
- Introduction to Economic Environment
- Importance of Business Decisions
- Types of Economic Systems
- Economic Indicators
- Role of Government Policies
- Globalization and Its Impact
- Economic Recession and Expansion
- Inflation and Deflation Effects
Introduction to Economic Environment
The Economic Environment refers to all external economic factors that influence buying habits, business performance, and overall market conditions. It encompasses elements such as inflation, interest rates, economic growth, unemployment levels, fiscal and monetary policies, and global economic trends. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers to make informed decisions. For instance, a stable economy fosters consumer confidence and encourages investment, while economic instability can lead to uncertainty and reduced spending. Additionally, the economic climate can vary significantly across countries and regions, affecting how businesses operate globally. Changes in government regulations, taxation policies, and trade agreements also form part of the broader landscape that can impact profitability and strategic planning. With globalization and rapid technological advancements, monitoring the Economic Environment has become more critical than ever. It helps in identifying opportunities and threats and aids in long-term forecasting and risk management. By analyzing trends and indicators, organizations can adapt strategies to remain competitive and resilient in dynamic markets. A solid grasp of these economic forces is fundamental for sustaining growth and achieving stability across all sectors.
Importance of Business Decisions
- Strategic Direction: Business decisions help define the goals and long-term vision of a company, ensuring that all actions align with its mission.
- Resource Optimization: Effective decisions ensure optimal use of resources like time, money, and manpower, improving overall efficiency.
- Risk Management: Timely and well-analyzed decisions help identify potential risks and create strategies to mitigate them.
- Economic Environment of Business: The economic environment includes factors like inflation, unemployment, GDP growth, and government policies, which influence business decisions, operations, and market dynamics.
Making the right Business Decisions is crucial for the success and sustainability of any organization. These decisions guide the direction of a company, influence growth, and determine how effectively resources are utilized. Whether it’s about launching a new product, entering a new market, or managing finances, well-informed business decisions help minimize risks and maximize opportunities. Here are six key reasons highlighting the importance of making sound Business Decisions:
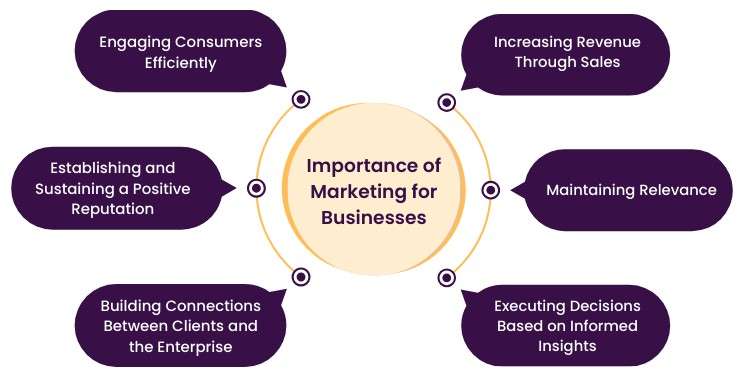
- Competitive Advantage: Good business decisions can give companies a strategic edge over competitors by identifying market trends and customer needs.
- Employee Morale: Transparent and confident decision-making boosts employee confidence, leading to better productivity and workplace harmony.
- Customer Satisfaction: Informed decisions that cater to customer preferences and feedback help build loyalty and trust in the brand.
Types of Economic Systems
Types of Economic Systems refer to the various ways societies organize and manage economic activities, such as the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The four main types are traditional, command, market, and mixed economies. A traditional economic system is based on customs, traditions, and beliefs, typically found in rural or undeveloped regions where economic roles and methods are passed down through generations. In a command economy, the government controls all major aspects of the economy, including what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. Examples include North Korea and, formerly, the Soviet Union. A market economy, on the other hand, relies on supply and demand with minimal government intervention; private individuals and businesses make economic decisions, as seen in capitalist economies like the United States. Lastly, a mixed economy combines elements of both market and command systems, balancing government involvement with private enterprise. Most countries today, including India and the UK, operate under mixed economic systems. Understanding these types of economic systems is essential for analyzing how different nations address economic challenges and prioritize resource allocation, social welfare, and growth. Each system has its strengths and limitations, influencing the standard of living and economic freedom of its citizens.
Economic Indicators
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country, indicating overall economic growth.
- Unemployment Rate: Shows the percentage of the labor force that is jobless and actively seeking employment, reflecting labor market conditions.
- Inflation Rate: Tracks the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, typically measured through the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Interest Rates: Set by central banks, they influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment activities.
- Consumer Confidence Index (CCI): Gauges consumer sentiment about the economy, which affects spending behavior and economic momentum.
- Balance of Trade: The difference between a country’s exports and imports; a surplus or deficit impacts currency value and economic strength.
- Economic Growth: Globalization opens up international markets, encouraging trade and investment, which boosts economic development and job creation.
- Access to Technology: It facilitates the rapid spread of technology and innovation across borders, improving productivity and connectivity.
- Cultural Exchange: Increased interaction between countries promotes cultural awareness and diversity, enriching societies globally.
- Improved Supply Chains: Businesses benefit from global supply chains that reduce costs and improve efficiency in production and distribution.
- Job Displacement: While globalization creates jobs in some sectors, it can lead to job losses in others due to outsourcing and automation.
- Environmental Challenges: Greater industrial activity and transportation linked to globalization contribute to environmental issues like pollution and climate change.
Economic Indicators are statistical tools used to assess the overall health and direction of an economy. They help governments, businesses, and investors make informed decisions by providing insight into economic performance and future trends. These indicators are typically classified into leading, lagging, and coincident types, depending on how they reflect changes in the economy. Here are six key economic indicators widely used for analysis:
Role of Government Policies
The Role of Government Policies in an economy is crucial for maintaining stability, promoting growth, and ensuring social welfare. Government policies influence the economic environment by setting rules and regulations that shape business operations. consumer behavior and market dynamics. Fiscal policies, such as taxation and government spending, help manage economic fluctuations and allocate resources efficiently. Monetary policies, controlled by central banks, regulate the money supply and interest rates to maintain price stability and control inflation. Trade policies impact imports, exports, and international competitiveness, while industrial and labor policies support specific sectors and protect workers’ rights. Environmental regulations promote sustainable development and address issues like pollution and resource conservation. In times of economic crisis, such as recessions or pandemics, government intervention through stimulus packages, subsidies, or public programs becomes essential to revive demand and restore confidence. Additionally, policies targeting education, healthcare, and infrastructure contribute to long-term economic development and improved quality of life. The government also plays a vital role in reducing income inequality and ensuring fair access to opportunities through social welfare programs. Overall, the role of government policies is to create a balanced framework that supports economic efficiency, equity, and stability, enabling both individuals and businesses to thrive in a well-regulated economy.
Globalization and Its Impact
Globalization and Its Impact refers to the growing interconnectedness of countries through trade, investment, technology, and cultural exchange. It has transformed the way businesses operate, influenced economies, and reshaped societies worldwide. While globalization offers numerous opportunities for growth and collaboration, it also presents challenges that need to be carefully managed. Here are six key impacts of globalization:
Economic Recession and Expansion
Economic Recession and Expansion are vital phases of the business cycle that indicate the overall condition of an economy. An economic recession is marked by a sustained decline in economic activity, often seen through decreasing GDP, rising unemployment, lower consumer spending, and reduced business investment. Recessions can lead to financial strain on both individuals and organizations, prompting governments and central banks to introduce measures such as tax cuts, interest rate reductions, or stimulus packages to stabilize the economy. In contrast, economic expansion is a period of growth when GDP increases, employment rises, consumer confidence strengthens, and businesses invest more actively. This phase brings about higher production, improved income levels, and increased demand for goods and services. Economic expansion often results in improved living standards and greater opportunities but may also carry risks like inflation if not managed carefully. Both recession and expansion are natural and recurring parts of economic cycles, influenced by domestic and global events, policy decisions, and market dynamics. Understanding how these phases work helps governments, investors, and businesses plan effectively, manage risks, and take advantage of favorable conditions while preparing for potential downturns.
Inflation and Deflation Effects
Inflation and Deflation Effects have significant impacts on an economy, influencing purchasing power, business decisions, and overall economic stability. Inflation refers to the general rise in prices of goods and services over time, which reduces the value of money and erodes consumers’ purchasing power. While moderate inflation can indicate a growing economy, high inflation can lead to increased costs of living, reduced savings value, and uncertainty in investment and business planning. It often prompts central banks to raise interest rates to control price levels. On the other hand, deflation is the decline in prices across the economy, often caused by reduced consumer demand, excess supply, or tight monetary policies. While falling prices may seem beneficial to consumers, deflation can lead to reduced business revenue, lower wages, job cuts, and an overall slowdown in economic activity. It can also increase the real value of debt, making it harder for individuals and companies to repay loans. Both inflation and deflation are critical components of the Economic Environment, and if not managed properly, can destabilize an economy. Therefore, understanding their effects within the broader Economic Environment is essential for maintaining balanced inflation, sustainable growth, and long-term financial health.

