
- Introduction and Background
- Types of Business Analytics
- Analytics vs Business Intelligence
- Importance in Decision-Making
- Common Tools and Software
- Career Opportunities in Analytics
- Role of Data Scientists vs Analysts
- Data Sources and Data Cleaning
- Challenges in Implementation
- Evolving Technologies (AI/ML in Analytics)
- Future of Business Analytics
- Conclusion
Introduction and Background
In today’s highly data-driven world, business analytics (BA) has emerged as a critical discipline that empowers organizations to convert raw data into meaningful insights. Business analytics involves the systematic exploration and investigation of past business performance to gain actionable insights that inform decision-making. It encompasses various techniques, including statistical analysis, predictive modeling, data mining, and optimization, to solve business problems and identify new opportunities. Organizations across industries leverage business analytics to improve operational efficiency, reduce risks, enhance customer experience, and Many practical business analytics applications now touch every industry. The evolution of digital technologies, increased data availability, and advances in computational power have accelerated the adoption of business analytics in recent years. From retail giants analyzing consumer buying patterns to financial institutions predicting credit risks, business analytics has become indispensable. As businesses strive to become more agile and data-centric, understanding business analytics and its applications is essential for professionals and organizations alike. This article explores the fundamentals of business analytics, types, tools, applications, challenges, and its future trajectory. Understanding business analytics and its applications is essential for professionals who aim to become a business analyst.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer Certification? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Online Training Today!
Types of Business Analytics
Business analytics can be broadly categorized into four types, each serving a distinct purpose and answering different questions within the business context:
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data to understand what has happened in the past. It uses techniques like data aggregation, data mining, and data visualization to produce reports, dashboards, and summaries. For example, a sales report showing last quarter’s revenue or customer demographics analysis falls under descriptive analytics. This type of analytics provides the foundational insight necessary for further analysis and is widely used across industries. However, it is limited to past data and is one of the most widely used business analytics applications.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics delves deeper into answering why certain events occurred. It uses techniques such as drill-down, data discovery, and correlations to uncover causes and patterns. For example, after observing a sales decline, diagnostic analytics might analyze marketing campaigns, competitor actions, or customer feedback to identify the cause. This approach allows businesses to address the root causes of issues, but typically requires a skilled analyst to interpret complex data relationships.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics employs statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. By identifying trends and one of the most widely used business analytics applications can predict customer behavior, market trends, equipment failures, and more. For example, a retailer might use predictive models to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels. This type of analytics enables proactive decision-making and risk management but relies heavily on data quality and sophisticated modeling.
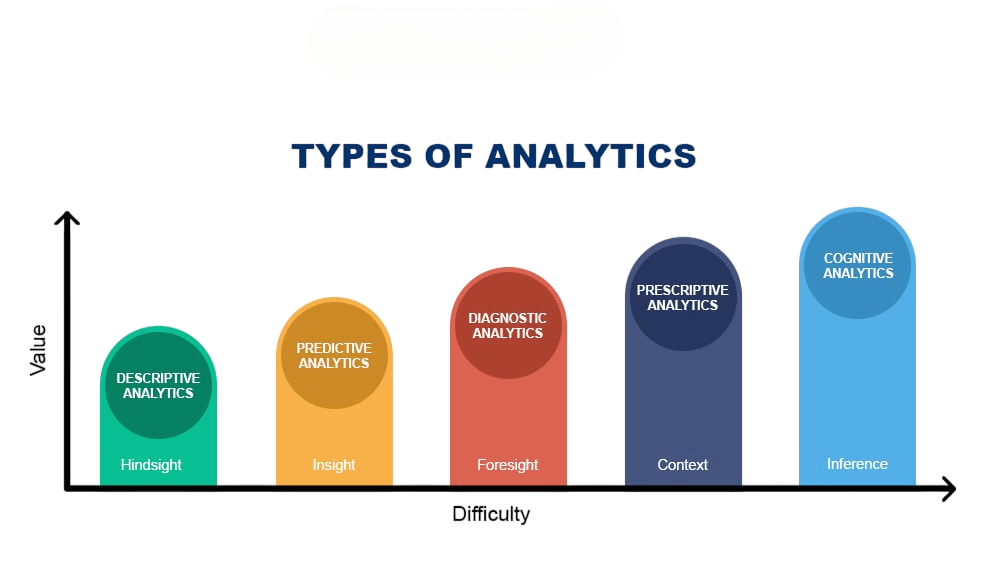
Prescriptive Analytics.
Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending specific actions to achieve desired outcomes. It combines predictive models with optimization and simulation techniques to suggest the best course of action among alternatives. For instance, an airline might use prescriptive analytics to optimize flight schedules and pricing strategies. This advanced form of analytics supports strategic planning and operational efficiency but requires the integration of multiple data sources and decision frameworks. Together, these four types provide a comprehensive analytics framework that helps organizations understand past performance, diagnose issues, anticipate future scenarios, and prescribe solutions.
Analytics vs. Business Intelligence
While business analytics and AI integrations have revolutionized business intelligence and analytics accessibility, they have distinct focuses and applications:
- Business Intelligence (BI): primarily deals with descriptive analytics. It involves collecting, organizing, and visualizing historical data through dashboards and reports. BI tools help organizations monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track operational metrics. It answers what happened and how the business is performing currently.
- Business Analytics (BA): encompasses a broader scope that includes diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. BA aims to understand why things happen, what will happen, and what should be done. It involves advanced statistical methods, machine learning, and scenario analysis.
In essence, BI is about reporting, and the distinction between business intelligence and analytics lies in their goals and depth of analysis, while BA is about deeper analysis and forward-looking insights. Many organizations integrate both to support comprehensive decision-making.
Are You Preparing for Business Analyst Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Business Analyst Interview Questions & Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Importance in Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making is a key competitive differentiator in today’s marketplace. Business analytics transforms raw data into actionable insights, enabling organizations to make informed, evidence-based decisions. Here are some reasons why BA is vital: This leads to better decision-making across all levels. Efficiency also improves as analytics helps identify bottlenecks and streamline operations, saving both time and cost. Another major advantage is risk mitigation. With predictive models, businesses can detect early signs of trouble and take action before issues escalate. Understanding customer behavior is another key benefit of analytics. By analyzing preferences and buying patterns, companies deliver more personalized marketing and valuable skills for anyone looking to become a business analyst. It also drives innovation by revealing new product opportunities, untapped markets, or even better business models. Most importantly, analytics ensures that daily decisions align with long-term goals. By connecting insights directly to strategy, companies stay focused and invest where it matters most. In short, analytics enhances both operational and strategic decisions, boosting organizational agility and competitiveness.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Business Analyst? Enroll For Business Analyst Masters Program Training course Today!
Common Tools and Software
The tools used in business analytics vary based on complexity, user expertise, and the goals of those who want to become a business analyst. Some popular tools include:
- Spreadsheet Tools: Microsoft Excel remains a staple for quick data analysis, pivot tables, and visualization for small to medium datasets. It’s user-friendly and widely accessible.
- Data Visualization and BI Platforms: Tableau and Power BI are industry-leading tools that create interactive dashboards and visual reports. They enable users to explore data intuitively and communicate insights effectively.
- Statistical and Programming Languages: R and Python are extensively used for statistical analysis, machine learning, and automation. Python’s rich libraries (pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow) make it popular among data scientists.
- Database and Query Languages: SQL (Structured Query Language) is essential for extracting and managing data from relational databases.
- Enterprise Analytics Platforms: Tools like IBM Cognos, SAP BusinessObjects, and Oracle Analytics cater to large-scale, enterprise-wide analytics needs.
- Cloud-based Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable analytics, AI services, and data warehouses (e.g., Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery).
Choosing the right tools depends on the business requirements, data volume, user skills, and budget.
Career Opportunities in Analytics
The growing importance of data in business has spurred a surge in analytics-related careers, including In the analytics field, different roles serve specific purposes. A Business Analyst works closely with stakeholders to gather requirements, analyze current processes, and suggest effective business solutions. A Data Analyst focuses on cleaning, interpreting, and visualizing data to help managers make informed decisions. A Data Scientist goes deeper by building predictive models and a path many follow after they become a business analyst. Machine Learning Engineers take these models and deploy them into real-world systems, ensuring they function smoothly in production environments. Meanwhile, a Business Intelligence Developer designs dashboards and generates reports that provide businesses with clear insights for monitoring performance. Ultimately, an Analytics Consultant provides expert guidance on developing and implementing data-driven strategies that align with business objectives. Entry-level roles often require skills in Excel, SQL, and basic statistics. Mid to senior-level roles demand programming (Python/R), machine learning, and domain knowledge. Certification programs, degrees in data science, and hands-on projects enhance employability.
Role of Data Scientists vs. Data Analysts
Understanding the distinction between data scientists and data analysts helps clarify career paths:
- Data Analysts primarily focus on interpreting existing data to generate reports, visualizations, and insights. Their work supports tactical and operational decisions.
- Data Scientists take on a more technical role involving algorithm development, predictive modeling, and handling large, complex datasets. They often work on creating new data products and automating analytics.
Both roles are complementary. Analysts translate business questions into data tasks; scientists develop advanced models to address them. Many professionals transition from analyst to scientist roles with experience and additional skills.
Data Sources and Data Cleaning
Business analytics depends heavily on data quality and variety. Common data sources include
- Internal systems: ERP, CRM, HR systems.
- External sources: Market research, social media, IoT devices.
- Public data: Government statistics, economic indicators.
Raw data is often incomplete, inconsistent, and messy. Data cleaning processes include:
- Removing duplicates and errors.
- Handling missing values through imputation or exclusion.
- Standardizing formats and units.
- Validating data accuracy.
Effective data cleaning is critical to producing reliable analytics results and avoiding misleading conclusions.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite its benefits, implementing analytics initiatives comes with challenges: Organizations often face several challenges when implementing analytics solutions. One major issue is data silos. Different departments store data separately, which makes it hard to get a complete view of the business. Data privacy and compliance are growing concerns as laws like GDPR require strict handling of personal information. A shortage of skilled professionals adds to the difficulty. Many companies struggle to hire qualified data experts. At the same time, there’s a tool overload. Businesses must choose from too many analytics platforms and ensure they integrate properly. Change management becomes another roadblock since teams may resist shifting from intuition-based to data-driven decision-making. Finally, poor data quality can ruin even the best analytics efforts by producing misleading or inaccurate results. Addressing these requires executive sponsorship, training programs, clear governance, and cross-functional collaboration.
Evolving Technologies: AI and ML in Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming business analytics by automating complex analyses and enabling new capabilities such as
- Predictive maintenance using sensor data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for sentiment analysis.
- Computer vision for quality inspection.
- Automated anomaly detection.
- AutoML platforms that simplify model building.
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 assist in generating insights, automating reports, and interpreting complex datasets. These advances make analytics more accessible and powerful.
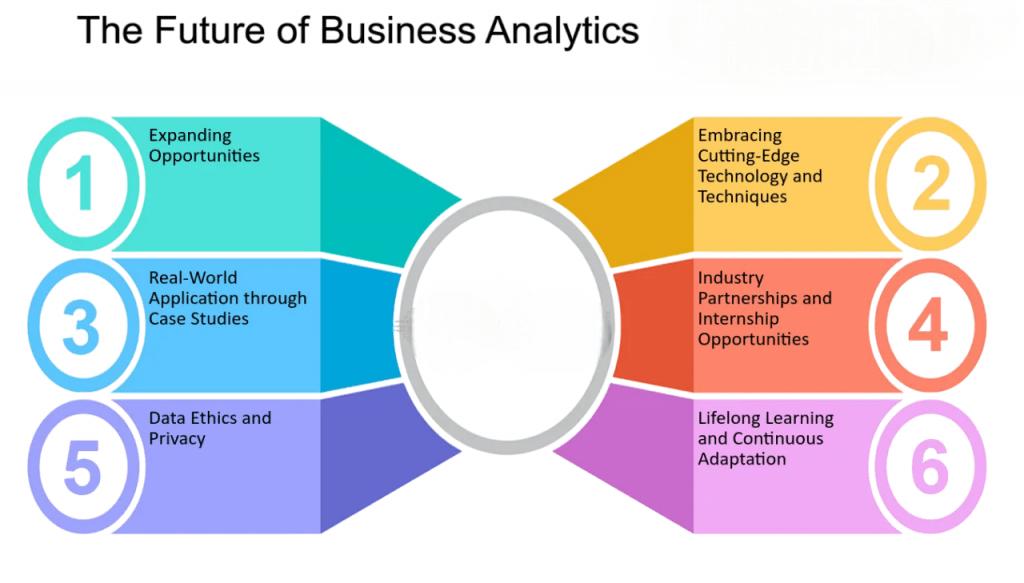
Future of Business Analytics
The future of business analytics is exciting and dynamic, with several emerging trends:
- Democratization of Analytics: Self-service tools empower non-technical users to analyze data.
- Augmented Analytics: AI-driven insights and recommendations reduce manual effort.
- Explainable AI: Improving transparency of machine learning models to build trust.
- Ethical Data Use: Increasing focus on data privacy, fairness, and governance.
- Hybrid Roles: Growing demand for professionals combining domain expertise with analytics skills.
- Real-Time Analytics: Processing streaming data to enable instant decision-making.
- Edge Analytics: Analytics performed on local devices for faster insights.
Organizations that embrace these business analytics applications will unlock innovation and growth.
Conclusion
Business analytics has evolved from simple reporting to a multifaceted discipline essential for modern business success. By leveraging data and advanced analytics techniques, organizations can uncover hidden insights, predict future outcomes, and prescribe optimal actions. As industries embrace digital transformation, the role of business analytics will only expand, requiring continuous learning, innovation, and strategic vision. For professionals, mastering business analytics opens diverse career paths, from analysis and data science to leadership roles driving organizational change. With the right combination of technical skills, domain knowledge, and business acumen, individuals can significantly influence their company’s success in the data-driven economy. As we move forward, the integration of AI, cloud computing, and real-time data will make business analytics more powerful and accessible. AI integrations have revolutionized business intelligence and analytics accessibility, intelligence for professionals seeking to become a business analyst, This evolving space offers endless potential.




