
Data Science and Data Analytics are two most trending terminologies of today’s time. Presently, data is more than oil to the industries. Data is collected into raw form and processed according to the requirement of a company and then this data is utilized for the decision making purpose. This process helps the businesses to grow & expand their operations in the market. But, the main question arises – What is the process called? Data Analytics is the answer here. And, Data Analyst and Data Scientist are the ones who perform this process.
What is Data Analytics?
Data or information is in raw format. The increase in size of the data has lead to a rise in need for carrying out inspection, data cleaning, transformation as well as data modeling to gain insights from the data in order to derive conclusions for better decision making process. This process is known as data analysis.
Data Mining is a popular type of data analysis technique to carry out data modeling as well as knowledge discovery that is geared towards predictive purposes. Business Intelligence operations provide various data analysis capabilities that rely on data aggregation as well as focus on the domain expertise of businesses. In Statistical applications, business analytics can be divided into Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) and Confirmatory Data Analysis (CDA).
EDA focuses on discovering new features in the data and CDA focuses on confirming or falsifying existing hypotheses. Predictive Analytics does forecasting or classification by focusing on statistical or structural models while in text analytics, statistical, linguistic and structural techniques are applied to extract and classify information from textual sources, a species of unstructured data. All these are varieties of data analysis.
The revolutionising data wave has brought improvements to the overall functionalities in many different ways. There are various emerging requirements for applying advanced analytical techniques to the Big Data spectrum. Now experts can make more accurate and profitable decisions.
In the next section of the Data Analytics tutorial, we are going to see the difference between Data Analysis and Data Reporting.
Key Features
- 3 hours of online self-paced learning
- Lifetime access to self-paced learning
- Industry-recognized course completion certificate
- Real-world case studies and examples
Introduction to Data Analytics Course Curriculum
Eligibility
This Data Analytics for beginners course is ideal for anyone who wishes to learn the fundamentals of data analytics and pursue a career in this growing field. The course also caters to CxO-level and middle management professionals who want to improve their ability to derive business value and ROI from analytics.
Pre-requisites
This Introduction to Data Analytics for Beginners course has been designed for all levels, regardless of prior knowledge of analytics, statistics, or coding. Familiarity with mathematics is helpful for this course.
Data Analysis Process
Now in the Data Analytics tutorial, we are going to see how data is analyzed step by step.
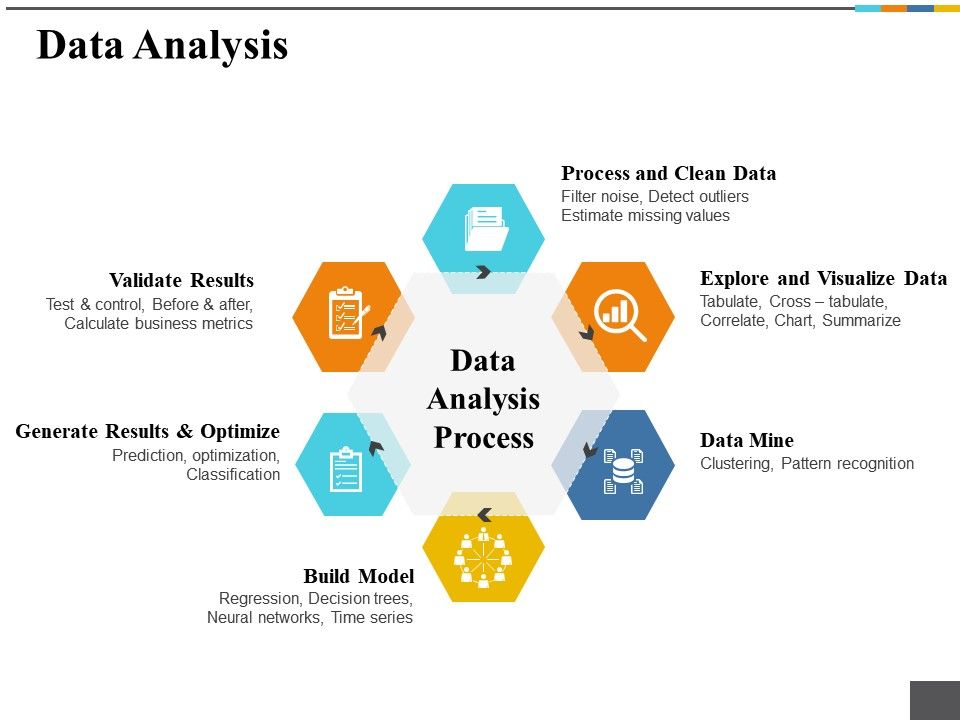
1. Business Understanding
Whenever any requirement occurs, firstly we need to determine the business objective, assess the situation, determine data mining goals and then produce the project plan as per the requirement. Business objectives are defined in this phase.
2. Data Exploration
For the further process, we need to gather initial data, describe and explore data and lastly verify data quality to ensure it contains the data we require. Data collected from the various sources is described in terms of its application and the need for the project in this phase. This is also known as data exploration. This is necessary to verify the quality of data collected.
3. Data Preparation
From the data collected in the last step, we need to select data as per the need, clean it, construct it to get useful information and then integrate it all. Finally, we need to format the data to get the appropriate data. Data is selected, cleaned, and integrated into the format finalized for the analysis in this phase.
4. Data Modeling
After gathering the data, we perform data modeling on it. For this, we need to select a modeling technique, generate test design, build a model and assess the model built. The data model is build to analyze relationships between various selected objects in the data. Test cases are built for assessing the model and model is tested and implemented on the data in this phase.
5. Data Evaluation
Here, we evaluate the results from the last step, review the scope of error, and determine the next steps to perform. We evaluate the results of the test cases and review the scope of errors in this phase.
6. Deployment
We need to plan the deployment, monitoring and maintenance and produce a final report and review the project. In this phase, we deploy the results of the analysis. This is also known as reviewing the project.
The complete process is known as the business analytics process.
Skills required to become a Data Analyst
Data Analytics Tutorial is incomplete without knowing the necessary skills required for the job of a data analyst. In today’s world, there is an increasing demand for analytical professionals.
All the data collected and the models created are of no use if the organization lacks skilled data analysts. A data analyst requires both skills and knowledge for getting good data analytics jobs.
To be a successful analyst, a professional requires expertise on the various data analytical tools like R & SAS. He should be able to use these business analytics tools properly and gather the required details. He should also be able to take decisions which are both statistically significant and important to the business.
Technical & Business Skills for Data Analytics
In this part of the data analytics tutorial, we will discuss the required technical and business skills.
Technical skills for data analytics:
- Packages and Statistical methods
- BI Platform and Data Warehousing
- Base design of data
- Data Visualization and munging
- Reporting methods
- Knowledge of Hadoop and MapReduce
- Data Mining
Business Skills Data analytics:
- Effective communication skills
- Creative thinking
- Industry knowledge
- Analytic problem solving





