
What is SCCM and How it Works?
In this article, we will understand products that help manage an organization’s infrastructure from inception to retiring the physical/virtual machines. There are various products that handle individual functionalities and all of these are handled from one suite for intercommunication amongst them. Following are the topics that we are going to cover in this article in detail.
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a Windows product which enables administrators to manage security and deployment of applications, devices that are part of an Enterprise. System Center is the family or suite of management tools from Microsoft. Organizations would rather purchase System Center Configuration Manager than purchasing a component in the System Center for updating or patching their systems.
How SCCM Works:
Now we will know the step by step procedure on how System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) works:
Step1: To install the application, create packages in the SCCM console which consists of the command line and executed files.
Step2: Configuration manager admin creates virtual application packages and replicates to selected Distribution Points.
(Distribution points are nothing but file servers, they store the packages for a particular region)
Step3: If the user wants to download any application, then the user can directly download the application from the distribution points rather than connecting to the SCCM primary server.
Step4: Now, install the SCCM agent which helps a machine to communicate with the SCCM servers.
Step5: In this step, the SCCM agent keeps on checking for the new policies and deployments. Using the updates SCCM admin creates deployment where an application is targeted on a bunch of machines.
Step6: Once the policy reaches the end machine, the SCCM agent evaluates the policy and reaches out to its particular regional distribution points for downloading the packages.
Step7: Once the executed files are downloaded in a temp folder, users can install those packages in the local system. Now the file status is sent back to the SCCM server to update in the database.
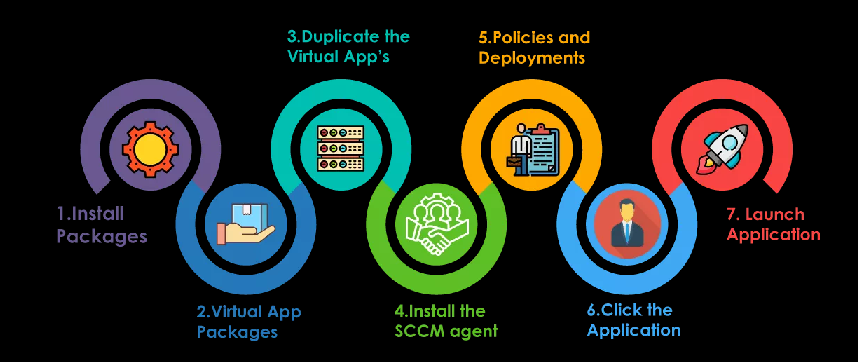
These are the basic steps to explain how SCCM works, and a lot more additional steps need to be considered in the background. But the core components used in the software distribution (Application packages, Distribution points, SCCM agents, servers) are the same for any infrastructure.
SCCM Version History:
SCCM 2019 Version
- SCCM 1902 – Released March 2019
SCCM 2018 Version
- SCCM 1810 – Released December 2018
- SCCM 1806 – Released July 2018
- SCCM 1802 – Released March 2018
SCCM 2017 Version
- SCCM 1710 – Released November 2017
- SCCM 1706 – Released July 2017
- SCCM 1702 – Released March 2017
SCCM 2016 Version
- SCCM 1610 – Released November 2016
- SCCM 1606 – Released July 22, 2016
- SCCM 1602 – Released March 11, 2016
SCCM 2015 Version
- SCCM 1511 – Released November 2015
SCCM 2012 Version
- SCCM 2012 – Released 2012
SCCM 2007 Version
- SCCM 2007 – Released 2007
SCCM 2003 Version
- SCCM 2003 – Released 2003
SCCM 1999 Version
- SCCM 2.0 – Released 1999
SCCM 1996 Version
- SCCM 1.2 – Released 1996
SCCM 1995 Version
- SCCM 1.1 – Released 1995
SCCM 1994 Version
- SCCM 1.0 – Released 1994
Let us dive into the SCCM concepts one by one.
Systems Management in Enterprise
Earlier to the advent of any Systems Management tools, IT departments struggled a lot with the server and client system management. With the tools like Microsoft System Center, patching a computer, imaging workstations, rolling out software, monitoring servers, network devices and backups were all done in a tedious manner. As tools evolved around the systems management, there used to be dedicated servers for these requirements and this had to repeat for another set of requirements. This was all a clumsy process as there was no communication between these separate servers.
To understand this, consider an example where an organization keeps track of assets through one product and has a separate one to put images onto these systems. It has a product to update or patch the systems when required and another one to monitor the system and alert the administrators in any unforeseen situations. Finally, a different product to backup data and a different product to provide security management of the system also exist. Having said this, Microsoft was in a situation like this for about 5 to 8 years when all of these were handled via different products.
After many years, Microsoft had put all of these products into a single suite of products called the System Center and spent enough time to get all of these products to work together.
Now, an organization which wants to buy a new license can actually buy a suite license to work with all these products under a single umbrella and leverage benefits out of these products for their own enterprises. The section focuses on bringing in a product like System Center which can handle all the activities of a system from imaging, deployment, patching, updating, maintenance, support, and retirement under a single life-cycle management tool.
System Center family of Products
There are many products that constitute System Center, and the whole suite complements each other with their functionalities. Based on the licenses that are purchased, organizations can work along with more than one of these products or tools within their Enterprise. With each successful release, more and more functionalities and capabilities are added which help each other. Let us now take a look at each of these products individually to see their functionality set:
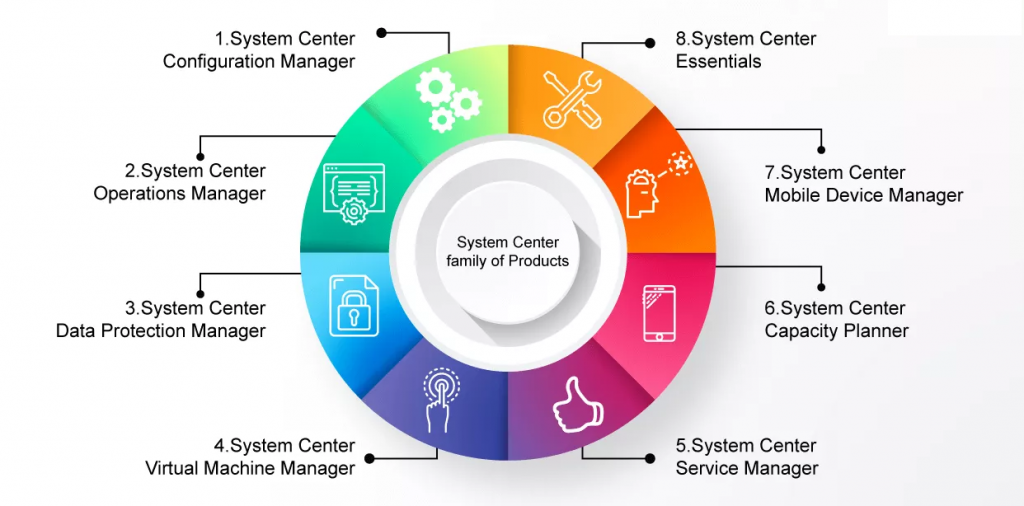
1. System Center Configuration Manager
System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) comes with the ability of imaging and installing the base operating system on a system based on the configuration provided. Once an operating system is installed, SCCM kicks in to update or patch the system. It keeps track of the system inventory and remote control capabilities. It enables IT, administrators, to keep up with the system configuration of all the machines based on a single and common organizational configuration.
2. System Center Operations Manager
SCCM is the product that lays down the base configuration of a system and keeps it updated and patched. System Center Operations Manager then takes over the responsibility of monitoring the health of the system along with all other applications installed on that specific system. There are specific sets of rules that track down the normal functioning of the system, and if there are any deviations, the necessary personnel is notified of the changes.
3. System Center Data Protection Manager
Data Protection Manager (DPM) comes in handy when SCOM reports any faults on a physical machine. DPM helps in recovery from the backups that it holds. DPM takes backups of the server file system, SharePoint data, exchange databases, SQL databases on a standard schedule. This helps in recovering a system by full data recovery which is either corrupted or damaged.
4. System Center Virtual Machine Manager
There is a shift of organization’s physical systems to virtual systems for development, maintenance, and production, and hence comes a tool that handles all the life cycle-related activities for the virtual machines – System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM). If there is an instance where a physical or a virtual system is about to fail, SCOM can trigger the automatic creation of a new session using SCCM and Hyper-V to build a new virtual system. VMM also helps in transferring the operating system, application, and data to a virtual machine in an automated Physical To Virtual (P2V) process.
5. System Center Service Manager
Most of the tools from the System Center suite of products revolve around the IT related tasks such as patching, imaging, monitoring, backups – there are other organizational needs such as managing processes and change control. System Center Service Manager (SCSM) is an incident management and change control system which integrates with SCCM and the like seamlessly. It helps in logging all the issues identified with these tools and gathers all the details around the issue for a one-point reference to the Desk personnel or the Support personnel.
6. System Center Capacity Planner
With the growing needs of an organization, there is always a need to upgrade the infrastructure for an organization. System Center Capacity Planner helps in identifying and testing performance demands from the current setup and plan for the future requirements aptly. Based on the current requirement, it helps in identifying the relative requirements on the hardware to meet the performance demands for your organization.
7. System Center Mobile Device Manager
Organizations run on Servers and Clients for their related operations, but with the advent of smartphones with equal computing power, mobile devices also have joined the bandwagon for operations carried out in organizations. System Center Mobile Device Manager (MDM) joins hands with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) to handle all the life cycle stages from inception to completion for all mobile devices and in simple words, MDM is to mobile devices what SCCM is for servers. Provisioning, monitoring, updating, securing, wiping the devices are all the activities that can be done with MDM.
8. System Center Essentials
Not every organization might have a dedicated IT wing to handle all the system, server related stuff (organizations with less than 500 users or 50 servers). Microsoft provides System Center Essentials which enables management functions related to tracking inventory, patching and updating these systems, monitoring, deploying newer software. All of these can be done from just this single tool, helping them to scale on their administration capabilities.
MajorBasic Features of System Centre Configuration Manager
In this section, let us try and understand the major features that are provided by System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM).
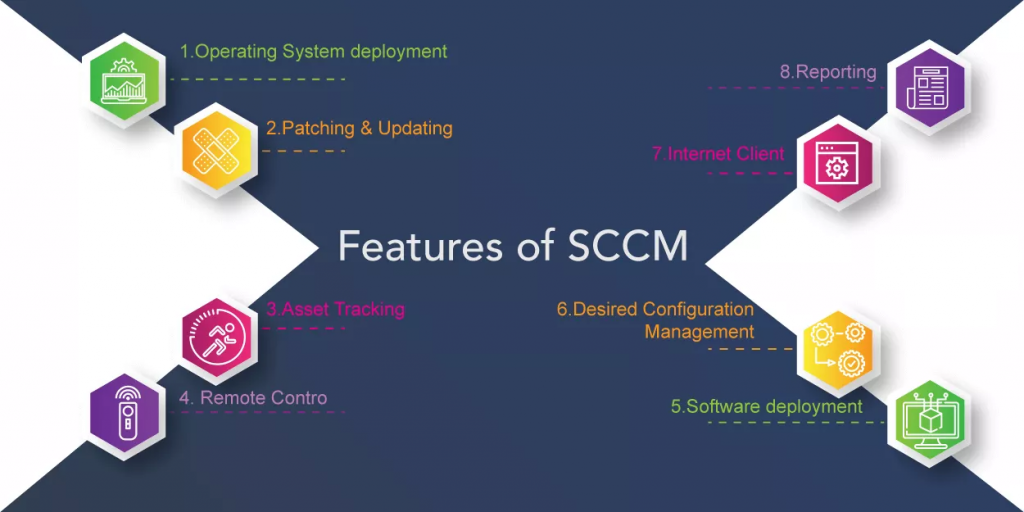
1. Operating System deployment:
Installation of the core Operating System is the very first step that needs to be done to initiate the life-cycle for a server altogether. SCCM provides all the tools an organization requires for Operating system deployment – either via the imaged installation or as a scripted method of installation.
2. Patching & Updating:
When the installation of the Operating system is completed successfully, SCCM initiates patching and updating these systems. Most of the organizations rely on the free service (Windows Server Update Services) to patch and update the systems but SCCM leverages everything that WSUS provides and over that, provides the IT administrators an active patching and updating in addition to WSUS.
The active update system enforces updates, forces systems to be patched or updated and later rebooted following the IT guidelines published by organizations.
3. Asset Tracking:
Once a system has been created with the Operating system that is required, and later updated, patched, such systems need to be kept in track of further timely updates or patches. SCCM includes the tools that are required to keep track of the hardware, software assets of the system that it is managing altogether.
4. Remote Control: If a user or a system encounters an issue which might require further assistance of an IT administrator, there is a provision to take remote access of the system to analyze the problem. SCCM has a remote control process that allows an IT administrator or a support engineer to access the system remotely.
5. Software deployment:
Installing the core operating system on a physical/virtual machine is one part and the other part is the additional softwares that is required on a system. SCCM provides a tool that allows users to install a simple plugin or a complex suite of applications with unique application configuration. This is one of a kind functionality that makes it more suitable for organizations where certain IT guidelines can be implemented without halting anything.
6. Desired Configuration Management:
This is the other feature that follows the IT guidelines outlaid by an organization where the standard configuration of a system cannot be altered. This ensures that the system has the same software setup, updates, drivers and configuration settings across all the systems. Desired Configuration Management (DCM) tool within SCCM ensures the stringent audit constraints are met and compliance is maintained.
7. Internet Client:
This is a significant component of the SCCM tool which enables devices like remote systems or mobile devices to be accessed remotely without specifically bringing them into the VPN network for any maintenance requirements. This can now happen via an Internet Client and a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificate installed on the system. With these prerequisites, SCCM will be able to connect to that device anywhere in the world automatically to inventory, patch, update, monitor the system.
8. Reporting:
SCCM provides an out of the box integration with a report generation tool that generates reports based on the requirements outlined by the IT administrators. These reports may vary based on the requirement like reports of systems that have missed the patches or updates, reports of standard configuration, inventory reports, etc.
Business Solutions addressed by SCCM
System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) helps an organization maintain consistency in the system configuration and management across all the systems. Rather than having to build a workstation or a server manually and individually, SCCM makes use of the templates to build these systems pretty quickly. IT personnel can create these templates based on the guidelines outlaid and also to meet the requirements of the organization. In the case of template-based installation, organizations can very well depend on the consistency in the build configuration for all the hardware systems throughout the enterprise.
SCCM in conjunction with other components ensures achieving different functionalities. One of the best examples of such a component is System Center Operations Manager (SCOM). System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) along with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) helps an organization stay ahead and proactive to identify issues, faults on time and helps take necessary actions to minimize the downtime on any issues. These tools also help recover systems that have failed for various other reasons with the help of a tool called Data Protection Manager (DPM). It also enables monitoring of the normal operations of the available set of servers, workstations, and applications.There are policies that are established to update systems of a specific functional role, be updated or patched at the same time. This is a feature that is provided by one of the SCCM components called the Desired Configuration Management (DCM). It ensures specific updates are pushed to systems that meet a functional role. This further helps in ensuring all the audit requirements, and also in maintaining compliance at an organization level. This helps in answering all the questions related to audits and compliance requirements with just reports and nothing at all.
New look of SCCM:
If you are well aware of the SCCM tool altogether, then you would be able to appreciate what has been developed and released in the new releases. If you are not aware of the tool anyway, then the following few points should be good enough to appreciate what is available in the latest releases. Let us take a closer look at the following points then:
1. User focus:
IT consumerization is the fact of day and resistance against this will not allow an organization to scale further. With more and more devices being available in the market, there is always an expectation to support all of these. As SCCM has always been about systems management, considering the changing landscape, users have been given all the attention that it requires. This allows them to gain more control over the software that is installed. An example of this is the definition of the user’s working hours and based on these timings, the upgrades and patches are applied on the system.
There can be more than one device tagged to a single user, meaning that there can be more than one primary user for every device that is being worked upon. These relationships are handled using the User Device Affinity (UDA). Users can manage their own systems using a new interface called the Software Center. This is more like a shopping cart approach where users search and find what they want to request for installations. Based on the applications, few might be installed right away and few others that require administrative approvals.
2. Role-based Access Control:
Based on the recent trends amongst the products in the industry (in general), there is a growing adoption towards role-based security. This has now been introduced in SCCM 2012 and is controlled by Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) hiding the elements that the user doesn’t have access to. The tasks are grouped into security roles administratively. There are few roles provided with the tool and, in addition to that, business-specific roles and scopes will be added later.
The multilayer approach helps you leverage the power of cloud, and at the same time protect on-premise clients from any possible potential threats from the internet. SCCM 2012 comes with a new console altogether. This no longer relies on Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Take a look at the following:
3. Smartphone support:
System Center Mobile Device Manager (MDM) 2008 wasn’t exactly a success but its functionality was rebuilt into SCCM 2012. Support for iPhone, Android, and Windows phones was covered through the Exchange Active-Sync connector.
What is SCCM Certification?
An SCCM Certification is required for an individual working with SCCM from a very close vicinity perspective. This will only enhance the usage of the tool to its fullest potential as it provides a deeper understanding of the tool itself. Though this can be achieved without certification, it would add a lot of weightage per se, if you claim that you are certified by the organization who provides timely updates to these tools themselves.Get ahead in your career by learning SCCM through Mindmajix SCCM Training.
Why SCCM Certification?
The expectation from these SCCM certifications is that an individual who is assigned with the related work does it with utmost confidence and performs tasks with utmost care and precision. With the deeper understanding that one has on a tool, comes the better usage of it for all the Organizational needs. If your work deals with SCCM and tasks related to it, then you might want to take up these certifications to ascertain your skills in this competitive world and stay ahead of others.
SCCM Certification Exams
Out of many certifications that are available on this suite of products, the following two certifications are suggested to be more apt, based on your role within your organization. Let us understand the requirements to these certifications and also the required pre-requisites to these Certifications:
(70-703): Administering Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager and Cloud Services Integration
This Certification exam is intended to test your technical skills in accomplishing the following tasks. Each of these topics carry a relative weightage percentage, mentioning how important the topic is for the actual examination. It is obvious that higher this weightage percentage, more questions would be asked on that topic.
This Certification exam is currently in the beta stage and considering that, the pass or fail notification might require around 12 weeks. Should you pass this examination, you’d be given all the credit towards it.Configure and Maintain a Configuration Manager Management Infrastructure (30-35%):
This section of the exam concentrates on topics like Configuring management infrastructure to support devices, distribute content, to use queries and reports, deploy operating systems and finally to manage the whole setup of management infrastructure outlined as below:
- Configure boundary and boundary groups
- Configure AD discovery methods
- Creating collections, user collections
- Configure maintenance window
- Configure resource discovery
- Configure Mobile Device Management (MDM) using Exchange Server connector
- Distribution point installation
- Content distribution management
- Content management infrastructure preparation
- Manage content on distribution points
- Configure SSRS (SQL Server Reporting Services)
- Creating data queries and sub-select queries
- Creating reporting services point
- Configure Data Warehouse Service point
- Report generation using ReportBuilder
- Operating system deployment
- Manage site system roles to support deployments
- Configure role-based administration
- Configure administrative users
- Remote control management
- Maintaining a Configuration Manager site
Conclusion:
In this article, we have tried to understand the business problem that Software Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) tries to resolve. We have understood the systems management in an enterprise and how SCCM resolves this problem with the features that it provides. We have then discussed the System Center suite of products and its features, along with it, we have also taken a closer look at the major features provided by SCCM. We have also seen the business use cases where SCCM finds its usage. We have also discussed the new features that are provided in the latest releases of SCCM.Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.






