
How To Create a Header – HTML Tutorial | The Ultimate Guide
Last updated on 27th Jan 2022, Blog, Tutorials
- Introduction to HTML Header
- Historical use
- What are HTML elements?
- HTML History
- HTML Heading
- Tag description
- Defines the HTML heading
- Definition and use of
- How to style <'header> tag?
- Shading text in <'header> tag
- Text format styles for <'header> tag
- Different properties worth checking out for <'header> tag
- Conclusion
- This element contains only global attributes.
- cases
- Page Header
- Main Page Title
- Copy to Clipboard
- Article Title
- Planet Earth
- Wednesday, October 4, 2017 Posted by Jane Smith
- We live on blue and green planets.
- Read more
- Copy to clipboard
- specification
- HTML standard (HTML)
- # Header element
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages.
- HTML describes the structure of the website
- HTML is made up of several elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements indicate content such as “This is a heading”, “This is a paragraph”, “This is a link”. Simple HTML document
- html>
- & Lt; html & gt;
- & Lt; head & gt;
- & Lt; title & gt; Page title & lt; / title & gt;
- & Lt; / head & gt;
- & Lt; body & gt;
- my first heading
- My first paragraph.
- & lt; / body & gt;
- & Lt; / html & gt;
- & Lt; html & gt; element is the root element of the HTML page
- & Lt; Head & gt;-Element contains meta information about the HTML page
- & Lt; Title & gt; element specifies the title of the HTML page (displayed in the browser title bar or page tab)
- The & lt; body & gt;
- my first heading
- My first paragraph. Start Tag Element Content End Tag
- My First Heading
- My First Paragraph.
- None None None
- In 1989 Tim Berners-Lee invented www
- In 1991 Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML
- 1993 Dave Raggett designed HTML +
- In 1995, the HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0.
- 1997 W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2
- 1999 W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01
- 2000 W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0
- 2008 WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft
- 2012 WHATWG HTML5 Standard of Living
- 2014 W3C Recommendation: HTML5
- 2016 W3C Candidate Recommendations: HTML 5.1
- 2017 W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition
- 2017 W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2
- Heading 1
- Heading 2
- Heading 3
- Heading 4
- Heading 5
- Heading 6
- HTML heading
- HTML headings are defined using tags
- Heading 1
- Heading 2
- Heading 3
- Heading 4
- Heading 5
- Heading 6
- Big heading
- Each HTML heading has a default size.
- Heading 1
- HTML exercises
- Test yourself in the exercises
- Exercise:
- Use the correct HTML tags to add the text heading “London”.
- It is the most populous city in the UK and has a population of over 13 million.
- HTML Tag Reference to Start Exercise
- The W3Schools Tag Reference contains additional information about these tags and their attributes.
- & Lt; html & gt; Defines the root of the HTML document
- & Lt; body & gt; Defines the body of the document
- HTML Header
- HTML & lt; Head> Element is a container of & lt ;. Title & gt ;, & lt; Style & gt ;, & lt; meta & gt ;, & lt; link & gt ;, [DATA EXPUNGED], & lt; Base & gt; Element.
- HTML Code & lt; Head> Element
- The & lt; Head> Element is a container for metadata (data about data) and is placed between & lt ;. html>. Tag and & lt; Body> Shield.
- HTML metadata is data about HTML documents. Metadata is not displayed.
- Metadata typically defines document titles, character sets, styles, scripts, and other metadata.
- html>
- & lt; html>
- <; Head>
- & lt; Title & gt; Descriptive Page Title & lt; / Title & gt;
- <; / Head & gt;
- <; Body>
- Document Contents.
- & lt; / Body & gt;
- <; / html>
- HTML & lt; Style & gt; Element
- & lt; Style & gt;
- Body {Background Color: Powder Blue;}
- h1 {Color: Red;}
- p {Color: Blue;}
- & lt; / Style & gt;
- HTML & lt; Link> Element
- The & lt; Link>- Elements define the relationship between the current document and external resources. The & lt; link> tag is most commonly used to link to external stylesheets. Example & lt; Link rel = “stylesheet” href = “mystyle.css” & gt;
- Tip: For more information on CSS, visit the CSS tutorial.
- HTML & lt; Meta> Element
- & lt; metacharset = “UTF8” & gt;
- & lt; Metaname = “Keywords” Content = “HTML, CSS, JavaScript” & gt;
- & lt; Metaname = “Description” Content = “Free Web Tutorial” & gt; Defines the author of the page: & lt; metaname = “author” content = “John Doe” & gt
- & lt; meta httpequiv = “update” content = “30” & gt;
- Sets the viewport so that the website looks great on all devices.
- & lt; meta name = “viewport” content = “width = devicewidth, initialscale = 1.0” & gt;
- & lt; metacharset = “UTF8” & gt;
- <; metaname = "description" content = "Free Web Tutorial" & gt;
- <; Metaname = "Keywords" Content = "HTML, CSS, JavaScript" & gt;
- <; metaname = "author" content = "John Doe" & gt;
- & lt; meta name = “viewport” content = “width = devicewidth, initialscale = 1.0” & gt;
- This tells the browser how to control the size and scaling of the page.
- width = Devicewidth part sets the width of the page according to the screen width of the device (depending on the device).
- initialscale = 1.0 Part sets the initial zoom level when the page is first loaded by the browser. Below is an example of a web page without the viewport meta tag and the same web page with the viewport meta tag.
- 1 More than one heading element ()
- Logo or icon
- Author information
- Note: An HTML document can contain multiple elements. However, cannot be placed inside or other elements.
- Page Header: Click here for Main Page Header
- HTML DOM Reference: Header Object
- CSS Default
- Most browsers display
- elements with the following default values:
- Header {
- Display: Block;
- }
- Normal properties to adjust the visual weight/accentuation/size of text in <'header> tag:
- CSS text style property sets the style of the text style. ordinary | italic | diagonal | introductory | acquire.
- CSS text style family property indicates a focused on rundown of at least one text style family names and additionally conventional family names for the chose component.
- CSS text dimension property sets the size of the textual style.
- CSS text style weight property characterizes whether the text style should be intense or thick.
- CSS text-change property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-enhancement property indicates the beautification added to message, and is a shorthand property for message embellishment line, message adornment tone, message design style.
- CSS shading property depicts the shade of the text content and text designs.
- CSS foundation shading property sets the foundation shade of a component.
- CSS text-indent property determines the space of the main line in a text block.
- CSS text-flood property determines how flooded substance that isn’t shown ought to be motioned to the client.
- CSS blank area property determines how void area inside a component is dealt with.
- CSS word-break property indicates where the lines ought to be broken.
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to message.
- CSS text-adjust last property sets the arrangement of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-tallness property indicates the stature of a line.
- CSS letter-dispersing property characterizes the spaces between letters/characters in a text.
- CSS word-dispersing property sets the dividing between words.
Introduction to HTML Header
The HTML element represents an introductory content, usually a set of introductory or navigation aids. It may contain some heading elements, but it may also include logos, search forms, author names, and other elements. Precautions for use. The element is not section content, so it does not add a new section to the outline. However, the element should normally include the enclosed section heading (h1-h6 element), which is not required.
Uses of HTML Header:
The element entered the spec only in HTML5, but it actually existed at the beginning of HTML. Originally called & lt; head & gt ;, as seen on the first website. element. Eventually they decided on a different name. This allowed the to take on another role later.
Attribute:
Posted:
Accessibility
The element defines a banner orientation element when its context is & lt; body & gt ;. element. HTML header elements are not considered banner landmarks if they are descendants of ,,,, or elements.
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language
Example:
Explained example
The DOCTYPE html> declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document.
Element defines the body of the document and is a container for all display content such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables and lists. The element defines a large heading.
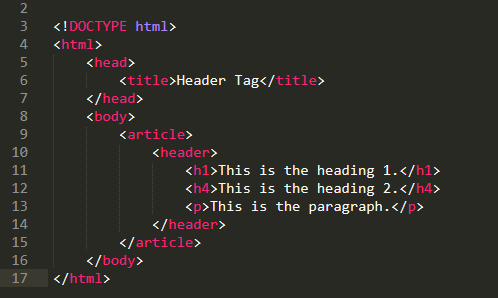
What are HTML elements?
HTML elements are defined by start tags, some content, and end tags. Content is here HTML elements are everything from start tag to end tag:
Note: Some HTML elements have no content (such as elements). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements have no end tag!.
HTML History:
Since the dawn of the World Wide Web, there are many versions of HTML:
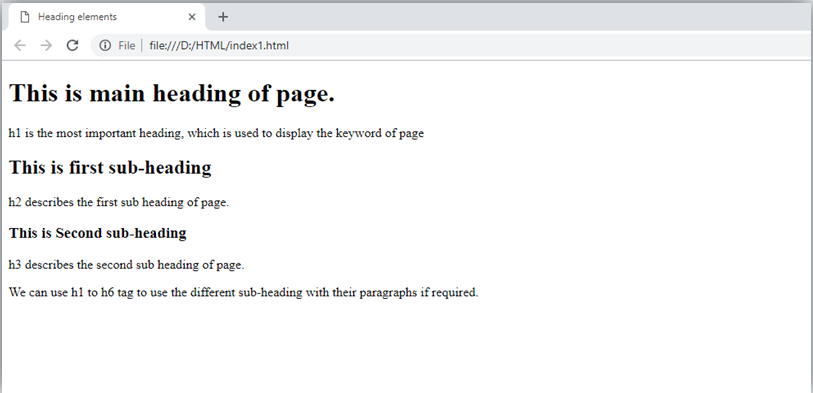
HTML Heading
HTML headings are titles or subtitles to display on web pages.
Example
Defines the least important headings.
Example
Note: The browser automatically adds white space before and after the heading. The heading is important Search engines use headings to index the structure and content of web pages.
Users often scan pages based on headings. It is important to use headings to show the structure of the document. The heading should be used for the main heading, then the heading, then the less important heading, and so on.
Note: Use HTML headings only for headings. Do not use headings to make the text larger or bold.
Example
Tag description
Defines the HTML heading
HTML Code & lt; Title & gt; Item
& lt; Title & gt; This element defines the title of the document. The title must be text only and will appear in the browser title bar or page tab.
& lt; Title & gt; HTML Documents Need Elements! The content of the title on page is very important for search engine optimization (SEO). Page titles are used by search engine algorithms to determine the order in which pages are displayed in search results.
& lt; Title & gt;
Element: Defines the title of the browser toolbar provides the page title when adding to favorites displays the page title in search engine results. Therefore title Try to be as specific and easy to understand as possible.
Simple HTML Documents:
Examples
The & lt; Style & gt; element is used to define style information for a single HTML page.
Example
The & lt; Meta> Element is typically used to specify the character set, page description, keywords, document author, and viewport settings. The metadata does not appear on the page, but is used by browsers (how to view or reload content), search engines (keywords), and other web services.
Case: Defines the character set to use
Defines search engine keywords:
Defines a site description:
Updates the document every 30 seconds:
<; meta> tag example:
Example
Set Viewport increase. The viewport is part of the website that users see. On some devices, mobile phones are smaller than computer screens. Below & lt; Meta> Displayed. All web page elements:

Definition and use of
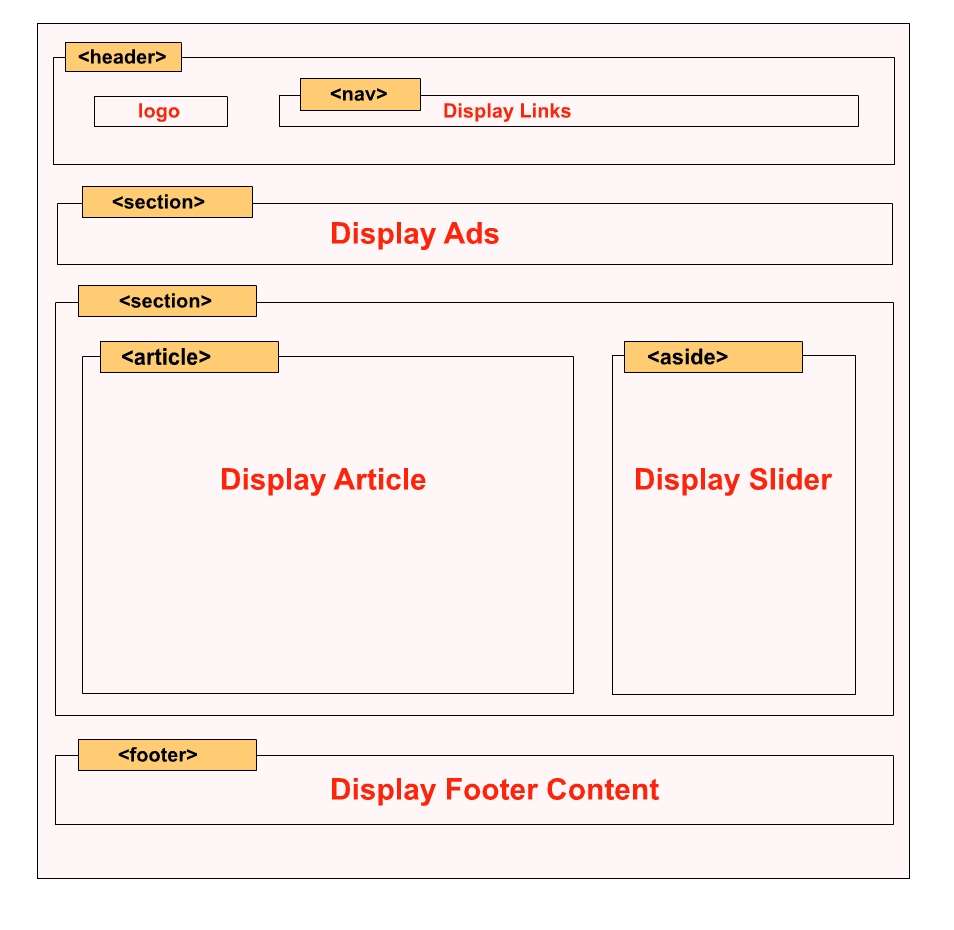
The element represents a container for referral content or a set of navigation links.
Elements typically include:
Browser support
The numbers in the table indicate the first browser version that fully supports the item. Elements 5.0 9.0 4.0 5.0 11.1.
Global attributes
The tag also supports HTML global attributes.
Other examples
How to style <'header> tag?
Shading text in <'header> tag:
Text format styles for <'header> tag:

Different properties worth checking out for <'header> tag:
Conclusion:
HTML is superfluous for the raising issues of crowd, reason, plan, and openness. Learning HTMLneed to be an obstruction to picking up a composition, that is feasible to utilize HTML to address composing issues. The <'header> HTML component addresses initial substance, ordinarily a gathering of early on or navigational guides. It might contain a few heading components yet in addition to a logo, a hunting structure, a creator name, and different components.

