
SAP ECM Interview Essentials: 50 Questions Covered With Answers
Last updated on 17th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
If you’re looking for SAP ECM Interview Questions for Experienced or Freshers, you are at the right place. There are a lot of opportunities from many reputed companies in the world. According to research SAP, ECM has a market share of about 0.2%. So, You still have the opportunity to move ahead in your career as SAP ECM Manager. ACTE offers Advanced SAP ECM Interview Questions that helps you in cracking your interview & acquire your dream career as SAP ECM Developer.
1. Describe the processing class. Why and in what contexts should they be used?
Ans:
The processing should be done during a payroll run depending on the wage type’s feature.
For the electronic arts, new media art, and visual design communities, Processing is a free graphical library and integrated development environment (IDE) designed to teach non-programmers the principles of computer programming in a visual context. Processing is paradigm-oriented and object-oriented.
2. Describe the course of evolution. When and why should we apply them?
Ans:
The series of connections that exist among the items in a hierarchy. O-S-P, or Organization->Position->Person, is one example.
Through genetic mutation, organisms change with each life cycle to improve their ability to survive, compete, and procreate. A variation in an organism’s genotype, or DNA, results in a variation in its extrinsic traits (phenotype) that improve an organism’s and its species’ prospects.
3. Explain how the internal payroll procedure works.
Ans:
To determine the employee’s base pay, the payroll process is carried out at a certain point in time to account for extra payments like incentives, overtime compensation, and other bonuses that need to be applied for a predetermined amount of time.
The steps your company takes to safeguard its payroll data are known as payroll internal controls. Payroll processes and restrictions keep workers from having access to private data. Internal controls also stop workers from overpaying and filing fictitious time sheets in order to steal money.
4. Describe the pay scale system and its setup.
Ans:
The term “Pay Scale structure” refers to the establishment of the Payroll area, group, and region, as well as the various EmpSub group levels that are utilized to group the caps.
A pay scale, sometimes referred to as a salary structure, is a system that establishes an employee’s wage or salary based on one or more variables, including the employee’s level, rank, or status within the employer’s organization, the duration of their employment, and the difficulty of the particular work they perform.
Salary structures with grades—which include minimums, midpoints, and maximums—are used by private businesses to specify the pay ranges that employees in each grade and range may expect.
5. Describe the process for bringing payscale information from non-SAP systems into SAP.
Ans:
- Verify that every individual included in the compensation data import file is an active, current user of the system.
- Import the user data file as often as necessary, excluding the compensation fields.
- If necessary, import the user data file containing the compensation fields.
- At least once during the planning cycle, import compensation.
6. Describe the process of assigning two distinct kinds of computer codes to two distinct individuals.
Ans:
Code is defined as a system of signals used for communication. as well as a set of symbols, such as( letters or numerals) that stand for given, frequently hidden meanings. Assigning a person to two distinct personnel numbers is almost impossible. Giving the individual two separate Personnel ID numbers with the same amount is one potential approach, and after that, compose an invoice.
7. Explain the Schema.
Ans:
A schema is a collection of programs that may be altered to meet the needs of the customers. Data collection from all of the detailed instructions paired with subschemas and PCRs is done using these programs.
A schema is the structure or organization of a database in computer programming and a formal description of an inference rule in artificial intelligence (AI).
8. How may information be prevented from reaching the payroll section?
Ans:
Their pay scale structure defines the company’s personnel. The indirect payroll is in charge of any limitations encountered while entering the pay structure’s data.
The payroll period dates are defined, and the workers for whom payroll is processed simultaneously are grouped in the SAP Payroll section. Employees from several employee subgroups can be part of the same payroll area. Payroll frequency and Pay Da are the fundamental requirements for a new payroll area.
9. How do you use the simple support interface?
Ans:
Depending on whether you need to change the personnel assignments, project profiles, or hierarchical structure, each zone has different maintenance capabilities. Simple Maintenance is the best option for Organizational Management clients when it comes to strengthening the fundamental framework for improving hierarchical arrangement.
Recommend switching to Infotype Maintenance for the final, detailed modification of individual authoritative protests in your hierarchical arrangement (changing particular positions or dependable units). With simplified techniques.
10. Describe usage within the Information Group.
Ans:
The standard architecture includes an information group for every labor activity. To customize the Personnel Administration, you can alter the formats of the various info groups to fit your company’s needs.
Info groups can be defined as clients assembling subordinates. The following info kinds are arranged in info groups that are used in Personnel Actions to indicate how you would use them to act. To describe an information group including each of these information categories, their execution requirements, and the client groups for whom it is relevant. You then let this information group engage in the action that you had described.
11. What’s used in them as a component?
Ans:
The actions that the framework activates are the dynamic ones. They result from some labor-related activities. The framework subsequently displays the data written in the unlikely event that you implement a change (faculty action) to the workforce information of information compose that subsequently influences the info of a moment data write. Among the primary causes of the dynamic activity (of the frame) is to have knowledge that is clear and predictable.
The best-case scenario is when you finish an action, like enrolling, and need to fill in a data write arrangement. Staff activity is your subheading of delicate bits in info type 0000. As you naturally complete this structure, more information will appear as a result of the dynamic action.
12. Describe the hiring cycle.
Ans:
The complete enrollment process is perfect, starting with identifying the vacancy, displaying the same, counseling them, greeting the applicants, screening them, having a conversation with them, picking them, and designating them (providing an authority place within the association: the enlistment cycles are made up of all proposition types.
The entire hiring process is known as full-cycle recruitment. It begins when the post becomes available for applications and concludes when a candidate joins the team.
There are six phases to this system : planning, sourcing, screening, choosing, recruiting, and onboarding.
13. What is the purpose of IT 41? How can IT 41 be set to default?
Ans:
- Date Details (Information creates 0041). The Date Specifications information form (0041) contains the relevant data. The type of data is indicated by the Date written.
- In a series of reports, a solid Date composition (provided by the client) is used, for example, to evaluate a passing date that is not obtained from the hierarchical task history but is stored in the data type 0041 for Date Specifications.These data can be used for such applications as well as in the field of finance.
- There are twelve combinations of Date compose and Date in the benchmarking framework. If, in the interim, you need more than twelve date determinations for a representative, you can use the time limitation feature.
14. Define Requesting access as an EsS authentication application process.
Ans:
Through Worker Self-Service, representatives may create, display, and edit HR-related content on the Enterprise Portal. It is typically associated with benefits and costs, working hours, careers and jobs, employee searching, personal information, and travel scheduling.
Therefore, the kind of data that the representatives are able to add, modify, or remove depends on the consent that the employees (customers and employees) have given.
15. Describe internal hiring.
Ans:
Searching for candidates within the company is known as internal recruiting. When combined with personal growth, they may be utilized to locate a profile match, which facilitates internal resource discovery. The AP symbolizes the external person in the recruiting process, whereas the P represents a person.
16. Describe the typical issues that arise when the FICO results are posted.
Ans:
The most frequent issue encountered while publishing results for the FICO is the discrepancy in the amount that is made public.
- Accounting using general ledgers.
- Control over all financial transactions.
- Managing materials.
- Management and scheduling of production.
- A human resource.
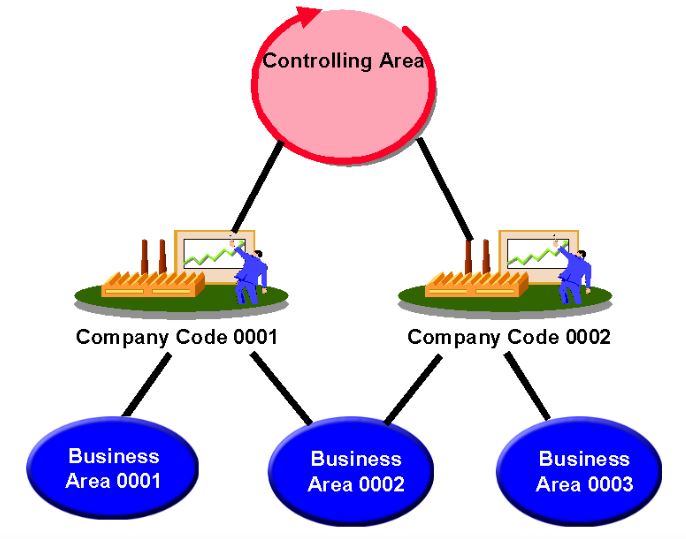
17. Define the Controlling Area.
Ans:
The FI of the person who assists in setting the costing objectives, which are based on the fiscal versions of an organizational unit inside a business that may have a full cost accounting done in a closed system, is known as the controlling area. One or more business codes that may function in several currencies may be present in a governing region.
18. Explain the rationale for the creation of AC and the transaction code.
Ans:
The reason behind constructing a symbolic account is contingent upon the kind of payroll needed to generate a salary on an analogous cost account, among other factors.
Area of payroll: It shows the set of workers for whom a single payroll is generated.
Pay scale region: This refers to a certain geographic area or personnel groupings for whom a specific CAP is a payroll.
19. What is the role of a manager in PA?
Ans:
Due to PA/PSA, the right of usage must be restricted to personnel organizations. The manager checks SAP for Payroll, Time Administration, and Personnel Administration. Every administrator is responsible for every individual conduct. You will obtain the head’s name on the pay slip, which will allow the employee to meet with the reliable executive (acquired via payslip. for any clarification.
20. How can representatives be assembled for their financial remittances?
Ans:
- Navigate to Payroll India’s Essential Compensation of India and collect the representative who is originally dependent on the stipends. This has to do with grouping the delegates according to their strengths based on their pay scales, Increasing the flow.
- Tax benefits may attract remittances, but they may also promote tax avoidance. While efforts to steer remittances toward investment have not had much success, matching-fund programs aimed at attracting remittances from migrant associations may divert monies from other local financing goals.
21. How are time management and finances coordinated?
Ans:
Payroll and TM MGMT are synchronized with the time data obtained from the data that makes up 0007. These hours are computed using basic factors such as the number of hours employed, time assessment, and, finally, diagram reconciliation. The X000 blueprint transmits XT00, and many modules can receive this information.
22. With what other modules are OM coordinated?
Ans:
Depending on the needs of the customer, OM includes any unit that has to be included. Regarding OM-PA, OM-RECT, and OM- BENEFITS,
The Event and OM Training in addition to MGMT, OM-PD.
Go to IMG, select CTRL F, and select Integration with OM to verify this. After checking each one, select the program.
Additionally, RHINTE20, RHINTE30, PHINTE40, RHINTE00, and PHINTE10.
23. Define ECR?
Ans:
A set of guidelines for altering several items in the engineering or production domains is known as an engineering change request, or ECR. It details the circumstances under which these modifications take effect, as well as the status of their release.
25. Explain the distinctions among the payrolls in the US and India.
Ans:
US payroll comprises a variety of US-specific taxes, benefits, garnishments, and other items. Strong command is required in order to work in this field. However, SAP HR elements like personnel administration and personal time management are also included in the Indian payroll. While benefits and garnishment are provided by US payroll, Indian salaries include allowances. Utilizing third-party software from the BSI, which is linked to the system, is necessary for US payroll.
26. What is meant by MAP?
Ans:
MAP stands for merchandise and assortment planning. The process of strategically planning and controlling the goods (merchandise. a retailer sells and variants of these goods that are offered to customers (assortment. based on market demand, customer preferences, and business objectives is known as merchandise and assortment planning in SAP Retail.
A map is often drawn on a level surface and is a symbolic depiction of certain aspects of a location. Maps provide basic visual information about the globe. They demonstrate the sizes and shapes of nations, the locations of characteristics, and the separations between regions to teach about the world.
27. What Makes a Macro and Subroutine Different?
Ans:
| Feature | Macro in SAP ECM | Subroutine in SAP ECM | |
| Purpose |
Facilitates automation by recording repetitive tasks. |
Performs specific tasks through reusable code segments. | |
| Creation | Involves recording a sequence of user interactions. | Comprises predefined, reusable segments of code. | |
| User Interaction |
Simulates user actions to automate tasks. |
Operates based on predefined logic, not user interactions. | |
| Code Structure | Typically consists of a series of recorded commands. | Represents modular code segments with specific functions. | |
| Reusability |
Limited to the specific recorded task. |
Can be invoked by other programs for increased reusability. |
28. How does SAP IS Retail manage promotions?
Ans:
- Transactions for Promotion Management: Open the SAP IS Retail system and log in.
- Make a fresh promotion: Enter the required information, including the promotion ID, the validity dates, and any other pertinent facts.As an alternative, promotions can also be made using SAP Retail’s Price Planning Workbench (PPW., a workspace for planning and executing manual price adjustments. The PPW incorporates the standard functions for calculating sales prices.
- Promotional Terms: Give a promotion to certain products, assortments, or product categories.
29. What does SAP be Retail offer, and what does Markdown mean?
Ans:
Prices have gradually decreased as a result of markdowns; this could be because of seasonal pricing, vendor-sponsored price adjustments, inventory reduction efforts, etc. In essence, markdowns offer a method for gradually lowering an item’s price, with a fixed or variable percentage of the price being lowered on a regular basis.
A plan to gradually lower an item’s price, with equal or different percentages of the price being dropped on a regular basis. SAP IS Retail offers management solutions for this. It offers resources to organize a discount, turn it on, and deliver the information to the retailers.
30. How do you attribute SAP IS Retail’s Markdown tool?
Ans:
Assign stores to utilize the markdown rules and schedules to manage which items are active at what prices throughout each phase by planning the markdown items, quantities, and pricing. The inventory and timing-based markdown schedule is automated by the Slow-Seller Management tool—pre- and in-season preparation and implementation to the expenses and major numbers.
31. How may a pointer be changed?
Ans:
The SAP concept known as “change pointers” enables a system to handle modifications made to pricing, master data, or any other type of data update in general. Several change points are made to get the modifications down to the other systems, such as BW, POS, eBusiness, Manugistics, etc.
The SAP standard solution for EDI (and ALE. messaging (Idocs. is compatible with the SAP standard solution for tracking modifications (Change document.
32. What are the disadvantages of utilizing shift pointers?
Ans:
- The possible volume of change pointers created and the system’s ability to handle those adjustments are some disadvantages of employing change pointers in a retail scenario.
- The more changes, the poorer the performance of batch operations mastery of SAP Retail is a full object, and you can define all the information needed for an item to be used in all processes with the help of the article maintenance function. There are various article types available to assist processes and requirements unique to the retail industry.
34. How do you feel about converting data for SAP projects?
Ans:
It is advised to use the actual migrated sample test data from an existing system instead of stinging test data, especially at the prototyping stage. The process of converting data from one format to another is the most general definition of data conversion and migration. To convert one set or type entails preparing the necessary processes and mapping the data fields.
- Converting data into an alternative,
- preferred format.
- Converting data for SAP projects
35. Define stock transfer order.
Ans:
The procedure used in inventory management to move commodities between storage locations within the same company code or between various company codes within a corporate group is called a Stock Transfer Order (STO.. Materials may be transferred between operations, storage facilities, or stock types. SAP’s Stock Transfer Order (STO. Organizations can transfer items internally between plants, storage facilities, or company codes using the SAP Stock Transfer Order (STO. process.
36. Which things are returned? How is the physical products issue recorded in SAP MM?
Ans:
Make a Purchase Order (PO. for a Return: Initially, you must make a
return purchase order with the merchandise’s original purchase order referenced. Indicate the amount and type of material being returned in the return PO.
Return of Goods (MIGO-Goods Movement:
- Post the returned goods using transaction code MIGO.
- Choose a PO Number under Goods Movement > Return Delivery in MIGO.
- Add any required information, including a return purchase order number.
37. How is the physical goods issue recorded in SAP MM?
Ans:
- To record a physical goods issue in SAP MM, use transaction code MIGO with movement type 601. Follow these steps:
- Access MIGO.
- Select document type (e.g., Goods Issue).
- Enter document and posting dates.
- Fill in document header details.
- Input movement type 601 in the Goods Movement Data tab.
- Enter material details in the Document Items tab.
- Save the document to generate a reference number.
38. What is SAP IS Retail’s definition of space management?
Ans:
The main goal of space management is to organize an article on a shelf in the most efficient way possible. In order to decide how space will be managed, key performance indicators (KPIs. are defined, typically utilizing sales, revenue, or gross margin data. A number of space management programs manage store goods placement. Based on several parameters like sales volume, margins, and so on, they compute the right amount of space to be allocated to the articles and decide the best location for them inside the shelves.
39. Is retail space management data useful?
Ans:
In short, space management is the process of optimizing a business’s or facility’s physical room. It entails consciously organizing, supervising, and planning how a particular workspace is used to guarantee that it is used successfully and efficiently. Able to plan and replenish requirements using space management data.
40. What is meant by the source list?
Ans:
The list that indicates where a specific article can be obtained is called a source list. The source list has vendor details, expiration dates, and other information. The store will also have a vendor. An inventory of all the sources you have used, arranged chronologically, is contained in a source list. Lists of references can be utilized for homework, talks, and blog posts.
41. What is the purpose of listing in Retail?
Ans:
The procedure that determines which stores receive which goods is called listing. Items that are assigned to a specific store or DC will not be eligible for processing.
Listing is the process that establishes the connection between items and assortments, as well as between items and websites. Users must create listings for any articles they wish to sell in any of the stores or DCs in order to do so. If not, selling the same in-store or through a DC will not be feasible.
42. What is meant by EAN/UPC?
Ans:
European Article Number (EAN.: The barcode symbology known as EAN was first used in Europe and is currently utilized worldwide. Its original purpose was to make effective product identification at the point of sale possible.
The barcode symbology often used in the United States and Canada is called UPC, or Universal Product Code. Numeric 12-digit codes make up UPC barcodes. Every digit in a UPC barcode, like the EAN, has a distinct function.
A 12-digit barcode, which is called a UPC, identifies the majority of products in North America. Thirteen-digit EAN barcodes are used to identify products in the rest of the globe.
43. For an article with three units of measurement, how many UPCs will be there?
Ans:
The product’s UPC (Universal Product Code. count may differ depending on the product’s presentation and packaging. Trade objects are uniquely identified by UPCs, which might vary depending on the container style and unit of measurement. It is possible for the same object to have distinct UPCs assigned to each of the three units of measurement.
44. What is kept in the WLK1 table?
Ans:
The SAP table WLK1 pertains to the Logistics Execution module, particularly to the Warehouse Management section. Information concerning transactions within the framework of warehouse management is contained in this table. In the SAP system, transfer order information is stored in WLK1. To transport materials within the warehouse, SAP WM (Warehouse Management. uses transfer orders.
SAP R~3 ERP systems come with a common table called WLK1 (Listing Conditions SAP Retail Assortments.. The technical specifications of the fields that comprise this table. Blue highlights indicate key fields.
45. How are additional tables updated upon the creation of the listing?
Ans:
In SAP systems, a number of tables are updated to hold pertinent data when a listing is created. The particular tables that are updated vary depending on the modules being used and the kind of listing. In SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning., the following tables are usually changed when a material is listed (added. for sale, particularly in the Sales and Distribution (SD. module: WLK2, MBEW, MARA, MAW1, and MARC.
Press show after entering the name of your table to get the technical settings screen. Select this tab. All fields will be in editable mode when you click the Change button. There is a Log data changes option at the bottom.
46. What is offered by the reference site?
Ans:
The source website offers certain logistics data that are needed while generating or editing an article. The model site, which acts as a reference point for configuration and master data settings for the many retail locations, is defined using the reference site concept. The reference website offers a uniform template that may be used as a foundation for building and setting up new retail websites.
47. What are generic articles?
Ans:
- The term “generic article” describes a kind of product representation that enables merchants to handle comparable or interchangeable items in their inventory and sales systems as a single unit.
- Generic articles are specific logistics information that’s required when writing or amending an article.
- The reference site concept is used to design the model site, which serves as a reference point for master data sets and set up for the numerous retail locations.
- A standard template is available on the reference website, which can serve as a starting point for creating and establishing new retail websites.
48. What does an article’s pricing profile mean?
Ans:
The set of guidelines that specify how a product’s price is computed or established is referred to as the pricing profile of an article in SAP Retail and other ERP systems. The article’s pricing elements are defined, including the base price, any applicable discounts or surcharges, taxes, and other elements that may have an impact on the ultimate selling price.
A price profile is the precise pricing plan that a company implements for a given good or service. It entails figuring out the best pricing range for the good or service depending on elements, including market demand, production costs, and competition.
49. Describe how SAP Retail integrates with other SAP modules.
Ans:
- SAP Retail and other systems interact with ease. SAP BW (Business Warehouse., SAP ERP, and SAP CRM are examples of SAP modules.
- This connection makes it easier for data to move seamlessly between departments, such as finance, customer relationship management, and business analytics, giving an integrated picture of retail operations.
- SAP Commerce Cloud’s connectivity with SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA gives it retail-specific functionalities. This integration requires the integration of reuse services with SAP Commerce Cloud.
50. Describe (IS-Retail. Buy One, Get One Free?
Ans:
This case can be resolved by utilizing the IS-Retail’s bonus buys capabilities. You can use sales condition master data or retail promotions to generate a bonus buy.
- If all the pieces in the combination are first created as a material grouping and then generated the purchase requirement for the bonus utilizing that material grouping.
- Verify bonus through IMG customization
- Distribution and sales
- Fundamental features
- Bonus.
51. What does the Industrial System’s counterpart of the Retail System’s MM43 transaction mean?
Ans:
The typical SAP MM (Materials Management. module in an industrial SAP system contains the MM43 from SAP Retail. The material master data at the retail site level is displayed using the SAP Retail module’s MM43, which enables users to examine information unique to that site or shop.
Within the Industrial System, transaction MM43. What is the Industrial System’s counterpart of the Retail System’s MM43 Transaction? MMo3 is the Industrial System’s equivalent of MM43 in the Retail System.
52. What are the disadvantages of shift pointers?
Ans:
One major drawback of segmentation fault is that it can occur due to an uninitialized pointer. Pointers are slower than normal variables. It requires one additional dereference step. If we forget to deallocate a memory, then it will lead to a memory leak. The disadvantage is that you need more flexibility and have to cram all your code into single update/draw functions. This will be hard to manage for anything but a tiny game. You allocate 2x pointers per object instance. Pointers are usually 4x to 8x bytes each (depending on your target platform and your compiler.
53. What is RETAIL SAP?
Ans:
- The IS retail solution combines supply chain, marketing, product, and IT to give businesses a competitive edge. The retail solution offers total integration for all departments and business operations of a retail organization, which usually consists of retailers of hard items, fashion, and food and drink. The solution can be tailored more easily to meet the different needs.
- SAP Retail offers all the features required for mapping business processes in a retail organization. This comprises Master Information: All pertinent information regarding sites, vendors, customers, and articles—including pricing and cycle control—is contained in master data.
54. What is HPR (High-Performance Retail?
Ans:
SAP is what HPR in retail comprises.to POS/BOS interface applications that enhance the master data IDoc generation’s runtime. Comparing these programs to conventional SAP programs, they are significantly more efficient. However, the final products are not the same, and the HPR does not offer some improvements. Software tailored to a particular industry is SAP IS Retail (ISR. Solution. It is an all-inclusive, fully integrated ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning. solution designed for the retail and corporate sectors. It works incredibly effectively for both small and large businesses.
55. How is unstructured data in SAP systems defined?
Ans:
The majority of SAP business processes include unstructured data. Invoices within the process of accounts payable Billing records and purchase orders in a financial or supply chain context produced reports that, in almost any application, summarize business interactions. This data is often required to be reachable from outside of the SAP program: Employees in the customer support department must have access to all customer transaction history.
56. Describe IBM and the fundamental components of an integrated ECM system.
Ans:
- By offering accurate information at the appropriate moment for all business operations across all platforms, the IBM ECM/ILG solution expands the capabilities of the SAP business solution—a company.
- An organization can maintain reduced infrastructure costs and system performance by using a strictly value-based archive and disposal paradigm.
- All stakeholders must agree on an organization-wide retention and hold model, which offers a framework for upholding strict adherence to intricate regulations under a single, justifiable disposal plan.
57.Define SAP use cases and solution architecture for ECM.
Ans:
IBM ECM portfolio software can raise the value of a SAP business infrastructure. The gateway solution that functions as a mediator between the SAP system and the ECM environment is IBM Content Collector for SAP Applications. 21’s article, “Business process enhancements through ECM for SAP solutions, “These documents could be anything—scanned photos, faxes, forms, emails, or even anything that started electronically. Other non-SAP applications and the ECM platform’s features, such as records management, e-discovery, and categorization, can access the documents that an SAP system has saved in the ECM repository.
58.Explain SAP ArchiveLink
Ans:
The main interface via which content management and storage solutions are integrated into a SAPIt is known as SAP ArchiveLink. Furthermore, SAP Release 4.5 defined the SAP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP. Content Server interface as a subset of SAP ArchiveLink with an emphasis on content management as opposed to storage management. The SAP business applications that are enabled can process documents in logical content repositories by connecting to a content server using the HTTP Content Server interface, a standard cross-application interface. 11 This content server may be an external archive, a file server, a database, or a SAP system.
59. Explain the Lifecycle of SAP Information.
Ans:
The purpose of managing the lifecycle of active or archived data and documents, SAP created SAP Information Lifecycle Management (ILM.. The ILM Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV. server houses data and documents. It offers the following retention management features:
- Establishing retention policies for data and documents to specify how long they must be preserved in the archive in order to abide by legal requirements.
- We are putting information and records required for a legal proceeding under legal hold.
- Allowing for the regulated disposal of records that are no longer required as part of legal holds and have reached the end of their retention period.
60. Define data archiving.
Ans:
Business records that have been items that are no longer regularly needed can be archivedusing the SAP ArchiveLink or HTTP Content Server protocols, or they can be bundled in an Application Development Kit (ADK. file that is a format specified by SAP. Organizations can maintain a manageable size of the SAP database by doing this. An SAP system can nevertheless transparently access this preserved data while saving money on storage, boosting output, and enhancing system efficiency.
61. Describe document preservation in DR.
Ans:
Companies are required to retain records of their business operations for a specific amount of time for legal and internal policy purposes. Because the documents are physical, filing them on paper has a number of drawbacks.
The following advantages come with electronically processing documents: Cost-effective storage media can be utilized by organizations. The documents are accessible to all authorized users immediately without the need to wait for standard archive inquiries.
62.Define “late archiving.”
Ans:
The SAP business object is created initially in late archiving, and it is then linked to the matching incoming document at a later stage. This procedure is comparable to a conventional paper-based procedure in practice. When an incoming document is collected and stored in a repository, the SAP business object already exists, and a connection is made between the incoming document and the business object.
63. Describe How to Use IBM ECM Products to Implement Use Cases
Ans:
The use cases that are pertinent to SAP archiving are covered in the preceding sections; some of them even go beyond what the SAP ArchiveLink standard specifies. To carry out these use cases, the IBM ECM portfolio items listed below can be employed: SAP Applications with IBM Content Collector, IBM Content Navigator, and IBM Datacap.
64. Describe the elements that make up the client interface
Ans:
- All of the client functionality that is covered in this section of IBM Content Collector for SAP Applications is based on IBM Content Navigator.
- See Customizing and Extending IBM Content Navigator for additional details regarding IBM Content Navigator’s extensibility, integration, and customization possibilities.SG24-8055. set up an instance of IBM Content Collector.
- Establish and manage profiles for index transfer, document linking, and archiving. Additionally, it interfaces with IBM Content Navigator’s sophisticated document viewing features, which are based on IBM.
65. Explain Sap Document Viewing Options.
Ans:
Based on the SAP business application being utilized, the kinds and formats of documents that are attached can differ significantly. This means that in order to access these documents, a highly adjustable set of parameters is required. Although there are numerous choices available inside the SAP GUI for document viewing, external viewers can also be incorporated and connected to the system. This use case is made even more flexible by the availability of IBM Content Navigator as the shared user interface for the content repositories.
66. Define SAP Netweaver.
Ans:
SAP NetWeaver, businesses can create unified SAP environments by integrating data, business processes, elements, and more from multiple sources. The technological backbone of many SAP application landscapes is SAP NetWeaver.
67. What is the SAP ACM process?
Ans:
SAP Agricultural Contract administration combines contract administration with data and procedures for finance, inventory, and risk management. Please find out how your farm can handle all of its contracts for a variety of commodities with thousands of business partners in one single location.
68. Define pooled tables in SAP.
Ans:
Control data is stored in a unique kind of table called a pooled table, which is found in the SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming. vocabulary.
69. Define transactional RFC defined?
Ans:
If a request was submitted in error, Transactional RFC, also known as Transactional Remote Function Call, enables retrieving the previous request.
70. What is the purpose of SAP?
Ans:
SAP facilitates profitable business operations, ongoing adaptation to changes, and sustainable growth for enterprises and organizations of all sizes.
The company will create SAP software solutions that smaller enterprises, mid-sized organizations, and larger corporations may all use. With the aid of industry solutions, technologies, platforms, and standard applications, every business process may be mapped and created.
The data will be gathered and processed by the SAP software on a single platform. The data may pertain to production, raw material purchases, customer satisfaction, etc.
71. What does SAP code pushdown mean?
Ans:
Code pushdown refers to moving computations involving a lot of data to the database layer. Only necessary computations will be taken into account and pushed into the database. For instance, it is optional to choose every place in the invoices and use a loop to calculate the sum if you only want to calculate the amount of each position. This may be accomplished with ease by utilizing the database’s SUM(aggregation function)
72. What is S/4HANA (SAP)?
Ans:
Based on the SAP HANA (in-memory database., SAP S/4HANA (SAP company Suite 4 SAP HANA. is an ERP software suite that enables businesses to conduct ERP transactions and analyze company data in real-time. S/4HANA is simple to use.
73. Describe the SAP Launchpad.
Ans:
SAP Launchpad offers a personalized and role-based launchpad website that streamlines access to corporate apps. With the help of this service, a company will be able to set up a single point of access for both on-premises and cloud-based SAP (for instance, SAP S/4HANA., bespoke apps, and other applications.
The SAP Launchpad service offers the following features:
- Application Integration: With infinite integration to various UI technologies and external apps, it offers a single point of access for tasks and applications.
- Simple and Interesting User Interface: It provides a customized, role-based launchpad with a customizable content structure that adheres to the SAP Fiori 3 design principles.
- Integrations: It can be integrated with cloud identity services and inbox services provided by the central SAP BTP (Business Technology Platform.
74. What is the posting key?
Ans:
The two-digit numeric posting key identifies the type of transaction submitted in the line item. It chooses the input screen style, posting kinds (Debit or Credit., and account types (A–>Assets, D–>Customers, K–>Vendors, M–>Materials, S–>General Ledger Account.. When posting unique General ledger transactions, specific posting keys are in handy.Key scenarios are being posted as follows:
The standard SAP system is in charge of providing the standard posting key. The items in a line item of document entries will be controlled by posting keys that SAP provides.
75. What is the model of information?
Ans:
The primary purpose of an information model, which is made up of analytical, attribute, and calculation views, is to conceal the details of data selection so that business users—who are limited to functional knowledge of databases—can more easily model their data. Thus, we can conclude that the information model gets around some of the questions’ problems and conceals their complexity.The process of transforming source data—which is in tables—into a format that businesses can understand. Utilize the hardware innovations that HANA has to offer.
76. What does transactional RFC mean?
Ans:
Transactional Remote Function Calls, or RFCs, permit the system to temporarily share a sent request in the event of an error. This is carried out following the assignment of a Transaction ID (TID. for the transaction process. At this point in the Transaction RFC, remote system access is not required.
77. What benefits does SQL scripting offer?
Ans:
SQL scripts may be saved and loaded as needed; they are simpler. It lowers the number of mistakes. An expert may be able to retrieve more data thanks to this fast speed. It can give consumers a rapid and effective way to access, modify, or store data.
78. Describe SQL Scripts.
Ans:
A collection of SQL commands saved as a file in SQL Scripts is called a SQL script. One or more PL/SQL blocks or SQL statements may be found in a SQL script. Script files can be created, edited, viewed, executed, and deleted using SQL Scripts.
79. What kinds of SAP products are there?
Ans:
SAP offers a vast array of goods categorized into distinct areas. A select few SAP products are:
ARIBA: One cutting-edge cloud-based system that enables suppliers and buyers to connect and do business on the same platform is called Ariba. It has simplified corporate processes and offered more affordable procurement options, which has enhanced the organization’s entire vendor management system.
SuccessFactors: is a cloud-based HR solution that facilitates the seamless management of various HR functions for enterprises. The Software as a Service (SaaS. paradigm is the foundation of SuccessFactors. Its primary purpose is to meet the demands of enterprise-class businesses.
Fieldglass: It has an open vendor management system and is cloud-based.
80. Define ECM transactions.
Ans:
The term “equity capital markets” (ECM. describes a wide range of markets, channels, and financial organizations that operate together to help businesses raise capital. Equity capital is raised through the public or private issuance of firm shares, and it is utilized to finance the company’s growth.
81. Define SAP Enterprise Content Management.
Ans:
A software program known as enterprise content management, or ECM, aids in the creation, organization, management, integration, security, preservation, distribution, and publication of unstructured content, including Word, PDF, PPT, XLS, picture, video, and audio files.
82. In what ways do we enforce other important performance indicators in SLA?
Ans:
With the wide range of functional roles, departments, and external resources that ECM and EIM (enterprise information management. applications touch, it is important to know exactly which KPIs should be collected; how those performance metrics will be measured and enforced, the tool sets that are used to manage and monitor an ECM system.
83. What are SAP tables used for?
Ans:
SAP Basis tables serve as the foundation for smooth business processes in this environment. As the core of system administration, they include essential system requirements and data, as well as sensitive and business-critical information.
84. What does software ECR mean?
Ans:
An Engineering Change Request (ECR.: What Is It? | Arena
A suggested improvement or correction to a product design is described using an engineering change request (ECR. form. The form starts the change process and encourages the engineering team to have discussions in order to assess the effects of a change and choose the most effective course of action.
85. In SAP, what is a release?
Ans:
The approval procedure for purchase requisitions and external purchasing documents is outlined in the release strategy. The release codes required and the order in which they must be made are specified by the strategy.
86. How many release codes are there in SAP?
Ans:
- Release Strategy: It outlines the order in which the purchase document will be made available. It also includes release prerequisites, codes, and conditions. It outlines every step of the approval or release procedure.
- Release Condition: It ascertains the appropriate release method.
- Release Group: The team of people in charge of disseminating the purchasing documents according to their designated plan.
- Release Code/Point: Each group (department. within the release group has its own unique two-character alphanumeric identification defined.
87. Define Release Signal and Requirement.
Ans:
Release Requirement: It specifies who must release the document initially.
Release Signal: It is a single-character ID that indicates the status of release.It has a document assigned to it.
When a group member modifies a document’s release using their release code, the document’s release indicator is assigned.] For example: Blocked = “B,” Released = “R.”
88. Describe any SAP RElease procedure in PR.
Ans:
In PR, there are two different kinds of release procedures:Classification (released at the item level and just for PR.Header/document level release for RFQ, PO, contract, and scheduling without classification
89. What is SAP’s ECN process?
Ans:
Only documents, bills of material, materials, and MPNs are supported by ECNs. It can be used to create and review the necessary changes, and you can assign the objects implicated in the change request to the ECN. One ECN can have more than one object assigned to it.
90. What does SAP ChaRM mean?
Ans:
The SAP Solution Manager’s intelligent tool, SAP Change Request Management (ChaRM., was created to assist businesses in streamlining their most important change request management tasks, such as organizing, creating, testing, authorizing, and implementing changes throughout their SAP environment.

