
[FREQUENTLY ASK] Palo Alto Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 10th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
Our Palo Alto Interview Questions and Answers guide provides a comprehensive overview of crucial topics related to Palo Alto Networks and their cybersecurity solutions. Covering a diverse range of subjects, the interview questions explore Palo Alto firewall functionalities, security policies, threat prevention mechanisms, SSL decryption, and integration with cloud environments. Additionally, the guide delves into network and application visibility, user identification, and threat intelligence utilisation for real-time updates. Whether for aspiring Palo Alto professionals or experienced practitioners, this resource is a valuable tool for interview preparation, offering insights into the complexities of Palo Alto Networks and their role in ensuring robust cybersecurity measures.
1. What are Palo Alto Networks and its primary products?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks is a cybersecurity company that provides various security products and services to organisations worldwide. The company is known for its innovative approach to network security, focusing on preventing cyber threats rather than just detection and response. Palo Alto Networks aims to offer comprehensive and integrated security solutions to help organisations protect their networks, data, and applications from various cyber threats.
2. Explain the key features of Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls boast vital features such as application awareness, user identification, and content inspection. They use an innovative App-ID technology to identify and control applications, enabling granular control over network traffic based on the specific applications.
3. Differentiate between traditional firewalls and Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
| Aspect | |||
| Traffic Inspection | Typically based on port and protocol. | Utilizes an application-aware approach for granular control. | |
| Application Visibility | Limited visibility into specific applications. | Offers detailed visibility into applications and content. | |
| User Identification | Primarily based on IP addresses. | Provides user-based identification for more granularity. | |
| Integration with Cloud | Limited integration capabilities with cloud environments. | Offers advanced integration options with cloud platforms. | |
| SSL Decryption | May lack robust SSL decryption capabilities. | Features advanced SSL decryption for enhanced security. | |
| Threat Intelligence | Relies on external threat intelligence feeds. | Integrates threat intelligence for real-time updates. |
4. What is the purpose of the PAN-OS (Palo Alto Networks Operating System)?
Ans:
The Palo Alto Networks Operating System (PAN-OS) is the proprietary operating system that powers Palo Alto Networks’ Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) and other security appliances. PAN-OS plays a central role in the functionality and security capabilities of Palo Alto Networks’ products. PAN-OS aims to provide a comprehensive and feature-rich platform that enables organisations to implement advanced security measures and effectively manage their network security.
5. How do Palo Alto Networks contribute to network security?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks contributes to network security by offering a comprehensive approach, combining next-generation firewall capabilities, threat intelligence, and advanced security features. This helps organisations prevent and respond to cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, and other sophisticated attacks.
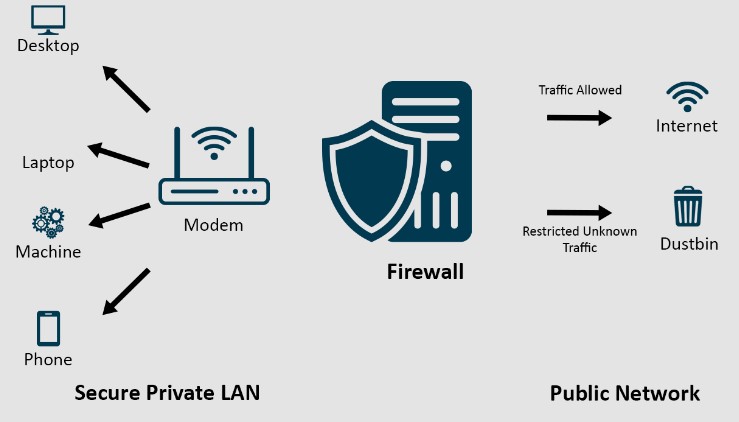
6. Define a firewall and its role in network security.
Ans:
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, preventing unauthorised access and protecting against malicious activities.
7. How does a stateful firewall differ from a stateless firewall?
Ans:
A stateful firewall keeps track of the state of active connections and makes decisions based on the context of the traffic. In contrast, a stateless firewall filters traffic based solely on source and destination information without considering the state of the connection. They cannot understand the relationship between individual packets and whether they belong to an established or legitimate connection.
8. Explain the concept of zones in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
In Palo Alto firewalls, zones represent logical groupings of interfaces with similar security requirements. Zones help define security policies, as traffic is allowed or denied between zones based on the security policy configurations. Zones help facilitate the implementation of security policies by providing a way to group different network segments and apply specific rules governing the flow of traffic between these segments.
9. What is the function of Security Policies in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Security policies in Palo Alto Networks firewalls play a crucial role in determining how network traffic is allowed or denied within the network.
- They define the rules and criteria for permitting or blocking traffic based on various attributes such as source and destination zones, IP addresses, applications, users, and services.
- The primary function of security policies is to enforce the network’s security posture and protect against unauthorised access and potential security threats.
10. Describe the purpose of NAT (Network Address Translation) in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
NAT (Network Address Translation) in Palo Alto firewalls involves the translation of private IP addresses to public IP addresses and vice versa. This process helps conserve public IP addresses, enhances security by hiding internal network structures, and facilitates communication between different networks. It allows devices using IPv6 internally to access IPv4 resources on the Internet through translation mechanisms.
11. Discuss the architecture of Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Single-Pass Architecture:
- Palo Alto firewalls use a single-pass architecture for traffic processing.
- Each packet is processed through all the necessary functions in a single pass.
Functional Modules:
- Network Processing Card (NPC): Handles networking functions.
- Content Inspection Engine (CIE): Performs application identification and content scanning.
- Management Plane: Controls device management and configuration.
Three Key Components:
- Management Plane
- Data Plane
- Control Plane
Policies and Rules:
- Policies are configured to allow or deny traffic based on various parameters.
- Rules are enforced in the order specified in policy rulesets.
12. What is the role of the data and control planes in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Dataplane:
- Responsible for processing and forwarding user traffic.
- Performs functions like packet inspection, filtering, and logging.
- Highly optimised for fast and efficient handling of data.
Control Plane:
- Manages the device’s overall operation.
- Handles tasks like routing updates, device management, and policy control.
- Ensures the correct operation of the firewall.
13. Explain the function of the management plane in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Device Management:
- Handles configuration and monitoring of the firewall.
- Allows administrators to configure settings and policies.
Logging and Reporting:
- Manages logging and reporting functions.
- Provides visibility into network activity and security events.
Security Policy Management:
- Security policies, including access control policies and threat prevention profiles, are configured and managed through the management plane.
- Administrators can define rules to control traffic based on applications, users, content, and threat prevention measures.
14. How does the Palo Alto firewall handle traffic processing?
Ans:
Single-Pass Processing:
- Each packet is processed through the entire security rule base in a single pass.
- Enables accurate application identification and threat detection.
App-ID Technology:
- Identifies and controls applications irrespective of ports and protocols.
- Allows fine-grained control over application usage.
Decryption and Inspection:
- Palo Alto firewalls can decrypt and inspect encrypted traffic using technologies like SSL decryption.
- This allows for identifying and preventing threats hidden within encrypted communication.
15. Define the difference between Layer 3 and Layer 7 in networking.
Ans:
Layer 3 (Network Layer):
- Involves routing and forwarding based on IP addresses.
- Focuses on moving packets between devices in different networks.
Layer 7 (Application Layer):
- Concerned with application-level interactions.
- Involves deep packet inspection, understanding specific applications, and enforcing policies based on them.
16. What is the purpose of Virtual Routers in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Virtual Routers enable the segmentation of routing instances.
- Useful for separating different parts of the network for routing purposes.
- Virtual Routers are associated with physical or virtual interfaces on the firewall.
- Administrators can assign interfaces to specific Virtual Routers, determining which routing instance is responsible for processing traffic on a particular interface.
- Palo Alto firewalls support dynamic routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, and RIP.
- Each Virtual Router can be associated with different dynamic routing protocols, allowing flexibility and adaptability to diverse network environments.
17. Explain the concept of Subinterfaces in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
The physical interface to which subinterfaces are attached is typically connected to a switch or a router. The switch may be configured to support VLANs, and the router may perform inter-VLAN routing. When configuring subinterfaces, administrators specify parameters such as VLAN tag, security zone, IP address, and other settings. Each subinterface is treated as a separate logical interface with its configuration.
18. How does Palo Alto support dynamic routing protocols?
Ans:
- Palo Alto supports dynamic routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, and RIP.
- Allows the firewall to learn and adapt to changes in the network dynamically.
- Palo Alto firewalls support the redistribution of routes between different routing protocols.
- Administrators can control routing information flow by specifying which routes should be redistributed from one protocol to another.
- Palo Alto firewalls use virtual routers to segment routing instances and manage routing tables independently.
19. What is the purpose of BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Internet Routing: BGP is primarily used for routing between different autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet.
- Interconnecting Autonomous Systems: Palo Alto firewalls may connect to multiple internet service providers (ISPs) or other organisations, each having its autonomous system.
- Path Selection and Advertisement: BGP enables Palo Alto firewalls to choose the best traffic path based on attributes such as AS path, prefix length, and others.
- Redundancy and High Availability: BGP supports mechanisms for achieving redundancy and high availability.
20. What are security policies in Palo Alto firewalls, and how are they configured?
Ans:
Access Control:
- Security policies define rules for allowing or denying traffic based on various criteria.
- Policies can be based on applications, users, content, etc.
Rule Configuration:
- Rules are configured with specific conditions and actions.
- Administrators can define source and destination zones, applications, users, and threat prevention profiles.
Policy Inheritance:
- Policies can be inherited, allowing for efficient and organised rule management.
- Inherited policies can be applied at different levels within the rule hierarchy.
21. Explain the purpose of Security Profiles in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Security Profiles in Palo Alto firewalls serve the crucial role of enhancing threat prevention by providing a layered approach to security. By inspecting and applying security measures at various levels, Security Profiles contribute to comprehensive threat prevention, ensuring that the firewall can identify, block, and mitigate a wide range of security risks in network traffic.
22. How are Address Objects used in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Address Objects in Palo Alto firewalls represent network addresses and simplify the configuration of security policies. Administrators define IP addresses or address ranges as objects, and these objects can be referenced in security policies. This abstraction facilitates easier management and updating of policies, mainly when dealing with multiple rules or policies that share common address elements.
23. Describe the function of Service Objects in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Service Objects in Palo Alto firewalls represent network services or protocols, such as specific applications, ports, or custom services. Administrators can easily reference services in security policies by defining services as objects, ensuring consistent and streamlined policy management.
24. What is the use of Application Objects in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Application Objects in Palo Alto firewalls enable administrators to categorise and control network traffic based on specific applications. By incorporating Application Objects in security policies, administrators can implement fine-grained control over applications, allowing or restricting them based on security and business requirements.
25. Discuss the importance of Threat Prevention in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Threat Prevention in Palo Alto firewalls is paramount for safeguarding networks against many cyber threats. By actively identifying and blocking malicious content, exploits, and known vulnerabilities, Threat Prevention ensures that the firewall acts as a robust defence mechanism. This is crucial in preventing malware infections, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining the overall integrity and security of the network.
26. How does Palo Alto handle antivirus protection?
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls handle antivirus protection by employing a Threat Prevention Security Profile. This profile includes antivirus capabilities that inspect files and web content for known malware signatures. Regular updates to antivirus databases ensure that the firewall is equipped to identify and block the latest threats. In addition to signature-based detection, behavioural analysis is employed to identify unknown or zero-day malware.
27. Explain the role of URL Filtering in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
URL Filtering in Palo Alto firewalls is a critical component of security profiles that controls website access based on predefined categories and policies. It allows administrators to enforce web access policies, block malicious or inappropriate websites, and manage bandwidth usage. URL Filtering enhances security by preventing users from accessing potentially harmful content, reducing the risk of malware infections, and ensuring compliance with acceptable use policies.
28. What are WildFire and Traps in the context of Palo Alto Networks?
Ans:
WildFire is Palo Alto Networks’ cloud-based threat analysis service that provides advanced malware detection and prevention. It leverages global threat intelligence to identify and analyse unknown and evasive threats. Conversely, traps are endpoint protection solutions that prevent advanced threats and exploits at the endpoint level.
29. How are logs generated and managed in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Logs in Palo Alto firewalls are generated to capture information about network traffic, security events, and system activities. These logs play a crucial role in monitoring and troubleshooting. Administrators can configure log settings to specify which events to log and can export logs for analysis.
30. Explain the purpose of traffic and threat logs.
Ans:
Traffic Logs:
Capture information about network traffic, including source and destination addresses, applications, and actions taken by security policies and used for monitoring network activity, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and analysing traffic patterns.
Threat Logs:
Record information about security threats the firewall detects, such as viruses, malware, and other malicious activities.Essential for investigating and responding to security incidents, understanding the nature of threats, and refining security policies.
31. What is the function of the Traffic Log Viewer in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Log Analysis: Allows administrators to analyse logs generated by the firewall for both traffic and threats.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time visibility into network activities, including allowed and denied traffic.
- Search and Filter Capabilities: Enables users to search and filter logs based on various criteria, facilitating targeted analysis.
- Historical Data: Retains historical data, assisting in identifying past security incidents.
- Export and Reporting: Allows exporting logs for further analysis or integration with external reporting tools.
32. How does Palo Alto support monitoring and reporting?
Ans:
- Web Interface: Palo Alto firewalls offer a user-friendly web interface for monitoring and reporting.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Dashboards provide real-time insights into network activity, threats, and system health.
- Custom Reports: Administrators can generate custom reports based on specific criteria.
- Integration with Logging Systems: Supports external logging and reporting systems integration.
- Scheduled Reports: Scheduled reporting allows regular updates on network performance and security status.
33. Define VPN and its importance in network security.
Ans:
VPN (Virtual Private Network):
A technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the Internet.
Importance in Network Security:
- Ensures secure communication over potentially insecure networks.
- Enables remote access for users and secure connections between geographically dispersed sites.
- Protects sensitive data from unauthorised access and eavesdropping.
- Facilitates secure connectivity for businesses, remote workers, and branch offices.
34. How does Palo Alto Networks implement site-to-site VPNs?
Ans:
- Configuration: Site-to-Site VPNs are configured through the Palo Alto web interface or CLI.
- Support for Standards: Palo Alto firewalls support standard VPN protocols such as IPsec and IKE.
- Tunnel Establishment: VPN tunnels are established between the firewalls at different sites.
- Encryption and Authentication: Provides encryption and mutual authentication to secure data in transit.
- Dynamic Routing Integration: Supports integration with dynamic routing protocols for efficient and automated routing between sites.
35. Explain the process of configuring GlobalProtect VPN in Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
- Portal and Gateway Configuration: Define GlobalProtect portal settings for user authentication—Configure GlobalProtect gateways to establish secure connections.
- Client Configuration: Set up GlobalProtect client settings on the firewall. Define VPN profiles and connection parameters for end-users.
- Security Policies: Create security policies to control traffic between GlobalProtect clients and internal resources.
- User Authentication: Integrate with user authentication systems like LDAP or Active Directory.
- Client Deployment: Distribute and deploy GlobalProtect VPN clients to end-user devices.
36. Discuss the significance of High Availability in network security.
Ans:
- Continuous Operation: High Availability ensures uninterrupted network services by minimising downtime.
- Fault Tolerance: Protects against hardware failures, link outages, or other disruptions.
- Redundancy: Provides redundant resources and paths to maintain network accessibility.
- Traffic Load Balancing: Distributes network traffic across multiple devices for optimised performance.
37. What are the different High Availability modes in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Active/Passive (A/P): One firewall operates actively while the other remains on standby. Failover occurs in case of an active firewall failure.
Active/Active (A/A): Both firewalls actively process traffic.Suitable for scenarios with load-balancing requirements.
Modes of Operation: Administrators can choose between these modes based on network design and redundancy needs.
38. Explain the Active/Passive and Active/Active HA concepts.
Ans:
Active/Passive (A/P):
One firewall actively processes traffic; the other is on standby. Failover occurs if the active firewall becomes unavailable.
Active/Active (A/A):
Both firewalls actively process traffic simultaneously.Suitable for load balancing and maximising resource utilisation.
Selection Considerations:
The choice between A/P and A/A depends on network requirements, traffic patterns, and redundancy goals.
39. What is User-ID in Palo Alto firewalls, and how does it work?
Ans:
- User-ID is a Palo Alto Networks feature associating network traffic with specific user identities.
- Utilises various methods such as user mapping, agent-based solutions, and integration with directory services to identify users.
- Associates IP addresses with user identities, allowing for user-based policy enforcement.
40. How does Palo Alto Networks integrate with Active Directory for User ID?
Ans:
- Agent-Based Integration: Utilises User-ID agents to collect user-to-IP mappings from Active Directory domain controllers.
- LDAP Integration: Directly queries Active Directory LDAP servers for user information.
- Kerberos Authentication: Supports Kerberos authentication for secure and automated user identification.
- Seamless User Mapping: Ensures accurate and up-to-date user-to-IP mappings for practical User-ID functionality.
41. Discuss the importance of multi-factor authentication in network security.
Ans:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is pivotal in enhancing network security by adding a layer of identity verification beyond traditional usernames and passwords. In today’s threat landscape, where cyber-attacks continually evolve, relying solely on passwords presents a significant vulnerability.
42. What is Palo Alto Panorama, and how is it used in firewall management?
Ans:
Palo Alto Panorama is a centralized management platform designed to streamline the administration of multiple Palo Alto firewalls from a single interface. Panorama’s role-based access control further refines security by ensuring administrators have appropriate access levels, making it an invaluable asset for large-scale deployments.
43. Explain the benefits of using Panorama for centralized management.
Ans:
Utilising Palo Alto Panorama for centralized management offers a range of benefits. It streamlines the complexity of managing multiple firewalls by providing a unified view of the entire network security infrastructure—centralized logging and reporting aggregate information from distributed firewalls, offering comprehensive insights for monitoring and analysis.
44. How do you troubleshoot connectivity issues in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Troubleshooting connectivity issues in Palo Alto firewalls involves a systematic approach. Administrators can start by analyzing traffic and threat logs for indications of problems, checking the status of interfaces, and reviewing security policies to ensure they align with connectivity requirements.
45. Discuss common issues related to NAT in Palo Alto Networks.
Ans:
Network Address Translation (NAT) issues in Palo Alto Networks often stem from misconfigurations. Effective troubleshooting involves reviewing NAT policies, ensuring policy order, and checking for conflicts. Proper logging and monitoring practices are essential to quickly identify and address NAT-related issues, ensuring the smooth operation of network services while preserving security configurations.
46. What steps would you take to troubleshoot a VPN connection problem?
Ans:
Troubleshooting VPN connection problems in Palo Alto firewalls requires a thorough approach. Administrators should start by analyzing VPN logs for error messages and checking the status of Phase 1 and 2 negotiations. Verification of pre-shared keys, authentication settings, and routing tables is crucial.
47. How do Palo Alto Networks handle advanced threats and zero-day attacks?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks employs a robust strategy to handle advanced threats and zero-day attacks. Leveraging WildFire, a cloud-based threat analysis service, the company conducts dynamic analysis of unknown files and URLs to identify and prevent emerging threats. Regular automatic updates to threat databases ensure the Palo Alto firewalls stay current with the latest threat intelligence, providing real-time protection against a wide range of advanced threats and zero-day attacks.
48. What is the WildFire cloud-based threat analysis service?
Ans:
WildFire is Palo Alto Networks’ cloud-based threat analysis service designed to provide advanced threat detection and prevention. It conducts in-depth analysis of unknown files, URLs, and email links in a sandboxed environment to identify and mitigate potential threats. WildFire offers real-time protection against advanced malware, zero-day exploits, and emerging cyber threats by leveraging behavioural analysis, global threat intelligence, and integration with Palo Alto firewalls.
49. Explain the importance of SSL decryption in network security.
Ans:
SSL decryption holds immense importance in network security by allowing organizations to inspect encrypted traffic and ensure the effectiveness of security policies. While essential for privacy, encrypted communications can also be exploited by malicious actors. SSL decryption enables visibility into encrypted traffic, helping to detect and prevent threats hiding within secure connections.
50. How do Palo Alto firewalls implement SSL decryption?
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls implement SSL decryption by configuring specific policies to define which traffic should undergo decryption. Certificates, including SSL/TLS certificates, are imported and managed to establish trust during decryption. SSL decryption is performed in the forward proxy mode, allowing the firewall to inspect and analyze encrypted traffic while maintaining security.
51. What is QoS, and how is it implemented in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Definition: QoS (Quality of Service) in Palo Alto firewalls refers to the set of mechanisms and policies used to prioritize and control network traffic flow based on defined criteria.
- Traffic Classification: Palo Alto firewalls can classify traffic into different categories, such as applications, users, or services.
- QoS Profiles: Administrators can create QoS profiles to define the treatment of various types of traffic.
- Bandwidth Management: Bandwidth can be allocated based on priority levels to guarantee sufficient resources for high-priority traffic.
- Policies: QoS policies specify the actions to be taken on classified traffic, such as marking, limiting, or prioritizing.
52. Discuss the importance of prioritizing network traffic.
Ans:
- Optimised Performance: Prioritizing network traffic ensures critical applications receive the necessary resources, optimizing overall network performance.
- Reduced Latency: Low-latency access to essential services is achieved by prioritizing time-sensitive traffic.
- Enhanced User Experience: Prioritizing network traffic contributes to a seamless and responsive user experience, especially for real-time applications.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient allocation of network resources prevents congestion and ensures a fair bandwidth distribution.
53. What are some best practices for securing Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- Regular Software Updates: Keep the firewall’s operating system and security policies up-to-date to address vulnerabilities.
- Least Privilege Principle: Follow the principle of least privilege when configuring firewall rules, granting only necessary access.
- Logging and Monitoring: Enable comprehensive logging and monitoring to detect and respond to security incidents.
- SSL Decryption: Utilise SSL decryption for inspecting encrypted traffic, enhancing threat detection capabilities.
54. How do you ensure that your Palo Alto firewall rules follow security best practices?
Ans:
- Rule Review and Cleanup: Periodically review and clean up firewall rules to remove unnecessary or redundant entries.
- Rule Documentation: Document each firewall rule with clear descriptions, making it easier to understand and manage.
- Rule Consolidation: Consolidate similar rules to reduce complexity and improve manageability.
- Least Privilege Principle: Follow the principle of least privilege, granting only the minimum permissions necessary for each rule.
55. What is the Palo Alto XML API, and how can it be used for automation?
Ans:
The Palo Alto XML API is an interface that allows programmatic access to the firewall’s configuration and management functions using XML-based requests. Enables automation of firewall configuration, monitoring, and management tasks. Provides real-time access to firewall status, logs, and other critical information for monitoring.
56. Discuss the role of APIs in firewall management.
Ans:
- Automation: APIs enable automation of configuration changes, policy deployments, and monitoring tasks.
- Integration with Third-Party Tools: APIs facilitate seamless integration with external tools and systems, enhancing overall network management.
- Scalability: Enables scalable management of multiple firewalls and network devices through centralized control.
57. Describe the current cybersecurity threat landscape.
Ans:
- Sophisticated Malware: The threat landscape is characterized by increasingly sophisticated malware and ransomware attacks.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals employ advanced phishing and social engineering tactics to target individuals and organizations.
- IoT and OT Vulnerabilities: Increasing vulnerabilities in Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) environments pose new risks.
- Cloud Security Challenges: As organizations embrace cloud services, new challenges in securing cloud environments emerge.
58. How does Palo Alto Networks stay updated on emerging threats?
Ans:
- WildFire Analysis: Utilises WildFire, a cloud-based threat analysis service, to analyze unknown files and URLs for emerging threats.
- Global Threat Intelligence: Integrates with global threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about the latest threat indicators.
- Community Collaboration: Collaborates with the cybersecurity community to share threat intelligence and insights.
- Research and Development: Invests in ongoing research and development to identify and address emerging threat vectors.
59. Explain the role of Palo Alto firewalls in achieving regulatory compliance.
Ans:
- Policy Enforcement: Palo Alto firewalls enforce security policies to align with regulatory requirements and compliance standards.
- Logging and Auditing: Comprehensive logging and auditing capabilities help organizations meet compliance reporting requirements.
- SSL Decryption: SSL decryption features enhance visibility into encrypted traffic, supporting compliance with regulatory mandates.
- Incident Response: Robust incident response features assist in addressing security incidents promptly, supporting regulatory obligations.
60. How does Palo Alto assist in meeting GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requirements?
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls contribute to GDPR compliance by implementing robust data protection measures. User identification capabilities help organizations trace and monitor data access, aligning with GDPR principles. SSL decryption provides visibility into encrypted traffic, supporting GDPR’s focus on data protection. Incident response features aid organizations in promptly addressing and reporting data breaches as required by GDPR.
61. Discuss Palo Alto Networks’ approach to cloud security.
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks adopts a holistic approach to cloud security, recognizing the dynamic nature of modern IT environments. Through offerings like Prisma Cloud, Palo Alto Networks enables organizations to gain visibility into their cloud assets, enforce consistent security policies, and protect against advanced threats.
62. How does Prisma Access enhance cloud security for organizations?
Ans:
Prisma Access is pivotal in enhancing organizations’ cloud security by providing a cloud-delivered security solution. By leveraging the power of the cloud, Prisma Access enables organizations to extend their security posture beyond traditional perimeters, safeguarding users and data with a unified and agile approach.
63. What is SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Networking), and how does Palo Alto support it?
Ans:
SD-WAN, or Software-Defined Wide Area Networking, is a technology designed to optimize and simplify the management of wide-area networks by leveraging software-defined networking principles. Palo Alto Networks supports SD-WAN through its Prisma SD-WAN solution.
64. Discuss the benefits of integrating SD-WAN with Palo Alto Networks.
Ans:
The integration ensures that SD-WAN deployments benefit from Palo Alto’s robust security measures, including threat prevention and access controls. Security policies can be enforced consistently across the WAN and branch offices, streamlining management and ensuring a unified security posture.
65. How does Palo Alto Networks integrate with SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks integrates seamlessly with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions to enhance an organization’s threat detection and incident response capabilities. Palo Alto firewalls contribute to a centralized and correlated view of the security landscape by forwarding logs and security events to SIEM platforms.
66. Discuss the role of Palo Alto firewalls in a comprehensive security architecture.
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls play a crucial role in a comprehensive security architecture by serving as a critical security enforcement point within the network. With advanced threat prevention, application visibility, and user identity controls, Palo Alto firewalls contribute to a unified and adaptive security posture.
67. Explain the Zero Trust security model, and how Palo Alto contributes to it.
Ans:
The Zero Trust security model is based on not trusting any entity by default, regardless of location or user context. Palo Alto Networks contributes to the Zero Trust model by providing comprehensive visibility, identity-based access controls, and threat prevention mechanisms.
68. What are the fundamental principles of a zero-trust approach to network security?
Ans:
Limit access rights for users and systems to the minimum necessary for their specific tasks. To identify and respond to potential anomalies, implement continuous monitoring of network activities, users, and devices. Segment the network into isolated zones to contain and limit the impact of potential security incidents.
69. How does Palo Alto Networks ensure high-performance firewall capabilities?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks ensures high-performance firewall capabilities through hardware and software optimizations. Palo Alto firewalls handle tasks efficiently by leveraging dedicated hardware acceleration, parallel processing, and optimized software algorithms. The company also designs firewall solutions with scalable architectures, enabling them to meet the demands of growing network environments.
70. What factors can impact the performance of Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
- High levels of network traffic can affect firewall performance, necessitating proper sizing and capacity planning.
- Enabling advanced security features, such as SSL decryption and threat prevention, may impact performance.
- The overall network architecture, including topology and routing configurations, can impact firewall performance.
71. How do Palo Alto Networks contribute to endpoint security?
Ans:
- Advanced Endpoint Protection: Palo Alto Networks offers advanced endpoint protection solutions, such as Traps, designed to defend against various threats.
- Multi-Layered Defence: Implements a multi-layered defence strategy, combining signature-based detection, behavioural analysis, and machine learning to identify and block malicious activities.
- Integration with Network Security: Ensures seamless integration with Palo Alto Networks network security solutions, creating a unified security posture that spans from endpoints to the network.
72. Discuss the integration of Palo Alto Traps with endpoint protection strategies.
Ans:
- Prevention of Advanced Threats: Palo Alto Traps integrates with endpoint protection strategies to prevent advanced threats, including ransomware and fileless attacks.
- Behavioral Analysis: Utilises behavioural analysis to detect and block malicious activities at the endpoint level, even for unknown or zero-day threats.
- Real-time Threat Intelligence Sharing: Facilitates real-time threat intelligence sharing between Traps endpoints and Palo Alto Networks’ security ecosystem for faster response to emerging threats.
73. Explain the importance of threat intelligence in network security.
Ans:
Threat intelligence provides proactive detection of potential security threats by analyzing patterns, indicators, and anomalies. Enables informed decision-making by offering insights into cyber adversaries’ latest tactics, techniques, and procedures. Identifies vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors, allowing organizations to prioritize patching and mitigation efforts.
74. How does Palo Alto Networks leverage threat intelligence for better security?
Ans:
- Global Threat Intelligence Feeds: Integrates with global threat intelligence feeds to enhance awareness of the latest threat indicators.
- WildFire Cloud Analysis: Utilizes the WildFire cloud-based threat analysis service to analyze unknown files and URLs, contributing to the identification of new and evolving threats.
- Information Sharing: Facilitates information sharing and collaboration with the broader cybersecurity community, contributing to a collective defence against cyber threats.
75. Discuss the role of automation in managing and securing Palo Alto firewalls.
Ans:
Automates the deployment of security policies, ensuring consistent and timely application of rules across the firewall infrastructure. Automates threat response actions based on predefined policies, allowing for rapid containment and mitigation of security incidents. Streamlines configuration management tasks, reducing manual errors and ensuring alignment with security best practices.
76. How can orchestration platforms be integrated with Palo Alto Networks?
Ans:
- API Integration: Utilises APIs to integrate Palo Alto Networks with orchestration platforms, enabling seamless communication and data exchange.
- Automated Workflows: Supports the creation of automated workflows that involve Palo Alto Networks’ security policies, incident response, and configuration changes.
- Visibility and Control: Provides enhanced visibility and control over security processes, allowing organizations to orchestrate responses across their entire security infrastructure.
77. What security challenges are specific to industries such as finance or healthcare?
Ans:
Finance:
- Threat of Financial Fraud: Financial institutions face the constant threat of fraud, including phishing attacks and fraudulent transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent regulatory requirements add complexity to security measures.
Healthcare:
- Patient Data Protection: Protecting sensitive patient data is critical, with healthcare organizations being prime targets for data breaches.
- Medical Device Security: Ensuring the security of connected medical devices is crucial to prevent potential risks to patient safety.
Others:
- Intellectual Property Protection: Industries with high-value intellectual property, such as technology and research, need robust measures against corporate espionage.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Various industries face challenges securing complex supply chains and third-party dependencies.
78. How can Palo Alto Networks address industry-specific security concerns?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks allows organizations to create tailored security policies to address industry-specific challenges and compliance requirements. Granular application visibility enables precise control over data flows, addressing unique challenges in industries with specific data handling requirements. Provides regulatory compliance modules to assist industries in adhering to specific data protection and privacy regulations.
79. What are some best practices for creating effective security policies?
Ans:
Begin with a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and prioritize potential security risks. Use clear and concise language in policy documents to ensure understanding and compliance. Include incident response plans within security policies, outlining steps to be taken in case of security incidents.
80. How often should security policies be reviewed and updated?
Ans:
- Regular Reviews: Security policies should be reviewed regularly, ideally at least annually, to ensure they remain effective against evolving threats.
- Trigger Events: Trigger events, such as significant changes in the organization’s infrastructure or a major security incident, should prompt immediate policy reviews.
- Technology Changes: Any significant changes in technology, applications, or network architecture should trigger a review of security policies to maintain relevance.
- Incident Post-Mortems: After security incidents, conduct post-mortems to identify any weaknesses in existing policies and make necessary updates for better preparedness.
81. Discuss the steps involved in incident response within a Palo Alto firewall environment.
Ans:
Incident response within a Palo Alto firewall environment involves a systematic approach to addressing and mitigating security incidents. In the preparation phase, organizations establish comprehensive incident response plans, defining roles and responsibilities while configuring the Palo Alto firewall to log pertinent events. The recovery phase focuses on restoring normal operations and validating the effectiveness of implemented changes.
82. How does Palo Alto Networks assist organizations in incident response planning?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks supports organizations in incident response planning through its comprehensive security solutions. The company also provides resources and expertise to help organizations develop and refine their incident response plans, ensuring they are well-prepared to address security incidents effectively.
83. What is network segmentation, and how does it enhance security?
Ans:
Network segmentation is a crucial security strategy that involves dividing a network into distinct segments to contain and control the spread of security incidents. Network segmentation also allows for more granular control over traffic, enabling organizations to apply specific security policies to different segments based on their risk profile and importance.
84. How can Palo Alto firewalls be used to implement effective network segmentation?
Ans:
Palo Alto firewalls can be instrumental in implementing effective network segmentation. Palo Alto firewalls support micro-segmentation implementation, enabling fine-grained control over communication between individual devices or applications. This helps organisations establish a robust security posture by containing potential threats and reducing the attack surface within their network.
85. Does Palo Alto Networks support IPv6, and how is it implemented?
Ans:
Yes, Palo Alto Networks supports IPv6, the next-generation Internet Protocol. Implementing IPv6 in Palo Alto Networks involves:
- Configuring the firewall to handle IPv6 traffic.
- Defining security policies for IPv6 addresses.
- Ensuring that logging and monitoring cover IPv6 events.
86. What considerations should be taken into account when transitioning to IPv6?
Ans:
Several considerations must be taken into account when transitioning to IPv6. These include ensuring compatibility with existing hardware and software, addressing potential security implications, and training staff to handle IPv6 configurations. Thorough testing and validation are crucial to identify and address any issues arising during the transition, ensuring a smooth and secure migration to IPv6.
87. What are some best practices for optimizing threat prevention in Palo Alto firewalls?
Ans:
Optimizing threat prevention in Palo Alto firewalls involves implementing best practices to enhance the platform’s efficacy. Organizations should regularly update threat intelligence feeds, leverage advanced features such as WildFire for dynamic analysis of unknown threats, and configure security policies based on a comprehensive understanding of their network’s traffic patterns.
88. How can organizations enhance their threat prevention strategies?
Ans:
Organizations can enhance their threat prevention strategies by adopting a multi-layered approach to security. Regularly conducting security assessments and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to address potential weaknesses proactively.
89. Discuss the importance of Palo Alto Networks certifications for professionals.
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks certifications hold significant importance for professionals in the cybersecurity field. These certifications validate an individual’s expertise in deploying, managing, and troubleshooting Palo Alto Networks solutions. Certifications from Palo Alto Networks are recognized globally, making certified professionals valuable assets for organizations seeking skilled cybersecurity professionals.
90. What certification paths are available for Palo Alto Networks?
Ans:
Palo Alto Networks offers a range of certification paths catering to different levels of expertise. The foundational certification is the Palo Alto Networks Certified Cybersecurity Entry-level Technician (PGCET), followed by the Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Administrator (PCNSA) for those involved in day-to-day management.
91. How can DevOps practices be integrated with security measures in Palo Alto Networks?
Ans:
- Automation: Leverage automation tools to enforce security policies and configurations consistently.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Implement security controls directly within code through IaC practices.
- Shift-Left Security: Embed security practices earlier in the development lifecycle to catch vulnerabilities sooner.
- Immutable Infrastructure: Use immutable principles to reduce the attack surface and enhance security.
92. Discuss the role of security in a DevOps-oriented environment.
Ans:
- Shift-Left Security: Embed security measures early in the development process.
- Continuous Security Testing: Implement automated security testing throughout the CI/CD pipeline.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess and manage code changes and deployment risks.
- Incident Response Integration: Seamlessly integrate security incident response into the DevOps workflow.
93. How does Palo Alto Networks handle custom applications in traffic inspection?
Ans:
Utilise Palo Alto’s App-ID to identify and classify custom applications. To enhance detection, create custom signatures for specific applications. Apply SSL decryption to inspect encrypted traffic for custom applications. Combine User-ID information to enhance context-aware traffic policies.
94. What steps can be taken to ensure the security of custom applications?
Ans:
- Regular Auditing: Conduct periodic security audits for custom applications.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Perform regular vulnerability scans to identify and patch security weaknesses.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls based on the principle of least privilege.
- Security Patching: Ensure timely application of security patches and updates.
95. What security considerations are unique to IPv6, and how does Palo Alto address them?
Ans:
- Address Format: Recognize the longer IPv6 address format and adjust firewall policies accordingly.
- Header Changes: Adapt to IPv6 header changes, including the absence of NAT and the use of IPsec.
- Transition Mechanisms: Address security concerns related to IPv6 transition mechanisms.
- Enhanced Security Features: Leverage IPv6’s built-in security features, such as IPsec and Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND).
96. How can organizations ensure the security of their networks as they transition to IPv6?
Ans:
To seamlessly transition to IPv6, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive testing of all network components, ensuring compatibility. Providing security training for personnel on IPv6 considerations and gradually implementing dual-stack support are essential steps. Enhancing monitoring and logging capabilities to cover IPv6 traffic and collaborating with vendors, such as Palo Alto, ensures robust IPv6 support in security solutions.
97. What is threat hunting, and how can Palo Alto firewalls support this activity?
Ans:
- Leverage behavioural analytics to identify potential threats.
- Analyse firewall logs for anomalies and indicators of compromise.
- Integrate threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging threats.
- Implement automated responses based on threat-hunting findings.
98. Discuss the role of threat hunting in proactive cybersecurity.
Ans:
- Early Threat Detection: Identify threats before they escalate by actively searching for signs of compromise.
- Continuous Improvement: Use threat-hunting findings to improve security controls and incident response plans.
- Proactive Mitigation: Take proactive measures to mitigate potential threats before they impact the organization.
99. What future trends do you anticipate in network security, and how can Palo Alto Networks stay relevant?
Ans:
Embrace the evolution towards Zero Trust security models. Integrate advanced AI and machine learning for more proactive threat detection. Address the growing importance of securing edge computing environments. Adapt to the increasing reliance on cloud-native technologies with robust security solutions.
100. How does Palo Alto Networks adapt to emerging technologies and security challenges?
Ans:
- Agile Development: Adopt agile development practices to respond to evolving security challenges quickly.
- Collaboration with Industry: Collaborate with industry partners to share threat intelligence and best practices.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Provide regular software updates and patches to address new vulnerabilities.

