
Best PowerShell Tutorial | Quickstart – MUST-READ
Last updated on 30th May 2020, Blog, Tutorials
What are the fundamental concepts of PowerShell?
PowerShell’s foundational ideas include the following:
Shell Environment:
PowerShell, a command-line shell, gives users an interactive environment through which to provide instructions to the computer.
Object-Oriented:
PowerShell is object-oriented because it deals with most data as objects rather than the text output used by previous shell scripting languages. Since these items are immediately manipulable, scripts have more freedom and power.Cmdlets:
The fundamental unit of a PowerShell command is a Cmdlet. They are short, specialized commands used to manage things like files, processes, and services. Verb-noun naming conventions are used for Cmdlets (like Get-Process and Set-Item).
Pipeline:
PowerShell’s pipeline feature enables the results of one command to be used as the input for another, allowing for more advanced data processing without the need for intermediary files.
Providers:
Providers provide users access to different data stores (such as file systems, registries, or certificates) in the same way they would a regular file. This uniformity streamlines the process of creating and managing scripts.
Variables:
PowerShell scripts may store and change data in variables for later use. The “$” sign is used to denote variables (such as “$name” and “$count”).
Control Flow:
Standard control flow structures, such as loops (foreach, while), conditionals (if-else, switch), and functions, are all supported in PowerShell, allowing for more flexibility and reusability in scripts.
Help System:
PowerShell’s extensive help system allows users to look up information on specific cmdlets, modules, and ideas without ever leaving the command prompt.
Modules:
Modules are collections of commands, functions, and scripts that work together to do a specified task. They facilitate the dissemination of code libraries.
Scripting Language:
PowerShell is a full-featured scripting language that allows you to work with variables, functions, loops, conditions, and errors. This makes it perfect for developing sophisticated automation routines.
Remoting:
PowerShell supports remote administration, letting IT personnel run scripts and commands on distant workstations.
Configuration Management:
PowerShell’s Desired State Configuration (DSC) is a configuration management function that lets administrators set the default configuration of a system to match a predefined ideal.
PowerShell’s underlying ideas allow system administrators, developers, and IT professionals to effectively control and automate processes in Windows settings.
Features of PowerShell
PowerShell has many important features and is a powerful scripting language and command line shell. Among PowerShell’s many helpful features are:
- PowerShell’s tab completion for cmdlets, parameters, and even file and folder locations is a great way to save time and avoid making mistakes.
- PowerShell is a full-fledged scripting language that supports things like variables, arrays, loops, conditionals, functions, and error handling, making it suitable for challenging jobs.
- All of PowerShell’s features, including as its cmdlets, functions, modules, and concepts, are well documented and demonstrated in the built-in help system. Users may get contextual assistance directly from the command line interface.
- PowerShell’s robust remoting capabilities simplify remote machine administration and script execution for system administrators.
- Jobs let users to put up commands and scripts to run in the background, improving efficiency for long procedures. This paves the way for parallelism and multitasking.
- Users of PowerShell may compile related pieces of code into reusable chunks called modules. Programs can share modular parts more easily.
- Script execution rules are one of PowerShell’s security features; they define the parameters under which a script may be launched on a system and help to prevent malicious scripts from being run.
- The dot source feature in PowerShell makes it feasible to include code from other scripts or functions, allowing for its reuse and organization.
- PowerShell’s adaptability stems from the fact that it supports the XML and JSON interchange formats, both of which are often used by APIs and web services.
- PowerShell’s compatibility with the.NET Framework means that its users may use all of the Framework’s features without ever having to leave the familiar environment of the scripting language.
- PowerShell DSC allows administrators to set up and maintain the desired configuration of systems with the goal of ensuring that the infrastructure is consistently configured.
- PowerShell’s numerous helpful characteristics make it an excellent tool for automating activities, controlling systems, and executing a broad variety of administrative tasks in Windows environments.
Most common mistakes made when using PowerShell
PowerShell users of all skill levels are susceptible to making frequent mistakes that might result in errors or unexpected behavior. Most often, people make these errors while working with PowerShell:
Incorrect Syntax: Errors may occur if the syntax for PowerShell’s cmdlets, functions, and other constructs is not followed correctly. Common PowerShell commands use the verb-noun structure (Get-Process, Set-Item, etc.).
Improper Quoting: Using single or double quotes incorrectly may lead to problems, particularly when working with strings that include special characters or variables.
Forgetting Semicolons: Semicolons are used to separate commands on the same line in PowerShell. Syntax mistakes may occur when semicolons are overlooked.
Not Using the Pipeline: This might cause scripts to run slower and take more effort. The pipeline may be used to reduce complexity and boost performance in coding.
Overwriting Variables: Accidentally overwriting crucial data or failing to validate the values assigned to vital variables might have serious implications.
Lack of Error Handling: This might make troubleshooting and debugging more difficult.
Insufficient Testing: The failure to properly test scripts or commands before deploying them in a production setting might result in unintended consequences.
Running Scripts from Untrusted Sources: Security vulnerabilities might be introduced when scripts are run from untrusted sources without proper comprehension of their contents.
Ignoring Execution Policies: Scripts may fail to run if the execution policy has not been correctly configured or is not in place.
Not Using the -WhatIf Parameter: Refraining from using the -what if argument, which provides a non-executable preview of a command’s output. Unwanted results may occur if this argument is ignored.
Using Aliases Excessively: Overuse of aliases may reduce the readability and maintainability of scripts, despite the fact that they save time on typing.
Not Updating PowerShell: Failure to update PowerShell might mean foregoing security patches and useful additions.
Inappropriate Object Manipulation: Mishandling objects by manipulating them as if they were strings might cause unexpected behavior or wrong outcomes.
Ignoring Best Practices: Ignoring standard practices may make scripts more difficult to comprehend and maintain, such as by not utilizing descriptive variable and function names or not properly commenting code.
Misusing Backticks for Line Continuation: Overusing backticks (‘) for line continuation may make scripts difficult to understand and cause unexpected results.
By avoiding these typical pitfalls, users may improve the quality and reliability of their PowerShell scripts and have a more satisfying and fruitful time when scripting. As an added bonus, your automation and administrative efforts will be more effective the more you understand and use PowerShell.
PowerShell commands for network administrators
Managing and troubleshooting network-related tasks is made much easier using PowerShell, a robust tool for network administrators. Important PowerShell commands for system administrators to know include:
- Information about the system’s network adapters, including as their names, statuses, MAC addresses, and IP settings, may be retrieved using the Get-NetAdapter command.
- With Get-NetIPAddress, you may see the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways set up for a network interface.
- Get-DnsClientCache allows you to inspect previously cached DNS responses and flush them if necessary.
- Ping, check for open ports, and trace routes are just some of the tests that can be run using Test-NetConnection.
- Use Resolve-DnsName if you need to resolve a DNS name to an IP address or vice versa when debugging a DNS problem.
- Get-NetRoute: Check the routing table to see how data is currently being routed.
- Get-NetTCPConnection will show all open TCP connections so you can quickly find them.
- Get-NetFirewallRule will display all of the current firewall rules, including incoming and outgoing.
- Turn on a network adapter that has been turned off using the Enable-NetAdapter command.
- Remove network connection by using the Disable-NetAdapter command.
- Invoke New-NetIPAddress to set up an IP address on a network interface for the first time.
- Create a new permanent route in the network using the New-NetRoute command.
- Set-DnsClientServerAddress enables admins to modify their network adapter’s DNS server settings.
- Troubleshoot connection problems by testing network connections and port availability with Test-NetConnection.
- TCP parameters such as the maximum number of connections and congestion management techniques may be seen using the Get-NetTCPSetting command.
How can PowerShell be used to manage and monitor Windows Server?
PowerShell excels as a Windows Server management and monitoring tool. It offers an extensive set of cmdlets and features that may be used to automate activities, configure the system, and collect crucial data. Uses for PowerShell in Windows Server administration and monitoring include the following.User Management: PowerShell’s user administration features include the ability to manage users, groups, passwords, and other security settings.
Service Management: PowerShell is useful for managing services on a server because it enables administrators to control and monitor the lifecycle of Windows services.
Event Log Monitoring: PowerShell allows administrators to obtain and filter event log entries, allowing them to keep tabs on and troubleshoot system occurrences.
Performance Monitoring: PowerShell may collect performance counter data to keep an eye on server performance and help pinpoint and fix any bottlenecks it finds.
Software Installation: Automation of Windows Server software installations and administration is made possible via PowerShell.
File and Folder Management: PowerShell’s scripting interface makes it easy for system administrators to manage the server’s file and folder structure.
Network Configuration: Management of network devices, IP address configuration, and DNS server settings are all possible using PowerShell.
Remote Server Management: Administrators may control a plethora of remote servers from a central location using PowerShell remoting.
Active Directory Management: PowerShell is capable of managing Active Directory objects including users, groups, OUs, and Group Policy, among other things.
Disk Management: PowerShell’s Disk Management features let you format and resize drives, partitions, and volumes via the program’s command line interface.
Scheduled Tasks: PowerShell has the capability to create and manage scheduled tasks, which automates the server’s regular activities.
Security Management: PowerShell is a powerful tool for managing the security of a Windows Server, allowing administrators to make changes to access controls, auditing, and other relevant settings.
Backup and Restore: Files, directories, and system configurations may all be backed up and restored mechanically with the help of PowerShell.
Windows Update Management: PowerShell’s Windows Update automation features help keep servers patched and safe.
Monitoring System Health: System Health Monitoring Scheduled PowerShell scripts may check on the status of servers and provide reports or alarms depending on predefined criteria.
PowerShell is an invaluable tool for Windows Server administrators due to its flexibility and scripting capabilities, which allow them to automate routine activities, guarantee consistent settings, and keep an eye on the health and performance of their servers. PowerShell allows administrators to swiftly and accurately administer Windows Server systems with little wasted effort.
SQL Server managing using PowerShell
The SQL Server management features available in PowerShell are extensive. Database management, query execution, backup and restoration, and server-side configuration are just some of the responsibilities that administrators may take care of using the SQL Server PowerShell module. Common PowerShell SQL Server administration includes the following tasks:
- Database administration is accomplished with the New-DbaDatabase and Set-DbaDatabase cmdlets, respectively.
- Database backup and restoration may be accomplished with the help of the Backup-DbaDatabase and Restore-DbaDatabase commands.
- Start-Service, Stop-Service, and Restart-Service are three useful cmdlets for managing SQL Server services.
- If you need to change any of the SQL Server configuration parameters, use the Set-DbaConfig command.
- To manage SQL Server logins and users, use the New-DbaLogin and New-DbaUser commands, respectively.
- To query the SQL Server instance and receive details such as the version, edition, and server attributes, use the Get-DbaInstance command.
- Check the health of SQL Server services with Get-DbaSqlService, and keep tabs on database activity with Get-DbaDbTransactionLog.
- Start-DbaAgentJob is the PowerShell cmdlet to use for launching SQL Server Agent jobs.
- The New-DbaLinkedServer and Remove-DbaLinkedServer cmdlets are used for managing connected servers.
- To administer SQL Server permissions, you may use commands like Grant-DbaPermission, Revoke-DbaPermission, and Test-DbaSqlEffectivePermission.
An extensive collection of cmdlets for administering SQL Server are provided by the SQL Server PowerShell module, often known as dbatools. This project is well-liked and community-driven. Installing the module using PowerShellGet or downloading it from the PowerShell Gallery is required before you can use it.
PowerShell modules for managing Active Directory
Several modules exist inside PowerShell for administering Windows Active Directory (AD). Using the cmdlets provided by these modules, administrators may manage AD objects including users, groups, OUs, and Group Policies, as well as create, change, and query AD objects. A few of the most important PowerShell modules for administering Active Directory are as follows:
Active Directory PowerShell Module (ActiveDirectory):
Users, groups, organizational units, and computers are just some of the AD objects that may be managed with the help of the cmdlets provided by this module, which is included into Windows Server by default. New users may be created, existing users can be added to groups, and administrators can query Active Directory properties.
Active Directory Certificate Services PowerShell Module (ADCertificateServices):
Certificate requests, revocations, and template management for certificates are just some of the Active Directory Certificate Services operations that may be handled by administrators with the help of this module.
Active Directory Migration Tool (ADMT):
The Active Directory Migration Tool (ADMT) is a robust solution for migrating and consolidating domains that has a PowerShell snap-in but is not itself a PowerShell module. Users, groups, and machines may all be transferred across domains and forests with its help.
Group Policy PowerShell Module (GroupPolicy):
Using PowerShell, administrators may now manage Group Policy settings with the help of this module. It has cmdlets for working with Group Policy objects (GPOs) and applying them to organizational units (OUs) and domains.
Active Directory PowerShell History Module:
Using this external module, administrators may track and examine all PowerShell operations run in relation to Active Directory.
Quest ActiveRoles Management Shell for Active Directory:
Active Directory administration is simplified with the help of this third-party module from Quest (formerly part of Quest Software), which adds to PowerShell with extra cmdlets.
After importing, you may use the provided cmdlets to administer Active Directory on your Windows system. These modules greatly reduce the complexity and increase the efficiency of AD administration duties, making PowerShell an invaluable resource for AD administrators.
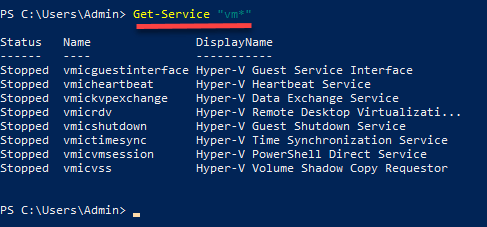
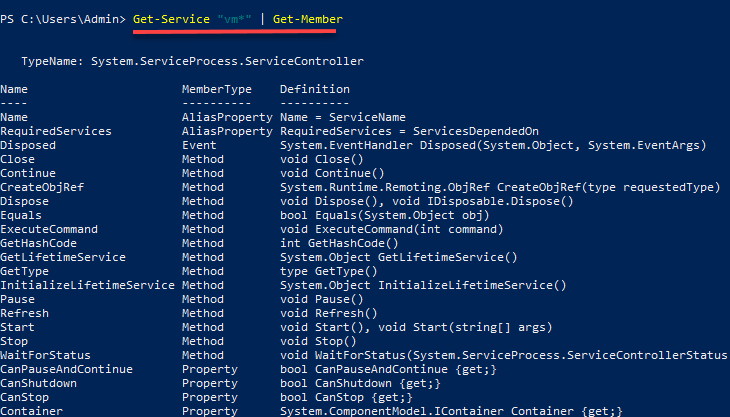

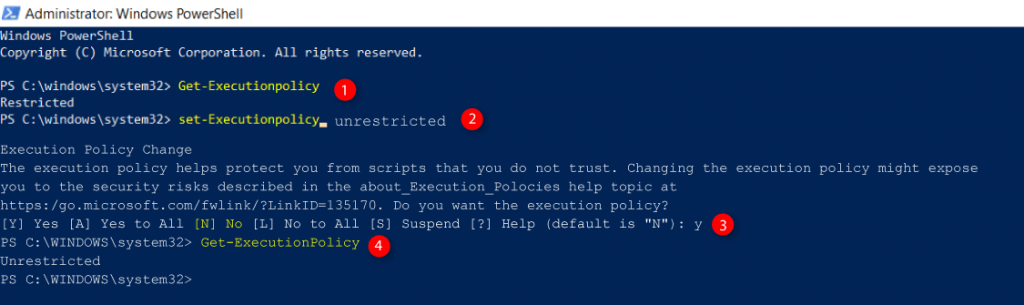
Difference between PowerShell and Command Prompt
- While the Windows Command Processor (cmd.exe) is used by the Command Prompt (CMD), the Windows PowerShell Engine (powershell.exe) is used by PowerShell. CMD is an older and more simplistic shell that mostly uses DOS commands, whereas PowerShell is a contemporary and sophisticated shell based on the.NET Framework and offering an object-oriented programming environment.
- CMD’s command syntax is based on those of DOS, which are notoriously rudimentary and lacking in object-oriented features. PowerShell, on the other hand, employs a more sophisticated and adaptable syntax, built on cmdlets (Verb-Noun instructions) that interact with.NET objects. Because of its object-oriented design, scripting and automation may be taken to new levels of sophistication.
- Batch files (.bat) are the primary scripting format used by CMD. These files contain a sequence of instructions that are executed in order. Many advanced features of today’s software are absent. PowerShell, on the other hand, is an extensive scripting language that includes all of the aforementioned features and more. It provides a more flexible and powerful setting for scripting.
- CMD’s primary focus on textual representations of data might be restrictive when working with more intricate systems. However, PowerShell is more suited to current system management because it handles data as objects, which enables direct manipulation of organized data.
- When compared to Cmdlets, conventional commands (such as dir, cd, and copy) run as external executables and might provide inconsistent results. PowerShell, on the other hand, makes use of built-in commands called cmdlets (such as Get-ChildItem, Set-Location, and Copy-Item). The rich output in object format offered by Cmdlets is consistent and standardized.
- CMD can only be expanded through third-party programs and batch files due to its lack of native extensibility. PowerShell, on the other hand, is extremely extendable, so new commands, functions, modules, and scripts may be written to meet any need.
How can be used to data center automation using PowerShell?
PowerShell’s extensive range of cmdlets and capabilities for controlling servers, virtual machines, networking, and storage, and other components often found in data centers, makes it a good tool for data center automation. Some examples of PowerShell’s application in data center automation are as follows:
Server Provisioning: PowerShell may be used to programmatically install an operating system, set up applications, and personalize a server that has just been created, whether the server is real or virtual.
Virtualization Management: PowerShell facilitates the management of virtualization technologies like Hyper-V and VMware, allowing for the deployment, customization, and tracking of VMs.
Configuration Management: Administrators may specify and enforce the intended configuration of servers and apps using PowerShell intended State Configuration (DSC), resulting in uniformity throughout the data center.
Monitoring and Alerting: Server health, system performance, and resource utilization may be tracked using scheduled PowerShell scripts that send out alarms and generate reports as necessary.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: PowerShell is useful for automating disaster recovery procedures and backup operations for data, apps, and virtual machines.
Network Automation: Switches, routers, and firewalls are just some of the networking devices that may be managed using PowerShell.
Storage Management: Data center administrators may use PowerShell to streamline SAN setup, disk management, and storage provisioning.
Automated Testing: Application testing, configuration validation, and security testing are just some of the testing activities that may be automated with the help of PowerShell scripts.
Patch Management: Patching and updating servers and apps can be done automatically using PowerShell, making sure they are always up-to-date and protected.
User and Access Management: Control who has access to what in the data center, and how they got there, using PowerShell.
Reporting and Documentation: Datacenter setups, server inventories, and system settings may all be documented using PowerShell scripts.
Workflow Automation: Automation jobs with numerous phases, conditions, and error handling may be easily crafted by administrators using PowerShell workflows.
Cloud Integration: Integration with on-premises data center operations is simplified by using PowerShell to automate functions in cloud environments like Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services.
Resource Monitoring and Scaling: PowerShell can track how much is being used and adjust accordingly, whether that’s via adding more servers or virtual machines.
Application Deployment: Building, packaging, and deploying programs across servers are all tasks that may be automated using PowerShell.
Text parsing and manipulation tasks using PowerShell
PowerShell is a useful tool for dealing with text files, log files, CSV, JSON data, and other types of data since it has strong text parsing and manipulation features. Here are some typical PowerShell tasks for text manipulation and parsing:
- Whether you need to read the contents of a text file or add new information to one, you may use the Get-information and Set-Content cmdlets, respectively.
- Using Select-String and Where-Object, you may filter lines of text depending on whether or not they meet specified criteria.
- Using the Split function, you may divide a string of text into several arrays separated by a certain character.
- Combine many strings into one by using the Join function to join together an array.
- For targeted text replacement, the Replace technique is your best bet.
- To extract substrings from a text string, you may either use string slicing or regular expressions.
- To determine how many times a certain word or character appears in a text file, you may use the Measure-Object command.
- If you need to change the case of some text, you may use the ToUpper() or ToLower() methods.
- You may import CSV files using the Import-Csv command, apply filters and transformations, and then export the results with the Export-Csv command.
- If you need to work with JSON data, you may use the ConvertFrom-Json and ConvertTo-Json cmdlets to parse JSON into PowerShell objects and then alter the data.
- Inserting Variables into Text Strings: Use String.Format(), the -f operator, or string interpolation (“Hello, $name!”) to format text strings with variables.
- To determine how long a string of text is, you may access its Length attribute.
- To get rid of extra whitespace, you may use the Trim(), TrimStart(), or TrimEnd() functions.
- Using the Replace() technique, you may change the line ending format from Windows (CRLF) to Unix (LF).
- Using Select-Object -Unique, you may pull out just certain words or lines from a text file.
- PowerShell is an excellent tool for automating text processing, managing data from many sources, and handling a broad range of text parsing and manipulation tasks due to its competency with text data and its vast string manipulation features and cmdlets.