
- Introduction to Polygon Blockchain
- The Need for Polygon: Ethereum’s Scalability Problem
- What is Polygon? Understanding the Technology
- Polygon Architecture and Components
- Polygon’s Ecosystem and Key Projects
- Use Cases and Real-World Applications
- Polygon vs Other Layer 2 Solutions
- Future Outlook and Challenges for Polygon
Introduction to Polygon Blockchain
Polygon, formerly known as Matic Network, is a Layer 2 scaling solution built to enhance the performance and usability of the Ethereum blockchain. Designed to address issues like high gas fees and network congestion, the Blockchain Polygon Matic Network offers faster, cheaper transactions without compromising on security. At its core, Polygon Architecture and Components include a modular framework with elements like the Polygon SDK, validators, checkpoints, and proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms, making it highly flexible and developer-friendly. This foundational knowledge is essential for anyone pursuing Blockchain Training as understanding Polygon’s structure provides practical insights into building and scaling decentralized applications efficiently.Polygon supports a multichain ecosystem, meaning it can seamlessly interact with various blockchains while maintaining interoperability with Ethereum. This enables developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) and custom blockchains that are both scalable and efficient. Interestingly, the term “polygon” also has a geometric context what are convex polygons, for example, refer to simple shapes in which all interior angles are less than 180°, a concept that metaphorically aligns with Polygon’s goal of creating straightforward, efficient blockchain pathways. With its powerful tools and strong community support, Polygon is rapidly becoming a preferred platform for DeFi projects, NFT marketplaces, and enterprise blockchain applications. As adoption grows, the Polygon network is playing a crucial role in pushing blockchain technology into the mainstream.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
The Need for Polygon: Ethereum’s Scalability Problem
- High Gas Fees on Ethereum: As demand increases, Ethereum users often face extremely high transaction fees. Polygon crypto enables fast and low-cost transactions, making blockchain more accessible.
- Network Congestion: Heavy traffic slows down the Ethereum Blockchain Network. Polygon’s Layer 2 solution offloads this pressure by processing transactions off-chain before settling them on Ethereum, offering a scalable approach that addresses the Blockchain Trilemma of scalability, security, and decentralization.
- User-Friendly Wallet Integration: Polygon works seamlessly with tools like Polygon Metamask and any standard Blockchain wallet, allowing users to transact easily without needing new setups.
Ethereum is one of the most widely used platforms in the blockchain space, but its popularity has brought a significant challenge, scalability. As more users and developers interact with the Blockchain Network, the congestion leads to slower transactions and higher gas fees. This is where Polygon steps in, offering a solution that improves speed, reduces costs, and enhances overall user experience. Here’s why Polygon is essential:
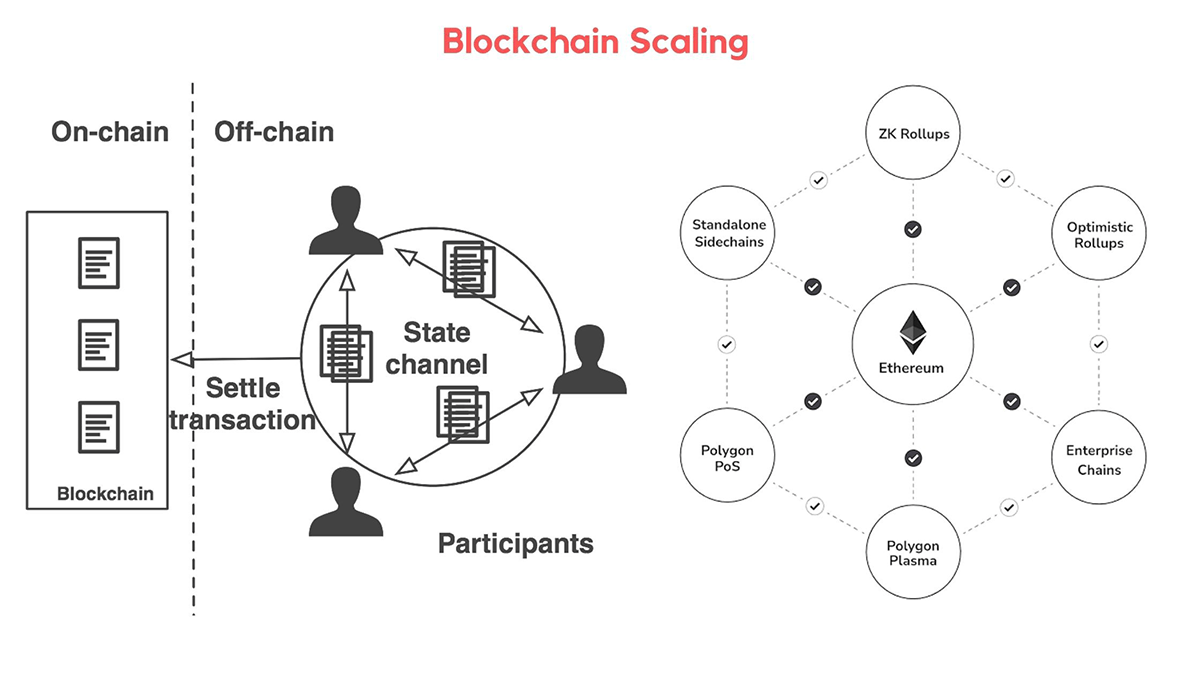
- Support for Developers: With strong support for Blockchain programming, Polygon offers developers scalable infrastructure and robust tools for building dApps.
- Interoperability: Polygon enables easy communication between different blockchains, enhancing the flexibility of decentralized applications.
- Improved User Experience: By reducing delays and costs, Polygon makes interacting with the Blockchain Network smoother and more efficient for both developers and end users.
What is Polygon? Understanding the Technology
Polygon is a powerful Layer 2 scaling solution designed to enhance the performance of the Ethereum Blockchain Network by addressing its limitations, like high gas fees and slow transaction speeds. Originally launched as Matic Network, Polygon crypto has evolved into a full-fledged platform that supports the development and deployment of scalable, user-friendly decentralized applications (dApps). At its core, Polygon uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and sidechains to process transactions off the main Ethereum chain, significantly reducing congestion. For users interacting with the network, Choosing the Best Ethereum Wallets is essential to ensure seamless access to Polygon’s ecosystem and secure transaction management. This not only improves throughput but also lowers costs for users and developers. One of the key benefits of using Polygon is its compatibility with existing Ethereum tools, allowing developers to leverage their knowledge of Blockchain programming without needing to learn new systems. For users, interacting with Polygon is seamless thanks to integrations with popular wallets like Polygon Metamask and other Blockchain wallet solutions, enabling easy management of tokens and assets across networks. Polygon’s architecture also supports interoperability between different blockchains, allowing for more flexible and innovative application development. As a result, Polygon is becoming a preferred platform for DeFi, gaming, and NFT projects, offering the speed, scalability, and low fees that are essential for the future of Blockchain crypto applications.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Polygon Architecture and Components
- Ethereum Layer: This base layer provides finality and security by anchoring Polygon chains to Ethereum, leveraging its robust Blockchain Network.
- Security Layer: An optional layer where validators offer services to multiple chains, adding an extra level of security to the Polygon ecosystem. This architecture also serves as inspiration for Top Blockchain Project Ideas especially for developers looking to explore cross-chain validation and enhanced security models.
- Polygon Networks Layer: This layer hosts multiple independent blockchain networks, each capable of handling its own consensus and block production.
- Execution Layer: Responsible for interpreting and executing smart contracts, this forms the core engine behind all on-chain actions.
- Polygon SDK: A developer-friendly toolkit that simplifies the creation of new custom chains using various consensus models, essential for Blockchain Polygon Matic Network development.
- Naming Inspiration – Convex Polygons: The name “Polygon” metaphorically references what are convex polygons, as these shapes are strong, stable, and multifaceted just like Polygon’s network architecture.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Aave and QuickSwap use Polygon to offer fast, low-cost DeFi services, making lending, borrowing, and trading accessible to millions globally.
- NFT Marketplaces: NFT platforms such as OpenSea and Zed Run operate on Polygon, benefiting from minimal gas fees and high-speed transactions, critical for digital collectibles and gaming assets. These same advantages are also driving interest in Exploring Blockchain in Banking, where efficiency, cost reduction, and transaction speed are equally vital.
- Gaming and Metaverse: Polygon supports blockchain-based games like Decentral Games, enabling in-game economies powered by crypto built on the flexible Polygon Architecture and Components.
- Enterprise Blockchain Solutions: Companies are building supply chain and identity management apps on Polygon, using its scalable infrastructure to handle high-volume operations efficiently.
- Education in Blockchain Programming: With its modular tools and documentation, Polygon is used to teach Blockchain programming, helping new developers enter the Web3 space with ease.
- Inspiration from Geometry – Convex Design: The term “Polygon” is inspired by geometric structures like what are convex polygons, symbolizing strength, simplicity, and interconnectedness, core traits of the network’s design.
Polygon, previously known as the Blockchain Polygon Matic Network, is designed to solve Ethereum’s scalability issues through a well-structured, modular architecture. The system is built to support multiple chains and ensure fast, secure, and cost-effective transactions. To fully grasp how it works, it’s important to understand the key parts of the Polygon Architecture and Components. Here are the six major components that power the network:
Polygon’s Ecosystem and Key Projects
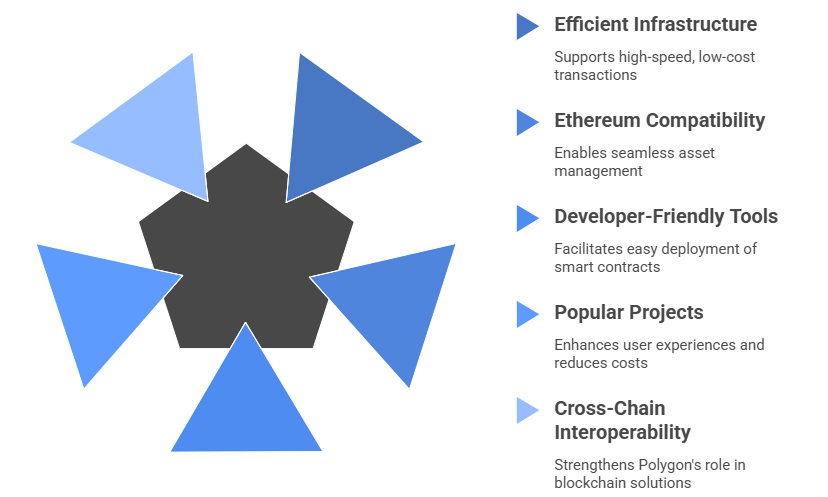
The Polygon ecosystem has rapidly expanded into one of the most vibrant and innovative spaces within the broader Blockchain Network, offering a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi protocols, NFT platforms, and gaming projects. At its core, Polygon leverages its efficient infrastructure to support high-speed, low-cost transactions, attracting both developers and users from across the globe. A major strength of this ecosystem is its compatibility with Ethereum, enabling seamless use of tools like Polygon Metamask, which allows users to easily manage their assets using a standard Blockchain wallet. Popular projects such as Aave, QuickSwap, and OpenSea have integrated with Polygon crypto, taking advantage of its scalability to provide better user experiences and reduce operational costs. The platform also encourages innovation through developer-friendly tools and documentation, making it ideal for those involved in Blockchain programming or undergoing Blockchain Training to gain hands-on experience with real-world development environments. Polygon’s architecture allows for easy deployment of smart contracts and dApps, making it a go-to solution for both startups and established crypto ventures. As the ecosystem grows, more cross-chain and interoperable projects are being developed, strengthening Polygon’s role as a key player in the next generation of blockchain-powered solutions. This dynamic and expanding environment continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible within decentralized technology.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
The Blockchain Polygon Matic Network is more than just a scaling solution it’s a robust ecosystem enabling real-world adoption across various industries. Thanks to the efficiency of the Polygon Architecture and Components, developers and enterprises are leveraging its tools to solve real problems, not just theoretical ones. Here are six key use cases that highlight its practical impact:
Polygon vs Other Layer 2 Solutions
When comparing Polygon to other Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, or zkSync, it becomes clear that Polygon offers a more versatile and developer-friendly environment within the Blockchain Network. While most Layer 2 solutions focus on a single scaling approach such as rollups, Polygon stands out with its multi-chain architecture and support for both optimistic and zk-based technologies. This flexibility makes it a preferred choice for developers involved in Blockchain programming who seek customization and performance. It’s also beneficial for those exploring topics like What Is an NFT In Crypto, as platforms like Polygon support efficient creation and management of NFTs through scalable infrastructure. Unlike some Layer 2s that are still in their early stages, Polygon is already home to a wide array of decentralized applications, NFT marketplaces, and DeFi platforms. Its seamless compatibility with Ethereum allows users to interact using familiar tools like Polygon Metamask and standard Blockchain wallet interfaces, making onboarding smooth and intuitive. Additionally, Polygon crypto transactions are significantly faster and more affordable, attracting both retail users and institutional players. The platform’s commitment to open-source development, strong community support, and scalability tools gives it a competitive edge in real-world adoption. As Layer 2 technology evolves, Polygon continues to lead with innovation, flexibility, and a growing ecosystem that pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in decentralized technology.
Are You Preparing for Blockchain Developer Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Future Outlook and Challenges for Polygon
The Blockchain Polygon Matic Network has established itself as a leading Layer 2 solution, but its journey is far from over. As blockchain adoption grows, Polygon is poised to play a central role in scaling Web3 applications, thanks to its modular and flexible Polygon Architecture and Components. With a focus on innovation, the network continues to evolve by exploring zk-rollups, cross-chain interoperability, and enterprise-grade scalability. However, this rapid growth also brings significant challenges. One of the primary hurdles is maintaining security and decentralization while scaling at high speed. As more applications migrate to the platform, ensuring stable performance and avoiding congestion will be critical. Additionally, with the blockchain space becoming increasingly competitive, Polygon must continue to differentiate itself from other Layer 2 and Layer 1 networks. These dynamics highlight the importance of Blockchain Training as developers and professionals need to stay updated on evolving platforms like Polygon to build scalable and efficient solutions. Regulatory uncertainties and the need for widespread developer education in decentralized technologies also present ongoing obstacles. Interestingly, the name “Polygon” draws inspiration from geometry specifically, what are convex polygons, which symbolize strength and simplicity through their balanced and stable shapes. This metaphor aligns with Polygon’s vision of creating a robust and well-structured blockchain framework. Moving forward, the network’s success will depend on its ability to innovate, scale, and adapt to the ever-changing dynamics of the decentralized world.





