
A stored process is a SAS program that is stored on a server and can be executed as required by requesting applications. You can use stored processes for Web reporting, analytics, building Web applications, delivering packages to clients or to the middle tier, and publishing results to channels or repositories.
- Introduction to SAS
- Stored Processes Uses
- Features of SAS
- Types of Predictive Analysis
- Stored Process Server Types
- SAS/IntrNet and Stored Processes
- Stored Process Samples
- Why SAS Stored Processes
- Components
- Benefits of SAS
- Conclusion
- A stored process. Many of the new clients within the SAS9 Intelligence Platform can run SAS programs that’s hosted on a server and characterized by metadata is basically like SAS/internet applications, but more adaptable because of the underlying metadata and security measures .The choice to keep your SAS programmes on the server provides an efficient technique for managing change control.
- When you think about how these SAS programs could also be launched from numerous client contexts, the stored process notion becomes even more powerful.
- Using stored processes also improves security and application integrity since the programs that access your sensitive data are confined on the server instead of being disseminated extensively with the client apps.
- Instead of embedding SAS code within client applications, this code could also be centrally maintained and managed from the server. this enables you to switch your SAS routines while also ensuring that each client that calls a stored process always gets the foremost recent version available.
Introduction to SAS:
- Stored processes can access
- SAS data source
- External files.
- data sets
- external files
- catalogs
- ODS output
- result packages.
- SAS Add-In for Microsoft Office
- SAS Enterprise Guide
- SAS Information Map Studio.
- Existing or new SAS code are often converted to a stored process which stored process is registered within the SAS management console.
- Beginning with version 3, SAS Enterprise Guide is that the preferred method for working with stored processes because it provides the power to make , register, and test stored processes from one interface.
- Stored Process Web Application
- SAS Web Report Studio
- SAS Information Delivery Portal.
- input parameters
- input data sources
- output options
- execution environment
- descriptive data
- security options.
Stored Processes Uses:
Stored processes are often used for:
Web reporting analytics delivering result packages to clients or the mid-tier publishing results to channels or repositories.
Stored Process Input
Stored Process Output
A stored process can produce any quite output that a SAS program can produce:
Stored Process Desktop Clients
Stored processes are often accessed/executed from several different client environments:
Stored Process Web Clients
Stored processes are often accessed/executed from different Web-based environments:
Stored Processes Metadata Structure
Metadata is employed in stored processes to describe:
- The first aspect of SAS software and programing language is its strong data analysis ability. SAS is analogous to a comprehensive data analysis programme. Its analysis covers from basic to high levels.
- It produces bar graphs with the info supplied, for instance , to calculate the correlation between complicated data sets.
- The Inbuilt Library in SAS software is that the biggest feature since it’s all of the required packages for data analysis and reporting.
- SAS may be a 4GL programing language , which is a crucial attribute since the SAS programing language features a simple syntax. Furthermore, the SAS programing language code is structured as statements, and these statements provide clear and succinct instructions to the systems.
- SAS’s built-in libraries have reduced code for typical applications, allowing us to modularize our work. it’s also simple to use for non-programmers.
- SAS may be a dynamic programing language . Its log window functions as a mirror, always providing directions to the user. It makes notes and marks mistakes.
- Also available is DS2, which aids with data manipulation. within the database, complex data could also be altered.
- SAS Studio may be a one-of-a-kind SAS capability. SAS Studio is conveniently accessible from any device and browser . Client installation isn’t required. All libraries and data files required by the SAS application are accessible via any browser .
- It’s extremely informative. As soon as someone begins typing, the autocomplete tool suggests several operations. A pop-up syntax and parameter list are presented for extra assistance.
- It also assists you in creating and adding personalised code snippets to the snippet library.
- We may use a point-and-click interface to assist us through the analytical process at various stages.
- Another aspect of SAS is its support for several data types. SAS can read data from any kind of file, in any format, and even from missing data files.
- SAS offers SQL support. It contains an outsized character encoding database and complete support for the foremost regularly used languages.
- SAS programing language supports singularity also , allowing SAS to figure with data during a sort of languages.
- SAS management is a crucial element of SAS software. SAS Environmental Manager monitors, alerts, and maintains the analytics environment. SAS functions in SAS
- Management Console are managed through the Extended Java Graphical interface.
- In addition, we will completely restart a failed application. It restarts from the purpose where the programme failed.
- XML Engines perform a spread of tasks, like importing and exporting XML documents and producing XML maps.
- The Application Response Measurement Interface examines multiple apps and verifies for transaction availability.
- SAS can present analytical results also as a spread of reporting alternatives. SAS 9.4 includes high-quality graphics like ODS statistical graphics, ODS graphics designers and editors, and so on.
- Reports could also be saved and created in conventional formats like RTF, PowerPoint, and PDF. we will also store them as eBooks and i-books, which allows us to perform visual analytics.
- We may tailor the output to the customer’s needs hierarchy. The output are often sent to several locations.
- SAS guarantees that security is at the guts of how we give access, and SAS 9.4 includes a security component named SAS / SECURE thereto end. We can also use several techniques to encrypt SAS data on disc.
- So it decreased to SAS characteristics. We hope you found our explanation helpful.
Features of SAS:
1.Strong Data Analysis Abilities
2. Flexible 4 Generation programing language (4GL)
3. SAS Studio
4. Support for Various format
5. Management
6. Report Output Format
7. Encoding Algorithms
- SAS Stored Process Servers.
- SAS Workspace Servers.
- Streaming output
- Sessions
- Multiple-value input parameters
- Support for stored process web services.
Stored Process Server Types:
Stored processes are often hosted by two sorts of servers:
These two servers are similar but have different capabilities.
Is a multiuser server.Is a single process shared by many purchasers. Runs under one shared user identity. Is dedicated to executing stored processes.
Incorporates various features that aren’t accessible on workspace servers, such as:
- _WEBOUT for streaming output
- same ODS options
- macro variables for input parameters
- similar debugging options.
SAS/IntrNet and Stored Processes:
In general, stored processes are backward compatible with the SAS/IntrNet Application Dispatcher. With little or no change, most current Application Dispatcher applications could also be registered as a stored process. this is often feasible thanks to the very fact that Application Dispatcher programmes and stored processes share several features, including:
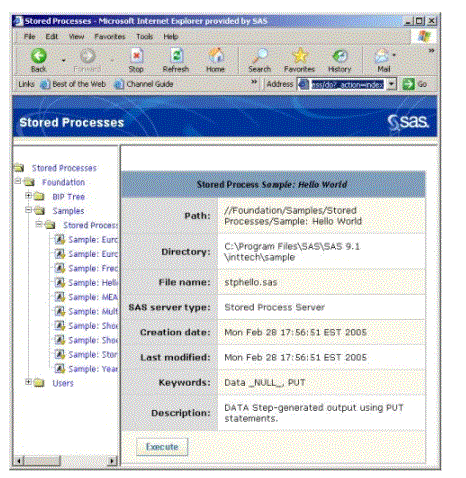
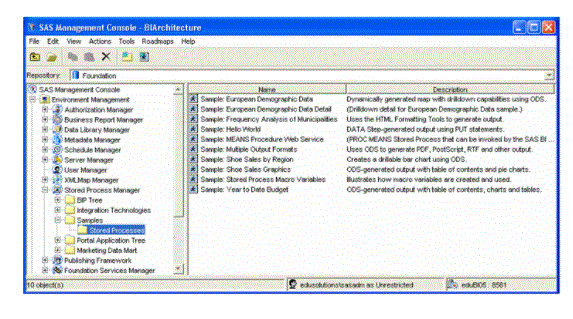
Stored Process Samples:
This presentation displays the metadata information for a sample saved process. Start the SAS Management Console by getting to Start All Programs SAS SAS Management Console, then:
1. Choosing the BI Architecture metadata profile and entering the login and password supplied by the trainer.
2. Expand Stored Process Manager within the Navigation Tree.
3. Expand the Samples group.
4. Select the Stored Processes group.
5. The sample stored processes are displayed within the Display Area.
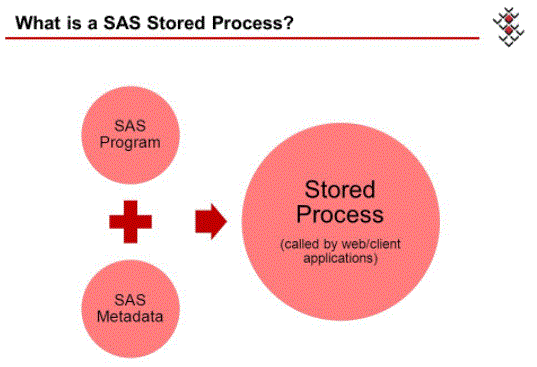
- A stored process might be an SAS programme that is kept on a server and executed as needed by requesting apps. Stored processes will be used for Web reporting, analytics, Web application development, distributing packages to clients or the centre tier, and publishing findings to channels or repositories. Stored processes can also access any SAS data source or an external file to create new data sets, files, or other SAS-supported data targets.
- The ability to store your SAS applications on the server is a powerful tool for managing change control. Instead of embedding SAS code in client apps, for example, you’ll centrally manage and administrate it from the server. This allows you to modify your SAS programmes while also assuring that any client that calls a stored process receives the most recent version available.
- When you consider that these SAS programmes are frequently invoked from numerous client contexts, the stored process notion becomes even more powerful. You might, for example, install Java applets and Windows-based programmes that launch your stored processes. If you want to employ a multi-tiered design, you will, for example, leverage Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) technology to execute similar stored processes from an application server.
- Because the programmes that access your sensitive data are confined on the server rather than being distributed with the client apps, using stored processes improves security and application integrity.
- Stored processes are classified into two categories. IOM Direct Interface Saved Processes, a restricted type of stored process, were added in Version 8. This type of stored process runs on an SAS Workspace Server and solely creates packages. IOM Direct Interface Stored Procedures continue to be fully supported. The primary focus of this work, however, is on SAS Stored Processes.
- To administrate SAS Stored Processes, you must utilize an SAS Metadata Server. To create a stored process that client applications may access, you must first establish a storage space that your server can access. Then, using BI Manager, create metadata describing the stored process and its location. This metadata is stored by BI Manager on the SAS Metadata Server, where it is often accessed by client applications.
Why SAS Stored Processes:
- Install SAS 9.1 on your designated SAS server. You want to install Base SAS and SAS Integration Technologies to run stored processes.
- SAS/GRAPH software is required to run a number of the sample stored processes.
- Install the other products that are employed by your stored processes.
- You want to also configure a SAS Metadata Server to make and use stored processes. you want to configure one or more stored process servers or workspace servers to execute stored processes.
- Install SAS Management Console on a system with network access to your SAS server.
- SAS Foundation Services
- You must install the SAS Foundation Services BI Manager plug-in component on the same system where SAS Management Console is installed. This plug-in allows you to register and manage stored processes from inside SAS Management Console.
- Java 2 Runtime Environment (JRE), Standard Edition is required for the Java interface to SAS Stored Processes. The SAS Foundation Services installation instructions will tell you the version you need for your operating system.
- Some development environments and servlet containers include a copy of the Java 2 JRE that has been authorised.
- If you need a copy, you may acquire one from the Third-Party software CD that comes with the SAS Installation Kit.
- If you’re developing Java applications or creating Java Server Pages (JSPs), then you furthermore may need the Java 2 Software Development Kit (SDK), which incorporates a replica of the Java 2 JRE.
- Java developers and servlet containers using Java Server Pages (JSPs) must have the Java 2 Software Development Kit (SDK), Standard Edition.
- For information on the exact version necessary for your operating environment, go to the SAS Foundation Services installation instructions.
- Some development environments and servlet containers include a copy of the Java 2 SDK that is suitable.
- If you want a duplicate, you can obtain one from the Third-Party software CD included with the SAS Installation Kit.
- A servlet container might be a Java server that provides middle-tier access to SAS Stored Processes.
- The SAS Web Infrastructure Kit, SAS Information Delivery Portal, or user-written servlets or Java Server Pages are frequently hosted by a servlet container.
- The product documentation contains specific servlet container requirements for the SAS Web Infrastructure Kit or SAS Information Delivery Portal software. A JRE version that matches the SAS 9.1 operating environment specifications must be used in servlet containers for user-written servlets or JSPs.
- The Apache Tomcat servlet container is available free of charge from the Apache Jakarta project’s website. SAS Web Infrastructure Kit and SAS Information Delivery Portal are also accessible.
- To run saved processes from Microsoft Office on a client Windows PC, the SAS Add-In for Microsoft Office must be installed. The SAS Integration Technologies Client for Windows must even be installed on an equivalent system.
- SAS BI Web Services for Java
- SAS BI Web Services for Java needs the installation of numerous additional components, notably the SAS Web Infrastructure Kit. More information on needed components may be found in the SAS BI Web Services for Java installation instructions.
- SAS BI Web Services for .NET
- SAS BI Web Services for .NET Need the Microsoft IIS Web server.
- SAS Enterprise Guide
- SAS Enterprise Guide may be a Microsoft Windows client application which will be installed on any system with network access to your SAS server
Components:
SAS System software
SAS Management Console
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java Development Kit (JDK)
Servlet Container
SAS Add-In for Microsoft Office
Benefits of SAS:
1. Easy to find out
SAS syntax is extremely easy to find out . It are often learned easily by anyone with none programming skills. Coding is within the sort of simple statements. It’s like instructing a machine what to try to.
2. Ability to handle large database
SAS has a good capacity to readily manage huge databases.
3. Easy to debug
SAS may be a very comprehensible language. the method of debugging is straightforward . we will understand and proper the error that the log window clearly states.
4. Tested algorithms
The SAS program’s algorithm is carefully tested and analysed by developers. Before being released, each version of SAS is tested in a controlled setting. This is frequently achievable since SAS is a closed language.
5. SAS Customer support
SAS belonging to a corporation performs proper monitoring. it’s sort of a complete organization. it’s very spontaneous customer support. As SAS may be a closed source tool, it can only be edited by the SAS organization. No external adulteration is feasible . SAS customer support handles all the issues .
6. Data Security
Extending the above point, data in SAS is totally secured. We cannot extract, just in case of office use without a license. Data security prevents it from manipulation. And this is often the rationale for its popularity within the corporate world. SAS may be a primary tool for several big companies. Being an in depth source, the company’s data is confidential here. Only freelancers use R. it’s open source, therefore, data security isn’t guaranteed. SAS is preferred professionally over the other language used for analysis.
Conclusion:
SAS/SHARE software provides concurrent access capabilities to SAS, allowing developers to create applications that allow their users to have up-to-date data and be more productive.
Such applications use SAS in new ways. This paper has discussed areas to remember of and ways to trade usage of 1 resource for an additional . This information enables developers of applications that cash in of concurrently accessed data to write down those applications to use the available computer resources within the most effective ways possible.





