
Cloud Computing Tutorial: A Complete Hands-on How To Use Guide For Free
Last updated on 09th Jul 2020, Blog, Tutorials

CLOUD COMPUTING is defined as storing and accessing of data and computing services over the internet. It doesn’t store any data on your personal computer. It is the on-demand availability of computer services like servers, data storage, networking, databases, etc. The main purpose of cloud computing is to give access to data centers to many users. Users can also access data from a remote serve
Types of Clouds
- There are four different cloud models that you can subscribe according to business needs:

- Private Cloud: Here, computing resources are deployed for one particular organization. This method is more used for intra-business interactions. Where the computing resources can be governed, owned and operated by the same organization.
- Community Cloud: Here, computing resources are provided for a community and organizations.
- Public Cloud: This type of cloud is used usually for B2C (Business to Consumer) type interactions. Here the computing resource is owned, governed and operated by the government, an academic or business organization.
- Hybrid Cloud: This type of cloud can be used for both types of interactions – B2B (Business to Business) or B2C ( Business to Consumer). This deployment method is called hybrid cloud as the computing resources are bound together by different clouds.
Cloud Computing Architecture
- Let’s have a look into Cloud Computing and see what Cloud Computing is made of. Cloud computing comprises two components front end and back end. Front end consists of the client part of the cloud computing system. It comprises interfaces and applications that are required to access the cloud computing platform.
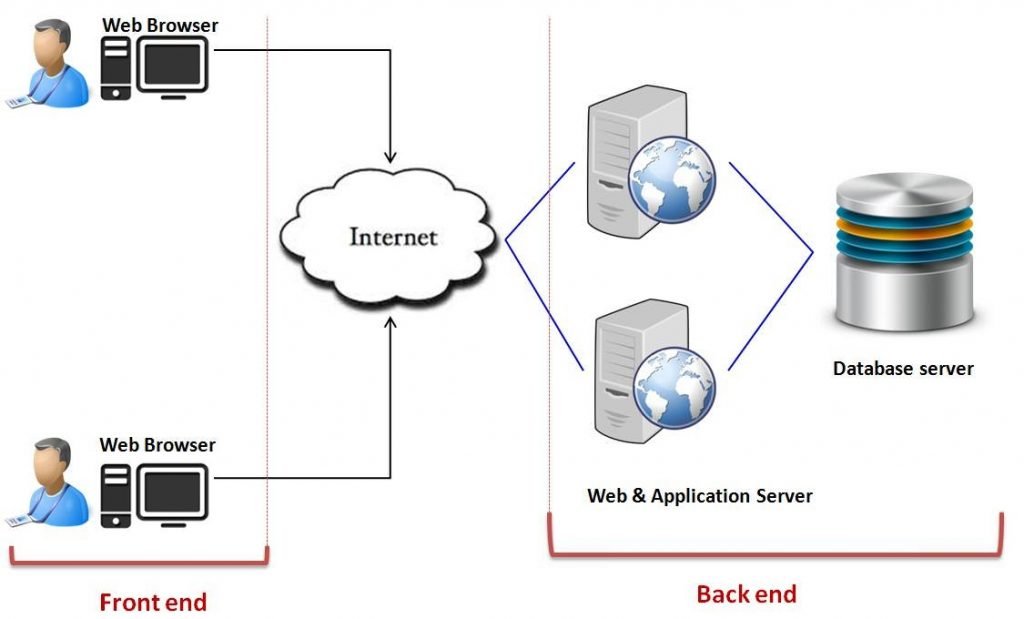
- While back end refers to the cloud itself, it comprises the resources that are required for cloud computing services. It consists of virtual machines, servers, data storage, security mechanism etc. It is under providers control.
- Cloud computing distributes the file system that spreads over multiple hard disks and machines. Data is never stored in one place only and in case one unit fails the other will take over automatically. The user disk space is allocated on the distributed file system, while another important component is algorithm for resource allocation. Cloud computing is a strong distributed environment and it heavily depends upon strong algorithms.
Cloud Computing Work
- To understand the workings of a cloud system, it is easier to divide it into two sections: the front end and the back end. They are connected to each other through a network, usually the Internet. The front end is the side of the computer user or client. The back end is ‘the cloud’ section of the system.
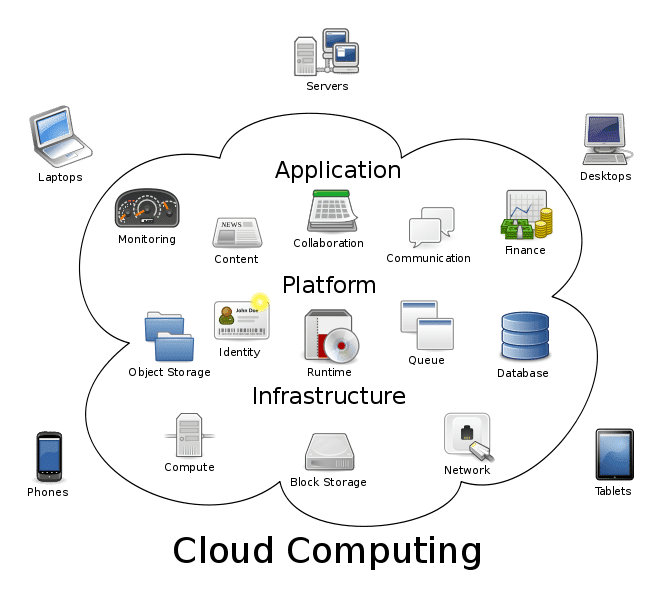
- The front end consists of the client’s computer or computer network. Also the application essential to access the cloud computing system. It is not necessary that all cloud computing systems have the same user interface.
- On the back end of the cloud technology system, there are various computers, servers and data storage systems that make up the cloud. A cloud computing system could potentially include any computer program, from data processing to video games. Generally, each application will have its own dedicated server.
Characteristics Of Cloud Computing
Some of the features are listed below:
1) Device and location independence: The users can connect to the cloud network from any location and any of the device, example, laptop or smartphones, as they are accessible through the Internet and servers that are centrally located (off-site, maintained by a service provider) regardless of any specific location-centric.
2) Pay as per-use: The users need to pay only for the resources they have used out of the pool of applications and services available and need not pay for the overall infrastructure.
3) Multi-tenancy: It offers sharing of services, software applications, platform and their costs among large scale users. The same physical infrastructure such as servers and hardware equipment is shared between many users but all of them retain information privacy and data security.
- The resource pool is large enough to serve multiple organizations and customers at the same time without an interruption in services between one another. This feature also makes the effective utilization of the resources at the right time which usually has a trend of having less utilization such as 10% to 20% during peak hours by performing load-balancing and sharing activity.
4) Reliability: The reliability of the system is improved by using multiple redundant servers for applications and data storage so that in case of failure the data can be restored easily.
5) Productivity and Performance: The productivity of the projects using cloud networks for the application running increases as multiple users work on the same database and software simultaneously. Thus it will give better output by analyzing in their way at the same instance of time.
Models Of Cloud Computing
1) Software- as- a -Service (SaaS)
- The web-based software applications are available on cloud servers and the end-user can access them via the Internet connection. The services can be accessed from any remote end device and the users need not install the software and setup of the application on its desktop to run it.
- In this model, the users get access to application software and databases. The cloud providers will manage the infrastructure of the services which run on the platform. SaaS is also known as “on-demand software” as it is used to pay for usage basis or on a subscription basis.
- The disadvantage with the SaaS model is that since the user data is stored on the cloud provider’s server, therefore, there can be some unauthorized access to the data by the third party.
- Examples of SaaS are websites that offer services to create and save documents online and playing games online. The Salesforce, Slack, Google Docs, Word online and Mail-chimp are examples of SaaS applications.
2) Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- In this model, the organizations rent the storage, tools, infrastructure and the operating systems to build up their applications from the cloud server and they don’t have any role in controlling and maintaining the overall infrastructure. They just hold the processes of the development of their applications and own them.
- Thus the PaaS will offer a software development and testing environment to the user and organizations. The cloud providers only dispense a computing platform to the users which are inclusive of operating systems, programming language, database, software development tools, and a web server.
- The software applications testers or developers will build up and run their applications on that cloud platform despite purchasing and managing the hardware and software of the applications directly.
- Examples of the PaaS application: Microsoft Azure and Heroku.

3) Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- In this model, the organizations will take on lease the storage and servers they require to fulfill their project requirement from the cloud service provider. Then by using the cloud storage and servers, they will build up their applications by using their software developing tools, operating systems, and programming languages, etc.
- Apart from providing storage and servers on the lease, the IaaS cloud also has provision for services like Virtual Local Area Networks(VLANs), IP addresses, virtual machines, software bundles, firewalls, and load balances, etc as shown in the figure above. But the cloud providers will provide these services based on consumer’s demand from the wide range of resources available at various data-hubs of the cloud provider.
- IaaS is widely used for Wide-Area Networking (WAN) systems.
4) Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
- It splits the cloud resources and applications down the line into smaller units that can be deployed and run only when there is a request generated for the application. Thus this is also called server-less computing.
- The organization or user who is using the applications doesn’t need to purchase, rent and manage the servers and virtual machines but they will use it on when they need a part of it.
Features of Cloud Computing
1. Resources Pooling
- It means that the Cloud provider pulled the computing resources to provide services to multiple customers with the help of a multi-tenant model. There are different physical and virtual resources assigned and reassigned which depends on the demand of the customer. The customer generally has no control or information over the location of the provided resources but is able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction
2. On-Demand Self-Service
- It is one of the important and valuable features of Cloud Computing as the user can continuously monitor the server up time, capabilities, and allotted network storage. With this feature, the user can also monitor the computing capabilities.
3. Easy Maintenance
- The servers are easily maintained and the downtime is very low and even in some cases, there is no downtime. Cloud Computing comes up with an update every time by gradually making it better. The updates are more compatible with the devices and perform faster than older ones along with the bugs which are fixed.
4. Large Network Access
- The user can access the data of the cloud or upload the data to the cloud from anywhere just with the help of a device and an internet connection. These capabilities are available all over the network and accessed with the help of the internet.
5. Availability
- The capabilities of the Cloud can be modified as per the use and can be extended a lot. It analyzes the storage usage and allows the user to buy extra Cloud storage if needed for a very small amount.
6. Automatic System
- Cloud computing automatically analyzes the data needed and supports a metering capability at some level of services. We can monitor, control, and report the usage. It will provide transparency for the host as well as the customer.
7. Economical
- It is a one-time investment as the company (host) has to buy the storage and a small part of it can be provided to the many companies which save the host from monthly or yearly costs. Only the amount which is spent is on the basic maintenance and a few more expenses which are very less.
8. Security
- Cloud Security is one of the best features of cloud computing. It creates a snapshot of the data stored so that the data may not get lost even if one of the servers gets damaged. The data is stored within the storage devices, which cannot be hacked and utilized by any other person. The storage service is quick and reliable.
9. Pay as you go
- In cloud computing, the user has to pay only for the service or the space they have utilized. There is no hidden or extra charge which is to be paid. The service is economical and most of the time some space is allotted for free.
10. Measured Service
- Cloud Computing resources used to monitor and the company uses it for recording. This resource utilization is analyzed by supporting charge-per-use capabilities. This means that the resource usages which can be either virtual server instances that are running in the cloud are getting monitored, measured and reported by the service provider. The model pay as you go is variable based on actual consumption of the manufacturing organization.
Benefits Of Cloud Computing
1) Cost-Effective:
- The use of cloud infrastructure in networking and computation will reduce the overall cost of purchasing and managing the hardware and software equipment for the project of the organizations.
- In this way, the project will become cost-effective as the organizations need not spend money on building data-centers, purchasing hardware, up-gradation of software and other resources needed to run the project as all of these services are managed by the cloud service provider.
- Also, the cost of renting these resources of the cloud is very economical for the companies in comparison to managing them rather than purchasing them.
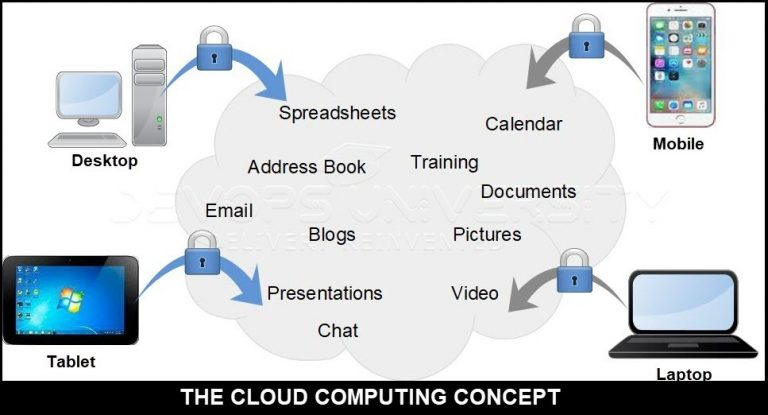
2) Mobility:
- The use of cloud computing infrastructure will provide the flexibility and mobility to the end-users to extract, store and share the data from anywhere, anytime just by having an Internet connection.
- This implies that the users are not required to carry the hard disks and CDs to carry their data from one place to another. They can just save their data at Google Drive or Drop Box and then can access them over the Internet from anywhere.
- They can also share these data with their other partners on this platform like with other employees of the company or, the users can share their images with their relatives by creating a family group on the cloud network.
3) Easy management of Data and Applications:
- Since the organizations need not configure the software and hardware of the applications and projects they are working on, therefore they can focus much on the development of the software applications easily.
- Also, all the data is stored at one centralized server so it is easy to manage the data and to track who is accessing which kind of data at that location by the management.
4) Device Flexibility:
- In cloud computing, the same data and applications can be accessed on various devices like smartphones, laptops, desktop PCs and iPads.
5) Enhanced Storage Capacity:
- The capacity of the servers to store data is much more than the storage capacity of the user device. Thus the cloud computing will make it easy for the users and the organizations to save their huge units of personal and project-related data in the data servers of the cloud networks.
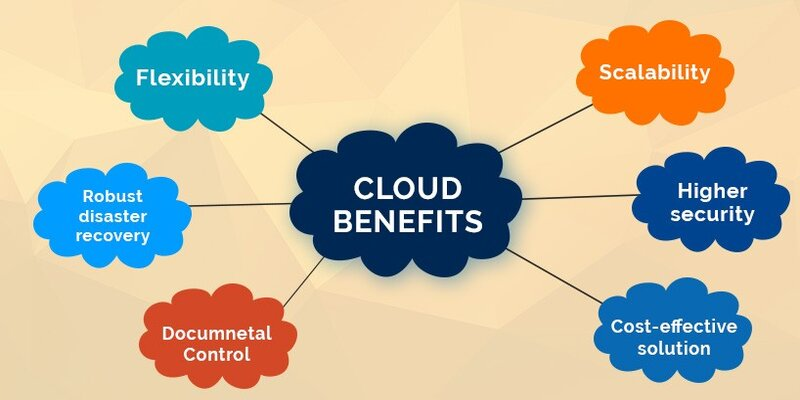
6) Automation in Up gradation of software:
- The cloud computing will offer the automatic up-gradation of all the applications and the software programs running on its platform on a timely basis.
Conclusion
- In this tutorial, we have understood the concept of cloud computing in the networking system and its merits and demerits. We have also understood various kinds of Cloud models and types of Cloud networks with the help of the examples and figures.
