Rated #1 Recognized as the No.1 Institute for Java Masters Program Training Course
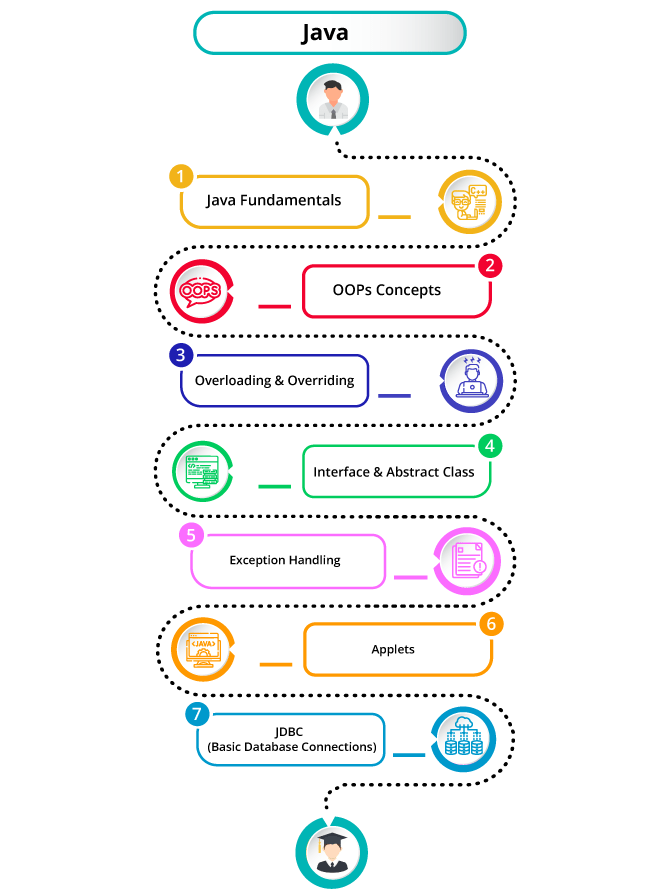
Elevate your career with the Java Masters Program Training Course. Master core Java concepts, object-oriented programming, web development, and advanced frameworks through hands-on learning.
This Java Masters Program is designed for professionals looking to gain expertise in Java development and earn a comprehensive certification. Learn how to build robust applications, implement Java-based solutions, and work with popular frameworks to solve real-world programming challenges.
- Access affordable, expert-led Java Training and support.
- Gain hands-on experience with industry-standard tools and technologies.
- Master Java programming to advance your career in software development.
- Join 10,000+ professionals who earned their Java Masters Certification Course.
- Take the Java Masters Program and become a Java expert to lead in the tech world.
- Unlock career opportunities with leading companies seeking skilled Java developers.