SAP HANA Define:
SAP HANA (High-Performance Analytical Tool) is a multi-model database that stores data in memory instead of on disk. This results in data processing that is faster than in disk-based data systems, allowing for advanced, real-time analytics. Serving as a platform for enterprise resource planning (ERP) software and other business applications, SAP HANA can be placed in hybrid cloud systems, on campus, in the cloud, or both.
SAP HANA integrates data from multiple areas within an organisation, for example:
Traditional business documents – including contracts and spreadsheets
UX/UI (User Experience/User Interface) – including website forms, email and other customer interactions
Mobile – information from customers and your workforce’s mobile devices
IoT (Internet of Things) – data from the many sensors running in every aspect of business, from warehouses and trucks to stores and offices. The SAP HANA system not only integrates all this data; It can apply machine learning and AI to perform quick and in-depth analysis, accelerating real-time decision-making by providing critical insights into company operations.
- Many organisations have large amounts of data that essentially sits in a data warehouse and provide no value, which amounts to terabytes of untapped capacity that can be used to accelerate business impact and provide greater customer value. can be done.
- With its lightning-fast, in-memory processing and real-time data analytics powered by machine learning, SAP HANA uses company data and makes it work for them, streamlining processes, eliminating errors , and providing benefits to customers, customers and employees. Enhance customer satisfaction with up-to-the-minute product availability that can be accessed on any smartphone. Keep employees happy with simplified accounting procedures, instant updates on benefits or vacation time, and advanced collaboration platforms. And help managers and executives plan for the future with predictive analytics that can forecast supply chain issues, manage cash flow, and integrate team workflows for higher efficiency.
Why is SAP HANA important?
- SAP (link remains outside ibm.com) (historically an acronym for systems, applications and products in data processing) is a German software company that specialises in enterprise resource planning to help manage operations and customer interactions. (ERP) systems and other business suites.
- SAP forayed into cloud-based products in 2012, when it first developed the SAP HANA tool. SAP launched SAP S/4HANA, a next generation business suite, in 2015 designed to run only on HANA servers.
What is SAP?
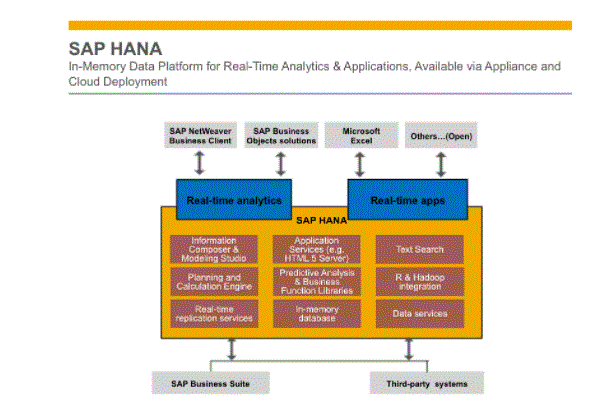
- SAP HANA’s in-memory, multi-modal data management engine takes full advantage of the capabilities of its hardware to minimise data movement, thus increasing application speed and agility as it analyzes data in real-time. Depending on the needs of an enterprise, SAP HANA can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or as a hybrid system, providing the privacy and control of on-premises systems with reduced cost, more memory, and increased accessibility. can be mixed Cloud.
- Its ability to efficiently process large amounts of data makes it easily scalable to suit a growing business without sacrificing security or stability. On the SAP HANA platform, developers can build their own tools and applications that integrate business logic, control logic, and the database layer with unprecedented performance.
SAP HANA Features:
Database enhancements:
Most database systems are organised around a single data model that limits how that data can be organised, stored, and manipulated. SAP HANA’s multi-model database supports multiple data models against a single unified backend, making it easy to establish relationships between data points.
Data management enhancements:
SAP HANA’s in-memory technology eliminates cumbersome batch processing, instead keeping all data highly available with no latency – all processing takes place in real time. Enterprises can dramatically simplify their management systems and change them as needed to improve efficiency.
Advanced analytics processing:
Real-time analytics makes it possible to exploit massive amounts of data, such as those coming from IoT sensors and mobiles. SAP HANA’s machine learning engine extracts and writes data to servers in real time, identifying problems and engineering solutions in every aspect of an enterprise, from payroll to human resources to customer service to supplier management and more
Application development:
Running on top of the SAP HANA database is a software stack system that acts as a technology-agnostic server for any web-based application – SAP or non-SAP – that a developer wishes to build. Since servers can interact with all file types and exchange data with any number of software, businesses can rapidly develop and deploy customised queries and processes that are uniquely helpful to them.
Equipment enhancement:
SAP HANA’s advanced analytical processing allows developers to create simple tools that business teams can use to easily generate custom reports – without the help of IT or external consultants.
- As global strategic partners, SAP and IBM have been collaborating and co-innovating for more than 25 years. Since the advent of SAP HANA in 2012, IBM has developed a variety of software and hardware solutions that help businesses maximise the potential of SAP’s flexible business suite over SAP HANA.
- Case study shows that companies that migrated their ERP environments to SAP HANA supported by IBM Power Systems™ enjoyed improved application performance, enhanced digital self-service for customers, agile mobile capabilities and more Is. Hear customers talk about their successes with the security, reliability and performance of SAP HANA backed by IBM Power Systems.
SAP HANA case studie:
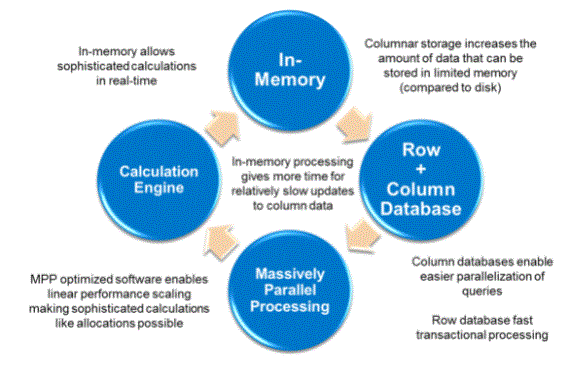
- The main difference between HANA and previous generation SAP systems is that it is a column-oriented, in-memory database, which combines OLAP and OLTP operations into a single system; Thus in general SAP HANA is an OLTP system. Storing data in main memory rather than on disk provides faster data access and, by extension, faster querying and processing. While storing data in memory provides performance benefits, it is a more expensive form of data storage. Observing data access patterns, up to 85% of data in enterprise systems can be accessed infrequently so it costs less to store frequently accessed, or “hot”, data in-memory. While less frequently accessed “hot” data is stored on disk, an approach SAP has called “dynamic tiering”.
- Column-oriented systems store all the data for a single column in one place, instead of storing all the data for a single row in one place (row-oriented systems). This can enable performance improvements for OLAP queries on large datasets and allows for more vertical compression of similar types of data in a single column. If the read times for column-stored data are fast enough, aggregated views of the data can be displayed on the fly, eliminating the need to maintain aggregate views and its associated data redundancy.
- Although row-oriented systems have traditionally been supported for OLTP, in-memory storage opens the way for developing hybrid systems suitable for both OLAP and OLTP capabilities, for OLTP and OLAP operations separately. Removes the need to maintain separate systems.
SAP HANA Architecture:
Index component:
The index server performs session management, authorization, transaction management, and command processing. Databases have both a row store and a column store. Users can create tables using any store, but columnar stores have more capabilities and are most commonly used. [citation needed] The index server manages persistence between cached memory images of database objects, log files, and permanent storage files. The XS engine allows the creation of web applications. SAP HANA Information Modelling (also known as SAP HANA Data Modelling) is a part of HANA application development. Modelling is the method of exposing operational data to the end user. Reusable virtual objects (named compute views) are used in the modelling process.
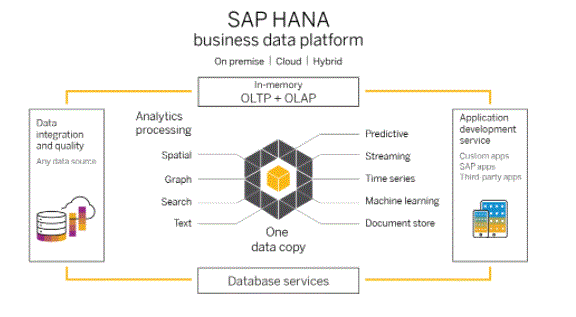
- HANA can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud by multiple cloud service providers.
- HANA can be deployed on-premises as a new device from a certified hardware vendor. Alternatively, existing hardware components such as storage and networks can be used as part of the implementation, an approach that SAP calls “tailored datacenter integration (TDI)”.
- HANA is certified to run on several operating systems [54] including SUSE Linux Enterprise Server [55] and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Supported hardware platforms for on-premises deployment include Intel 64 [57] and Power Systems.
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- IBM Softlayer
- Huawei FusionSphere
Application development:
In addition to database and data analytics capabilities, SAP HANA is a web-based application server that allows user-facing applications to tightly integrate with HANA’s database and analytics engine. The “XS Advanced Engine” (XSA) works natively with the Node.js and JavaEE languages and runtimes. XSA is based on the Cloud Foundry architecture and thus supports the notion of “bring your own language”, allowing developers to develop and deploy applications written in languages and those in runtimes other than XSA, As well as deploying applications as microservices. XSA also allows Server-Side JavaScript (XSJS).
Supporting an application server is a suite of application lifecycle management tools that allow development deployment and monitoring of user-facing applications.
Edit deployment:
Multiple cloud providers offer SAP HANA on a service basis infrastructure, including:
- During the initial development of SAP HANA, several technologies were developed or acquired by SAP SE. These include the TREX search engine (in-memory column-oriented search engine), P*TIME (in-memory online transaction processing (OLTP) platform acquired by SAP in 2005), and MaxDB with its in-memory live cache engine. Were.
- The first major demonstration of the platform took place in 2008: teams from SAP SE, the Hasso Plattner Institute and Stanford University demonstrated an application architecture for real-time analytics and aggregation called HYRISE. Former SAP SE executive Vishal Sikka referred to this architecture as “HASSO’s new architecture”. The software was previously called “SAP High-Performance Analytical Appliances”. The first research paper on HYRISE was published in November 2010. [10] The research engine was later released open source in 2013, and was reworked in 2016 to become HYRISE2 in 2017.
- The first products shipped in late November 2010. By mid-2011, the technology had attracted interest but more experienced business customers considered it “early”. HANA support for SAP Netweaver Business Warehouse was announced in September 2011 for availability by November. In 2012, SAP promoted aspects of cloud computing. In October 2012, SAP announced a platform-as-a-service offering called the SAP HANA Cloud Platform and a version called the SAP HANA One, which used less memory. Gaya. In May 2013, a managed private cloud offering called HANA Enterprise Cloud Service was announced.
- In May 2013, the Business Suite on HANA became available, enabling customers to run SAP enterprise resource planning functions on the HANA platform. S/4HANA, released in 2015, written specifically for the HANA platform, combines functionality for ERP, CRM, SRM and others into a single HANA system. S/4HANA is intended to be a simplified business suite to replace earlier generation ERP systems. Although it is likely that SAP will focus its innovations on S/4HANA, non-HANA systems are being used. Some customers in the U.S. have raised concerns about closure in SAP products. Since a SAP HANA system is required to run S/4HANA, customers running SAP Business Suite applications on hardware not certified by SAP will need to migrate to a SAP-certified HANA database if they are provided by S/4HANA. Select the features to go with. Instead of versioning, the software uses service packs for updates, called the Support Package Stack (SPS). The Support Package Stack is released every 6 months.
- In November 2016 SAP announced SAP HANA 2, which provides enhancements in several areas such as database management and application management and includes two new cloud services: text analysis and semantic observation analysis. HANA customers with SPS10 and above can upgrade to HANA 2. Customers running SPS9 and lower must first upgrade to SPS12 before upgrading to HANA 2 SPS01
SAP HANA History:
- SAP HANA (High-Performance Analytical Tools) is an in-memory, column-oriented, relational database management system developed and marketed by SAP SE. As the software running a database server, its primary function is to store and retrieve data requested by applications. In addition, it performs advanced analytics (predictive analysis, spatial data processing, text analytics, text search, streaming analytics, graph data processing) and includes extract, transform, load (ETL) capabilities as well as an application server Is.
- SAP HANA is the latest, in-memory database and platform that can be deployed on-premises or on the cloud. SAP HANA is a combination of hardware and software, which integrates various components such as SAP HANA database, SAP SLT (System Landscape Transformation) replication server, SAP HANA Direct Extractor Connection and Sybase Replication.There has been a phenomenal adoption of HANA by SAP customers. SAP HANA is capable of processing large amounts of real-time data in a short span of time.
Conclusion: