
SAP E-Recruitment Interview Success with 50+ Best Questions and Answers!
Last updated on 17th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
We provide a comprehensive set of interview questions and answers, offering a thorough preparation guide for individuals aspiring to become experts in SAP E-Recruitment. These questions cover various aspects of SAP E-Recruitment, ensuring that professionals are well-equipped to handle different job roles within enterprise SAP E-Recruitment. From installation and configuration to in-depth knowledge of SAP E-Recruitment processes, the interview questions provide a broad spectrum of topics that candidates may encounter during their job interviews. By delving into these questions, individuals can enhance their understanding of SAP E-Recruitment, making them well-prepared to tackle any challenges in the competitive job market. This resource serves as a valuable tool for those seeking to excel in their SAP E-Recruitment interviews and stand out as proficient professionals in the field.
1. What does SAP E-Recruitment mean?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment is a module within the SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) suite that focuses on managing and streamlining the recruitment process. It provides tools for attracting, hiring, and retaining the best talents through an electronic platform.
2. Enumerate the primary functionalities of E-Recruitment SAP.
Ans:
The primary functionalities of SAP E-Recruitment include:
- Job posting
- Candidate management
- Applicant tracking
- Interview scheduling
- Offer management
- Integration with other HR processes
3. Outline the essential features of the SAP E-Recruitment controlling process.
Ans:
The controlling process in SAP E-Recruitment involves budgeting, cost tracking, and compliance monitoring. Essential features include budget control, expenditure tracking, and reporting capabilities.
4. Elaborate on the term ‘compliance’ and its significance in the procedure.
Ans:
- Compliance in SAP E-Recruitment refers to adhering to legal and organizational regulations during the hiring process.
- It ensures that recruitment activities align with equal opportunity laws, privacy regulations, and internal policies.
5. What is included in the initial retroactive accounting period?
Ans:
The initial retroactive accounting period in SAP E-Recruitment includes the retroactive calculation of salaries and benefits for employees from their start to the current period.
6. Describe the concept of financial planning while maintaining headcount.
Ans:
Financial planning in SAP E-Recruitment involves aligning the recruitment strategy with budget constraints. It ensures the hiring process is financially sustainable, considering factors like salaries, benefits, and recruitment costs.
7. Clarify the idea of termination and transfer accounting.
Ans:
| Concept | |||
| Definition | Manages financial aspects of employee terminations, including final pay and benefits settlement. | Handles financial transactions for employee transfers, covering salary adjustments and benefits transfer. | |
| Key Components | Final Pay Calculation, Benefits Settlement and Compliance Check | Salary Adjustment, Benefits Transfer and Position Change Accounting | |
| Objective | Ensure accurate financial transactions during terminations, preventing discrepancies and legal issues. | Facilitate smooth financial transitions for transferred employees, supporting internal mobility initiatives. | |
| Importance | Ensures financial accuracy and compliance during employee exits. | Facilitates smooth transitions for employees moving between roles, maintaining financial clarity. | |
| Process in SAP E-Recruitment |
|
|
8. What does ‘Hire and Offer’ signify in the context of E SAP recruitment?
Ans:
‘Hire and Offer’ in SAP E-Recruitment refers to extending job offers to selected candidates and completing the hiring process, including contract generation, onboarding, and integration into the organisation.
9. Define LSMW.
Ans:
LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench) is a tool in SAP used for data migration and conversion from legacy systems to SAP systems. It supports the import of large volumes of data during system implementations or upgrades.
10. Explain dynamic actions and discuss the configuration method.
Ans:
Dynamic actions in SAP E-Recruitment are system-triggered events based on predefined conditions. Configuration involves setting rules to automate actions like status changes, notifications, or data updates in response to specific events.
11. Can you outline the fundamental structure of SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
The fundamental structure of SAP E-Recruitment includes modules for Job Posting, Candidate Management, Interview Scheduling, Offer Management, and Integration with Core HR functions. These modules work together to support the entire recruitment lifecycle.
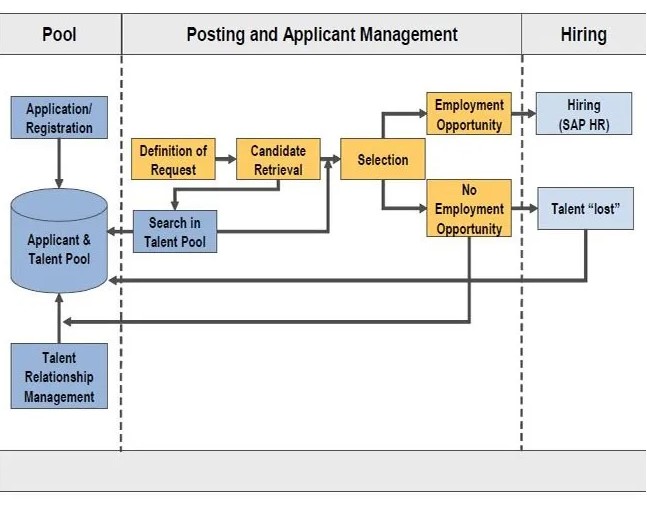
12. Explain the concept of a primary index in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
In SAP E-Recruitment, a primary index is a data structure that enhances the efficiency of data retrieval. It serves as a key for quick access to specific records within the system, optimizing search performance and improving overall system responsiveness.
13. How has the process and organization evolved in E-SAP Recruitment?
Ans:
The evolution of the process and organization in SAP E-Recruitment involves the adoption of advanced technologies, increased automation, improved user interfaces, and enhanced integration with other HR processes. This evolution has led to a more streamlined, efficient, and data-driven recruitment process, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and adapt to changing workforce needs.
14. What are your thoughts on the concept of an additional headcount request?
Ans:
The concept of an additional headcount request in SAP E-Recruitment involves a formal process to request and justify the need to hire additional staff. It ensures alignment with organizational goals and budget constraints.
15. Explain the significance of posting jobs in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Posting jobs in SAP E-Recruitment is crucial for attracting potential candidates. It involves advertising job openings on various platforms to reach a wider audience and increase the pool of qualified applicants.
16. List the non-anchored or user-defined features.
Ans:
Non-anchored or user-defined features in SAP E-Recruitment are customizable elements that users can define based on specific organizational requirements. These may include additional fields, workflow steps, or reporting criteria.
17. Define the term statistical subjective order in E-Recruitment.
Ans:
- A statistical subjective order in SAP E-Recruitment is a measurement or assessment of the success and effectiveness of the recruitment process.
- It involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to evaluate the recruitment strategy’s impact.
18. Highlight and illustrate the fundamental structure of SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
The fundamental structure of SAP E-Recruitment includes modules for job posting, candidate management, interview scheduling, offer management, and integration with core HR functions. It forms a comprehensive system for end-to-end recruitment processes.
19. Explain the concept of primary index.
Ans:
In SAP E-Recruitment, the primary index is a key component for efficient data retrieval. It enhances search and access performance by providing a quick and direct way to locate specific records within the system.
20. How has the process and organization evolved in E-SAP Recruitment?
Ans:
The evolution of the process and organization in SAP E-Recruitment involves:
- Advancements in technology.
- Integration with other HR modules.
- Improved user interfaces.
- Enhanced features for a more streamlined and effective recruitment process.
21. Define a buffer and enumerate its categories.
Ans:
In SAP E-Recruitment, a buffer is a temporary storage area that holds data to improve system performance. The buffers’ categories include database, application, and presentation, each serving specific purposes.
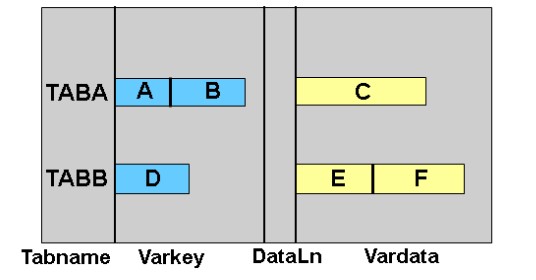
22. What is a pooled table in SAP recruitment?
Ans:
A pooled table in SAP E-Recruitment is a type of table that stores data shared by multiple programs. It is suitable for data that does not change frequently, such as organizational or master data. Pooled tables help optimize storage space and improve overall system performance by efficiently managing and accessing shared information.
23. What does MDM stand for?
Ans:
MDM stands for Master Data Management. It is a method of managing the organization’s critical data, often referred to as master data, to ensure consistency and accuracy across the enterprise.
24. According to you, what does the entire recruitment process include?
Ans:
The entire recruitment process is a multifaceted cycle that starts with identifying the need for a new position and concludes with successfully integrating a new employee into the organization. It includes steps such as job requisition, job posting, candidate sourcing, resume screening, interview scheduling, assessment, offer management, onboarding, and integration with other HR processes. The goal is to attract, select, and retain qualified candidates while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
25. Explain the method of payroll DEBUG.
Ans:
Payroll DEBUG is a process in SAP where the system is run in debug mode to analyze and troubleshoot issues related to payroll processing. It allows step-by-step execution of payroll programs, helping developers or administrators identify and rectify errors in the payroll calculation.
26. Name some personal actions typically taken on an employee in the E-Recruitment process.
Ans:
Personal actions in E-Recruitment may include hiring, onboarding, transfers, promotions, and terminations. The system records and manages these actions to ensure accurate and timely updates to employee records.
27. What is EVALUATION PATH, where is it done, and why?
Ans:
In SAP E-Recruitment, an EVALUATION PATH is a predefined sequence of relationships used to determine the reporting structure of an employee. It is configured in the SAP system and is essential for organizational management and reporting purposes. The path defines how positions, jobs, and organizational units are linked for evaluation.
28. Can you list the key modules within SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
- Job Posting: Involves creating and advertising job openings.
- Candidate Management: Manages the pool of applicants, including resume screening and candidate communication.
- Interview Scheduling: Facilitates the scheduling and coordination of interviews.
- Offer Management: Manages the process of extending job offers to selected candidates.
- Integration with Core HR: Ensures seamless integration with other HR processes for a holistic approach to talent management.
29. What are the core functionalities of SAP E-Recruitment controlling?
Ans:
Core functionalities of SAP E-Recruitment controlling include budget management, cost tracking, and compliance monitoring. The system allows organizations to set budgets for recruitment activities, track expenditures, and ensure compliance with legal and internal policies.
30. What is the significance of financial planning while maintaining headcount in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
Financial planning in SAP E-Recruitment ensures that the recruitment process aligns with budget constraints. It helps organizations maintain financial sustainability by considering factors like salaries, benefits, and recruitment costs while planning for an increase in headcount.
31. Enumerate the non-anchored features or user-defined features in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Non-anchored or user-defined features in SAP E-Recruitment can include custom fields, workflow steps, or reporting criteria. These features allow organizations to tailor the system to meet their specific requirements and capture additional information as needed.
32. Define the term “statistical subjective order” in the context of E-Recruitment.
Ans:
A statistical subjective order in E-Recruitment refers to the analysis and measurement of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to evaluate the success and effectiveness of the recruitment process. It involves using statistical data to assess the impact of the recruitment strategy subjectively.
33. Define a buffer in SAP E-Recruitment and discuss its categories.
Ans:
In SAP E-Recruitment, a buffer is a temporary storage area that holds data to improve system performance. Categories of buffers include:
- Database Buffers: Store frequently accessed data to reduce database read times.
- Application Buffers: Store program-specific data to speed up data access.
- Presentation Buffers: Temporarily store user-specific data to enhance system responsiveness.
34. How does SAP E-Recruitment contribute to the modern recruitment industry?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment contributes to the modern recruitment industry by providing a centralized platform for end-to-end recruitment processes. It enhances efficiency through automation, streamlines candidate management, supports data-driven decision-making, and facilitates seamless integration with other HR functions, enabling organizations to stay competitive and responsive to talent needs.
35. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle retroactive accounting periods?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment handles retroactive accounting periods by allowing for the retroactive calculation of salaries and benefits for employees. The system considers the period from the employee’s start date to the current period, ensuring accurate and retrospective adjustments in financial calculations.
36. Explain the term “additional headcount request” in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
An additional headcount request in SAP E-Recruitment is a formal process to request and justify the need to hire additional staff. It involves providing details such as the role’s requirements, reasons for the request, and the potential impact on organizational goals. This process ensures that hiring decisions align with strategic objectives and budget constraints.
37. What is the role of MDM (Master Data Management) in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
MDM in SAP E-Recruitment ensures the consistency, accuracy, and integrity of master data related to recruitment processes. It centralizes the management of critical data such as candidate information, job profiles, and organizational structures, ensuring that all HR systems have access to reliable and standardized data.
38. How does SAP E-Recruitment support dynamic actions during the hiring process?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports dynamic actions by allowing the system to trigger events automatically based on predefined conditions.
For example, when a candidate’s status changes, the system can initiate actions such as sending notifications, updating data, or triggering workflow steps. Dynamic actions enhance automation and efficiency in the hiring process.
39. Explain the term “E-Recruitment controlling” and its role in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
E-recruitment controlling in SAP involves managing and monitoring the financial aspects of the recruitment process. This includes budget management, cost tracking, and compliance monitoring. E-recruitment control ensures that recruitment activities align with budgetary constraints and adhere to legal and organizational regulations.
40. What types of personal actions can be taken on an employee within the E-Recruitment process?
Ans:
Personal actions in E-Recruitment can include hiring, onboarding, transfers, promotions, and terminations. These actions are recorded and managed within the system to ensure accurate and up-to-date employee records throughout the recruitment lifecycle.
41. Describe the emergence of SAP E-Recruitment and its impact on traditional recruitment methods.
Ans:
The emergence of SAP E-Recruitment marked a shift towards technology-driven and centralized recruitment processes. It has significantly impacted traditional recruitment methods by introducing automation, data analytics, and seamless integration with HR functions. This evolution has led to more efficient, transparent, and scalable recruitment practices.
42. How does SAP E-Recruitment contribute to financial planning and budgeting for headcount?
Ans:
- SAP E-Recruitment contributes to financial planning by aligning recruitment strategies with budget constraints.
- The system provides tools for setting budgets, tracking expenditures, and ensuring that headcount planning is financially sustainable.
- This allows organizations to make informed decisions about expanding their workforce while considering financial limitations.
43. Discuss the importance of compliance in SAP E-Recruitment and its regulatory aspects.
Ans:
Compliance with SAP E-Recruitment is crucial for ensuring recruitment activities adhere to legal and organizational regulations. This includes compliance with equal opportunity laws, privacy regulations, and internal policies. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues and reputational damage for the organization.
44. Can you name some commonly used personal actions in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
Commonly used personal actions in SAP E-Recruitment include:
- Hiring: Bringing a new employee into the organization.
- Onboarding: Managing the orientation and integration of new hires.
- Transfers: Moving an employee from one department or location to another.
- Promotions: Elevating an employee to a higher position.
- Terminations: Ending the employment relationship with an employee.
45. Explain the purpose of statistical subjective orders in the context of E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Statistical subjective orders in E-Recruitment involve analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to assess the success and effectiveness of the recruitment process subjectively. It allows organizations to evaluate the impact of their recruitment strategies and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and outcomes.
46. How does SAP E-Recruitment enhance the efficiency of the recruitment industry?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment enhances efficiency by providing a centralized platform for managing the entire recruitment lifecycle. Automation of tasks, seamless integration with other HR processes, data-driven decision-making, and improved candidate management contribute to streamlining processes, reducing manual efforts, and enhancing overall efficiency in the recruitment industry.
47. What is the role of LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench) in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
LSMW in SAP E-Recruitment plays a role in data migration and conversion from legacy systems. It assists in importing large volumes of data, such as candidate information, into the SAP system during implementations or upgrades, ensuring a smooth transition and maintaining data accuracy.
48. Describe the structure and organization of SAP E-Recruitment from a high-level perspective.
Ans:
At a high level, SAP E-Recruitment comprises modules for Job Posting, Candidate Management, Interview Scheduling, Offer Management, and Integration with Core HR functions. Collectively, these modules form an integrated system that supports end-to-end recruitment processes, providing a structured and comprehensive approach to talent acquisition.
49. How does SAP E-Recruitment support real-time recruitment processes?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports real-time recruitment by providing instant access to candidate data, facilitating quick decision-making, and enabling seamless communication throughout the hiring process. Real-time updates on job postings, candidate status, and interview schedules contribute to a more agile and responsive recruitment process.
50. Can you provide examples of user-defined features in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
User-defined features in SAP E-Recruitment may include:
- Custom Fields: Additional data fields in candidate profiles or job requisitions.
- Custom Workflow Steps: Tailoring the recruitment workflow to match organizational processes.
- Reporting Criteria: Customizing reporting parameters to capture specific data for analysis.
- Role-Based Permissions: Defining user roles and access levels based on organizational requirements.
51. Explain the term “headcount request” and its significance in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
A headcount request in SAP E-Recruitment is a formal process to request and justify the need to hire additional staff. It is significant as it helps organizations align their hiring strategies with business objectives and budget constraints. The process ensures that the recruitment efforts are in line with the overall workforce planning and that new hires contribute to achieving organizational goals.
52. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle the integration of master data with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment integrates master data with other SAP modules through seamless data sharing. Master data related to candidates, positions, and organizational structures is stored centrally, and integration points with other SAP modules, such as SAP HR or SAP ERP, are configured. This integration ensures consistency, reduces data redundancy, and allows for a unified view of HR-related information across the organization.
53. Discuss the role of compliance monitoring in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Compliance monitoring in SAP E-Recruitment involves ensuring that recruitment activities adhere to legal and organizational regulations. The system can be configured to perform checks during various stages of the recruitment process, helping prevent non-compliance with equal opportunity laws, privacy regulations, and internal policies. This feature is essential for risk mitigation and maintaining a fair and ethical hiring process.
54. What is the purpose of the “hire and offer” functionality in SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
- The “hire and offer” functionality in SAP E-Recruitment streamlines the process of extending job offers and completing the hiring process.
- It involves generating employment contracts, managing offer negotiations, and facilitating the onboarding of new hires.
- This functionality ensures a smooth transition from the selection phase to the onboarding phase, contributing to a positive candidate experience.
55. How can SAP E-Recruitment contribute to diversity and inclusion in hiring practices?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment can contribute to diversity and inclusion by providing tools to track and analyze diversity metrics. The system can support unbiased job postings, inclusive language in job descriptions, and data-driven decision-making to enhance diversity in the candidate pool. Analytics and reporting features enable organizations to monitor and improve diversity in their hiring practices.
56. Explain the role of E-Recruitment in streamlining the onboarding process.
Ans:
E-recruitment plays a crucial role in streamlining the onboarding process by seamlessly integrating with onboarding modules. It facilitates the transfer of candidate data to onboarding workflows, automates documentation processes, and ensures a smooth transition from the recruitment phase to the employee’s integration into the organization. This streamlining enhances efficiency and reduces manual efforts in onboarding procedures.
57. What are the key challenges in implementing SAP E-Recruitment, and how can they be addressed?
Ans:
Key challenges in implementing SAP E-Recruitment may include data migration complexities, user training, and integration issues.These challenges can be addressed through thorough planning, effective change management, comprehensive user training programs, and engaging with experienced consultants or support from SAP experts during the implementation process.
58. Discuss the impact of SAP E-Recruitment on reducing time-to-fill for open positions.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment can significantly impact reducing time-to-fill by automating various stages of the recruitment process. Efficient candidate sourcing, streamlined workflows, and automated communication contribute to quicker decision-making and offer processes. This, in turn, helps organizations fill open positions faster, reducing the overall time-to-fill metric.
59. Explain the concept of “posting jobs” and the associated functionalities in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Posting jobs in SAP E-Recruitment involves creating and advertising job openings across various platforms. Functionalities associated with posting jobs include defining job requirements, setting up job postings, managing candidate applications, and tracking the effectiveness of job advertisements. This feature enhances visibility and attracts a diverse pool of qualified candidates.
60. Discuss the significance of evaluating paths in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Evaluating paths in SAP E-Recruitment involves assessing the reporting structure of employees within the organization. It is significant for organizational management and reporting purposes, providing insights into hierarchical relationships. Evaluating paths helps ensure that the organizational structure aligns with business objectives and supports effective decision-making.
61. What are the steps involved in configuring and maintaining dynamic actions?
Ans:
Configuring and maintaining dynamic actions in SAP E-Recruitment involves the following steps:
- Define the action type and specify the triggering event.
- Set up the conditions that determine when the dynamic action should be executed.
- Define the actions to be performed, such as status changes, notifications, or data updates.
- Test and validate the dynamic actions to ensure they function as intended.
- Monitor and maintain dynamic actions as needed based on organizational changes or process improvements.
62. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle payroll integration and ensure data accuracy?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment integrates with SAP Payroll and other HR modules to ensure accurate payroll processing. The system transfers relevant employee data seamlessly, reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors. Integration points are configured to maintain data consistency between E-Recruitment and payroll systems, ensuring accurate financial calculations and compliance with payroll regulations.
63. Explain the term “buffer” in the context of SAP E-Recruitment and its role in data processing.
Ans:
- In SAP E-Recruitment, a buffer is a temporary storage area that holds data to enhance system performance.
- The buffer reduces the need to repeatedly access the database for frequently used data, speeding up data processing and improving overall system responsiveness.
- Different types of buffers, such as database, application, and presentation buffers, play a role in optimizing data processing.
64. What role does e-Recruitment play in organizations’ talent acquisition strategy?
Ans:
E-recruitment is a central component of talent acquisition strategies, contributing to efficient and strategic hiring. It supports organizations in attracting, selecting, and retaining top talent by providing tools for job posting, candidate management, interview scheduling, offer management, and integration with other HR functions. E-recruitment helps align hiring practices with organizational goals and enhances the overall talent acquisition strategy.
65. Discuss the advantages and challenges of implementing SAP E-Recruitment for small businesses.
Ans:
Advantages:
SAP E-Recruitment for small businesses offers streamlined processes, improved efficiency, and access to a centralized platform. It facilitates better candidate management and supports compliance with hiring regulations.
Challenges:
Small businesses may face challenges related to implementation costs, resource constraints, and the need for tailored configurations. However, these challenges can be addressed through careful planning, cost-effective solutions, and leveraging SAP E-Recruitment’s scalability.
66. How does SAP E-Recruitment contribute to building a talent pipeline for future needs?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment contributes to building a talent pipeline by maintaining a database of potential candidates and their qualifications. The system allows organizations to nurture relationships with candidates over time, creating a pool of pre-qualified individuals who can be considered for future job openings. This proactive approach helps organizations respond quickly to staffing needs.
67. Explain the role of SAP E-Recruitment in supporting internal mobility within an organization.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports internal mobility by providing tools for employees to explore and apply for internal job opportunities. The system facilitates the transfer of employee data, ensuring a smooth transition when moving between roles or departments. This functionality encourages career development within the organization and optimizes internal talent utilization.
68. Discuss the features and benefits of statistical subjective orders in E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Statistical subjective orders in E-Recruitment involve analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics subjectively to assess the success of recruitment processes. Features include data-driven evaluation, monitoring of recruitment effectiveness, and continuous improvement. Benefits include informed decision-making, improved efficiency, and the ability to refine recruitment strategies based on performance data.
69. Can you provide examples of scenarios where SAP E-Recruitment can improve recruitment efficiency?
Ans:
Examples of scenarios where SAP E-Recruitment can improve efficiency include:
- Automated Application Screening: Using predefined criteria to automate the screening of candidate applications, saving time.
- Interview Scheduling Automation: Streamlining the interview scheduling process through system-generated notifications and automated calendar integration.
- Onboarding Workflows: Automating onboarding processes, reducing manual paperwork, and ensuring a smooth transition for new hires.
- Reporting and Analytics: Leveraging data-driven insights to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and enhance overall recruitment efficiency.
70. How does SAP E-Recruitment address security and data privacy concerns in the hiring process?
Ans:
- SAP E-Recruitment addresses security and data privacy concerns through role-based access controls, encryption measures, and compliance features.
- Access to sensitive data is restricted based on user roles, and data transmission is secured.
- The system can be configured to comply with data privacy regulations, ensuring that candidate information is handled in accordance with legal and organizational requirements.
71. Explain the role of E-Recruitment in supporting and enhancing employer branding.
Ans:
E-recruitment supports employer branding by providing a platform to showcase an organisation’s culture, values, and job opportunities. It allows companies to create branded career pages, share compelling job descriptions, and engage with candidates through personalised communication. Positive candidate experiences during the recruitment process contribute to building a strong employer brand, attracting top talent, and fostering a positive perception of the organisation.
72. Discuss the integration capabilities of SAP E-Recruitment with external job portals and career websites.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment integrates with external job portals and career websites, enabling organisations to publish job openings seamlessly. This integration allows for automatic posting of job advertisements, updates on application status, and centralized management of candidate data. It enhances visibility, extends the reach of job postings, and streamlines the recruitment process by connecting with popular external platforms.
73. What strategies can organisations implement to maximise the effectiveness of SAP E-Recruitment?
Ans:
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to users on SAP E-Recruitment features.
- Regular Updates: Stay current with system updates and new functionalities.
- Streamlined Processes: Optimise and standardise recruitment processes for efficiency.
- User Engagement: Encourage user engagement and feedback for continuous improvement.
- Integration Planning: Ensure seamless integration with other HR modules and external systems.
74. Describe the role of SAP E-Recruitment in facilitating collaborative hiring processes within teams.
Ans:
- SAP E-Recruitment facilitates collaborative hiring by providing a centralized platform for team members to collaborate on candidate evaluation.
- It supports features such as shared candidate profiles, collective feedback, and interview scheduling.
- Team members can access a unified view of candidate information, enhancing communication and collaboration throughout the hiring process.
75. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle candidate relationship management (CRM) aspects?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment handles CRM aspects by maintaining a database of candidate interactions, preferences, and histories. It supports personalized communication, allows for tracking candidate interactions, and enables targeted engagement through automated email campaigns. This CRM functionality helps organizations build and nurture relationships with candidates, fostering a positive candidate experience.
76. Explain the impact of SAP E-Recruitment on reducing recruitment costs for organizations.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment can reduce recruitment costs by automating manual processes, improving efficiency, and streamlining workflows. It minimizes the need for paper-based documentation, optimizes candidate sourcing, and enhances collaboration, leading to overall cost savings. Additionally, data-driven insights enable organizations to allocate resources more effectively, reducing costs.
77. Discuss the role of SAP E-Recruitment in ensuring a positive candidate experience.
Ans:
- SAP E-Recruitment ensures a positive candidate experience through user-friendly interfaces, transparent communication, and efficient processes.
- It provides candidates with clear information about job opportunities, enables easy application submissions, and offers timely updates on application status.
- Integration with other HR modules ensures a seamless transition from recruitment to onboarding, contributing to an overall positive candidate journey.
78. How can SAP E-Recruitment contribute to workforce planning and strategic talent acquisition?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment contributes to workforce planning by providing insights into recruitment metrics, such as time-to-fill and candidate sources. It supports strategic talent acquisition by aligning recruitment efforts with organizational goals, helping identify skill gaps, and enabling proactive talent pipelining. The system aids in building a strategic approach to talent acquisition based on data-driven decision-making.
79. Explain the concept of retroactive accounting and its application in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Retroactive accounting in SAP E-Recruitment involves adjusting financial records retrospectively. In the context of hiring, it allows organizations to account for salary and benefits retroactively from an employee’s start date. This ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting principles by considering the entire employee service period.
80. What are the common challenges organisations may face during SAP E-Recruitment implementation, and how can they be mitigated?
Ans:
Common challenges may include data migration complexities, user resistance, and integration issues. Mitigation strategies include:
- Thorough planning.
- Change management initiatives.
- Comprehensive training programs.
- Engaging with experienced consultants.
- Conducting pilot implementations to identify and address potential issues.
81. Discuss the role of SAP E-Recruitment in supporting diversity and inclusion initiatives in hiring.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports diversity and inclusion by providing tools to monitor and analyze diversity metrics, ensuring inclusive language in job postings, and facilitating unbiased candidate selection processes. The system creates a diverse talent pool and promotes fair and equitable hiring practices.
82. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle requisition management and approval workflows?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment streamlines requisition management by automating approval workflows. Requisition creation involves defining job requirements, and approval workflows ensure that requisitions go through the appropriate authorization channels before initiating the recruitment process. This ensures transparency, compliance, and efficient requisition handling.
83. Explain the role of SAP E-Recruitment in talent pipelining and succession planning.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports the talent pipeline by maintaining a pool of potential candidates for future openings. It contributes to succession planning by identifying internal candidates for critical roles. The system allows organizations to proactively develop and nurture talent, ensuring a continuous pipeline of qualified individuals for critical positions.
84. Discuss the features and functionalities of SAP E-Recruitment that enhance recruitment analytics.
Ans:
- Reporting Tools: Robust reporting tools to generate insights on crucial recruitment metrics.
- Data Visualization: Graphical representations of data for more straightforward interpretation.
- Candidate Source Analysis: Tracking and analyzing the effectiveness of different candidate sources.
- Time-to-Fill Metrics: Monitoring and optimizing the time required to fill open positions.
85. How can SAP E-Recruitment contribute to building a talent pool for future hiring needs?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment contributes to building a talent pool by storing candidate data and qualifications. It allows organizations to maintain relationships with potential candidates, track their skills and experiences, and engage with them over time. This proactive approach helps organizations quickly identify and reach out to qualified candidates when future job openings arise.
86. Explain the considerations and best practices for data migration in SAP E-Recruitment.
Ans:
Considerations for data migration in SAP E-Recruitment include:
- Data Cleanliness: Ensure data accuracy and completeness before migration.
- Mapping and Transformation: Define explicit mappings and transformation rules for data conversion.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to validate data migration processes.
- Data Security: Implement measures to secure sensitive candidate information during migration.
- Backup: Maintain backups of data to mitigate risks.
87. Discuss the impact of SAP E-Recruitment on reducing time-to-fill and improving hiring efficiency.
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment reduces time-to-fill by automating processes, improving candidate sourcing, and enhancing collaboration among hiring teams. Streamlined workflows, automated communication, and efficient candidate management contribute to faster decision-making, reducing time-to-fill and improving overall hiring efficiency.
88. How does SAP E-Recruitment handle compliance with labor laws and regulations in different regions?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment provides flexibility to configure compliance checks based on labor laws and regulations. The system can be customized to incorporate legal requirements specific to various regions, ensuring that the recruitment process aligns with local and international regulations. Regular updates from SAP also address changes in compliance standards.
89. Can you provide examples of industries or sectors where SAP E-Recruitment has shown significant benefits?
Ans:
- Information Technology: Efficiently sourcing and hiring skilled IT professionals.
- Healthcare: Streamlining recruitment processes for medical and administrative staff.
- Manufacturing: Managing recruitment for diverse roles in the manufacturing sector.
- Financial Services: Meeting talent needs in the financial industry, focusing on compliance.
90. How does SAP E-Recruitment support global recruitment processes and international hiring?
Ans:
SAP E-Recruitment supports global processes by providing multilingual and multicurrency capabilities. It enables the creation of job postings and candidate profiles in multiple languages, facilitates compliance with international hiring regulations, and allows organizations to manage diverse workforce requirements efficiently. Integration with other global SAP modules ensures a unified approach to HR processes on a global scale.

