- Introduction to Mining Pools
- How Cryptocurrency Mining Works
- Why Mining Pools Were Created
- How Mining Pools Operate
- Types of Mining Pools
- Advantages of Joining a Mining Pool
- Disadvantages and Risks of Mining Pools
- The Future of Mining Pools
- Conclusion
Introduction to Mining Pools
In the world of cryptocurrency using best mining pool for beginners guide, mining pools play a crucial role in making mining more accessible and profitable. But what exactly is a mining pool? A mining pool is a collective group of cryptocurrency miners who combine their computational resources (hash power) over a network to increase their chances of solving complex mathematical puzzles required to validate and add new blocks to a blockchain. When the mining pool successfully mines a block, the rewards are distributed among the participants, usually in proportion to the computational power they contributed. Mining pools have transformed mining from a solo activity into a collaborative effort, leveling the playing field and allowing miners with smaller setups to earn more consistent rewards.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Today!
How Cryptocurrency Mining Works
Before diving deeper into mining pools, it’s essential to understand the basics of all about crypto mining
What is Mining? Mining is the process by which transactions on a blockchain are verified and added to the public ledger. It involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles known as Proof of Work (PoW). Miners use specialized hardware (like ASICs or GPUs) to perform trillions of hash calculations per second. When a miner solves the puzzle, they get to add a new block to the blockchain technology mining and earn block rewards, which usually consist of newly minted coins and transaction fees. The difficulty of these puzzles adjusts over time to keep block production steady, usually around every 10 minutes for Bitcoin.
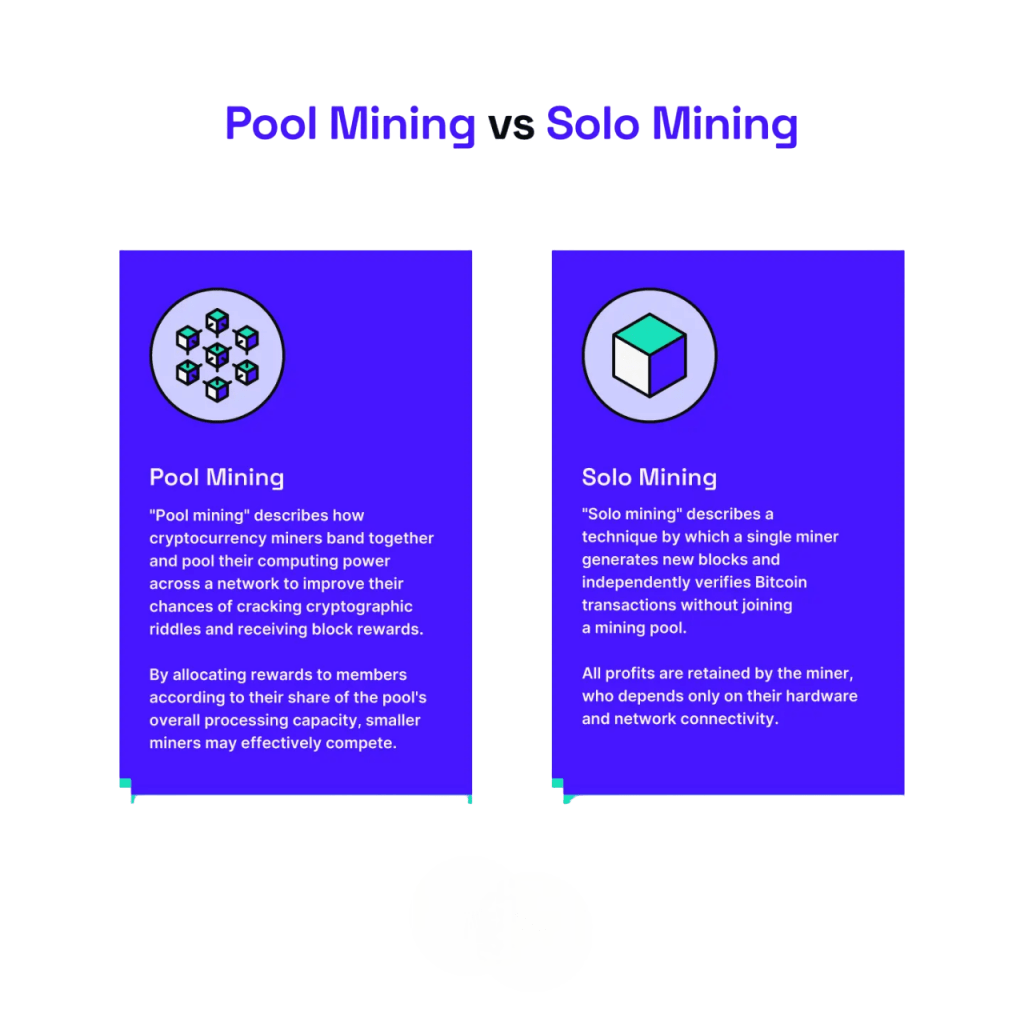
- Solo mining: Mining independently; you keep all rewards, but the chances of solving a block are very low unless you have massive computational power.
- Pool mining: Mining collectively with others; you share rewards but get more frequent payouts.
Why Mining Pools Were Created
As cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin gained popularity, mining became more competitive and resource-intensive. Here’s why mining pools emerged: Understanding every facet of cryptocurrency mining requires a knowledge of the shift from solo mining to best mining pool for beginners. The emergence of large-scale farms and ASIC miners significantly increased competition, making it harder for those with mediocre setups to succeed. Miners also had to wait a long period between payouts due to the unpredictable returns from solo mining. Mining pools changed this by offering members more consistent income and smaller but more frequent rewards. Anyone with simple hardware can participate and earn money thanks to this arrangement. These trends show why discussions all about crypto mining in general have focused on mining pools.
To Explore Database in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Database Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
How Mining Pools Operate
This is the main function of the pool server in a mining pool system. The mining operation is managed by a pool manager, who distributes small parts of BF/T to several miners in a block-mining job. Condensed share mining is a form of problem-solving with small parts. Miners receive all the shares, then sort them and reorganize them before returning to the server. Although these shares are not used directly as a block incentive, they indicate how much mining contributes to the group’s effort. Once a true block is found in the miner pool and successfully completes the cryptographic challenge, it is sent to the blockchain technology mining network. The entire block is given to the block reward, which is distributed based on the contribution of each miner. There are many parts to this incentive program. Miners are given a uniform reward for each valid share that they contribute to the PPS scheme, whether a block is discovered or not. Through this method, the miners are compensated. Those who continuously donate are awarded the prize through a salary to the previous N shares (PPLNS) approach, which considers recent shares and pays them when they reach a particular point. The allocation of block rewards in a proposal approach is determined by the total share submitted by each miner during each mining round.
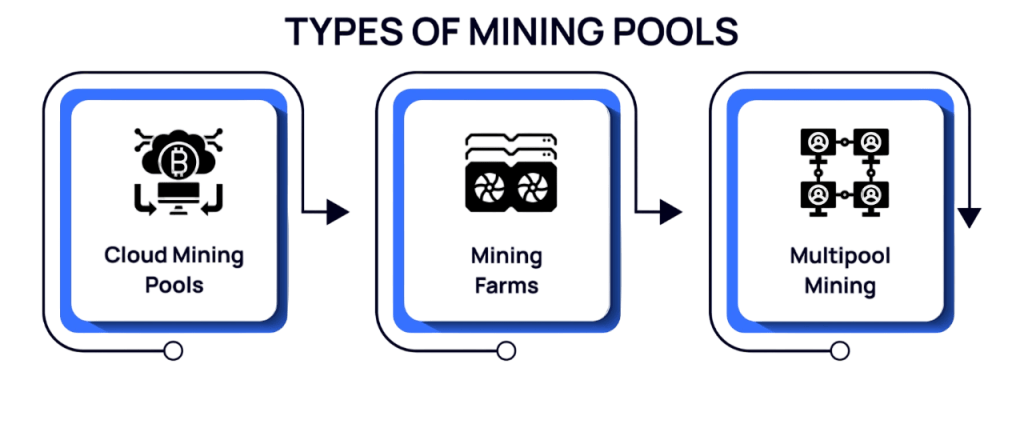
Types of Mining Pools
Mining pools vary by structure and reward system. The most common types include
- Centralized Pools: Most popular pools are centralized, meaning they are operated by a single entity controlling the pool’s server and reward distribution.
- Decentralized Pools: These pools use protocols that allow miners to connect and coordinate mining without a central operator, increasing trustlessness.
- Pooled Mining via Mining Contracts: Miners can buy hash power on cloud mining platforms and participate without managing hardware.
- Solo Pools: Pools where miners pool hash power, but only the miner who finds the block receives the reward, are used less often.
Advantages of Joining a Mining Pool
Mining pools offer several benefits, especially for small to medium miners: Pool miners receive smaller, more regular payouts compared to the infrequent and unpredictable rewards of solo mining. Pooling reduces the variance in mining rewards, providing steady income streams. Mining pools enable miners with less computational power to compete alongside industrial-scale operations. Pooling distributes the risk of mining and reduces the impact of unlucky mining rounds. Pool operators often handle technical maintenance, allowing miners to focus on hardware and hashing.
Disadvantages and Risks of Mining Pools
- While mining pools have many benefits, they also come with some drawbacks and risks: Large mining pools can control significant portions of the network’s hash power, raising concerns all about crypto mining centralization and potential 51% attacks.
- Mining pools charge fees (typically 1-3%) for operation and maintenance, reducing overall miner earnings. Centralized pools require trusting the operator to distribute rewards fairly and maintain uptime.
- Large pools may censor transactions or block certain miners, impacting network neutrality. Mining pools can be targets for cyberattacks or DDoS attempts, disrupting mining activity.
Want to Learn About Database? Explore Our Database Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
The Future of Mining Pools
- The mining landscape continues to evolve, with several trends shaping the future of mining pools: Projects aim to reduce centralization risks by developing decentralized pooling protocols that do not rely on a single operator.
- Mining is moving toward greener energy sources to combat environmental concerns and regulatory pressure. Some pools issue tokens representing miner shares or allow pooled mining participation via DeFi platforms.
- As hardware improves, mining pools may adjust their structures to accommodate new equipment and strategies. Governments worldwide are increasing scrutiny of mining operations, affecting pool operations and miner participation.
Conclusion
Best mining pool for beginners have fundamentally transformed cryptocurrency mining, making it more inclusive and economically viable for a broad range of participants. By pooling resources, miners can enjoy steady rewards, mitigate risks, and remain competitive in an increasingly challenging environment. However, mining pools also present challenges like centralization risks and all about crypto mining trust dependencies. One goal is to create more decentralized pools, so no single group has too much control. New ideas might include more transparent methods for distributing rewards or using blockchain technology itself to manage pools more fairly. There’s also a push to make mining more sustainable, reducing energy use and environmental impact. Some believe that integrating pool operations with broader blockchain ecosystems could bring more transparency and fairness. Innovations could also give individuals more control of their mining power, helping the network stay healthy and decentralized. As technology advances, fixing these issues and opening up the mining process even further will likely become a major focus in the industry. The future will likely see innovations aimed at decentralizing pool operations, improving sustainability, and integrating with broader blockchain technology mining ecosystems.