
BlueCat Interview Questions and Answers [SCENARIO-BASED ]
Last updated on 18th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
Looking for the top BlueCat interview questions to prepare for your interview. Go through some of the best BlueCat interview questions with detailed answers before you get ahead. BlueCat to become an Expert in BlueCat and learn all the instructions required to install and configure the server. Therefore, BlueCat professionals need to encounter interview questions on BlueCat for different enterprise BlueCat job roles. The following discussion offers an overview of different categories of interview questions related to BlueCat to help aspiring enterprise BlueCat Professionals.
1. What is BlueCat?
Ans:
BlueCat is an industry-leading DNS, DHCP, and IP Address Management (DDI) solutions provider. Renowned for its innovative approach to network infrastructure management, BlueCat offers organisations powerful tools to simplify, automate, and secure their critical network services.
2. What is the primary purpose of BlueCat’s DDI solutions?
Ans:
BlueCat’s DDI solutions serve as a cornerstone for organisations seeking to streamline and automate the management of DNS, DHCP, and IP addresses. By centralising these critical functions, BlueCat empowers enterprises to enhance their network infrastructure’s overall efficiency, security, and reliability.
3. How does BlueCat contribute to network security?
Ans:
BlueCat plays a crucial role in network security by providing centralised control over DNS and DHCP services. This centralized control allows organisations to enforce security policies, detect anomalies in network traffic, and proactively mitigate potential security threats. BlueCat’s solutions are instrumental in safeguarding the integrity of network operations against various cyber threats.
4. Can you explain the role of DNS in BlueCat’s offerings?
Ans:
DNS, or Domain Name System, is fundamental to BlueCat’s offerings. It is the backbone for translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, enabling seamless communication across networks. BlueCat ensures the reliability and security of DNS services, making it a critical component in the company’s commitment to delivering robust network management solutions.
5. What is the significance of DHCP in BlueCat’s solutions?
Ans:
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, holds great significance in BlueCat’s solutions as it facilitates the automatic assignment of IP addresses to devices on a network. This dynamic allocation optimises resource utilisation, simplifies network administration, and ensures that devices connect seamlessly to the network with minimal manual intervention.
6. What distinguishes BlueCat from other DDI solutions?
Ans:
| Feature/Area | BlueCat DDI Solutions | |
| Security Emphasis |
Focus on advanced threat protection and DNS security |
|
| Automation and Orchestration | Implementation of advanced automation and orchestration | |
| Scalability |
Provision of scalable solutions catering to businesses of all sizes | |
| User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive and user-friendly interface for ease of use | |
| Integration with Other Technologies |
Inclusion of integrations with various networking and cybersecurity technologies |
|
| Customization and Flexibility |
Offering a high level of customization and flexibility |
7. What is the BlueCat Address Manager?
Ans:
BlueCat Address Manager is a comprehensive DDI solution that offers centralised management for IP addresses, DNS configurations, and DHCP settings. It is a robust platform for organisations to efficiently address their needs, ensuring consistency and control across the network.
8. How does BlueCat contribute to cloud adoption?
Ans:
BlueCat facilitates cloud adoption by seamlessly integrating its DDI solutions with cloud environments. This integration ensures consistent DNS, DHCP, and IP address management across both on-premises and cloud infrastructure, providing organisations with a unified approach to network services in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
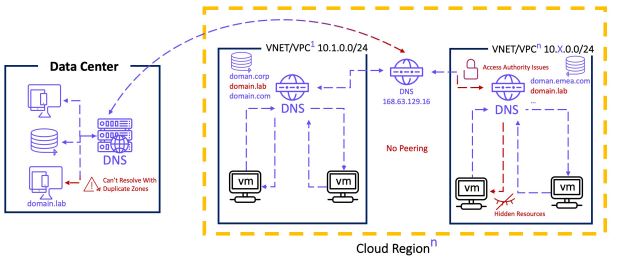
9. Explain the role of BlueCat Gateway.
Ans:
BlueCat Gateway is a key component that enhances the extensibility and automation capabilities of BlueCat’s solutions. It provides a RESTful API interface, enabling users to interact programmatically with BlueCat’s Address Manager and other modules. This flexibility empowers organisations to seamlessly integrate BlueCat into their existing workflows and toolchains.
10. How does BlueCat help in ensuring compliance with network policies?
Ans:
BlueCat aids organisations in ensuring compliance with network policies by offering tools to define and enforce policies related to DNS, DHCP, and IP address allocation. This ensures that network operations align with regulatory requirements and internal policies, reducing the risk of configuration drift and ensuring a secure and compliant network environment.
11. What is BlueCat DNS Integrity?
Ans:
BlueCat DNS Integrity is a robust security feature designed to enhance network security by detecting and preventing DNS-related threats. It ensures the integrity of DNS services by monitoring DNS transactions, identifying anomalies, and proactively mitigating potential security risks, thereby safeguarding the organization from malicious activities.
12. How does BlueCat handle DNS security in the context of DNS cache poisoning?
Ans:
BlueCat addresses DNS cache poisoning by implementing DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC). This cryptographic technology adds a layer of security by digitally signing DNS data, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of DNS responses. BlueCat’s approach to DNS security is proactive, providing a robust defence against cache poisoning attacks.
13. Can BlueCat integrate with existing network infrastructure and tools?
Ans:
BlueCat is designed with extensive integration capabilities, allowing seamless integration with various network infrastructure components and third-party tools through APIs. This ensures compatibility with existing infrastructure, enabling organisations to leverage BlueCat’s capabilities without significant disruptions to their established workflows.
14. What is BlueCat’s role in supporting IPv6 adoption?
Ans:
BlueCat supports IPv6 adoption by providing IPAM solutions that seamlessly manage bot6 and IPv4 addresses. This capability allows organisations to transition to IPv6 smoothly, ensuring compatibility with emerging technologies and addressing the growing demand for IP addresses in the modern digital landscape.
15. Explain the concept of BlueCat Gateway Workflows.
Ans:
BlueCat Gateway Workflows empower users to automate complex tasks by creating custom workflows that leverage BlueCat’s APIs. This capability streamlines and accelerates processes, allowing organisations to implement automation tailored to their needs and improve operational efficiency.
16. How does BlueCat help in reducing network downtime?
Ans:
BlueCat mitigates the risk of network downtime by providing automated and centralised control over DNS and DHCP services. This reduces the likelihood of configuration errors, ensures consistency in network operations, and facilitates rapid issue resolution, ultimately minimising the impact of disruptions on business continuity.
17. What is the role of BlueCat Address Manager in supporting multi-tenancy?
Ans:
BlueCat Address Manager supports multi-tenancy by allowing organisations to manage IP address spaces for multiple tenants or business units within a centralised platform. This ensures efficient resource allocation, security isolation, and streamlined management of diverse network environments within a shared infrastructure.
18. How does BlueCat assist in capacity planning for IP address allocation?
Ans:
BlueCat provides valuable tools for capacity planning by offering insights into IP address utilization trends. This allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently, proactively identify potential shortages, and plan for future requirements, ensuring a well-managed and scalable network infrastructure.
19. What is the significance of BlueCat’s DNS and DHCP Integrity Modules?
Ans:
BlueCat’s DNS and DHCP Integrity Modules are critical components that enhance network security. These modules actively monitor and validate DNS and DHCP transactions, detecting and preventing unauthorized or malicious activities. By ensuring the integrity of these core network services, BlueCat effectively safeguards against security threats and maintains the reliability of network operations.
20. What is the role of BlueCat Gateway in automation?
Ans:
- RESTful API interface
- Integration facilitator
- Workflow automation
- Third-party tool interaction
- Customization capabilities
- Streamlining complex tasks
21. How does BlueCat contribute to network visibility?
Ans:
BlueCat enhances network visibility by providing comprehensive insights into DNS, DHCP, and IP address usage. The visibility offered by BlueCat’s solutions empowers organizations to make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues effectively, and gain a deeper understanding of their network infrastructure, ultimately contributing to improved operational efficiency.
22. Explain BlueCat’s role in supporting DevOps practices.
Ans:
BlueCat supports DevOps practices by providing automation tools and seamless integrations that foster collaboration between development and operations teams. The ability to automate DNS, DHCP, and IP address management tasks aligns with the principles of DevOps, accelerating application delivery and ensuring a more agile and collaborative development lifecycle.
23. How does BlueCat contribute to IPv6 adoption?
Ans:
- Seamless IPv6 and IPv4 management
- Transition support
- Dual-stack capabilities
- Address space planning
- IPv6 readiness insights
- Simplified migration processes
24. What is the BlueCat Gateway REST API, and how is it used?
Ans:
The BlueCat Gateway REST API is a programmable interface that allows users to interact with BlueCat’s solutions. It automates tasks, integrates with third-party tools, and streamlines workflows. The API-first approach of BlueCat Gateway promotes extensibility, enabling organizations to tailor their interactions with BlueCat based on their specific requirements.
25. How does BlueCat address the challenge of IP address conflicts?
Ans:
BlueCat minimizes the risk of IP address conflicts through intelligent IPAM solutions. These solutions track and manage IP address allocations, reducing the likelihood of overlapping assignments and ensuring efficient resource utilization. BlueCat’s proactive approach to IP address management contributes to a more stable and conflict-free network environment.
26. Can BlueCat be deployed in hybrid cloud environments?
Ans:
BlueCat is designed for deployment in hybrid cloud environments, offering consistent DNS, DHCP, and IP address management across both on-premises and cloud infrastructure. This flexibility ensures organisations can maintain unified network services in complex, hybrid IT architectures.
27. How does BlueCat help in ensuring DNS availability and reliability?
Ans:
BlueCat ensures DNS availability and reliability through features such as load balancing, DNSSEC, and DNS Integrity Modules. These capabilities optimize DNS performance, distribute traffic efficiently, and actively monitor and secure DNS transactions, contributing to a resilient and reliable DNS infrastructure.
28. Explain BlueCat’s approach to DNS load balancing.
Ans:
- Distributes DNS requests
- Optimizes server performance
- Prevents server overloads
- Enhances availability
- Improves responsiveness
- Scalable and efficient traffic management
29. How does BlueCat contribute to network automation?
Ans:
BlueCat contributes to network automation by providing tools and APIs that enable the automation of DNS, DHCP, and IP address management tasks. Automation reduces manual effort, accelerates processes, and ensures consistency in network configurations, aligning with automation principles central to modern IT and network operations.
30. What is BlueCat’s approach to DNS load balancing?
Ans:
BlueCat’s approach to DNS load balancing involves the distribution of incoming DNS requests across multiple servers. This ensures optimal performance, prevents server overloads, and enhances the availability and responsiveness of DNS services. BlueCat’s DNS load balancing provides a more robust and scalable network infrastructure.
31. Can BlueCat help in reducing the complexity of network configurations?
Ans:
Yes, BlueCat helps reduce the complexity of network configurations by providing centralized control over DNS, DHCP, and IP address management. This centralized approach minimizes the risk of configuration errors, streamlines network changes, and simplifies overall network administration, leading to a more manageable and efficient network environment.
32. What sets BlueCat’s IP Address Management (IPAM) apart?
Ans:
- Centralized platform
- Efficient resource management
- Proactive IP conflict prevention
- Capacity planning tools
- Multi-tenancy support
- Seamless integration with existing tools
33. What is the significance of BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration?
Ans:
BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration is significant for enhancing network security. By integrating with threat intelligence feeds, BlueCat enables organisations to block malicious domains and defend against cyber threats proactively. This proactive approach to security aligns with the evolving threat landscape and ensures a robust defence against emerging risks.
34. How does BlueCat handle DNS performance optimization?
Ans:
BlueCat handles DNS performance optimization through features like caching, load balancing, and traffic management. These capabilities ensure low latency and high responsiveness for DNS queries, improving overall network performance and user experience.
35. Can BlueCat support organizations with complex network infrastructures?
Ans:
Yes, BlueCat is designed to support organizations with complex network infrastructures. Its scalable and flexible DDI solutions adapt to diverse and evolving network environments, providing the necessary tools and capabilities to manage complexity effectively and ensure the stability of network operations.
36. How does BlueCat help streamline compliance audits?
Ans:
BlueCat facilitates compliance audits by providing centralized visibility into DNS, DHCP, and IP address configurations.
This visibility simplifies the audit process, allowing organizations to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
BlueCat’s contribution to compliance auditing ensures a transparent and accountable network infrastructure.
37. Explain the role of BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS in network optimization.
Ans:
BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS dynamically adjusts to changing network conditions, optimizing DNS performance. This adaptability ensures efficient domain name resolution, improves overall network optimization, and allows organizations to respond effectively to varying network demands.
38. How does BlueCat assist in disaster recovery planning?
Ans:
BlueCat aids in disaster recovery planning by providing tools for backing up and restoring DNS, DHCP, and IP address configurations. This ensures quick recovery in the event of network disruptions, minimizing downtime and contributing to the overall resilience of the network infrastructure.
39. What is the importance of BlueCat’s API-first architecture?
Ans:
BlueCat’s API-first architecture holds significant importance in fostering integrations and extensibility. It allows organizations to easily integrate BlueCat’s solutions with other tools and systems, enabling a collaborative and automated network environment that aligns with modern IT practices and supports diverse workflows.
40. How does BlueCat help organizations adapt to changing IP address requirements?
Ans:
BlueCat assists organizations in adapting to changing IP address requirements by providing scalable and flexible IPAM solutions. These solutions accommodate growth, changes, and evolving network demands, ensuring organizations can effectively manage and allocate IP addresses based on their specific requirements.
41. What sets BlueCat apart from other DDI solutions in the market?
Ans:
- DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
- Threat Feed Integration
- DNS Integrity Modules
- Anomaly detection
- Proactive threat mitigation
- Real-time monitoring
42. How does BlueCat contribute to network visibility?
Ans:
BlueCat’s DNS and DHCP Integrity Modules are critical components that enhance network security. These modules actively monitor and validate DNS and DHCP transactions, detecting and preventing unauthorized or malicious activities. By ensuring the integrity of these core network services, BlueCat effectively safeguards against security threats and maintains the reliability of network operations.
43. How does BlueCat handle DNS traffic management?
Ans:
BlueCat offers DNS traffic management capabilities to optimise DNS performance. This involves distributing incoming DNS requests across multiple servers, balancing the load efficiently, and ensuring high availability for critical services. BlueCat’s approach to DNS traffic management contributes to improved performance and responsiveness in resolving domain names.
44. What role does BlueCat play in supporting digital transformation initiatives?
Ans:
BlueCat supports digital transformation initiatives by providing a foundational layer for efficient and secure network operations. BlueCat’s DDI solutions’ centralization, automation, and security features enable organizations to adapt to evolving technologies, enhance agility, and meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
45. How does BlueCat assist in preventing IP address exhaustion?
Ans:
BlueCat assists in preventing IP address exhaustion by offering tools for capacity planning and insights into IP address utilization. This allows organizations to reclaim unused addresses, proactively plan for future requirements, and ensure a sustainable and well-managed pool of IP addresses.
46. How does BlueCat assist in disaster recovery planning?
Ans:
- Backup and restore capabilities
- Quick recovery mechanisms
- DNS, DHCP, and IP address configuration backup
- Minimises downtime impact
- Ensures network resilience
- Supports business continuity
47. How does BlueCat secure DNS transactions and prevent DNS threats?
Ans:
BlueCat ensures the integrity of DNS transactions through advanced mechanisms such as DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC). This cryptographic technology digitally signs DNS data, providing a secure and authenticated way to verify the authenticity of DNS responses.
Additionally, BlueCat employs DNS Integrity Modules that actively monitor DNS transactions in real-time, detecting anomalies and preventing potential threats. This proactive approach safeguards the DNS infrastructure against unauthorized activities, ensuring the reliability and security of the entire network.
48. What makes BlueCat a DevOps-friendly solution?
Ans:
- Automation tools
- Seamless integration
- Collaboration facilitator
- API-driven approach
- Accelerated application delivery
- Agile and collaborative development lifecycle
49. How does BlueCat prevent DNS cache poisoning for network security?
Ans:
BlueCat is crucial in preventing DNS cache poisoning, a malicious attack that manipulates the DNS cache to redirect users to fraudulent websites. BlueCat addresses this by implementing DNSSEC, which digitally signs DNS data to ensure its authenticity.
By doing so, BlueCat strengthens the security of the DNS infrastructure, preventing attackers from injecting false information into the cache. This robust defence mechanism safeguards users against phishing attempts and other DNS-related security threats, contributing significantly to overall network security.
50. How does BlueCat address the challenge of IP address conflicts?
Ans:
- Intelligent IPAM solutions
- Tracking and managing IP allocations
- Efficient resource utilization
- Minimizes risk of conflicts
- Proactive management approach
- Stable and conflict-free network environment
51. How does BlueCat support secure and compliant networks?
Ans:
BlueCat is crucial in preventing DNS cache poisoning, a malicious attack that manipulates the DNS cache to redirect users to fraudulent websites. BlueCat addresses this by implementing DNSSEC, which digitally signs DNS data to ensure its authenticity.
By doing so, BlueCat strengthens the security of the DNS infrastructure, preventing attackers from injecting false information into the cache. This robust defence mechanism safeguards users against phishing attempts and other DNS-related security threats, contributing significantly to overall network security.
52. Explain BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS in network optimization.
Ans:
- Dynamic adjustment to network conditions
- Optimizes DNS performance
- Efficient domain name resolution
- Responsive to changing demands
- Improves overall network optimization
- Adaptable to varying network conditions
53. What’s BlueCat Gateway’s role in network workflow automation and integrations?
Ans:
BlueCat Gateway is critical in enhancing automation and integrations within network workflows.
It provides a RESTful API interface, allowing users to interact programmatically with BlueCat’s Address Manager and other modules.
This capability empowers organizations to automate complex tasks, streamline processes, and integrate BlueCat seamlessly into existing workflows and toolchains.
BlueCat Gateway’s role in facilitating automation contributes to increased operational efficiency, reduced manual effort, and improved collaboration between different network infrastructure components.
54. How does BlueCat support digital transformation initiatives?
Ans:
- Foundational layer for network operations
- Centralization and automation
- Security features for modern landscapes
- Adaptable to evolving technologies
- Enhances agility
- Meets demands of a changing digital landscape
55. How does BlueCat help with IPv6 adoption alongside IPv4?
Ans:
BlueCat plays a vital role in supporting organizations through the complexities of IPv6 adoption alongside IPv4. Its IP Address Management (IPAM) solutions seamlessly manage IPv6 and IPv4 addresses, ensuring a smooth transition. BlueCat provides dual-stack capabilities, allowing organizations to operate in mixed IPv4 and IPv6 environments. This adaptability enables businesses to address the growing demand for IP addresses in the modern digital landscape while ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and applications.
56. What is the significance of BlueCat’s API-first architecture?
Ans:
- Seamless integration capabilities
- Extensibility and customization
- Supports diverse workflows
- Collaborative network environment
- Alignment with modern IT practices
- Enhances interoperability with other tools
57. How does BlueCat manage DNS traffic and impact network performance?
Ans:
BlueCat’s approach to DNS traffic management is designed to optimize network performance by efficiently distributing incoming DNS requests across multiple servers. This load-balancing mechanism prevents server overloads, ensures optimal server performance, and enhances the availability and responsiveness of DNS services. By efficiently managing DNS traffic, BlueCat contributes to reduced latency in resolving domain names, ultimately improving the overall performance and user experience within the network.
58. How does BlueCat handle DNS traffic management efficiently?
Ans:
- Load balancing features
- Distributes incoming DNS requests
- Optimizes DNS server performance
- Prevents server overloads
- Enhances DNS availability
- Efficient and scalable traffic management
59. How does BlueCat aid disaster recovery and provide quick network recovery tools?
Ans:
BlueCat contributes to disaster recovery planning by providing essential tools for backing up and restoring DNS, DHCP, and IP address configurations. These tools are crucial for quick network recovery during disruptions, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. By allowing organizations to back up and restore critical network configurations efficiently, BlueCat empowers them to respond rapidly to unforeseen incidents, maintaining the integrity and availability of network services.
60. Explain BlueCat’s role in multi-tenancy support.
Ans:
- Centralized platform for multiple tenants
- Efficient resource allocation
- Security isolation between tenants
- Streamlined management
- Effective IP address space management
- Shared infrastructure control
61. What sets BlueCat’s IPAM apart in capacity planning and resource allocation?
Ans:
BlueCat’s IPAM solutions stand out in capacity planning and efficient resource allocation through advanced tools and insights.
Organisations benefit from granular insights into IP address utilisation trends, allowing them to plan for future requirements proactively.
BlueCat’s IPAM solutions facilitate efficient resource allocation by providing a centralised platform for managing IP addresses, reducing the risk of IP conflicts, and ensuring optimal utilization of address spaces.
This proactive approach to IP address management sets BlueCat apart in enabling organizations to maintain a well-managed and scalable network infrastructure.
62. How does BlueCat contribute to cloud adoption?
Ans:
- Seamless integration with cloud environments
- Consistent DNS, DHCP, and IPAM across on-premises and cloud
- A unified approach to network services
- Facilitates hybrid and multi-cloud environments
- Supports diverse infrastructure architectures
- Ensures operational continuity in cloud transitions
63. How does BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration enhance cybersecurity and address threats?
Ans:
BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration contributes to a proactive cybersecurity stance by integrating with threat intelligence feeds, enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats. The integration allows BlueCat to proactively block access to known malicious domains, defending against a wide range of cyber threats such as malware, phishing attacks, and other forms of cyber espionage. By leveraging threat intelligence, BlueCat enhances the security posture of organizations, protecting them from evolving and sophisticated cybersecurity threats.
64. What makes BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration effective?
Ans:
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds
- Proactive blocking of malicious domains
- Cyber threat defence mechanism
- Enhanced security posture
- Real-time threat prevention
- Mitigates risks from emerging threats
65. How does BlueCat optimize DNS performance for low latency and high responsiveness?
Ans:
BlueCat plays a crucial role in DNS performance optimization through caching, load balancing, and traffic management features. These capabilities ensure low latency and high responsiveness for DNS queries. Caching mechanisms store frequently accessed DNS data, reducing the time required to resolve domain names. Load balancing efficiently distributes DNS requests across servers, preventing bottlenecks and enhancing responsiveness. BlueCat’s approach to DNS performance optimization contributes to a smooth and efficient DNS resolution process, ensuring a seamless user experience within the network.
66. How does BlueCat handle DNS performance optimization?
Ans:
BlueCat’s IP Address Management (IPAM) capabilities provide organisations with a centralised platform for planning, allocating, and tracking IP addresses. This ensures efficient resource management, reduces the risk of IP conflicts, and allows for proactive planning to accommodate the evolving needs of the network.
67. How does BlueCat support complex networks and its scalability features?
Ans:
BlueCat is designed to support organizations with complex network infrastructures by providing scalable and flexible DDI solutions. These solutions adapt to diverse and evolving network environments, offering the tools and capabilities to manage complexity effectively.
BlueCat’s scalability features include the ability to handle large and dynamic IP address spaces, support for multi-tenancy, and the capacity to scale resources to meet the demands of growing networks. This scalability ensures that organizations can efficiently manage and optimize their network infrastructure regardless of size or complexity.
68. How does BlueCat support IP Address Management (IPAM)?
Ans:
- Comprehensive DDI solution
- Threat Feed Integration for security
- Adaptive DNS for dynamic optimization
- API-first architecture for flexibility
- Strong focus on security
- Innovation in addressing network challenges
69. How does BlueCat streamline compliance audits with centralized features?
Ans:
BlueCat streamlines compliance audits by providing centralized features that contribute to audit readiness. The platform offers centralized visibility into DNS, DHCP, and IP address configurations, simplifying the audit process by consolidating critical information in one location. This centralized visibility allows organizations to efficiently demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies. BlueCat’s commitment to transparency and accountability in network configurations ensures that organizations can easily navigate compliance audits, providing a comprehensive and organized view of their network infrastructure.
70. How does BlueCat facilitate compliance audits?
Ans:
- Centralised visibility into DNS, DHCP, and IP address configurations
- Simplified audit process
- Demonstration of adherence to regulatory requirements
- Internal policy compliance
- Transparent and accountable network infrastructure
- Efficient handling of compliance documentation
71. How does BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS optimize networks and adapt to changing conditions?
Ans:
BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS plays a crucial role in network optimization by dynamically adjusting to changing network conditions. This adaptability ensures optimal DNS performance in response to varying demands. The Adaptive DNS feature actively monitors network conditions, adjusting DNS responses based on traffic patterns and server loads. This dynamic adjustment allows BlueCat to optimize domain name resolution, contributing to improved overall network efficiency.
72. How does BlueCat assist in preventing IP address exhaustion?
Ans:
- Tools for capacity planning
- Insights into IP address utilization
- Reclamation of unused addresses
- Proactive planning for future requirements
- Sustainable and well-managed IP address pool
- Mitigation of IP address shortages
73. How does BlueCat improve network visibility and usage insights?
Ans:
BlueCat significantly contributes to network visibility by providing comprehensive insights into DNS, DHCP, and IP address usage.
The platform offers visibility into the entire lifecycle of these critical network services, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and troubleshoot issues effectively.
BlueCat’s reporting and analytics capabilities provide detailed information on DNS query patterns, IP address allocations, and DHCP lease information.
This deep visibility empowers organizations to optimize their network configurations, identify potential issues, and understand their network infrastructure holistically.
74. How does BlueCat handle DNS cache poisoning?
Ans:
- DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
- Digital signing of DNS data
- Protection against tampering
- Ensures the authenticity of DNS responses
- Mitigates DNS cache poisoning risks
75. How does BlueCat secure DNS from cache poisoning and employ extra security measures?
Ans:
BlueCat addresses DNS cache poisoning by implementing DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC), a cryptographic technology that adds a layer of security to DNS transactions. DNSSEC involves digitally signing DNS data, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of DNS responses. By employing DNSSEC, BlueCat actively prevents cache poisoning attacks by verifying the legitimacy of DNS information.
In addition to DNSSEC, BlueCat employs other security measures, such as Threat Feed Integration and DNS Integrity Modules, to proactively detect and mitigate security threats, contributing to a robust defence against a wide range of DNS-related attacks.
76. What role does BlueCat play in supporting hybrid cloud environments?
Ans:
- Consistent DNS, DHCP, and IPAM
- Integration with on-premises and cloud
- Unified network services
- Seamless deployment in hybrid environments
- Adaptability to diverse infrastructure architectures
77. Explain BlueCat Gateway Workflows
Ans:
- Automation of complex tasks
- Customized workflows
- API-driven automation
- Streamlined processes
- Improved operational efficiency
78. How does BlueCat prevent IP address exhaustion and provide capacity planning tools?
Ans:
BlueCat assists in preventing IP address exhaustion by offering advanced tools for capacity planning. Organizations can leverage BlueCat’s IPAM solutions to gain insights into IP address utilization trends, allowing for proactive planning and efficient resource allocation. BlueCat provides tools for reclaiming unused addresses, mitigating the risk of exhaustion. By actively managing and planning for IP address requirements, BlueCat ensures a sustainable and well-managed pool of IP addresses.
79. How does BlueCat handle DNS integrity in real time?
Ans:
- Real-time monitoring
- Anomaly detection
- Proactive threat mitigation
- Security event alerts
- Continuous validation of DNS transactions
80. How does BlueCat contribute to DNS traffic management efficiency?
Ans:
- Load balancing features
- Efficient distribution of DNS requests
- Optimization of server performance
- Prevention of server overloads
- Enhanced DNS availability and responsiveness
81. What is BlueCat’s role in supporting network automation?
Ans:
- Automation tools and APIs
- Streamlined network tasks
- Integration with third-party tools
- Reduction of manual effort
- Acceleration of network processes
82. What is BlueCat’s approach to supporting DevOps practices?
Ans:
- Automation tools and integrations
- Collaboration between development and operations
- API-driven approach
- Acceleration of application delivery
- Alignment with agile development methodologies
83. Explain BlueCat’s Threat Feed Integration in more detail.
Ans:
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds
- Proactive blocking of malicious domains
- Enhances cybersecurity defenses
- Real-time threat prevention
- Mitigation against emerging cyber threats
84. How does BlueCat ensure compliance with network policies?
Ans:
- Policy definition and enforcement
- DNS, DHCP, and IP address policy management
- Centralized control over network policies
- Reduction of configuration drift
- Adherence to regulatory requirements
85. Explain BlueCat’s role in supporting capacity planning.
Ans:
- Tools for capacity planning
- Insights into IP address utilization
- Efficient resource allocation
- Proactive management of IP address space
- Avoidance of potential address shortages
86. What is the significance of BlueCat’s DNS and DHCP Integrity Modules?
Ans:
- Real-time monitoring and validation
- Proactive threat detection
- Prevention of unauthorized activities
- Enhanced network security
- Maintenance of DNS and DHCP integrity
87. How does BlueCat assist in DNS performance optimization?
Ans:
- Caching mechanisms
- Load balancing capabilities
- Traffic management features
- Low-latency DNS responses
- High responsiveness to queries
88. What is BlueCat DNS Integrity, and how does it enhance security?
Ans:
- DNS transaction monitoring
- Anomaly detection
- Proactive threat mitigation
- Ensures DNS service integrity
- Guards against malicious activities
89. How does BlueCat help organizations adapt to changing IP address requirements?
Ans:
- Scalable and flexible IPAM solutions
- Accommodates growth and changes
- Supports evolving network demands
- Seamless management of changing IP requirements
- Future-proof IP address allocations
90. What sets BlueCat’s DNS and DHCP Integrity Modules apart?
Ans:
- Real-time monitoring and validation
- Proactive threat detection
- Prevention of unauthorized activities
- Continuous validation of DNS and DHCP transactions
- Enhanced network security posture
91. How does BlueCat address the challenge of IP address conflicts efficiently?
Ans:
- Intelligent IPAM solutions
- Tracking and managing IP allocations
- Efficient resource utilization
- Minimization of overlapping assignments
- Proactive prevention of IP conflicts
92. What is BlueCat’s role in DNS availability and reliability?
Ans:
- Load balancing features
- DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
- DNS Integrity Modules
- Mitigation against DNS attacks
- Ensures high availability and reliability
93. Explain BlueCat’s Adaptive DNS and its dynamic capabilities.
Ans:
- Dynamically adjusts to network conditions
- Optimizes DNS performance
- Efficient domain name resolution
- Adaptable to changing demands
- Improves overall network optimization
94. How does BlueCat contribute to streamlined compliance audits?
Ans:
- Centralized visibility into configurations
- Simplifies audit processes
- Demonstrates regulatory adherence
- Ensures internal policy compliance
95. What role does BlueCat play in DNS load balancing efficiency?
Ans:
- Distribution of incoming DNS requests
- Optimizes server performance
- Prevents server overloads
- Enhances DNS availability
- Scalable and efficient traffic management

