
- Introduction to Blockchain Trilemma
- Understanding the Three Pillars: Scalability, Security, and Decentralization
- Why the Trilemma Exists
- Impact of the Trilemma on Blockchain Projects
- Current Approaches to Solve the Trilemma
- Layer 1 Solutions and Their Trade-offs
- Layer 2 Solutions and Innovations
- Future Outlook: Is the Blockchain Trilemma Solvable?
Introduction to Blockchain Trilemma
The Blockchain Trilemma refers to the challenge of balancing three core aspects of blockchain technology: decentralization, scalability, and security. It suggests that improving one of these elements often compromises the others, making it difficult to achieve all three simultaneously in a single blockchain network. For instance, Bitcoin prioritizes security and decentralization but struggles with scalability, while some newer platforms focus on speed and scalability at the cost of decentralization. Understanding this concept is crucial for developers and enthusiasts exploring Blockchain projects with source code, as it directly influences architectural decisions and network performance making it a core component of effective Blockchain Training Many new crypto mining projects are attempting to solve this trilemma by adopting innovative consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake, sharding, or Layer 2 solutions, which aim to enhance transaction throughput without compromising security or decentralization. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, addressing the Blockchain Trilemma remains a key area of research and experimentation. Developers are increasingly contributing open-source solutions and collaborating on hybrid models that strive to strike the right balance. Whether you’re mining, coding, or investing, grasping the implications of the Blockchain Trilemma can provide valuable insight into the strengths and limitations of different blockchain systems and the innovations shaping the future of decentralized technology.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Understanding the Three Pillars: Scalability, Security, and Decentralization
- Scalability: Scalability refers to the blockchain’s ability to handle a growing number of transactions. A scalable system can maintain speed and efficiency as demand increases, vital for supporting global adoption and mass usage in decentralized apps and platforms.
- Security: Security ensures that the data on the blockchain is immutable and protected from attacks. Through cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms, blockchain offers high resistance to fraud, which is crucial for safeguarding assets in Blockchain Wallets, maintaining trust across the network, and understanding the fundamentals of How Does Bitcoin Work.
- Decentralization: Decentralization removes single points of control, distributing authority across nodes in the Blockchain network. This democratic structure prevents censorship and manipulation, fostering transparency and user empowerment.
Understanding the three foundational pillars of blockchain, Scalability, Security, and Decentralization, is essential for anyone engaging with blockchain technology, whether through Blockchain programming, developing a Blockchain Wallet, or contributing to a Blockchain network. These three elements form the basis of what makes blockchain both powerful and complex. Here’s a breakdown of each pillar and its impact:
- Administrative Decentralization: This concept involves redistributing governance, decision-making, and operational control from centralized entities to the community, aligning with blockchain’s core philosophy of freedom and fairness.
- Balancing Trade-offs: Achieving all three pillars simultaneously is a major challenge. Enhancing scalability often requires compromises in decentralization or security, known as the Blockchain Trilemma.
- Impact on Blockchain Programming: Developers must consider these pillars while building dApps, smart contracts, or infrastructure. Efficient Blockchain programming involves choosing the right frameworks and protocols that best align with the desired balance of scalability, security, and decentralization.
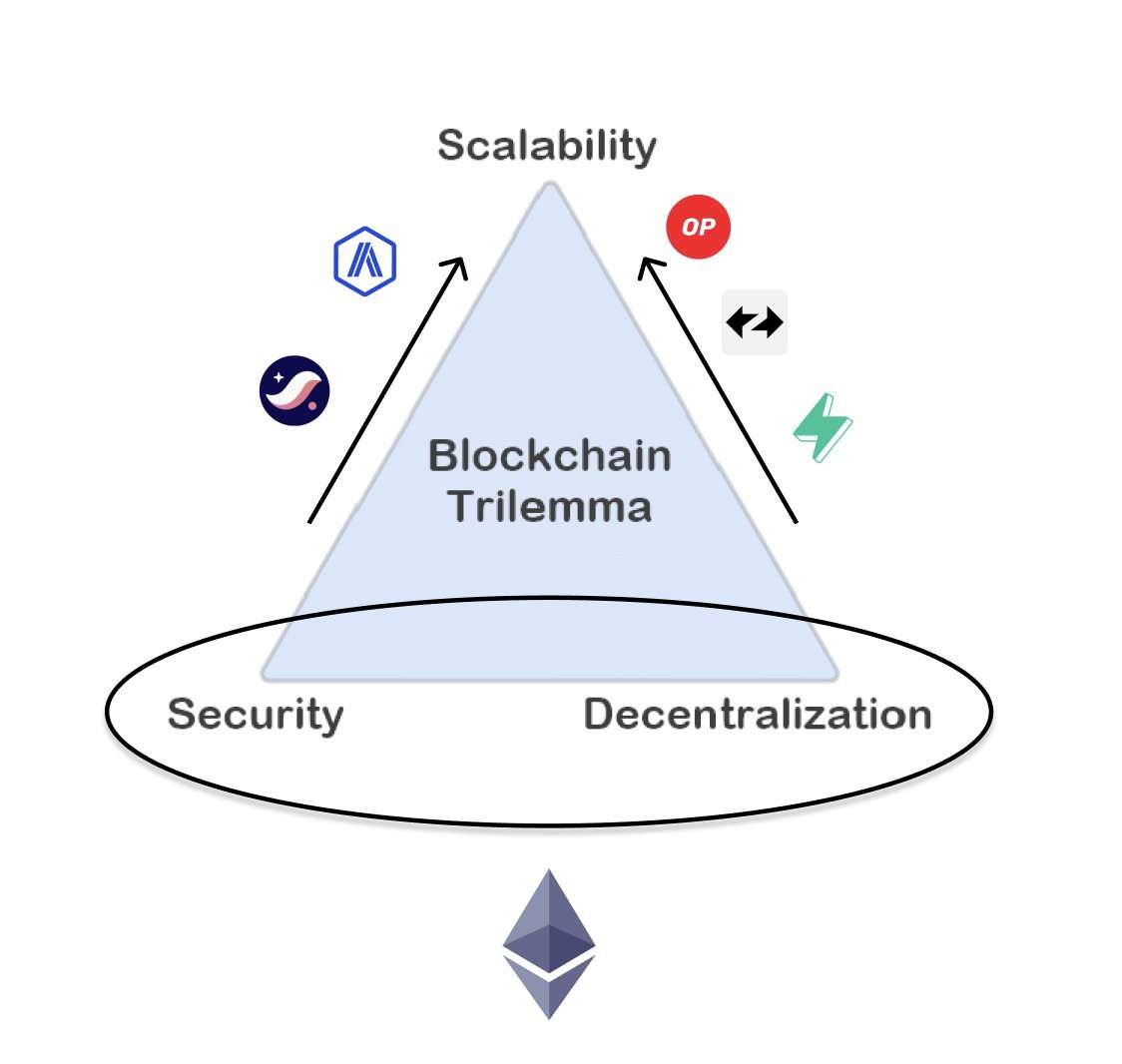
Why the Trilemma Exists
The Blockchain Trilemma exists because achieving decentralization, scalability, and security simultaneously within a single blockchain system is technically challenging due to inherent design trade-offs. When a network prioritizes decentralization, like Bitcoin, it often sacrifices scalability, resulting in slower transaction speeds. On the other hand, platforms that focus on high scalability may rely on fewer nodes or centralized validators, which can compromise security or decentralization a common challenge illustrated by the Blockchain Trilemma. Ensuring top-notch security typically involves complex consensus mechanisms, which can slow down the system and limit scalability. This delicate balancing act explains why no blockchain has yet perfectly solved the trilemma. Many Blockchain projects with source code available today are open experiments aimed at resolving these conflicts using various strategies like sharding, sidechains, or Layer 2 solutions. These approaches attempt to scale without weakening decentralization or opening security vulnerabilities. Meanwhile, New Crypto Mining projects are exploring alternative consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake and hybrid models, to improve network performance while maintaining secure and distributed validation processes. As blockchain technology matures, developers continue to innovate with the goal of overcoming the Blockchain Trilemma, and understanding why this trilemma exists is crucial for anyone building or investing in decentralized systems and next-generation blockchain platforms.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Impact of the Trilemma on Blockchain Projects
- Design Trade-offs: Developers must choose which pillar to prioritize, often compromising one aspect. For instance, prioritizing security and decentralization may slow down transaction speeds, affecting user experience.
- Network Architecture Decisions: The structure of a Blockchain network, whether fully decentralized or partially centralized, often reflects how it addresses the trilemma, influencing everything from node distribution to consensus mechanisms — insights that are especially valuable when exploring Top Blockchain Project Ideas
- Blockchain Programming Complexity: Building scalable and secure decentralized applications requires advanced Blockchain programming techniques, including optimizing smart contracts and managing on-chain vs. off-chain processes.
- User Experience in Blockchain Wallets: A Blockchain Wallet must balance security with usability. Overemphasis on decentralization might complicate recovery or access, while scalable designs may risk compromising privacy or control.
- Limits to Administrative Decentralization: To maintain governance efficiency, some projects adopt partial Administrative Decentralization, blending community involvement with structured oversight, often due to scalability needs.
- Innovation and Experimentation: The trilemma drives continuous innovation, pushing developers to experiment with new models and protocols that aim to achieve a better balance without compromising the integrity of the blockchain.
- Consensus Mechanism Shifts: Switching from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake increases scalability and energy efficiency but may reduce decentralization by favoring wealthier validators.
- Block Size and Time Adjustments: Increasing block size or reducing block time boosts transaction throughput but can strain network nodes, leading to centralization risks in the Blockchain network.
- Improved Cryptographic Algorithms: New algorithms enhance security and privacy, benefiting users of Blockchain Wallets, but they can add complexity and require extensive testing and adoption time especially in sectors focused on Enhancing Blockchain in Agriculture
- Governance Layer Enhancements: Introducing on-chain voting and upgrades supports Administrative Decentralization, but may lead to governance capture by a few influential stakeholders.
- Native Smart Contract Optimization: Enhanced support for smart contracts streamlines Blockchain programming, yet may increase the network’s attack surface if not carefully secured.
- Infrastructure Reconfiguration: Structural changes for scalability may reduce the need for full nodes, improving efficiency but potentially weakening Decentralization if fewer entities control consensus.
The Blockchain Trilemma, the challenge of achieving scalability, security, and decentralization simultaneously, has a profound impact on how blockchain projects are designed, developed, and deployed. Whether you’re creating a Blockchain Wallet, developing apps through Blockchain programming, or contributing to a Blockchain network, understanding this trilemma is essential for making informed decisions. Here are six key ways the trilemma influences blockchain projects:
Current Approaches to Solve the Trilemma
To address the Blockchain Trilemma, developers and researchers are actively exploring innovative solutions that aim to balance scalability, security, and decentralization without sacrificing one for the other. Current approaches include Layer 2 scaling solutions like rollups and state channels, which process transactions off-chain and settle them on the main chain, thereby enhancing throughput without compromising core security. Another popular method is sharding, which breaks the blockchain into smaller, manageable segments to improve scalability while maintaining a decentralized structure. Proof of Stake (PoS) and its variations are also being adopted in many New Crypto Mining projects, offering a more energy-efficient and scalable alternative to Proof of Work (PoW), with added benefits in network participation and security a critical topic covered in Blockchain Training. Interoperability protocols and modular blockchain frameworks are also gaining traction, allowing separate layers to handle consensus, execution, and data availability. These approaches are being tested and refined in numerous Blockchain projects with source code openly available for community collaboration and improvement. As the technology evolves, these diverse strategies represent a collective effort to overcome the Blockchain Trilemma, driving the development of next-generation blockchain platforms that aim to deliver secure, scalable, and decentralized ecosystems for real-world adoption.
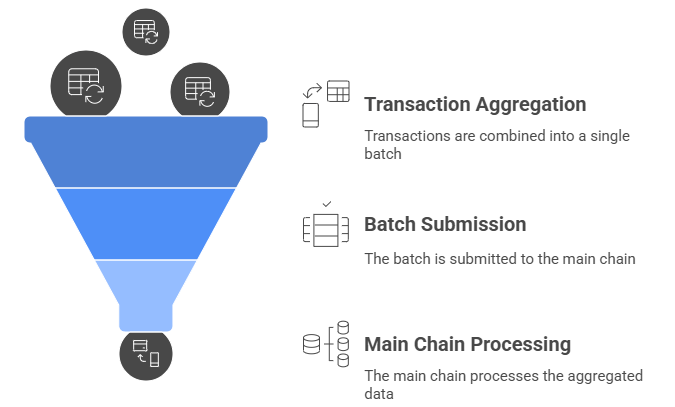
Layer 1 Solutions and Their Trade-offs
Layer 1 solutions refer to upgrades or changes made directly to the base Blockchain network to enhance scalability, security, or decentralization. These foundational improvements play a key role in addressing the Blockchain Trilemma, but they often involve trade-offs that impact developers, users, and system governance. Understanding these compromises is essential for those working in Blockchain programming, designing Blockchain Wallets, or engaging in decentralized ecosystems. Here are six key points outlining Layer 1 solutions and their trade-offs:
Layer 2 Solutions and Innovations
Layer 2 solutions have emerged as powerful innovations aimed at scaling blockchain systems without altering the underlying Blockchain network. These solutions work by offloading transactions from the main chain, reducing congestion, and improving transaction speeds while maintaining the security and decentralization of Layer 1. Examples include rollups (Optimistic and ZK-Rollups), state channels, and sidechains, all of which allow multiple transactions to be processed off-chain and then recorded on-chain as a single proof or summary. This significantly enhances scalability and reduces gas fees, improving user experiences, especially when interacting with decentralized applications or managing assets through a Blockchain Wallet, while also raising important considerations around What is a Private Blockchain in controlled environments. For developers, Blockchain programming becomes more flexible and efficient, as Layer 2 technologies enable faster transaction confirmations and lower costs, facilitating a smoother dApp environment. Additionally, Layer 2 networks support more complex logic and user interactions without compromising the base layer’s security. From a governance standpoint, Administrative Decentralization is maintained, as most Layer 2 systems preserve the trustless principles of blockchain while introducing new layers of community control and decision-making. As blockchain adoption grows, Layer 2 solutions are proving to be essential in pushing the boundaries of what decentralized systems can achieve, paving the way for scalable, secure, and inclusive digital infrastructures.
Are You Preparing for Blockchain Developer Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Future Outlook: Is the Blockchain Trilemma Solvable?
The Blockchain Trilemma, which highlights the difficulty of achieving scalability, security, and decentralization simultaneously, has driven years of research and development across the blockchain ecosystem. While once considered an unsolvable challenge, ongoing innovation suggests that practical solutions are emerging. New architectures, such as modular and multi-chain frameworks, are being implemented in many cutting-edge Blockchain projects with source code that is openly shared for collaboration and improvement. These projects experiment with combinations of Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions, such as sharding, rollups, and proof-based systems, to find optimal balances between the three core pillars a key focus area in Blockchain Training Meanwhile, New Crypto Mining projects are moving beyond traditional Proof of Work models, embracing more sustainable and scalable consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake and Proof of Space-Time. These innovations not only improve performance but also aim to enhance security and maintain decentralized participation. Although no single project has definitively solved the Blockchain Trilemma, the progress being made indicates that it may not require a perfect solution but rather a flexible, use-case-specific approach. As technology evolves and blockchain communities grow more collaborative, the gap between theory and application continues to close, making a balanced and scalable decentralized future increasingly achievable.





