Open Tableau Desktop and navigate to a new or existing worksheet. Select Map > Geocoding > Import Custom Geocoding. In the Import Custom Geocoding dialog box, click the button to the right of the text field to browse to the folder your import file is saved in. All files in the folder will be imported into Tableau.
- Introduction
- Imported Custom Geocoding into Tableau
- Involving Custom Geographic Units in a Map
- Supplanting scene’s standard guides
- Conclusion
Introduction :-
Custom geocoding is a strategy used to allocate scope and longitude directions to areas so Tableau can plot them precisely on a guide. Geocoding is of extraordinary use for some, businesses, including transportation and operations organizations. These organizations frequently partition clients into geological zones for deals, conveyance, promoting, and client support viewpoints. Geocoding is additionally utilized for scientific policing purposes in which knowledge offices watch wrongdoing touchy areas utilizing topographical directions.
- Assuming that your geographic information doesn’t squeeze into the implicit geographic jobs, you can make new geographic jobs and allot them to the geographic fields in your information. For instance, assuming that your information contains country, state/area, and road address information, Tableau Desktop will total your information to the nation and state/territory level, yet won’t perceive the road address information as a geographic job. For this situation, you can make a custom geographic job for the road address information.
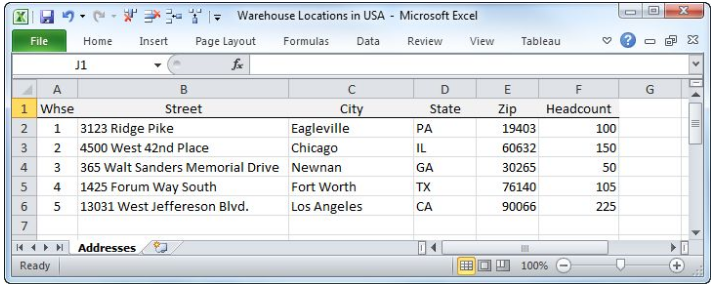
- Assuming you needed to go through the difficulty to add redid geographic directions, wouldn’t it be smarter to make it accessible to others inside your association? This is finished by bringing the location facilitates straightforwardly into Tableau Desktop. Later they are imported, the custom areas act like Tableau’s default geographic units. The import record ought to have the accompanying attributes:
- Give every area to record a special identifier (a key record).
- Save the area record in comma-delimited CSV design.
- Mark the direction fields as Latitude and Longitude (these watchwords should be utilized).
Imported Custom Geocoding into Tableau :-
- Whenever you have made a .csv document with custom geocoding you can bring that record into Tableau. Follow the means beneath to import another geographic job.
- Click Map > Geocoding > Import Custom Geocoding.
- In the Import Custom Geocoding exchange box, click the button to one side of the text field to peruse to the envelope your import record is saved in. All documents in the organizer will be brought into Tableau.
- When gotten done, click Import.
- The custom geocoding information is brought into the exercise manual and the new geographic jobs become accessible. To appoint another geographic job to a field, right-click the field in the Data sheet, select Geographic Role, and afterward select the job you need to allocate it.
It’s best not to remember a great deal of extra layered information for these significant records. Be certain that you have just one case of Tableau open when you play out the import. To impart this custom information to others building reports in Tableau, store the rundown in a common organization index with the goal that different clients can import it from a similar rundown too.
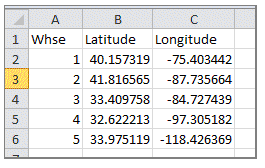
In the wake of saving the custom rundown in comma-delimited CSV design, the custom geographic information can be brought into Tableau. Start the import utilizing the primary menu (map/geocoding/import custom geocoding). A little document will just require a couple of moments to stack. Huge records can take as long as a few minutes. Running the import will make another information record on your PC inside (My Tableau Repository/Local Data). The custom information is put away as a Tableau information source document (TDS) with a similar name as the source CSV record which was imported before.
- In the wake of bringing custom geocodes into Tableau Desktop you can utilize them with different information documents to assemble maps as long as those records contain a similar area key record characterized in your information import table.
- Notice that there is no longitude or scope information. Notwithstanding, the (Whse) field can be utilized to interface the imported information from the custom geocode table showed. The means to utilize custom geocoding in this model are:
- Join Tableau to an information source.
- Adjust the geographic job of the key records (utilize the imported custom topography).
- Utilize the critical record in your view to plot the area on a guide.
Involving Custom Geographic Units in a Map :-
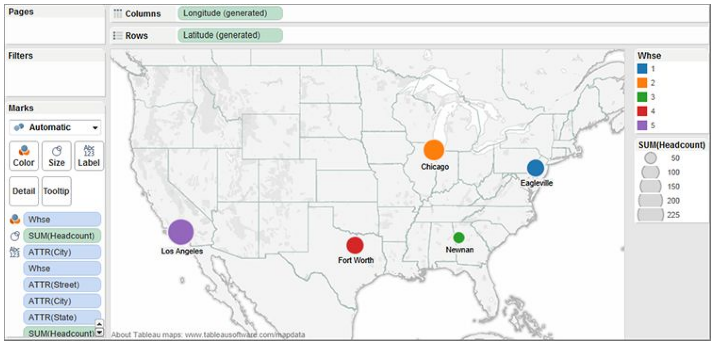
The entire field symbol will change to a symbol that is like a standard geographic symbol, however with a little rundown before the globe. Scene will presently perceive the imported geographic information.
Notice that the segment and column racks are utilizing scene’s (produced) scope and longitude fields. Notwithstanding, the stockroom marks utilize imported custom areas to put the imprints. Floating over the Los Angeles area causes a modified tooltip to show up, showing points of interest about the distribution center focusing in on the Los Angeles area.
The request for the means for empowering custom geocodes, toward the start of this segment isn’t the best way to accomplish the outcome. You can import the custom geocoding anytime even later a guide plot is finished utilizing standard geographic plotting.
Supplanting scene’s standard guides :-
Scene maps representation is exceptional dissipate plots that utilization map pictures for foundations and extraordinary measures (longitude and scope) to plot blemishes on the guide. This infers that you can supplant Tableau’s standard guide pictures with other picture documents.
Conclusion :-
In this aide, you figured out how to utilize custom geocoding in Tableau. You additionally figured out how to physically relegate scope and longitude facilitates if there should be an occurrence of missing areas. This will reinforce your abilities in managing spatial information.





