
[BEST & NEW] SAP BPC Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 12th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
SAP BPC is an enterprise performance management solution that empowers organizations in budgeting, planning, and consolidating financial data. It offers a collaborative platform for diverse departments to contribute to the planning process and ensures compliance with regulatory standards during financial consolidation. With features for forecasting and integration with other SAP modules, BPC provides a comprehensive solution for accurate financial management, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and adapt to dynamic business environments.
1. What is SAP BPC?
Ans:
SAP BPC, or SAP Business Planning and Consolidation, is an enterprise performance management (EPM) tool developed by SAP. It is designed to streamline and optimize an organization’s financial and operational planning processes, consolidation, and reporting. SAP BPC helps businesses align their strategic goals with operational activities by providing a unified platform for planning, budgeting, forecasting, and financial consolidation.
2. How is data stored in SAP BPC?
Ans:
In SAP BPC, data is typically stored in a central data warehouse, such as SAP BW, which acts as a repository for financial and operational information. The data is organized into cubes and dimensions, providing a structured and efficient way to store and retrieve information for planning, budgeting, and consolidation processes. The system provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial and operational data for effective decision-making.
3. Define the term “dimensions” in SAP BPC.
Ans:
In SAP Business Planning and Consolidation (BPC), dimensions are organizational structures that categorize and provide context to data. Dimensions represent different perspectives or aspects of the business, such as time, entities, accounts, or custom attributes. Each dimension consists of members that define the specific elements within that dimension. It allows users to analyze and plan data over particular time intervals.
4. What is a dimension member in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A dimension member in SAP BPC refers to a specific instance or element within a dimension. For example, if the dimension is “Time,” members could be individual periods such as months or quarters. In the “Product” dimension, members could represent different product categories or unique products. Dimensions are organizational structures that categorize and provide context to data in a multidimensional database.
5. Differentiate between input forms and reports in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Input forms in SAP BPC are used for data entry and capture during planning and budgeting. They provide a user-friendly interface for inputting numerical data, enabling users to contribute to the planning cycle.
- On the other hand, reports present summarised and analyzed data for decision-making purposes, offering insights into financial performance, key metrics, and additional relevant information.
6. What is the purpose of a Business Rule in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Automates calculations and transformations within the SAP BPC environment.
- Ensures consistency and accuracy in financial and operational data.
- Facilitates complex business logic and calculations.
- Supports the automation of data consolidation and aggregation.
- Streamlines and standardizes the planning, budgeting, and forecasting processes.
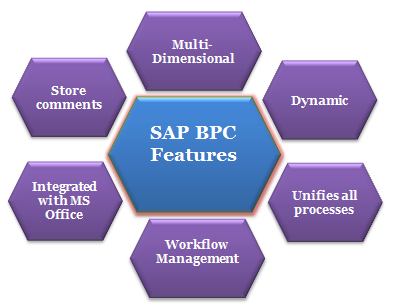
7. What are the key features of SAP BPC?
Ans:
The key components of SAP BPC include the web-based interface for end-users to access and interact with the system, a central database or data warehouse for storing financial and operational data, a set of predefined business rules and logic for calculations and consolidations, as well as reporting and analytics tools for visualizing performance and making informed decisions. It provides a user-friendly environment for entering, analyzing, and reporting financial and operational data.
8. Explain the purpose of the Business Process Flows (BPFs) in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Business Process Flows (BPFs) in SAP Business Planning and Consolidation (BPC) guide users through a predefined sequence of activities or tasks related to financial planning, budgeting, consolidation, and reporting processes. BPFs help structure and streamline these processes, providing a systematic and guided approach to users involved in planning and consolidation activities.
9. Explain the difference between SAP BPC Standard and SAP BPC Embedded.
Ans:
| Feature | SAP BPC Standard | SAP BPC Embedded | |
| Architecture | Standalone system, separate from SAP BW | Integrated with SAP BW, leveraging its capabilities | |
| Integration with SAP BW | No direct integration with SAP BW | Tight integration with SAP BW | |
| Data Storage | Relational Database (like Microsoft SQL Server) | Uses SAP BW InfoProviders (such as InfoCubes or Advanced DataStore Objects) | |
| Data Modeling | Basic data modeling capabilities | Leverages advanced BW modelling features | |
| Planning Capabilities | Basic planning and budgeting features | Advanced planning and forecasting capabilities | |
| Consolidation | Supports basic consolidation processes | Provides advanced consolidation capabilities through SAP BW |
10. How do you perform data audit and traceability in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Data audit and traceability in SAP BPC ensure transparency and accountability in the financial and operational processes. SAP BPC provides features to track changes made to data, helping organizations maintain an audit trail and trace the origins of any modifications. Users can leverage the system’s built-in audit functionality to monitor data entry, approvals, and other system activities.
11. What is the role of the Data Access Profile in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Data Access Profile in SAP BPC is critical in managing user access to data within the system. By configuring Data Access Profiles, administrators can control which users can read, write, or execute specific tasks, ensuring data security and confidentiality. This feature helps organizations enforce segregation of duties, comply with regulatory requirements, and establish a granular and controlled access framework based on the roles and responsibilities of users.
12. How do you create a new model in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Access the SAP BPC web interface.
- Navigate to the “Administration” module.
- Select “Models” and choose “Create Model.”
- Specify model details such as name, description, and currency.
- Define dimensions and dimension properties.
- Configure security settings and access controls.
- Set up business rules, scripts, and data manager packages as needed.
- Save and activate the new model.
13. What is the difference between a script logic and a business rule in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Script Logic is a procedural language for creating custom calculations, while a Business Rule is a declarative approach for defining calculations.
- Business Rules provide a more user-friendly and intuitive way to express calculations without the need for extensive programming knowledge.
- Script Logic is generally used for complex, custom calculations, while Business Rules are suitable for standard and recurring calculations.
14. Explain the importance of a data manager package in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Facilitates the import and export of data between SAP BPC and external sources.
- Supports data transformation, mapping, and data cleansing processes.
- Automates data loading tasks, improving efficiency and reducing manual errors.
- Enables integration with various data sources, such as databases and flat files.
15. Describe the significance of the audit trail in SAP BPC.
Ans:
The audit trail in SAP BPC is essential for tracking and documenting changes to financial and operational data within the system. The audit trail enhances transparency, accountability, and compliance by allowing organizations to trace the history of data modifications. This feature is essential for financial reporting and auditing purposes, as it ensures the integrity and reliability of the data by recording the who, what, and when of each change.
16. How can you manage security in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Security in SAP BPC is managed through various components and settings, ensuring only authorized users can access and manipulate sensitive financial and operational data. They assign roles and permissions to users and groups based on their responsibilities. Defining permissions for data entry, approval processes, and report generation and assigning roles aligning with users’ functional responsibilities allows for a structured and controlled access environment.
17. What is the purpose of the Task Recorder in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Task Recorder in SAP BPC is a tool that allows users to capture and document step-by-step processes within the system. It records user interactions, such as navigating screens, entering data, and executing tasks. The recorded tasks can be saved as documentation or used to create training materials. The Task Recorder is valuable for knowledge transfer, training new users, and ensuring consistency in executing critical processes.
18. How does consolidation work in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Consolidation in SAP BPC refers to aggregating and combining financial data from various entities, business units, or subsidiaries to create a unified and accurate view of the organization’s financial position. The consolidation process involves activities such as currency translation, intercompany eliminations, adjustments for minority interests, and the creation of consolidated financial statements.
19. What is the significance of the dimension property “Time-dependent” in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Allows for the representation of time-dependent changes in the data model.
- Enables the management of historical data and analysis of trends over time.
- Facilitates scenario planning and forecasting by considering changes in time dimensions.
- Enhances the flexibility of the data model to accommodate evolving business requirements.
20. How do you integrate SAP BPC with other SAP modules?
Ans:
- Leverage SAP Process Integration (PI) or SAP Data Services for data integration.
- Utilise SAP BW as a central data warehouse for SAP BPC Embedded deployments.
- Integrate SAP BPC with SAP ERP modules for seamless financial planning and consolidation.
- Implement SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT) for real-time data replication.
- Use SAP HANA as a high-performance database for improved data processing.
21. What is the significance of the ownership manager in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The ownership manager in SAP BPC is a tool that allows organizations to manage and track the ownership and responsibility for different parts of the planning and consolidation processes. It helps define and assign ownership of specific tasks, promoting accountability and transparency in the financial management processes.
22. Describe the difference between local and global master data in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Local master data in SAP BPC is specific to a particular application or environment, while global master data is shared across multiple applications. Local master data is relevant only within the scope of a particular SAP BPC instance. In contrast, global master data ensures consistency and uniformity across various instances or deployments within an organization. These terms are particularly relevant in managing dimensions and their members, such as accounts, entities, or periods.
23. What is a Business Process Flow (BPF) in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A Business Process Flow (BPF) in SAP BPC is a predefined sequence of tasks and steps that guide users through a structured business process, such as planning, budgeting, or consolidation. BPFs help organize and streamline workflows, ensuring users follow a predefined methodology. They enhance collaboration, reduce errors, and provide transparency by clearly outlining the sequence of actions within the system.
24. What is a dimension override in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Allows temporary modification of dimension member properties for specific scenarios or calculations.
- Facilitates the customization of dimension properties without permanently altering the underlying data model.
- Useful for ad-hoc analysis and scenario-based planning.
- Enables users to test and evaluate the impact of dimension property changes without affecting the core data structure.
25. How can you handle currency translation in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Configure currency translation rules within the SAP BPC model.
- Utilise exchange rates and currency conversion methods.
- Implement currency translation business rules to perform the conversion.
- Specify translation methods for individual accounts or dimensions.
- Consider factors such as average, closing, and historical rates based on business requirements.
26. How do you create a custom hierarchy in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Creating a custom hierarchy in SAP BPC involves defining a structure of dimension members in a specific order to represent a hierarchy. Choose the dimension for which you want to create a custom hierarchy. Typical dimensions include Time, Accounts, Entities, etc. Look for an option to create a new hierarchy within the selected size. Depending on your system configuration, this might be labelled as “Create Hierarchy” or a similar option.
27. Describe the role of a transformation file in SAP BPC.
Ans:
A transformation file in SAP BPC is used to map and transform data during the data-loading process. It provides instructions on how source system data should be mapped to the target SAP BPC model, including data conversion, formatting, and validation rules. The transformation file helps ensure data consistency and accuracy by defining the relationships between source and target data elements.
28. What is the purpose of data validation in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Ensures the accuracy and integrity of data entered into the system.
- Validates data against predefined business rules and criteria.
- Prevents the entry of incorrect or inconsistent data.
- Facilitates error identification and resolution during the data entry process.
- Improves data quality and reliability for reporting and analysis.
29. Explain the concept of dynamic formatting in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Allows for the dynamic adjustment of report formatting based on changing conditions or user inputs.
- Enables the customization of report appearance, such as font styles, colours, and conditional formatting.
- Enhances the visual presentation of data by adapting formatting to specific contexts.
- Improves the usability and effectiveness of reports for decision-making purposes.
30. Describe the purpose of the Report Logic dimension in SAP BPC.
Ans:
The Report Logic dimension in SAP BPC serves multiple purposes. It enables dynamic reporting by allowing the incorporation of logic directly into the reporting structure, providing flexibility for scenario-based reporting. Users can apply custom calculations or adjustments within reports, facilitating detailed financial analysis. The dimension also supports ad-hoc analysis, empowering users to apply logic on the fly while interacting with reports. Overall, the Report Logic dimension enhances the versatility of reporting processes in SAP BPC, catering to diverse analytical needs.
31. Explain the concept of currency conversion in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Currency conversion in SAP BPC involves managing exchange rates, utilizing currency dimensions, creating business rules, and implementing the conversion during data loading. Exchange rates are defined and maintained for different currencies, currency dimensions represent various currencies in the data model, and business rules specify conversion methods like average rates or closing rates. This ensures consistent reporting across different currencies, supporting accurate financial analysis and planning.
32. How do you handle rounding in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Rounding in SAP BPC is managed through predefined business rules or custom logic to ensure precision and consistency in numerical data. The rounding process is typically incorporated into calculations, especially in financial planning and consolidation scenarios where accurate representation of currency and economic values is crucial. This involves specifying rounding methods, precision levels, and rules for rounding adjustments.
33. What is the importance of a dimension filter in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Data Focus
- Performance Optimization
- User Flexibility
- Data Precision
- Scenario Analysis
34. How can you optimize performance in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Data Aggregation: Aggregating data at higher levels of the hierarchy to reduce the volume of data processed.
- Indexing: Ensuring that relevant database indexes are in place for optimized query performance.
- Data Compression: Implementing compression techniques for efficient data storage and retrieval.
- Partitioning: Utilizing partitioning strategies to divide data into manageable segments for improved performance.
35. Explain the purpose of a work status in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Process Control: Manages the workflow and approval processes for planning, budgeting, and consolidation activities.
- Data Locking: Prevents unauthorized modifications to data during critical stages of the planning cycle, ensuring data integrity.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration by allowing users to indicate the status of their work and providing visibility into the overall progress of tasks.
- Auditability: Enhances auditability by tracking changes in work status, documenting approvals, and maintaining a reliable history of planning activities.
36. Describe the significance of a member formula in SAP BPC.
Ans:
A member formula in SAP BPC allows users to define calculations or logic specific to individual dimension members. Provides a way to customize calculations for particular members, offering granular control over data processing.Enables adjustments or modifications to data for individual members without affecting the entire dimension.Facilitates the incorporation of member-specific logic based on different planning scenarios or business requirements.
37. What is a consolidation monitor in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The consolidation monitor in SAP BPC is a tool that allows users to track the progress and status of the consolidation process. It provides insights into critical aspects of consolidation, such as data validation, intercompany eliminations, currency conversion, and overall consolidation status. It assists organizations in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of consolidated financial information by providing a centralized view of the consolidation process.
38. How can you troubleshoot data load issues in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Verify the integrity and correctness of the source data being loaded into SAP BPC. Ensure that the mapping between source and target dimensions is accurate. Review and validate the transformation rules applied during data loading. Implement validation checks to identify data inconsistencies or errors. Examine error messages and logs generated during the data load process for insights into issues. Utilize the logs generated by the Data Manager to identify the specific problems and error details.
39. What is the significance of data slices in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Selective Data Loading: Allows for loading specific data subsets, optimizing data loading processes.
- Efficient Data Retrieval: Facilitates faster data retrieval by focusing on relevant dataset slices.
- Scenario Analysis: Supports scenario analysis by enabling users to work with specific data slices for planning, budgeting, and forecasting.
- Reduced Complexity: Simplifies data management by allowing users to work with more minor, manageable portions of the overall dataset.
40. How do you handle intercompany eliminations in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Identification of Intercompany Transactions: Identify intercompany transactions within the data model.
- Interunit Matching: Match corresponding transactions between intercompany units.
- Elimination Entries: Create elimination entries to remove intercompany transactions from consolidated results.
- Consolidation Rules: Define consolidation rules to automate the intercompany elimination process.
41. How do you configure a data manager package in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Access Data Manager
- Create Package
- Define Source and Target
- Mapping and Transformation
- Validation Rules
- Execution Parameters
- Execute Package
42. Explain the purpose of a business add-in (BAdI) in SAP BPC.
Ans:
A Business Add-In (BAdI) in SAP BPC is a mechanism for enhancing or customizing standard functionalities. Allows developers to extend existing functionalities or add custom logic to meet specific business requirements.Facilitates seamless integration with other SAP components or external systems.Enables adding new features or modifications to standard processes without altering the core system.
43. What is a data manager script in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A Data Manager Script in SAP BPC is a set of instructions or commands written in the Data Manager Scripting language. It is used to automate and execute data-related tasks during the data loading. Data Manager Scripts can include data extraction, transformation, validation, and loading commands. Leveraging scripts allows users to streamline repetitive tasks, improve data consistency, and ensure adherence to predefined business rules.
44. How do you perform a mass data copy in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Access the SAP BPC web interface and navigate to the Data Manager module. Create a new Data Manager package and select the appropriate model. Choose the “Copy Package” option and specify the mass data copy’s source and target dimensions or members. Configure any required mapping or transformation rules. Set additional parameters, such as data ranges and filters. Execute the package to perform the mass data copy operation.
45. What is the significance of the Application Set in SAP BPC?
Ans:
An Application Set in SAP BPC is a container for one or more applications. It helps organize and manage multiple applications within a logical grouping. Enables the definition of security settings at the application set level for shared configurations.Facilitates consistent application management, particularly when multiple applications share similar settings or configurations—Simplifies user access by providing a unified entry point for users working with various applications within the set.
46. What is the difference between a fact table and a dimension table in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Fact Table:
- Stores quantitative, numeric data related to business transactions or events.
- Contains measures or key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Typically larger and contains a high volume of detailed, numerical data.
Dimension Table:
- Stores descriptive attributes that provide context to the quantitative data.
- Contains textual or categorical information such as names, dates, and descriptions.
- Smaller in size compared to fact tables.
- Used for organizing and categorizing data for meaningful analysis.
47. What are the types of script logic in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Default Logic: Automatically generated logic based on the structure of the data model.
- Custom Script Logic: User-defined scripts that allow for specific calculations and data manipulations.
- Standard Business Rules: Predefined business rules provided by SAP BPC for everyday calculations.
- Currency Conversion Logic: Script logic designed explicitly for currency conversion tasks.
- Data Transformation Logic: Logic used during data loading processes to transform and map source data to target dimensions.
48. Explain the role of the default logic in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Default Logic in SAP BPC represents automatically generated calculations based on the structure of the data model. Provides automatic calculations for standard financial and operational processes without manual intervention.Streamlines planning and consolidation processes by eliminating users’ need to define basic calculations manually.Ensures consistency in calculations across various dimensions and members within the data model.
49. How do you manage currency translation in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Set up currency dimensions to represent different currencies in the data model. Define and maintain exchange rates between foreign currencies. Create business rules or scripts for currency conversion during data loading and consolidation. Consider adjustments for translation differences based on business requirements. Review and validate translated data to ensure accuracy and consistency in financial reporting across multiple currencies.
50. What is the purpose of the Data Access Profile in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Data Access Profile in SAP BPC serves the crucial purpose of managing user access to data within the system. It enables administrators to define and control the data visibility and manipulation level each user or user group has. Data Access Profiles help ensure that users can only access the data necessary for their roles, maintaining data integrity and confidentiality. By configuring these profiles, organizations can enforce security measures and comply with data access and privacy regulations.
51. Describe the purpose of the Dynamic Calculations dimension in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Scenario-Based Logic: Allows for including dynamic or scenario-specific calculations within the data model.
- Flexibility in Reporting: Enhances flexibility in reporting and analysis by providing a dimension dedicated to dynamic calculations.
- Custom Calculations: Facilitates the creation of member-specific formulas or logic for calculations.
- Ad-Hoc Analysis: Supports ad-hoc analysis by empowering users to apply calculations to selected members dynamically.
- Scenario Planning: Enables the implementation of different calculation scenarios based on changing business conditions.
52. How do you create a custom member property in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Access the SAP BPC web interface and navigate to the “Model” or “Dimensions” section.
- Select the dimension for which you want to create a custom member property.
- Choose the option to create a new member property.
- Define the properties, such as name, data type, and description.
- Save the custom member property configuration.
53. How can you customize the appearance of reports in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Customizing the appearance of reports in SAP BPC involves several options to tailor the visual presentation of financial and operational data. Users can use formatting, grouping, and sorting to organize data meaningfully. Additionally, SAP BPC allows the incorporation of charts and graphs to enhance data visualization. Users can choose templates, styles, and colour schemes to align with corporate branding or reporting standards.
54. Explain the role of a business add-in (BAdI) in SAP BPC.
Ans:
A Business Add-In (BAdI) in SAP BPC is a programming enhancement option that allows developers to extend and customize the application’s functionality. In the context of SAP BPC, BAdIs enable users to incorporate additional logic or business rules into the standard processes. This flexibility is crucial for organizations with unique business requirements that cannot be addressed through standard configuration alone.
55. What is a data manager package in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A Data Manager Package in SAP BPC is a set of instructions or commands that automate data integration processes. It facilitates data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) between different systems and sources. Data Manager Packages streamline data import/export tasks, ensuring consistency and accuracy across the organization’s financial and operational data. These packages are handy for managing large volumes of data efficiently and maintaining data integrity within the SAP BPC environment.
56. What is the significance of the Transformation File in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Data Mapping: Specifies how source system data maps to the target SAP BPC model, defining relationships between dimensions and members.
- Data Transformation: Provides instructions for transforming and manipulating source data during the data loading.
- Data Validation: Ensures data integrity and accuracy by applying validation rules defined in the transformation file.
- Custom Logic: Allows for the inclusion of custom logic and calculations during data loading.
- Efficient Data Integration: Optimises data integration from external sources into the SAP BPC environment.
57. What is the purpose of the data import/export wizard in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Data Transfer: Facilitates the import and export of data between SAP BPC and external sources or flat files.
- Mapping: Provides a user-friendly interface for mapping source system data to target SAP BPC dimensions and members.
- Data Transformation: Allows users to define transformation rules and manipulate data during the import/export.
- Validation: Supports validation checks to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
58. What is a dimension member formula in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A Dimension Member Formula in SAP BPC empowers users to define custom calculations specific to individual members within a dimension. This feature provides granular control, allowing unique calculations or adjustments to be applied selectively to data for chosen members. It facilitates member-specific logic without affecting the entire dimension, supporting scenario-based adjustments aligned with different planning scenarios or business requirements.
59. How do you handle data validation in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Data validation in SAP BPC is a critical step to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial and operational data. Users can implement various validation rules and checks to verify data integrity, consistency, and adherence to predefined business rules. This process involves defining validation criteria, establishing data quality standards, and implementing error-handling mechanisms to address discrepancies.
60. What is the role of the Data Load Monitor in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Data Load Monitor in SAP BPC plays a crucial role in tracking and managing the progress of data loading processes. The Data Load Monitor displays vital information such as the number of records processed, elapsed time, and any errors encountered during the data loading process. Using the Data Load Monitor, administrators can identify issues promptly, take corrective actions, and ensure the smooth and efficient execution of data loading tasks in SAP BPC.
61. How do you handle rounding differences in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Rounding Rules: Define rounding rules within business rules or scripts to ensure consistent and accurate rounding.
- Precision Levels: Specify the precision level or number of decimal places to which data should be rounded.
- Rounding Methods: Choose appropriate rounding methods, such as rounding half-up, rounding half-down, or rounding to the nearest even or odd number.
- Adjustments: Consider incorporating rounding adjustments as needed to reconcile rounding differences in financial reporting.
62. How can you optimize the performance of data loads in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Data Aggregation: Aggregate data at higher levels of the hierarchy to reduce the volume of data processed.
- Parallel Processing: Leverage parallel processing capabilities for concurrent execution of tasks.
- Data Compression: Implement compression techniques for efficient data storage and retrieval.
- Partitioning: Utilise partitioning strategies to divide data into manageable segments for improved performance.
- Hardware Optimization: Ensure hardware resources (CPU, memory, disk) are appropriately sized for the SAP BPC environment.
63. Describe the importance of a work status in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Work status in SAP BPC refers to a feature allowing organizations to control and monitor data status during planning and consolidation. By defining work status settings, administrators can enforce specific states for data, such as “input,” “review,” or “locked.” This ensures that only authorized users can change data during particular workflow stages. Work status is crucial for maintaining data consistency, preventing unauthorized modifications, and establishing a structured financial and operational data approval process.
64. What is the significance of the Ownership Manager in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Ownership Manager in SAP BPC plays a significant role in managing the ownership structure of entities within the organization. It allows users to define and analyze the ownership relationships between entities, such as subsidiaries and parent companies. The Ownership Manager facilitates the consolidation of financial data by providing a comprehensive view of the ownership hierarchy.
65. How do you manage intercompany eliminations in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Managing intercompany eliminations in SAP BPC involves eliminating transactions or balances between different entities within the same organization. Intercompany transactions can distort financial reporting, and the Intercompany Eliminations functionality in SAP BPC helps address this issue. Proper management of intercompany eliminations is crucial for organizations with multiple subsidiaries or business units to present an accurate and fair view of their financial performance.
66. Explain the concept of currency conversion methods in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- Average Rate: Uses the average exchange rate over a specified period for currency conversion.
- Closing Rate: Utilises the exchange rate at the end of a specific reporting period for currency conversion.
- Historical Rate: Applies historical exchange rates for currency conversion based on a chosen point in time.
- User-Defined Rate: Users can specify custom exchange rates for currency conversion.
- Translation Date Rate: Uses the exchange rate on the transaction date for currency conversion.
67. What is the significance of the Consolidation Monitor in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Progress Tracking: Tracks the progress and status of the consolidation process, including critical steps such as validation, intercompany eliminations, and currency conversion.
- Error Identification: Flags errors or discrepancies encountered during consolidation, aiding in identifying and resolving issues.
- Process Visibility: Provides visibility into the overall consolidation workflow, enabling users to monitor and manage the process effectively.
- Audit Trail: Captures an audit trail of consolidation activities, ensuring accountability and supporting compliance requirements.
68. Explain the purpose of the Task Recorder in SAP BPC.
Ans:
The Task Recorder in SAP BPC is a tool that enables users to record and automate sequences of tasks within the system. It captures user interactions and system responses, allowing users to create reusable scripts or macros for repetitive processes. The Task Recorder is beneficial for increasing efficiency, reducing manual effort, and minimizing the risk of errors in routine tasks.
69. What is a data slice in SAP BPC?
Ans:
In SAP BPC, a data slice refers to a specific view or subset of multidimensional data within the system. Data slices are instrumental in creating customized reports and analyses tailored to particular business requirements. Users can define and save different data slices to quickly access relevant information, enhancing the flexibility and usability of SAP BPC for reporting and decision-making purposes.
70. What is the significance of a dimension override in SAP BPC?
Ans:
In SAP BPC, a dimension override holds significant importance as it allows users to customize the behaviour of dimensions for specific scenarios or reports without altering the global structure. Different scenarios may require unique perspectives on dimensions such as Time or Entity when implementing planning or consolidation processes. Dimension overrides enable users to define specific properties, structures, or members for a dimension within a particular application or scenario, ensuring flexibility in data representation.
71. How can you troubleshoot script logic issues in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Review Syntax and Logic
- Debugging Tools
- Logging and Tracing
- Check Data and Dimensions
- Review Security Settings
- Compare with Previous Versions
72. What is the purpose of a member formula in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- A member formula in SAP BPC is associated with a specific member in a dimension.
- It allows users to dynamically define calculations or derive values based on other members’ data within the same dimension.
- Member formulas are beneficial for customizing calculations at the member level, providing a more granular approach to data manipulation.
- These formulas contribute to the flexibility and adaptability of SAP BPC, enabling users to express complex business rules at a detailed level within the application.
73. Explain the significance of the Application Set in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- The Application Set in SAP BPC is a logical grouping of applications with standard dimensions and properties.
- It simplifies the management of multiple applications within the same environment.
- By associating related applications in an Application Set, administrators can streamline security management and data integration tasks.
- It enhances the organization and maintenance of applications, especially in scenarios where different departments or business units use distinct but related planning applications.
74. How do you manage data audit and traceability in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Managing data audit and traceability in SAP BPC is essential for ensuring financial and operational data accuracy, reliability, and compliance. Activate logging features in SAP BPC to capture detailed information about user activities, data changes, and system events. Tracing capabilities can help administrators identify issues and track data flow within the system. Utilize versioning features to create snapshots of data at different points in time.
75. How can you optimize the performance of reports in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Limit the level of detail in reports by aggregating data at higher levels. Utilise data caching mechanisms to store previously retrieved data, reducing the need to fetch the same data repeatedly. This is particularly useful for frequently accessed reports. Ensure that relevant dimensions are correctly indexed, enabling faster data retrieval. Indexing improves the efficiency of data access operations and contributes to overall report performance.
76. What is the significance of the Dynamic Calculations dimension in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Dynamic Calculations dimension in SAP BPC is significant as it allows users to perform on-the-fly calculations or adjustments during planning or consolidation processes. This dimension provides a flexible mechanism for applying dynamic logic without the need for predefined scripts or business rules. This flexibility enhances the agility of the SAP BPC system, allowing users to adapt calculations quickly to evolving business scenarios without extensive reconfiguration.
77. How do you integrate SAP BPC with SAP BW?
Ans:
- Leverage the SAP BW Open Hub Destination functionality to extract data from SAP BPC.
- Define Open Hub Destination in SAP BW to connect to SAP BPC and extract relevant data.
- Use Data Manager Packages or Process Chains to automate data transfer between SAP BPC and SAP BW.
- Ensure proper mapping of dimensions and data between the two systems to maintain consistency.
- Implement appropriate security measures to control data access and integrity during integration processes.
78. Explain the difference between fact and dimension tables in SAP BPC.
Ans:
Fact Table:
Represents the central repository for numeric data or measures.Contains quantitative values such as sales figures, expenses, or quantities. Typically, each row in the fact table corresponds to a unique combination of dimension members, representing a specific intersection of business entities and metrics.
Dimension Table:
Stores descriptive attributes or characteristics of data. It contains information about entities, periods, and other dimensions that provide context to the numeric data stored in the fact table.
79. How do you handle rounding in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Define and configure the appropriate decimal places for each dimension, especially for numeric data. Utilize rounding functions in scripts or business rules to ensure consistent and accurate rounding methodologies. Be mindful of data types to avoid unintended consequences during calculations. Consider using appropriate data types to accommodate rounding requirements. Adjust report formatting settings to display rounded values appropriately in user interfaces and reports.
80. Explain the concept of data slices in SAP BPC.
Ans:
In SAP BPC, a data slice represents a specific subset or view of multidimensional data. Users can create data slices by selecting members from different dimensions, allowing them to focus on a particular portion of the dataset. Users can quickly access and analyze relevant information by defining and saving other data slices without navigating the entire dataset.
81. What is a consolidation monitor in SAP BPC?
Ans:
The Consolidation Monitor in SAP BPC is a central tool for overseeing and managing the financial consolidation process. It provides:
- Real-time visibility into the status of consolidation activities.
- Displaying critical information such as the progress of consolidation tasks.
- Data validation results.
- Any errors encountered during the process.
82. How can you customize the appearance of input forms in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- Form Design Mode
- Adjust Column and Row Layout
- Format Cells
- Apply Conditional Formatting
- Add Headers and Footers
- Include Images and Logos
- Control Visibility
- Define Input Ranges
- Save and Share
83. Describe the importance of a transformation file in SAP BPC.
Ans:
A transformation file in SAP BPC plays a crucial role in the data import process by defining the relationship between source and target dimensions, members, and data types. It ensures accurate and consistent data mapping, facilitating the seamless integration of data from external sources into SAP BPC. By providing a standardized mapping mechanism, the transformation file streamlines the data import process, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing overall data quality.
84. What is a custom member property in SAP BPC?
Ans:
A custom member property in SAP BPC is an attribute that users can define and assign to a member within a dimension. Unlike standard properties, custom member properties are user-defined, allowing the storage of additional information about members that may not be covered by default properties. These custom properties enhance the descriptive attributes associated with dimension members, offering users the flexibility to include specific details that contribute to a richer context for analysis and reporting in SAP BPC.
85. How do you perform data validation in SAP BPC?
Ans:
Performing data validation in SAP BPC involves several steps. First, users need to define validation rules based on business requirements. They can then utilize built-in validation options or create custom validation rules tailored to their specific needs. Validations can be applied to specific dimensions, members, or data ranges within the system. Additionally, users can configure error messages and specify actions to be taken upon validation failure.
86. What is the role of a dimension filter in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- A dimension filter in SAP BPC allows users to focus on specific subsets of data within a dimension.
- It enables dynamic data filtering based on predefined criteria or user input.
- Dimension filters enhance user experience by customising views and reports according to specific dimension member selections.
87. Describe the purpose of the consolidation monitor in SAP BPC.
Ans:
- The Consolidation Monitor in SAP BPC provides real-time visibility into the status and progress of the financial consolidation process.
- It displays vital information such as consolidation task execution, validation results, and any issues encountered during the consolidation.
- The Consolidation Monitor helps users track the workflow, identify errors, and take corrective actions, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of consolidated financial data.
88. What is the purpose of a data manager script in SAP BPC?
Ans:
- A Data Manager script in SAP BPC automates data-related tasks, such as data loading, transformation, and validation.
- It allows users to define a series of commands and logic to be executed in a specific sequence.
- Data Manager scripts enhance efficiency by automating routine processes and ensuring consistency in data handling.
- Scripts can include actions like data extraction, transformation, cleansing, and loading, providing a comprehensive tool for managing data in SAP BPC.
89. What is the concept for plan data from BPC?
Ans:
Plan data in BPC (Business Planning and Consolidation) refers to the set of financial or operational projections and forecasts that organizations create as part of their planning processes. It involves the development of strategic targets, budgetary plans, and other forward-looking data to guide business activities. In BPC, plan data serves as a foundation for decision-making, helping organizations align their resources and strategies with anticipated future scenarios.
90. What is BPC?
Ans:
BPC, or Business Planning and Consolidation, is an enterprise performance management (EPM) software solution developed by SAP. It provides a unified platform for financial planning, budgeting, forecasting, and consolidation activities within an organization. BPC facilitates collaboration among different business units and supports the creation of integrated plans that align with strategic objectives.

