. Ethereum came right once the evolution of Bitcoins, and is one in all the favored public platforms for building. Blockchain primarily based applications.
Then there’s a Hyperledger community for building enterprise-based solutions. Also, Qtum, IOTA, EOS are a number of the widely used platforms for building Blockchain.
97. What are the advantages of Blockchain that you simply know?
Ans: There are plenty of benefits for Blockchain:
- Settlement in real time
- Cost saving
- Immutability
- Security
- User Pseudonymity
98. Each and every block of Blockchain consist of what elements?
Ans: Each and every block include three major parts
- A hash pointer to the previous block
- Timestamp
- List of transactions
99. Which one Bitcoin or Ethereum was the first distributed blockchain implementation?
Ans: The answer is Bitcoin as it was found on 8th August 2008
100. What are the forms in which Blockchain can be stored?
Ans: The blockchain is a distributed ledger which can be stored in 2 Forms
- A flat file
- A Database




