
[SCENARIO-BASED ] IBM Lombardi BPM Admin Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 17th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
Aspiring IBM Lombardi BPM Admin professionals seeking to excel in administering IBM BPM can benefit from a thorough preparation of ACTE professionals’ interview questions. To become an expert in IBM Lombardi BPM Admin, it is crucial to acquire in-depth knowledge of server installation and configuration. The journey involves encountering a range of interview questions tailored to various enterprise IBM Lombardi BPM Admin job roles. This overview aims to provide a comprehensive insight into different categories of interview questions related to IBM Lombardi BPM Admin, offering valuable guidance for individuals aspiring to thrive in their enterprise BPM administration roles.
1. What is IBM Lombardi BPM, and what is its primary purpose?
Ans:
IBM Lombardi BPM, now known as IBM Business Process Manager (BPM), is a comprehensive business process management suite that enables organizations to design, implement, and optimize business processes. Its primary goals are to increase productivity, optimize and automate corporate procedures, and boost overall operational performance.
2. Explain the key components of the Lombardi BPM architecture.
Ans:
- The Lombardi BPM architecture consists of two main components: the Process Center and the Process Server.
- The Process Center serves as the design and management hub for business processes, while the Process Server executes and manages the runtime processes.
- Additionally, Lombardi BPM includes other components such as the Lombardi Database, Lombardi Coach Views, and the Lombardi Process Portal.
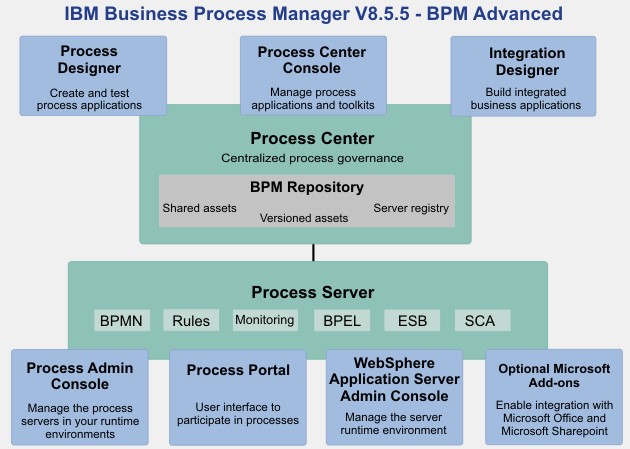
3. How do you install and configure IBM Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
The installation and configuration of IBM Lombardi BPM involve deploying the Process Center and Process Server components. It includes tasks like installing the required software, configuring database connections, setting up security, and deploying the necessary applications using IBM Installation Manager and Lombardi Configuration Wizard.
4. What does the term Durable Subscription refer to?
Ans:
In the context of IBM Lombardi BPM, a Durable Subscription refers to a long-lasting connection between a process application and an external service. It allows the process application to receive events or messages from the external service even if the application is temporarily offline or unavailable.
5. In what manner can a Business Process Diagram (BPD) be segmented?
Ans:
A Business Process Diagram (BPD) in Lombardi BPM can be segmented by dividing it into multiple Lanes. Each Lane represents a participant or role in the process, and the segmentation helps in visualizing the flow of activities among different participants.
6. How do you go about accessing processes in Business Process Management (BPM)?
Ans:
Processes in IBM Business Process Manager can be accessed through the Process Portal. The Process Portal provides a web-based interface for users to view, start, and manage processes. It offers a centralized location for process-related tasks, notifications, and collaboration.
7. What constitute the key elements of BPM?
Ans:
The key elements of Business Process Management (BPM) include,
- Process modeling
- Execution
- Monitoring
- Optimization
8. Can you elaborate on the meaning of UCA (Under Cover Agent)?
Ans:
Under Cover Agent (UCA) in Lombardi BPM refers to a mechanism that allows background processing and asynchronous communication between different components of a process. UCAs are used to trigger events or activities based on certain conditions, providing a way to handle background tasks without affecting the main flow of the process.
9. Define an Event Listener.
Ans:
An Event Listener in Lombardi BPM is a component that listens for specific events or messages within a process. It can be configured to trigger actions or activities based on the occurrence of predefined events, allowing for flexible and responsive process execution.
10. Enumerate the various types of Event Listeners.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM supports several types of Event Listeners, including
- Timer Event Listeners
- Message Event Listeners
- Intermediate Event Listeners
- Start Event Listeners
11. Shed light on the Start Message Event Listener.
Ans:
The Start Message Event Listener is a type of Event Listener in Lombardi BPM that initiates a process based on the reception of a specific message. It allows a process to be triggered externally by sending a designated message to the Process Server, initiating the execution of the associated process.
12. Provide insights into the Intermediate Message Event Listener.
Ans:
- The Intermediate Message Event Listener in BPM facilitates communication between different process instances.
- It acts as a message receiver, capturing and processing messages sent by other process instances or external systems.
- This event listener enables the orchestration of processes based on asynchronous messaging, providing flexibility and modularity in BPM implementations.
13. Clarify the concept of a Coach.
Ans:
In BPM, a Coach refers to a user interface component that guides users through a specific task or process within a business application. Coaches are instrumental in providing a structured and user-friendly interface, often incorporating forms, decision logic, and data displays. They are essential for improving user experience and guaranteeing smooth communication with BPM processes.
14. Define Routing in the context of BPM.
Ans:
- Routing in BPM involves directing process instances or tasks to specific paths based on predefined conditions or business rules.
- It determines the flow of activities within a process, ensuring that each task is routed to the appropriate user, system, or group.
- Effective Routing is crucial for optimizing process efficiency and meeting business objectives.
15. Elaborate on the significance of Durable.
Ans:
In BPM, ‘Durable’ typically refers to the durability of messages or events in an event-driven architecture. A Durable message or event persists even if the system experiences failures or interruptions, ensuring that important information is not lost. This resilience contributes to the reliability and fault-tolerance of BPM processes.
16. Explain the concept of Tracking.
Ans:
- Tracking in BPM involves monitoring and recording the progress and status of process instances, tasks, or events.
- It provides visibility into the execution of BPM processes, allowing stakeholders to analyze performance, identify bottlenecks, and ensure compliance with defined business rules and objectives.
17. What does the term serialization entail?
Ans:
In BPM, serialization is the process of transforming complicated objects or data structures into a serial format, usually for exchange, transfer, or storage. It ensures that data can be reconstructed accurately when needed, supporting efficient communication and data management in BPM systems.
18. Can you outline the different categories of Exceptions?
Ans:
Exceptions in BPM can be categorized into several types, including System Exceptions (related to technical issues), Business Exceptions (resulting from rule violations or business logic errors), and User Exceptions (arising from user interactions). Effective exception handling is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of BPM processes.
19. Define Coaches in the context of BPM.
Ans:
Coaches in BPM refer to user interface components that guide users through specific tasks or processes within a business application. They encompass a range of elements, including forms, decision logic, and data displays, providing a cohesive and intuitive user experience in BPM applications.
20. Clarify the distinctions between Coaches and Coach Views.
Ans:
While both Coaches and Coach Views are UI components in BPM, Coaches are higher-level containers that can include multiple Coach Views. Coach Views are individual elements within a Coach, representing specific user interface elements or functionalities. Coaches offer a broader organizational structure, while Coach Views contribute to the detailed presentation and interaction within a Coach.
21. How can you activate an undercover agent (UCA) to initiate a Business Process Diagram (BPD)?
Ans:
To activate an Undercover Agent (UCA) in Lombardi BPM for initiating a Business Process Diagram (BPD), you typically configure the UCA to listen for specific events or triggers within the system. These events could be predefined conditions or changes in the environment that signal the need to start the BPD. Once the UCA detects the specified conditions, it triggers the activation of the associated BPD, initiating the defined business processes.
22. How would you assess the time duration between the different activities within the process?
Ans:
To assess the time duration between different activities within a process in Lombardi BPM, you can utilize the built-in monitoring and reporting features. These features allow you to generate reports and analyze performance metrics, providing insights into the time taken by each activity in the process. By examining these metrics, you can identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and ensure efficient execution of the business processes.
23. Describe the role of the Process Center and Process Server in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
- In Lombardi BPM, the Process Center serves as the centralized repository for process design, management, and administration.
- It provides a collaborative environment for process modelling, version control, and access control.
- On the other hand, the Process Server is responsible for executing and managing the runtime instances of the business processes.
- It handles process execution, task assignments, and communication between different components, ensuring the smooth running of processes defined in the Process Center.
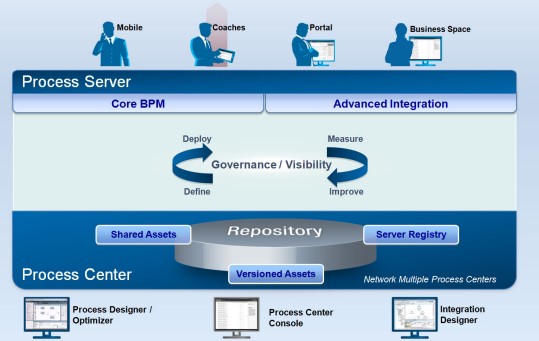
24. What is a snapshot in Lombardi BPM, and how is it used?
Ans:
A snapshot in Lombardi BPM is a frozen version of a process application or a snapshot of its current state. It captures the entire configuration, design, and metadata associated with a specific version of the process application. Snapshots are crucial for version control, allowing users to roll back to a previous state if needed, track changes, and maintain a history of process application iterations. They ensure consistency and reproducibility when deploying and managing business processes.
25. How do you troubleshoot performance issues in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Troubleshooting performance issues in Lombardi BPM involves using various monitoring and diagnostic tools provided by the platform. Analyzing logs, utilizing performance monitoring dashboards, and identifying bottlenecks in the system are common approaches. Additionally, reviewing system resource usage, optimizing database queries, and ensuring hardware resources are appropriately allocated can help address and resolve performance issues in Lombardi BPM.
26. Explain the significance of the Process Inspector in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
- The Process Inspector in Lombardi BPM is a powerful tool for monitoring and analyzing in-flight process instances.
- By giving users real-time access to the data and status of active processes, it enables them to monitor the development of individual instances, spot bottlenecks, and troubleshoot problems.
- The Process Inspector is instrumental in gaining insights into the execution of processes, facilitating better decision-making, and improving overall process efficiency.
27. How do you create and manage users and groups in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Creating and managing users and groups in Lombardi BPM involves using the administration capabilities of the Process Center. Administrators can define users, assign roles, and organize them into groups based on their responsibilities. This ensures proper access control, as users can be granted specific permissions and roles, allowing them to participate in and manage different aspects of the BPM processes.
28. Discuss the role of Decision Tables in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
Decision Tables in Lombardi BPM are used to model complex business rules in a structured and easy-to-understand format. They allow you to define conditions and corresponding actions, making it simple to express and manage business logic. Decision Tables facilitate the automation of decision-making within processes, enabling more flexible and adaptable business process management.
29. How do you handle deployment and migration in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Handling deployment and migration in Lombardi BPM involves using the deployment capabilities of the Process Center. Users can package process applications, snapshots, and associated artifacts and deploy them to different environments. The migration process ensures that configurations, versions, and dependencies are accurately transferred, maintaining consistency across development, testing, and production environments.
30. Explain the purpose of the Lombardi BPM REST API.
Ans:
- The Lombardi BPM REST API provides a set of web services that allow external applications to interact with Lombardi BPM processes and data.
- It enables integration with other systems, facilitating the exchange of information and triggering processes from external sources.
- The REST API is essential for building custom applications, connecting Lombardi BPM with external services, and enabling a broader ecosystem of interconnected business processes.
31. What is the Lombardi BPM Performance Data Warehouse, and how is it utilized?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Performance Data Warehouse is a repository that stores historical data and performance metrics related to executed processes. It allows users to perform in-depth analysis, generate reports, and gain insights into process performance over time. By leveraging the Performance Data Warehouse, organizations can make informed decisions, optimize processes, and ensure continuous improvement in their business process management strategies.
32. How is validation performed on Coach Views?
Ans:
Validation on Coach Views in BPM involves ensuring that user inputs and interactions meet specified criteria or business rules. It includes the verification of data entered into forms or user interfaces within the Coach Views. Proper validation enhances data integrity and helps prevent errors in BPM processes.
33. What is the role of undercover agents (UCA)?
Ans:
- Undercover Agents (UCA) in BPM serve as background processes that continuously monitor specific conditions or events.
- When these conditions are met, UCA triggers predefined actions or events within the BPM system.
- They operate independently and provide a mechanism for handling asynchronous or background tasks in BPM processes.
34. Enumerate the components of Teamworks.
Ans:
Teamworks, which is part of IBM BPM, consists of several key components:
- Process Designer: Used for designing and modeling business processes.
- Integration Designer: Facilitates the integration of external systems and services into BPM processes.
- Performance Data Warehouse: Stores historical data and metrics for performance analysis.
- Process Center: Centralized repository for process design, version control, and administration.
- Process Server: Executes and manages the runtime instances of business processes.
- Process Portal: Provides a web-based interface for end-users to interact with and complete tasks within BPM processes.
- Process Inspector: Allows real-time monitoring and analysis of running process instances.
35. What is the definition of an Activity in IBM BPM?
Ans:
In IBM BPM, an activity is a fundamental unit of work within a business process. It represents a specific task, operation, or step that needs to be performed as part of the overall process flow. Activities can include user tasks, system tasks, automated services, or any other type of work that contributes to the completion of a business process.
36. Define BPD (Business Process Diagram).
Ans:
A Business Process Diagram (BPD) in IBM BPM is a graphical representation of a business process. It visually depicts the flow of activities, decision points, and interactions within a business process. BPDs help in understanding, modeling, and optimizing complex business processes by providing a clear and intuitive representation of the workflow.
37. What are the diverse types of tasks in BPM?
Ans:
In BPM, tasks can be categorized into various types:
- User Tasks: Require human interaction and input.
- Service Tasks: Represent automated activities performed by external services.
- System Tasks: Involve automated actions performed by the BPM system.
- Script Tasks: Execute custom scripts or code.
- Milestone Tasks: Indicate the completion of a significant phase in the process.
- Sub-Process Tasks: Embed another subprocess within the main process.
38. How do you set up security configurations in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Setting up security configurations in Lombardi BPM involves defining users, groups, and roles in the Process Center. Access permissions are assigned based on roles, ensuring that users have the appropriate level of access to process applications and functionalities. Security configurations also involve managing authentication mechanisms, integrating with LDAP systems, and implementing secure communication protocols.
39. Discuss the integration capabilities of Lombardi BPM with other systems.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM provides integration capabilities through Integration Designer, allowing seamless connectivity with external systems. It supports various integration techniques, including web services, messaging protocols, and RESTful APIs. Integration Designer enables the creation of integration services and connectors to interact with databases, applications, and services, facilitating the exchange of data and events between Lombardi BPM and external systems.
40. What are Event Handlers, and how do they work in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Event Handlers in Lombardi BPM are mechanisms that respond to specific events or triggers within a business process. They are associated with activities and define actions to be executed when a predefined event occurs. Event Handlers can handle events such as task completion, process start, or timer expiration. They enhance the flexibility and adaptability of business processes by allowing dynamic responses to various scenarios during runtime.
41. Explain how to monitor and manage processes in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
- Monitoring and managing processes in Lombardi BPM involve using the Process Portal and Process Inspector.
- The Process Portal provides a user interface for end-users to view and complete tasks, while the Process Inspector allows administrators to monitor running instances, identify bottlenecks, and gain insights into process performance.
- Additionally, Lombardi BPM offers performance dashboards and reporting tools for in-depth analysis and management of process execution.
42. How do you handle versioning and rollback in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Versioning in Lombardi BPM involves creating snapshots of process applications at different stages of development. This allows for easy rollback to a previous version if issues arise. The Process Center provides version control features, enabling users to manage and deploy different versions of process applications across environments while maintaining a history of changes.
43. Describe the Lombardi BPM database schema and its components.
Ans:
- The Lombardi BPM database schema comprises tables that store metadata, configuration, and runtime data related to process applications.
- Components include tables for process instances, tasks, variables, snapshots, and user and group information.
- The schema design facilitates efficient data retrieval and storage, supporting the execution and management of business processes within the Lombardi BPM environment.
44. How do Coaches differ from Heritage Coaches?
Ans:
| Feature | |||
| Flexibility | Modern, highly flexible, and responsive. | Limited flexibility, may lack adaptation to modern standards. | |
| Responsive Design | Inherently supports responsiveness. | May need additional effort for optimal compatibility. | |
| User Interaction | Supports enhanced interactions. | Limited interactive features, may lack dynamic behavior. | |
| Out-of-the-Box UI | Modern styling and design elements. | Classic appearance, may require additional styling. | |
| Mobile Compatibility | Inherently compatible with mobile devices. | May need adjustments for optimal mobile compatibility. | |
| Technological Stack | Leverages newer web technologies. | May rely on older frameworks, potentially affecting alignment. |
45. How do you perform system maintenance and backups in IBM Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
- Performing system maintenance and backups in IBM Lombardi BPM involves regular monitoring, updates, and data backups.
- System administrators should schedule maintenance windows to apply patches and updates, ensuring the platform’s stability and security.
- Additionally, a robust backup strategy includes regular backups of configuration data, snapshots, and the underlying database to facilitate quick recovery in case of system failures or data loss.
46. Explain the role of the Lombardi BPM Performance Modeler in administration.
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Performance Modeler is a tool that assists administrators in analyzing and optimizing the performance of business processes. It allows users to create performance models, simulate various scenarios, and identify potential bottlenecks in the process. By using this tool, administrators can make informed decisions to improve process efficiency and overall system performance.
47. How do you configure and manage server clusters in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
- Configuring and managing server clusters in Lombardi BPM involves setting up multiple Process Servers to work together seamlessly.
- This enhances performance, scalability, and fault tolerance.
- System administrators configure server clusters through the Process Center, defining the cluster topology and assigning processes to specific servers.
- Proper load balancing and failover mechanisms ensure that the system efficiently distributes workload and recovers from server failures.
48. Discuss the role of Coaches in user interfaces and their impact on administration.
Ans:
Coaches in Lombardi BPM serve as the building blocks for designing user interfaces within business processes. Administrators can use Coaches to create custom forms and views, tailoring the user experience to specific needs. By utilizing Coaches effectively, administrators enhance the usability and efficiency of BPM applications, contributing to a more user-friendly and intuitive environment.
49. How do you handle security vulnerabilities and updates in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Handling security vulnerabilities and updates in Lombardi BPM requires a proactive approach. Administrators should stay informed about security patches and updates released by IBM and promptly apply them to the environment. Regular security assessments, vulnerability scanning, and adherence to best practices ensure a secure BPM system.
50. What is the Lombardi BPM health check tool, and how is it used?
Ans:
- The Lombardi BPM health check tool is a diagnostic tool provided by IBM to assess the health and performance of a Lombardi BPM environment.
- It performs checks on various components, configurations, and system parameters, identifying potential issues and providing recommendations for optimization.
- Administrators use the health check tool to ensure that the BPM system is running efficiently and to address any performance or configuration issues.
51. Describe how to set up and maintain email notifications in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
Configuring and managing email notifications in Lombardi BPM involves setting up communication channels to notify users about task assignments, deadlines, or other relevant events. Administrators define notification templates, configure email servers, and establish rules for triggering notifications based on specific conditions within the business processes. This ensures timely and effective communication with users involved in BPM workflows.
52. How do you optimize and tune the performance of Lombardi BPM processes?
Ans:
- Optimizing and tuning the performance of Lombardi BPM processes requires a comprehensive approach.
- Administrators can review and optimize database configurations, allocate sufficient system resources, and fine-tune the JVM parameters.
- Additionally, performance monitoring tools, such as the Lombardi BPM Performance Modeler, can be used to analyze process execution and identify areas for improvement.
- Regular performance assessments and adjustments help maintain optimal system performance.
53. What is the Lombardi BPM Process Portal, and how do you customize it?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Process Portal is a web-based interface that allows end-users to interact with and manage tasks within BPM processes. Administrators can customize the Process Portal by configuring the layout, themes, and branding to align with organizational standards. Furthermore, they can define user access roles, personalize dashboards, and integrate external content to tailor the portal according to specific user needs.
54. Explain the integration options available for Lombardi BPM with external systems.
Ans:
- Web Services: Allows communication with external services through SOAP or RESTful APIs.
- JMS (Java Message Service): Enables messaging between Lombardi BPM and other systems.
- Database Integration: Facilitates interaction with external databases.
- Custom Connectors: Integration Designer supports the creation of custom connectors to interface with specific external applications or services.
55. How can Lombardi BPM databases be troubleshooted and resolved?
Ans:
Troubleshooting database-related issues in Lombardi BPM involves analyzing database logs, monitoring database performance, and identifying potential bottlenecks. Administrators use database management tools to optimize queries, ensure proper indexing, and resolve connectivity issues. Collaborating with database administrators may be necessary to address more complex database-related challenges.
56. What is the Lombardi BPM Document Store, and how is it managed?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Document Store is a repository for storing documents and attachments associated with BPM processes. Administrators manage the Document Store by configuring storage locations, setting access controls, and monitoring storage capacity. Regular maintenance involves archiving and purging to manage document retention policies efficiently.
57. Discuss the importance of system monitoring and logging in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
- System monitoring and logging in Lombardi BPM are crucial for identifying and addressing issues proactively.
- Monitoring tools track system metrics, resource utilization, and performance.
- Logging captures events, errors, and transaction details, facilitating troubleshooting.
- Admins analyze logs to detect anomalies, track user activities, and ensure system health, contributing to overall system reliability.
58. How do you handle user access and permissions in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Admins manage user access and permissions in Lombardi BPM through role-based access control. They define roles, assign permissions, and control access to specific functions and data. Regular reviews of user roles and permissions ensure compliance with security policies. Integration with LDAP or other identity management systems may be utilized for centralized user access management.
59. What are the different types of events in Lombardi BPM, and how are they managed?
Ans:
Lombardi BPM handles various events, including timer events, message events, and user events. Admins manage these events by configuring event triggers, defining actions, and specifying event handlers in process models. They monitor event logs to track event occurrences, troubleshoot issues, and optimize process execution based on event-driven conditions.
60. How do you manage and monitor task assignments and escalations in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
- Admins manage task assignments by configuring user roles, defining task participants, and establishing task assignment rules.
- Monitoring involves tracking task status, assignment history, and escalations.
- Admins use monitoring tools to ensure tasks are completed within defined timelines, and escalations are triggered appropriately based on process requirements.
61. Discuss the process of upgrading IBM Lombardi BPM to newer versions.
Ans:
Upgrading Lombardi BPM involves careful planning, including backing up data, validating system requirements, and testing in a non-production environment. Admins follow a step-by-step upgrade process provided by IBM, which may include installing the new version, migrating configurations, and updating database schemas. Thorough testing and validation are crucial before deploying the upgrade in the production environment.
62. How can high availability and disaster recovery be guaranteed?
Ans:
High availability in Lombardi BPM is ensured through server clustering, load balancing, and redundant configurations. Disaster recovery involves regular backups, offsite storage, and documented recovery procedures. Admins test disaster recovery plans periodically, ensuring a quick and reliable recovery in case of unexpected events, minimizing downtime and data loss.
63. What is the Lombardi BPM Admin Console, and how is it utilized?
Ans:
A web-based interface called the Lombardi BPM Admin Console enables administrators to set up, track, and control several BPM environment features. Admins utilize the console to set up server configurations, manage user roles, monitor system metrics, configure integrations, and troubleshoot issues. It serves as a centralized tool for overall BPM system administration.
64. How do you handle custom logging and error handling in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
Admins implement custom logging and error handling in Lombardi BPM by incorporating logging activities and error events within process models. They define custom error messages, capture relevant data, and log information to facilitate troubleshooting. Custom logging ensures that admins can gather specific details about process executions, aiding in the identification and resolution of issues.
65. Explain SLA (Service Level Agreement).
Ans:
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) in Lombardi BPM defines agreed-upon performance metrics and expectations for process execution.
- It includes parameters such as response times, completion deadlines, and quality standards.
- Admins configure SLAs to ensure that BPM processes adhere to predefined timelines and meet performance criteria, enabling effective monitoring and management.
66. Explain the concept of a sub-process.
Ans:
A sub-process in Lombardi BPM represents a set of activities grouped within a more extensive process. It allows for modularization and abstraction, enhancing process design and readability. Admins use sub-processes to encapsulate specific functionalities or logic, promoting reusability and maintainability within complex BPM workflows.
67. Highlight the distinctions among different subprocess types.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM supports different types of sub-processes, including Embedded Sub-Processes, Multi-Instance Sub-Processes, and Ad Hoc Sub-Processes. Embedded Sub-Processes contain a sequence of activities within the primary process. Multi-Instance Sub-Processes execute in parallel for multiple instances. Ad Hoc Sub-Processes allow dynamic instantiation of activities based on runtime conditions. Admins choose the appropriate type based on the specific requirements of the BPM process.
68. How would you assign activities to users?
Ans:
- Admins assign activities to users in Lombardi BPM by defining user roles, task participants, and assignment rules.
- Roles are associated with specific activities, and users assigned to those roles receive tasks based on their assigned roles.
- To make sure that tasks are assigned to the right people according to their roles and responsibilities, administrators set up user assignments inside process models.
69. Discuss the significance of Lombardi BPM environment tuning and optimization.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM environment tuning and optimization are crucial for maximizing system performance. Admins fine-tune configurations related to database connections, memory allocation, and caching. Optimization efforts aim to enhance process execution speed, resource utilization, and overall system efficiency. Regular tuning ensures that the BPM environment operates at peak performance levels.
70. Explain the Lombardi BPM Advanced Integration Services and their use cases.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM Advanced Integration Services provide enhanced capabilities for integrating BPM processes with external systems. Admins use these services to configure advanced integration scenarios, including invoking external services, handling complex data transformations, and managing asynchronous interactions. Use cases may involve integrating with enterprise systems, web services, or external databases to enhance BPM process functionality.
71. Discuss the process of implementing and managing horizontal scaling in Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
Horizontal scaling in Lombardi BPM involves deploying multiple server instances to distribute processing loads. Admins configure load balancing mechanisms to ensure even distribution of tasks across server instances. This approach enhances system performance, scalability, and fault tolerance by allowing the BPM environment to handle increased workloads more effectively.
72. What is the Lombardi BPM Archive and Purge feature, and how is it configured?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Archive and Purge feature allows admins to archive and remove historical process data, reducing database clutter. Admins configure archival policies, specifying which process instances and data to archive based on predefined criteria. Purging involves permanently removing archived data to free up storage space and optimize database performance.
73. Discuss the role of Lombardi BPM Gateways in process routing and decision-making.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM Gateways are decision points within BPM processes where different paths are determined based on specified conditions. Admins configure gateways to route process flow, make decisions, and control the logical flow of activities. Gateways support decision-making based on data conditions, allowing for dynamic and flexible process execution.
74. How do you handle the migration of Lombardi BPM artifacts between environments?
Ans:
- Admins manage artifact migration in Lombardi BPM by exporting and importing process applications and snapshots.
- They use the Lombardi Application Deployment Manager (LAD) tool to package and move artifacts between environments.
- Proper planning, version control, and testing are essential to ensure a smooth and reliable migration process while maintaining data integrity and consistency.
75. Explain the steps involved in configuring LDAP integration for Lombardi BPM.
Ans:
Configuring LDAP integration in Lombardi BPM involves steps such as defining LDAP connection settings, mapping LDAP attributes to BPM user attributes, and configuring security settings. Admins establish a connection to the LDAP server, synchronize user data, and enable single sign-on (SSO) capabilities. This integration enhances user management and authentication by leveraging existing LDAP directories.
76. How do you monitor and optimize long-running processes in Lombardi BPM?
Ans:
- Monitoring and optimizing long-running processes in Lombardi BPM require admins to use tools like Lombardi BPM Process Portal and Performance Modeler.
- They identify bottlenecks, analyze process execution metrics, and optimize activities and gateways for better performance.
- Tuning database connections and adjusting system settings contribute to the efficient handling of long-running processes.
77. Discuss the integration options for Lombardi BPM with external databases.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM integrates with external databases using connectors, JDBC (Java Database Connectivity), and custom SQL queries. Admins configure data mappings, define connection details, and use SQL queries to interact with external databases. This integration enables seamless data exchange between Lombardi BPM processes and external database systems.
78. What is the Lombardi BPM Process Inspector, and how is it used?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Process Inspector is a tool for monitoring and analyzing process instances. Admins use it to view real-time process data, track instance progress, and identify potential issues. The Process Inspector facilitates efficient troubleshooting and decision-making by providing a complete overview of the entire BPM process.
79. Explain the significance of Lombardi BPM Process Versioning.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM Process Versioning allows admins to manage changes and updates to BPM processes over time. It involves creating and managing different versions of a process, ensuring that existing instances continue running on their original version while new instances follow the updated version. Versioning supports process evolution and maintains continuity during process improvements.
80. How do you handle security configurations for Lombardi BPM coaches?
Ans:
- Admins configure security for Lombardi BPM coaches by defining access controls, user roles, and permissions.
- They set up coach views with appropriate visibility based on user roles.
- Security configurations ensure that users only access and interact with coach elements relevant to their roles, enhancing data confidentiality and process integrity.
81. What is the purpose of the Lombardi BPM Case Administration Console?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Case Administration Console is a web-based tool that allows admins to manage case instances, view case details, and perform administrative actions. Admins use this console to monitor case progression, update case data, and make decisions related to case management. It provides a centralized interface for efficient case administration.
82. How do you troubleshoot Lombardi BPM Process Server connectivity issues?
Ans:
Troubleshooting Lombardi BPM Process Server connectivity issues involves checking server logs, verifying network configurations, and ensuring database connectivity. Admins use tools like the Lombardi BPM Process Admin Console to view server status, analyze error messages, and diagnose connectivity problems. Collaboration with network and database administrators may be necessary for comprehensive issue resolution.
83. Explain the Lombardi BPM task assignment and escalation process.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM task assignment involves defining roles, assigning users to roles, and configuring task assignments within process models. Escalation processes are configured to trigger actions automatically when tasks exceed defined time limits. Admins set up escalation rules to ensure timely task completion and use monitoring tools to track task status and escalations.
84. Discuss the impact of Lombardi BPM snapshots on the deployment process.
Ans:
Lombardi BPM snapshots capture the point-in-time state of a process application, including process models, data mappings, and configurations. Admins use snapshots for version control and deployment. The impact on the deployment process is positive, as snapshots provide a reliable mechanism to package and move artifacts between environments, ensuring consistency and reproducibility during application deployment.
85. What is the Lombardi BPM Monitor?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Monitor is a tool designed for real-time monitoring and analysis of BPM process instances. Admins use this tool to gain insights into process performance, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and identify areas for improvement. The Monitor provides graphical representations of process data, allowing administrators to make informed decisions and optimize ongoing process executions.
86. Explain the role of Lombardi BPM Global Transactions in process execution.
Ans:
- Lombardi BPM Global Transactions allow admins to define a group of related services or activities within a BPM process that need to be executed as a single, atomic unit.
- To preserve data consistency, the complete transaction is rolled back if any portion of it fails.
- Global Transactions ensure that complex processes involving multiple steps are executed reliably without data inconsistencies.
87. What is the Lombardi BPM Dynamic Process Assignment feature?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Dynamic Process Assignment feature enables admins to dynamically assign process instances to specific users or groups based on runtime conditions. Admins configure rules within the process model to determine the assignment criteria, allowing for flexibility in routing instances to appropriate individuals or teams during execution. This feature enhances adaptability in handling various scenarios within BPM processes.
88. Discuss the considerations for optimizing Lombardi BPM database performance.
Ans:
Optimizing Lombardi BPM database performance involves considerations such as configuring database connection pools, tuning SQL queries, and managing indexes efficiently. Admins monitor database performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and optimize data access patterns. Regular database maintenance, including archiving and purging, contributes to overall database performance and responsiveness.
89. How do you configure Lombardi BPM to use SSL for secure communication?
Ans:
Configuring Lombardi BPM for SSL involves obtaining and installing SSL certificates, configuring the application server (e.g., WebSphere) to enable SSL, and updating Lombardi BPM settings to use HTTPS. Admins set up SSL certificates for secure communication between clients and the BPM server, enhancing data confidentiality and integrity during data transmission.
90. What is the Lombardi BPM Shared Resources feature, and when is it used?
Ans:
The Lombardi BPM Shared Resources feature allows admins to define reusable resources, such as services, variables, and configurations, that can be shared across multiple processes. Admins use Shared Resources to promote consistency, reduce redundancy, and simplify maintenance across process applications. This feature enhances modularity and reusability in BPM process design.
91. How do you troubleshoot Lombardi BPM email listener configuration issues?
Ans:
Troubleshooting Lombardi BPM email listener configuration involves checking email server settings, verifying connection details, and reviewing error logs. Admins use the Lombardi BPM Process Admin Console to monitor email listener activities and diagnose configuration problems. Configuring appropriate logging levels and collaborating with email server administrators help in resolving issues related to email integration.

