
Get 50+ SAS CDM Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on 14th Nov 2021, Blog, Interview Questions
SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) uses SAS (Statistical Analysis System) software for managing and analyzing clinical trial data in clinical research and pharmaceutical development. It involves organizing, cleaning, and validating data collected during clinical trials to ensure accuracy and reliability. SAS CDM is crucial for maintaining data integrity and meeting regulatory requirements in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries.
1. What is SAS CDM?
Ans:
The pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors use software called SAS Clinical Data Management, or SAS CDM, to manage and analyze data from clinical trials. A complete platform called SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) makes it easier to gather, organize, and analyze data from clinical trials. Data entry, validation, cleansing, and reporting are among the activities it supports. SAS CDM is extensively utilized in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors to guarantee the quality and integrity of clinical trial data. This helps with regulatory compliance and decision-making procedures.
2. What is the purpose of SAS CDM in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM organizes, cleans, and validates clinical trial data, ensuring its accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) is used in clinical trials to organize, manage, and analyze the data collected during the research process. It ensures data accuracy, consistency, and compliance with regulatory standards, facilitating the efficient and reliable generation of clinical trial reports.
3. Can you explain the role of SAS CDM in data integration?
Ans:
- SAS CDM integrates data from various sources in clinical trials, allowing for a comprehensive view and analysis of the collected data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) plays a crucial role in data integration within clinical trials by consolidating and standardizing diverse data sources.
- It helps harmonize data from various formats and systems, promoting consistency and accuracy in the clinical trial data. This facilitates seamless integration, enabling researchers to analyze and interpret the data effectively for regulatory submissions and decision-making.
4. How does SAS CDM handle data cleaning and validation?
Ans:
SAS CDM employs tools for data cleaning, validation checks, and error identification to ensure high-quality and reliable clinical trial data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) uses various features to handle data cleaning and validation in clinical trials. It includes data cleaning activities such as identifying and resolving inconsistencies, missing values, and outliers. SAS CDM also supports data validation by implementing checks for compliance with predefined criteria, ensuring data accuracy and integrity. Additionally, it enables the creation of validation, editing, and data quality checks to systematically review and clean clinical trial data.
5. What are the key features of SAS CDM?
Ans:
- Data Integration
- Data Validation
- Electronic Case Report Forms (eCRF)
- Clinical Trial Metadata Repository
- Data Cleaning and Query Management
- Audit Trails
- Clinical Data Warehousing
6. How does SAS CDM support regulatory compliance?
Ans:
SAS CDM facilitates compliance with regulatory standards by providing audit trails and validation checks and ensuring data integrity in clinical trials.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) supports regulatory compliance by providing tools and features that help ensure data integrity, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements in clinical trials. It includes features for data validation, audit trails, and electronic submission capabilities, aligning with industry standards and regulations such as CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) and FDA guidelines. This helps organizations maintain high-quality and compliant clinical data throughout the data management lifecycle.
7. Can SAS CDM handle electronic data capture (EDC) systems?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can integrate with EDC systems, streamlining the capture and management of electronic data in clinical trials.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can integrate with electronic data capture (EDC) systems. It supports importing and integrating data collected through various EDC platforms, allowing seamless collaboration between EDC systems and the data management processes within SAS CDM. This integration helps streamline the flow of clinical trial data, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with industry standards.
8. What is SDTM, and how does SAS CDM relate to it?
Ans:
SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) is a standard for organizing and formatting clinical trial data. SAS CDM supports the conversion of data into SDTM format.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) is crucial in supporting SDTM compliance. It helps transform and manage raw clinical trial data into the required SDTM format. SAS CDM facilitates the mapping, transformation, and validation processes to ensure data conforms to SDTM standards. This is essential for regulatory submissions and supports the industry’s goal of standardizing clinical trial data for improved consistency and efficiency in the regulatory review process.
9. How does SAS CDM assist in creating clinical trial datasets?
Ans:
- SAS CDM facilitates the creation of datasets by transforming and standardizing raw data into formats suitable for analysis and reporting.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) enables the creation of clinical trial datasets by providing data integration, transformation, and validation tools.
- It helps organize and standardize data from various sources, ensuring consistency and quality in clinical trial datasets. CDM allows for efficient data cleaning, mapping, and transformation, supporting the generation of analysis-ready datasets for statistical analysis.
10. Differentiate between SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) and ADaM (Analysis Data Model) in the context of SAS CDM.
Ans:
| SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) | ADaM (Analysis Data Model) |
|---|---|
| Organizing and formatting clinical trial data | Creating analysis datasets for statistical analysis |
| Structure of collected data | Data transformation for statistical analysis |
| Defines standard domains for specific types of data | Ensures consistency and reproducibility of analysis |
11. How does SAS CDM handle missing data in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM provides tools for identifying and managing missing data through imputation methods or by implementing specific strategies defined in the study protocol.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) typically employs imputation methods or statistical techniques to handle missing data in clinical trials. These approaches help maintain data integrity and ensure that analyses are conducted with the most accurate and representative information available.
12. What is the role of metadata in SAS CDM?
Ans:
Metadata in SAS CDM describes the structure and characteristics of clinical trial data, aiding in the standardization and understanding of variables and datasets. In SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM), metadata plays a crucial role by providing information about the clinical trial data’s structure, organization, and meaning. It defines data attributes, relationships, and standards, facilitating proper data interpretation, integration, and analysis. Metadata in SAS CDM helps ensure consistency, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements throughout the clinical trial data lifecycle.
13. Explain the concept of data mapping in SAS CDM.
Ans:
- Data mapping in SAS CDM involves defining relationships between source and target variables, ensuring accurate transformation and data integration during the study.
- Data mapping in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) establishes relationships between data collected in a clinical trial and the corresponding variables or fields in the database.
- It defines how raw data from various sources align with the standardized data structures used for analysis.
- Proper data mapping ensures that information is accurately transformed and integrated into the database, maintaining consistency and adherence to protocol requirements during clinical trial data management.
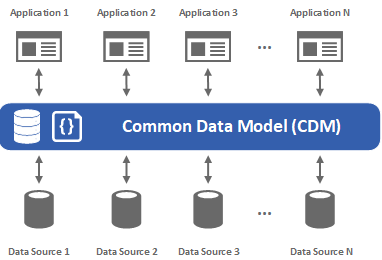
14. How does SAS CDM handle data discrepancies and query management?
Ans:
SAS CDM includes features for detecting data discrepancies, generating queries for resolution, and tracking the status of query resolutions to maintain data quality.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) addresses data discrepancies through a systematic query management process. When inconsistencies or errors are detected, SAS CDM generates queries sent to investigative sites for resolution. The system tracks and manages these queries, ensuring timely resolution and documentation of discrepancies. This proactive approach helps maintain data quality and integrity throughout the clinical trial by resolving issues promptly and providing accurate and reliable study results.
15. Can SAS CDM generate data listings and summary tables?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can generate data listings and summary tables, providing a comprehensive overview of clinical trial data for analysis and reporting purposes.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can cause data listings and summary tables. It leverages SAS programming capabilities to create detailed data listings and summary tables presenting critical clinical trial data information. This functionality aids in the analysis and interpretation of study results, providing valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of the investigational product.
16. What is the role of the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit in SAS CDM?
Ans:
- SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit helps implement and manage CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) standards within SAS CDM.
- The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) helps implement and manage industry standards for clinical trial data.
- It facilitates adherence to standards such as CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) by providing tools to validate, convert, and visualize data based on these standards. The toolkit promotes consistency, interoperability, and compliance with regulatory requirements in clinical trial data management processes
17. How does SAS CDM support collaboration among stakeholders in clinical trials?
Ans:
- SAS CDM facilitates collaboration by allowing different stakeholders, such as data managers and statisticians, to work on the same platform, ensuring data consistency and accuracy.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) supports collaboration among different stakeholders in clinical trials by providing a centralized platform for data management.
- It enables seamless sharing of standardized data and metadata, facilitating communication between clinical research teams, data managers, statisticians, and other stakeholders. Throughout the clinical trial lifecycle, this collaborative environment improves productivity, lowers mistakes, and guarantees all parties involved access to correct and up-to-date information.
18. Can SAS CDM handle adaptive clinical trial designs?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM supports adaptive designs by allowing dynamic changes to the trial protocol and accommodating modifications in data collection and analysis.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can handle adaptive clinical trial designs. Its flexibility and robust programming capabilities allow for adapting data management processes to meet the dynamic needs of adaptive trials. SAS CDM can support adjustments in study design, data collection methods, and analysis approaches as the trial progresses, ensuring efficient and accurate data management in adaptive clinical trials.
19. What is the significance of SDTM in data submission to regulatory authorities?
Ans:
- SDTM provides a standardized format for submitting clinical trial data to regulatory authorities, ensuring consistency and facilitating the review and approval.SDTM is significant in data submission to regulatory authorities because it provides a uniform structure for arranging and submitting data from clinical trials.
- For regulatory assessment, sponsors must frequently submit trial data in SDTM format by oversight agencies like other agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- SDTM ensures consistency and facilitates data exchange, making it easier for regulatory authorities to analyze and assess the safety and efficacy of investigational products during the drug approval process.
20. How does SAS CDM integrate external data sources in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM can integrate external data sources through various means, including data import functionalities, to incorporate relevant information into the clinical trial database.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) integrates external data sources in clinical trials through data mapping and transformation processes. It allows for incorporating diverse external data types, such as laboratory results or electronic health records, into the standardized data structure used in the clinical trial database. By defining explicit mappings and transformations, SAS CDM ensures that external data seamlessly integrates with the trial database, maintaining consistency and quality across all data sources.
21. Can SAS CDM handle data encryption and ensure data security in clinical trials?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM provides features to implement data encryption and ensures data security to comply with privacy regulations and protect sensitive information.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can implement data encryption and ensure data security in clinical trials. It incorporates security measures, including encryption protocols, to protect sensitive and confidential information. This helps safeguard patient data, ensure compliance with privacy regulations, and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of clinical trial data throughout the data management processes.
22. How does SAS CDM handle data versioning and change control?
Ans:
- SAS CDM includes mechanisms for versioning datasets and implementing change control processes, allowing traceability and maintaining data integrity throughout the study.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) typically employs version control mechanisms and change tracking to manage data versioning and changes.
- It maintains a record of different versions of datasets and tracks modifications made during the data management process. This allows for traceability, auditability, and the ability to revert to previous versions if necessary. Effective change control in SAS CDM ensures data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards in clinical trials.
23. What role does SDTM play in data standardization across different studies and sponsors?
Ans:
SDTM facilitates standardization by providing a standard structure for organizing and presenting clinical trial data, enabling consistency across studies and sponsors.SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) is crucial in standardizing data across different studies and sponsors in clinical research. It provides a standard format for organizing and tabulating data, ensuring consistency in the structure and representation of clinical trial information. This standardization facilitates easier integration, analysis, and regulatory data submission, promoting interoperability and harmonization in the pharmaceutical industry.
24 . How does SAS CDM assist in validating clinical trial databases?
Ans:
- Through thorough validation tests, SAS CDM facilitates database validation, guaranteeing the precision and comprehensiveness of the data gathered throughout the clinical trial.
- SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) aids in validating clinical trial databases by offering tools and functionalities to ensure data quality and compliance.
- It provides data validation checks, discrepancy management, and data cleaning features. SAS CDM helps implement and execute validation rules, ensuring the data collected meets predefined criteria and follows regulatory standards.
- This validation process enhances the integrity and reliability of clinical trial data, supporting the overall quality of research outcomes.
25. Explain the concept of data pooling in the context of SAS CDM.
Ans:
- Data pooling in SAS CDM involves combining data from multiple studies or sources to enhance statistical power and generate more robust analyses. In the SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) context, data pooling refers to combining or merging data from multiple studies or sources into a single integrated dataset.
- This integration makes it possible to analyze and examine data from various clinical studies thoroughly. SAS CDM facilitates data pooling by providing tools to standardize and harmonize datasets, ensuring consistency in variables, formats, and structures. This consolidated view of data from various studies enhances the ability to draw meaningful insights, perform cross-study analyses, and make informed decisions in clinical research.
26. What is the significance of CDISC standards in the context of SAS CDM?
Ans:
CDISC standards, such as SDTM and ADaM (Analysis Data Model), promote consistency and interoperability in data management and analysis within SAS CDM. They provide a standardized framework for organizing, collecting, and reporting clinical trial data. Using CDISC standards in SAS CDM ensures consistency and interoperability and facilitates regulatory submissions. This helps streamline the entire data management process, from data collection to analysis, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of clinical trials.
27. Can SAS CDM integrate real-world data (RWD) in clinical trials?
Ans:
- Yes, SAS CDM supports integrating real-world data, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of patient outcomes and treatment effectiveness.
- For incorporating real-world data into clinical trials, SAS offers solutions like SAS Real-World Evidence, which are tailored for managing and analyzing diverse data sources outside traditional clinical trials.
- So, while SAS CDM may not be optimal for handling extensive real-world data integration, other SAS solutions are more suitable for that purpose.
28. How does SAS CDM address data reconciliation challenges in multi-site clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM provides tools for data reconciliation across multiple sites, ensuring consistency and resolving discrepancies to maintain data quality.SAS Clinical Data Integration (CDM) helps address data reconciliation challenges in multi-site clinical trials by providing a centralized platform for managing and integrating clinical trial data. It offers tools for standardizing data formats, defining mapping rules, and automating data reconciliation processes across various sites. This aids in ensuring consistency and accuracy in data, reducing errors, and facilitating easier reconciliation across multiple locations involved in the trial.
29. What are the key considerations when designing data collection forms in SAS CDM?
Ans:
- Data Integrity: Ensure accuracy and completeness.
- User-Friendly Interface: Design for efficiency and minimal errors.
- Compliance: Adhere to regulatory standards.
- Standardization: Use consistent coding and formats.
- Data Relationships: Clearly define element relationships.
- Validation Checks: Implement robust error checks.
- Audit Trails: Include tracking for data modifications.
- Version Control: Manage form updates effectively.
- Data Dictionary: Provide clear element definitions.
- Training: Ensure users understand form usage.
30. How does SAS CDM handle the storage and retrieval of electronic signatures in compliance with regulatory requirements?
Ans:
SAS CDM incorporates features for secure storage and retrieval of electronic signatures, ensuring compliance with regulatory data integrity and authenticity standards.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) typically adheres to regulatory requirements by implementing secure storage and retrieval mechanisms for electronic signatures. It often employs encryption, access controls, and audit trails to ensure data integrity and traceability, meeting regulatory standards like 21 CFR Part 11. Depending on the version and configuration of SAS CDM, specifics could change. It’s best to consult the product manual or contact SAS support for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
31.What is the role of Define-XML in the context of SAS CDM?
Ans:
Define-XML is used to define and document the structure and attributes of clinical trial data collected, facilitating regulatory submission and data interpretation in SAS CDM.SAS CDM often leverages Define-XML to facilitate the exchange of metadata between different systems and tools involved in clinical research, ensuring consistency and interoperability. Define-XML files accompany submission data to regulatory agencies, aiding in the interpretation and validation of the clinical trial data.
32.How does SAS CDM handle data transfers between different phases of a clinical trial?
Ans:
- SAS CDM supports seamless data transfers between different phases by ensuring compatibility and consistency in data structures and formats.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates data transfers between different phases of a clinical trial by providing a structured framework for managing and integrating clinical data.
- It involves processes like data collection, transformation, and validation. SAS CDM supports standard data formats, such as CDISC standards, ensuring consistency and compliance throughout the trial lifecycle. Additionally, it offers tools for data cleaning, standardization, and mapping between different data representations, contributing to the seamless transition of data across trial phases.
33.Can SAS CDM automate the process of generating SDTM domains?
Ans:
- Yes, SAS CDM provides tools for automating the creation of SDTM domains, saving time and reducing manual effort in the conversion process.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can automate the process of generating Standard for the Exchange of Nonclinical Data (SEND) domains.
- It offers tools and functionalities that facilitate the transformation of raw clinical trial data into compliant SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) domains. By utilizing SAS CDM’s features, you can automate the mapping, validation, and generation of SDTM domains, streamlining the process and ensuring adherence to industry standards. This automation helps improve efficiency and reduces the likelihood of errors in the SDTM domain creation process.
34.How does SAS CDM handle discrepancies between electronic and paper-based data collection methods?
Ans:
SAS CDM includes mechanisms to reconcile discrepancies between electronic and paper-based data, ensuring consistency and accuracy in data representation.SAS CDM facilitates the identification of inconsistencies or discrepancies through validation checks and data reconciliation processes. It enables users to compare and reconcile data collected through different methods, ensuring data integrity and consistency. Additionally, SAS CDM supports the implementation of data validation rules and quality checks to identify and resolve discrepancies efficiently during the data management process.
35 .Explain the role of Annotated CRFs (aCRFs) in SAS CDM.
Ans:
Annotated CRFs provide a detailed description of how data collected on Case Report Forms (CRFs) should be mapped to datasets, aiding in data interpretation in SAS CDM.SAS CDM leverages aCRFs to streamline the creation of data validation checks, derivation rules, and data transformations. It helps data managers and programmers understand the relationships between CRF data and the database, facilitating efficient data mapping, cleaning, and validation processes throughout the clinical trial lifecycle.
36.What are the advantages of using CDISC standards like SDTM and ADaM in SAS CDM?
Ans:
- CDISC standards enhance interoperability, streamline regulatory submissions, and improve consistency in data representation and analysis in SAS CDM.Using CDISC standards like SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) and ADaM (Analysis Data Model) in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) offers several advantages.
- These standards enhance data interoperability, facilitate regulatory compliance, and promote efficiency in clinical trial data management. In SAS Clinical Data Management, incorporating SDTM and ADaM standards can enhance data consistency, quality, and overall management throughout the clinical trial lifecycle.
37. How does SAS CDM handle coding of medical terms and adverse events?
Ans:
SAS CDM supports standardized coding systems (e.g., MedDRA, WHO Drug) for medical terms and adverse events, ensuring consistency and comparability across studies.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates coding of medical terms and adverse events using standardized dictionaries like MedDRA and WHO Drug. This helps ensure consistency in data representation across studies. The coding process involves mapping verbatim terms to standard codes for accurate and uniform reporting in clinical trials.
38.Can SAS CDM integrate with external data visualization tools for analysis and reporting?
Ans:
- Yes, SAS CDM allows integration with external data visualization tools to enhance the analysis and reporting capabilities of clinical trial data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can integrate with external data visualization tools for analysis and reporting.
- SAS provides flexibility in exporting data to various formats, allowing compatibility with popular visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, or others. This integration enables users to create compelling visualizations and reports based on the clinical data managed by SAS CDM.
39.How does SAS CDM ensure data traceability throughout the clinical trial lifecycle?
Ans:
SAS CDM maintains data traceability through audit trails, version control, and metadata management, ensuring a complete history of changes made to the data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) ensures data traceability in clinical trials by maintaining an audit trail, version control, and metadata documentation. It tracks changes made to the data, captures who made the changes, and when they occurred, ensuring transparency and compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, SAS CDM facilitates data reconciliation and provides comprehensive metadata for datasets, promoting traceability throughout the clinical trial lifecycle.
40.In what ways does SAS CDM contribute to the efficiency of database lock activities at the end of a clinical trial?
Ans:
- SAS CDM streamlines database lock activities by automating validation checks, resolving discrepancies, and providing comprehensive documentation, expediting the closure of the clinical trial database.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) enhances efficiency during database lock activities by automating data validation checks, facilitating streamlined data cleaning, and supporting efficient query management.
- It allows for easier identification and resolution of data discrepancies, accelerating the review process. SAS CDM’s capabilities in metadata documentation and audit trails contribute to the transparency required for regulatory submissions. Overall, these features help expedite the database lock process at the end of a clinical trial, ensuring a smoother and more efficient closure of the study.
41. How does SAS CDM handle the reconciliation of safety and efficacy data in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM facilitates the reconciliation process by integrating safety and efficacy data, ensuring consistency and accuracy in reporting adverse events and outcomes.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) assists in the reconciliation of safety and efficacy data by providing tools for data integration, validation, and consistency checks. It allows for the comparison and reconciliation of safety and efficacy datasets, ensuring alignment with study protocols and regulatory requirements. Through automation, SAS CDM helps identify and resolve discrepancies between safety and efficacy data efficiently, promoting data accuracy and reliability. This contributes to a comprehensive and reliable dataset for analysis, supporting the overall integrity of clinical trial results
42.Explain the role of the SDTM Implementation Guide in SAS CDM.
Ans:
- The SDTM Implementation Guide provides guidelines on how to structure and standardize clinical trial data in SDTM format, aiding data transformation in SAS CDM.This guide defines the standard variables and domains necessary for representing clinical trial data, facilitating interoperability and data sharing across different systems and organizations.
- SAS CDM leverages this guide to map, transform, and validate data into SDTM-compliant datasets, supporting regulatory compliance and streamlining the submission process for clinical trial data to health authorities.
43.Can SAS CDM generate datasets for analysis based on ADaM standards?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can generate analysis datasets conforming to ADaM standards, ensuring consistency and facilitating statistical analysis of clinical trial data.By adhering to ADaM standards, SAS CDM facilitates the preparation of analysis-ready datasets, supporting efficient statistical analysis and providing a foundation for regulatory submissions. This helps ensure the integrity and reliability of the data throughout the analysis phase of a clinical trial.
44. How does SAS CDM handle the integration of electronic health records (EHR) data in clinical trials?
Ans:
- SAS CDM supports the integration of EHR data, enabling a comprehensive view of patient information and enhancing the analysis of clinical trial outcomes.SAS CDM supports the standardization of diverse data formats and structures from different EHR sources, ensuring consistency and compatibility. Through its data transformation capabilities, it aligns EHR data with the specific requirements of the clinical trial, allowing for a unified and comprehensive dataset.
- By integrating EHR data, SAS CDM enhances the completeness and richness of clinical trial datasets, potentially improving the overall understanding of patient profiles and outcomes. This integration contributes to more robust analyses and facilitates a more holistic view of patient health within the context of the trial.
45. What measures does SAS CDM take to ensure data confidentiality and privacy compliance?
Ans:
- SAS CDM implements data encryption, access controls, and other security measures to maintain data confidentiality and comply with privacy regulations.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) typically follows industry best practices and standards to ensure data confidentiality and privacy compliance.
- This may include encryption protocols for data transmission, access controls, audit trails, and adherence to relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA, depending on the context and jurisdiction. It’s essential to consult SAS CDM documentation and work with your organization’s legal and compliance teams to ensure proper implementation and alignment with specific privacy requirements.
46.How can SAS CDM assist in the implementation of risk-based monitoring (RBM) in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM supports RBM by providing tools for centralized monitoring, data quality checks, and identification of potential risks during the clinical trial.SAS CDM aids RBM in clinical trials through centralized data management, integrated analytics, customized reporting, quality control, protocol adherence monitoring, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring.SAS CDM enhances the implementation of Risk-Based Monitoring in clinical trials by providing comprehensive data management and analytics tools to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively.
47.What role does SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit play in the validation of SDTM datasets?
Ans:
The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit aids in the validation of SDTM datasets by implementing CDISC standards, ensuring compliance and data quality in SAS CDM.SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit assists in validating SDTM datasets by providing tools for checking compliance with CDISC standards, ensuring data consistency, and facilitating the creation of submission-ready datasets for regulatory compliance in clinical trials.
48.Can SAS CDM generate submission-ready datasets for regulatory authorities?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can generate datasets in a format suitable for regulatory submission, meeting the requirements of health authorities like the FDA.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can generate submission-ready datasets for regulatory authorities by ensuring data integrity, compliance with standards, and facilitating the creation of datasets that meet regulatory requirements in clinical trials.
49. How does SAS CDM handle the reconciliation of data collected from different clinical trial sites?
Ans:
SAS CDM provides tools for reconciling data from different sites, identifying discrepancies, and ensuring consistency across the dataset for analysis.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) handles the reconciliation of data from different clinical trial sites by providing tools for centralizing, integrating, and comparing data. It enables cross-site data consistency checks, identifies discrepancies, and supports the resolution of data discrepancies to ensure accuracy and reliability across all trial sites.
50.Explain the role of SDTM domains in SAS CDM and their impact on analysis.
Ans:
- SDTM domains organize data into standardized structures, enhancing the consistency and comparability of data, ultimately facilitating analysis in SAS CDM.SDTM domains represent specific data sets, such as demographics, adverse events, laboratory results, etc. These domains provide a standardized format for presenting data, ensuring uniformity across different studies and sponsors.
- When integrated with SAS for analysis, SDTM domains streamline the process by allowing researchers to analyze data consistently, improving efficiency, and minimizing errors. This standardized structure also aids in regulatory compliance, as it aligns with industry standards endorsed by regulatory authorities like the FDA.
51. How does SAS CDM handle the coding of lab data and ensure standardization across different studies?
Ans:
SAS CDM supports standardized coding for lab data, utilizing coding dictionaries and ensuring consistency across studies through CDISC standards.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) provides tools for coding lab data and ensures standardization across studies through predefined coding libraries and controlled vocabularies. It allows for consistent application of coding rules, facilitating uniformity in data representation. Additionally, SAS CDM supports integration with external coding dictionaries, enhancing interoperability and adherence to industry standards.
52.Explain the process of data reconciliation between clinical and laboratory databases in SAS CDM.
Ans:
Data reconciliation involves comparing and resolving discrepancies between clinical and laboratory databases to ensure coherence and accuracy in SAS CDM.SAS programming language is utilized to manipulate, analyze, and reconcile the clinical and laboratory data efficiently. It is crucial to follow industry standards and regulatory guidelines to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data, especially in clinical research and healthcare settings.
53.What role does CDASH (Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization) play in SAS CDM?
Ans:
- CDASH provides standardized data collection guidelines, promoting consistency in data acquisition and facilitating integration into SAS CDM.
- CDASH (Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization) plays a crucial role in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) by providing standardized data collection conventions. It helps ensure consistency in data collection across clinical trials, making it easier to integrate and analyze data using SAS CDM.
- CDASH standards facilitate efficient data mapping and transformation processes within the SAS CDM framework, ultimately enhancing the overall quality and interoperability of clinical trial data.
54.How does SAS CDM handle the management of data from external vendors and partners in a clinical trial?
Ans:
SAS CDM allows integration of data from external vendors, streamlining the management and validation of data obtained from various sources.SAS CDM typically includes tools for data transformation, validation, and mapping to standard formats, ensuring consistency and compliance with regulatory requirements. This enables efficient collaboration with external vendors and partners, streamlining the process of incorporating their data into the overall clinical trial database. Additionally, SAS CDM often supports data reconciliation processes to identify and address any discrepancies between internally collected data and data received from external sources.
55. Can SAS CDM handle the merging of data from different studies or therapeutic areas?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM supports the merging of data from different studies or therapeutic areas, facilitating a comprehensive analysis of combined datasets.The platform typically supports robust data management practices, enabling users to efficiently merge, validate, and reconcile data from different sources. This capability is valuable for organizations conducting multiple studies or working across various therapeutic areas, as it facilitates a comprehensive view of data across the entire clinical research landscape.
56.What steps can SAS CDM take to ensure data consistency in multi-arm clinical trials?
Ans:
- SAS CDM maintains data consistency in multi-arm trials by implementing standardized processes, validation checks, and cross-arm reconciliation.In multi-arm clinical trials, SAS CDM (Clinical Data Management) can ensure data consistency by implementing standardized data collection processes, thorough validation checks, and utilizing CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) standards for data representation.
- Additionally, employing data reconciliation processes, implementing data review and cleaning procedures, and maintaining clear documentation practices contribute to ensuring data consistency across multiple arms of the trial. Regular training for study personnel and utilizing advanced data management tools can also enhance the overall quality and consistency of clinical trial data.
57.How does SAS CDM handle the pooling of safety data across multiple studies in an integrated analysis?
Ans:
SAS CDM facilitates safety data pooling by ensuring standardized formats and structures, allowing for an integrated analysis of safety outcomes.the software supports data integration through advanced programming techniques, such as merging datasets from different studies, applying statistical methodologies for combining safety data, and performing comprehensive safety analyses across the pooled datasets. By adhering to regulatory guidelines and leveraging SAS programming capabilities, SAS CDM helps ensure a unified and accurate analysis of safety data across multiple studies in an integrated manner.
58. What strategies can SAS CDM employ to ensure proper blinding and confidentiality of study data in clinical trials?
Ans:
- Role-based Access Control: Restrict data access based on user roles.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data during storage and transmission.
- Audit Trails: Monitor and track data access with detailed audit trails.
- Anonymization: Remove or encrypt personally identifiable info.
- Secure Transmission: Use specific channels for data transfer.
- Masking/Redaction: Conceal sensitive info in reports and outputs.
- Data Separation: Physically/logically segregate sensitive data.
- Secure Programming: Follow certain coding practices.
- Regular Audits: Conduct frequent audits to identify breaches.Vendor Compliance: Ensure external vendors adhere to security standards.
59. Can SAS CDM automate the process of generating patient profiles for clinical trial subjects?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM provides tools for automating the generation of patient profiles, offering a comprehensive overview of individual subject data. The software supports data integration through advanced programming techniques, such as merging datasets from different studies, applying statistical methodologies for combining safety data, and performing comprehensive safety analyses across the pooled datasets. By adhering to regulatory guidelines and leveraging SAS programming capabilities, SAS CDM helps ensure a unified and accurate analysis of safety data across multiple studies in an integrated manner.
60.How does SAS CDM handle the conversion of legacy data into standardized formats like SDTM?
Ans:
SAS CDM supports the conversion of legacy data into SDTM formats by applying transformation rules and ensuring compatibility with CDISC standards.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates the conversion of legacy data to standardized formats like Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) through a series of steps. It involves mapping legacy data variables to SDTM domains, defining transformation rules, and executing the conversion process. SAS CDM provides tools and utilities to streamline this process, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
61.Explain the role of the Study Data Reviewer’s Guide (SDRG) in SAS CDM.
Ans:
- The SDRG provides reviewers with a guide to understanding and reviewing SDTM datasets, ensuring consistency and accuracy during the data review process in SAS CDM.The Study Data Reviewer’s Guide (SDRG) in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) serves as a comprehensive reference document for reviewers to assess and understand the structure and content of clinical study data.
- It outlines the expectations for data quality, consistency, and adherence to standards like CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium). SAS CDM integrates the SDRG to aid reviewers in efficiently validating and verifying study data during the review process, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards.
62. How does SAS CDM handle the standardization of adverse event terms and coding across different studies?
Ans:
SAS CDM uses standardized coding dictionaries such as MedDRA to ensure consistent adverse event term representation across various studies.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) addresses the standardization of adverse event terms and coding across different studies by utilizing standardized dictionaries such as MedDRA (Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities) or WHO Drug. The system maps adverse event terms from individual studies to the standardized dictionary terms, ensuring consistency and comparability across studies. This mapping process facilitates the generation of standardized datasets, enabling regulatory submissions and analysis while adhering to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
63. Can SAS CDM incorporate patient-reported outcomes (PRO) data in clinical trials?
Ans:
- Yes, SAS CDM supports integrating and managing PRO data, ensuring its inclusion and accurate representation in clinical trial databases.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) is equipped to incorporate Patient-Reported Outcomes (PRO) data in clinical trials. It provides tools and processes to collect, manage, and analyze PRO data, ensuring its integration with other clinical trial data.
- SAS CDM supports implementing industry standards, such as CDISC PRO standards, to maintain consistency and facilitate regulatory submissions. This enables researchers and clinicians to utilize PRO data better to understand patients’ experiences and outcomes in clinical trials.
64. Explain the role of SAS Clinical Data Integration in conjunction with SAS CDM.
Ans:
SAS Clinical Data Integration complements SAS CDM by providing tools for integrating data from diverse sources into a unified view for analysis and reporting.SAS Clinical Data Integration plays a crucial role in conjunction with SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) by facilitating the integration, transformation, and movement of clinical trial data across the entire data lifecycle. It enables seamless data flow from various sources to SAS CDM, ensuring standardized and well-organized clinical datasets.
65. How does SAS CDM address issues related to data standardization when working with global clinical trials?
Ans:
- SAS CDM addresses global standardization challenges by adhering to CDISC standards, facilitating consistent data representation across international studies.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) addresses data standardization in global clinical trials by providing a platform for consistent data handling.
- It ensures adherence to industry standards like CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) and supports integration with various data sources, promoting uniformity across diverse datasets. This aids in efficient data management, analysis, and reporting, which is essential for the success of global clinical trials.
66. Can SAS CDM support the creation of custom data listings and reports based on specific study requirements?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM allows the creation of custom data listings and reports tailored to the specific requirements of individual clinical trials.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) supports the creation of customized data listings and reports based on detailed study requirements. It provides flexibility in designing outputs tailored to the needs of a particular clinical trial. This capability allows researchers and study teams to generate customized reports, enhancing their ability to analyze and interpret study data effectively.
67. Explain the concept of metadata-driven programming in the context of SAS CDM.
Ans:
- Metadata-driven programming in SAS CDM involves dynamically generating programs and streamlining and automating the analysis and reporting processes. Using metadata, SAS CDM enables a more flexible and dynamic approach to programming.
- Instead of explicitly specifying details in the code, programmers can leverage metadata to define and control the program’s processing steps, data transformations, and other aspects. This approach enhances the code’s reusability, maintainability, and adaptability, allowing for more accessible updates and modifications as metadata changes.
68. How does SAS CDM handle the validation of electronic signatures in compliance with regulatory guidelines?
Ans:
- SAS CDM provides mechanisms for validating electronic signatures, ensuring compliance with regulatory data integrity and security requirements.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) typically follows regulatory guidelines for handling electronic signatures, such as those from the FDA or EMA.
- It employs validation processes to ensure the integrity and authenticity of electronic signatures, adhering to 21 CFR Part 11 requirements. Specific details may vary, so consulting the SAS CDM documentation or contacting SAS support would provide the most accurate and up-to-date information on how it handles electronic signature validation in compliance with regulatory guidelines.
69. Can SAS CDM integrate with clinical trial management systems (CTMS) for streamlined data flow?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can integrate with CTMS, facilitating seamless data flow between clinical trial management and data management systems.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can integrate with Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) to facilitate streamlined data flow between these systems. This integration is essential for efficient collaboration and data sharing across different components of clinical trials. It helps maintain consistency, accuracy, and timeliness in managing clinical trials and data management activities. Integration methods may include data exchange standards, APIs, or other interoperability solutions, depending on the specific capabilities and configurations of the systems involved
70. What role does SDTMIG (SDTM Implementation Guide) play in mapping datasets in SAS CDM?
Ans:
- SDTMIG provides guidelines for mapping datasets to SDTM standards, ensuring consistent data representation and adherence to CDISC standards in SAS CDM. The SDTMIG (SDTM Implementation Guide) is a standardized guide for implementing the Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) in clinical research.
- In the context of SAS Clinical Data Integration (CDI), the SDTMIG provides guidelines and rules for mapping datasets to SDTM domains. It helps ensure consistency and standardization in the representation of clinical trial data, making it easier to exchange and analyze across different systems and studies.
71. How does SAS CDM handle the validation of derived datasets in the analysis process?
Ans:
SAS CDM validates derived datasets by implementing checks and procedures to ensure accuracy and reliability in the analysis phase of clinical trials. Validation in SAS CDM ensures that the derived datasets meet the required standards, follow defined data structures, and align with the intended analysis objectives. Any discrepancies or issues identified during the validation process are flagged for review and correction, helping maintain data integrity and reliability throughout the analysis phase of clinical data management.
72 . How does SAS CDM manage the incorporation of external data standards, such as CDASH, into the overall clinical data strategy?
Ans:
SAS CDM can align with CDASH standards, incorporating them into the data strategy to ensure consistency in data collection and representation across studies. In SAS CDM, data mapping tools are often utilized to align the data collected in CDISC-compliant datasets with the internal data model. This mapping ensures that data collected according to CDASH standards can seamlessly integrate with the overall clinical data strategy. Transformation scripts or processes may be implemented to convert CDASH data structures into the desired format within the SAS CDM environment, maintaining consistency and adherence to internal standards.
73. What are the key considerations in designing a data validation plan for a clinical trial using SAS CDM?
Ans:
Designing a data validation plan involves specifying validation checks, defining acceptance criteria, and ensuring comprehensive data quality in SAS CDM. Creating a data validation plan for a clinical trial using SAS CDM involves considering data quality, consistency, and adherence to regulatory standards. Key considerations include:
- Defining validation checks.
- Ensuring data accuracy.
- Handling missing or inconsistent data.
- Implementing edit checks.
- Validating against the protocol and regulatory requirements.
Regular monitoring and documentation are crucial to maintaining data integrity throughout the trial.
74. How does SAS CDM handle data transfers and exchanges between stakeholders, including sponsors and regulatory agencies?
Ans:
SAS CDM facilitates secure data transfers and exchanges between stakeholders through standardized formats, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates data transfers and exchanges between stakeholders through standardized formats like CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium). It supports data submission to regulatory agencies by generating datasets compliant with regulatory requirements. SAS CDM also provides data mapping, transformation, and validation tools to ensure data consistency. Collaborative platforms and secure data-sharing mechanisms enable seamless communication between sponsors, regulatory agencies, and other stakeholders involved in the clinical trial process.
75. Can SAS CDM support the implementation of risk-based monitoring (RBM) to ensure data quality in clinical trials?
Ans:
- Yes, SAS CDM can be configured to support RBM by providing tools for risk assessment, monitoring key risk indicators, and ensuring data quality in a targeted manner.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can support the implementation of risk-based monitoring (RBM) in clinical trials.
- It offers tools for designing and executing RBM strategies by providing centralized tracking, data visualization, and risk identification capabilities. SAS CDM helps identify potential data quality risks and enables proactive monitoring of key data elements. By leveraging statistical algorithms and visualization tools, it assists in focusing monitoring efforts on high-risk areas, enhancing overall data quality and trial integrity.
76. Explain the role of the Analysis Data Reviewer’s Guide (ADRG) in SAS CDM.
Ans:
The ADRG guides reviewers in understanding and reviewing analysis datasets (ADaM), ensuring consistency and accuracy during the analysis phase in SAS CDM. In SAS CDM, the ADRG promotes consistency and transparency during the data analysis. It helps reviewers understand the nuances of the datasets, ensuring they can accurately interpret and analyze the clinical trial data according to protocol requirements and regulatory standards.
77. How does SAS CDM handle discrepancies between electronic data capture (EDC) systems and the clinical trial database?
Ans:
SAS CDM includes reconciliation processes to identify and resolve discrepancies between EDC systems and the clinical trial database, ensuring data consistency.SAS CDM provides tools for comparing and reconciling data from various sources, identifying discrepancies, and resolving inconsistencies. This may include implementing data validation checks, cleaning, and ensuring data accuracy and integrity. The goal is to harmonize data collected through EDC systems with the clinical trial database, maintaining consistency for accurate analysis and regulatory compliance
78. What steps can be taken in SAS CDM to ensure the reproducibility of analysis results in a clinical trial?
Ans:
- Ensuring reproducibility involves documenting analysis steps, version control, and maintaining an audit trail in SAS CDM to recreate results consistently.
- Document code and steps.
- Use version control (e.g., Git).
- Standardize programming practices.
- Ensure data traceability.
- Leverage metadata for information.
- Modularize code for readability.
79. How does SAS CDM integrate data from biomarker assays and genetic studies in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM supports integrating data from biomarker assays and genetic studies, ensuring comprehensive analysis and representation of patient characteristics.SAS Clinical Data Integration (CDM) is a complete solution for managing clinical trial data. It supports integrating data from various sources, including biomarker assays and genetic studies. SAS CDM facilitates the mapping, transforming, and loading of diverse data types into a unified format, ensuring consistency and quality in clinical trial datasets. Specific details on handling biomarker assays and genetic studies depend on the project’s requirements and how data is structured. It’s recommended to consult SAS documentation or seek guidance from SAS support for more precise information tailored to your use case.
80. Explain the role of CDISC ADaM standards in SAS CDM and their impact on statistical analysis.
Ans:
- CDISC ADaM standards guide the structure and content of analysis datasets in SAS CDM, facilitating consistency and aiding in the statistical analysis of trial data.
- CDISC ADaM (Analysis Data Model) standards play a crucial role in SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) by providing a standardized framework for organizing and formatting analysis datasets. This ensures consistency and facilitates the integration of data across different studies.
- In SAS CDM, the ADaM standards impact statistical analysis by promoting a structured and standardized representation of analysis datasets.
81. Can SAS CDM accommodate data from early-phase clinical trials with adaptive designs and frequent protocol amendments?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can adapt to the dynamic nature of early-phase trials by accommodating frequent protocol amendments and changes in the study design. Adaptive designs allow for modifications to the trial protocol based on interim data analysis, and SAS CDM provides the flexibility to manage and integrate data from such adaptive trials. It can effectively handle changes in study design, treatment arms, and data collection methods.
82. How does SAS CDM handle data transformation and normalization for different data sources in a clinical trial?
Ans:
- SAS CDM employs data transformation techniques to normalize and standardize data from various sources, ensuring consistency and comparability.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates data transformation and normalization in clinical trials by providing tools for standardizing, cleaning, and integrating data from various sources.
- It supports transforming raw data into a consistent format, ensuring uniformity across diverse datasets. This involves data cleaning, coding, and deriving variables to meet regulatory standards. SAS CDM employs a comprehensive approach to handle various data sources, ensuring data quality and compliance in clinical trial processes.
83. Can SAS CDM be integrated with electronic lab notebooks (ELN) for streamlined data capture and management?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can integrate with ELN systems to streamline data capture, ensuring efficient management and analysis of laboratory data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can be combined with Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN) to enhance data capture and management in clinical trials. This integration facilitates streamlined workflows, allowing seamless data transfer between ELN and SAS CDM. By connecting these systems, researchers can optimize data collection, ensure data integrity, and improve overall clinical trial data management efficiency.
84. Explain the role of the Analysis Results Metadata (ARM) in SAS CDM and its impact on traceability.
Ans:
ARM provides metadata that describes the relationships between analysis results and their source data, enhancing traceability and transparency in SAS CDM. By documenting this information, ARM enhances traceability, making understanding how analysis results were derived easier. It provides a comprehensive record of the analytical processes, contributing to regulatory compliance and auditability. ARM in SAS CDM helps maintain a transparent and well-documented trail of data transformations and analysis, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of clinical trial results.
85. How does SAS CDM handle harmonizing data collected from countries with varying regulatory requirements?
Ans:
- ASAS CDM adheres to global standards, and during data collection, it accommodates country-specific regulatory requirements, ensuring harmonization in multinational trials.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates the harmonization of data from diverse sources by providing a comprehensive data collection, standardization, and integration platform.
- It supports mapping data elements to common standards, ensuring consistency across different countries and regulatory requirements. The system allows customization to accommodate specific data formats and requirements, enabling efficient cross-country data management and analysis.
86. What are the challenges and strategies in SAS CDM when dealing with adaptive design clinical trials?
Ans:
Challenges may include evolving data structures. Strategies in SAS CDM involve flexible database designs and adaptive programming for changing trial requirements. Challenges in SAS CDM for adaptive design clinical trials include dynamic protocol changes and data complexity. Strategies involve:
- Implementing flexible data structures
- Adaptive data management plans
- Utilizing SAS tools for real-time data integration and analysis
Continuous collaboration between data managers and statisticians is crucial to adapt to evolving trial designs, ensuring proper handling of data updates and maintaining regulatory compliance throughout the trial.
87. Can SAS CDM support integrating imaging data, such as radiology images, in clinical trials?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM can integrate imaging data, allowing for the comprehensive analysis and inclusion of radiology images in the clinical trial dataset.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can support integrating imaging data, including radiology images, in clinical trials. It facilitates the management, standardization, and analysis of diverse data types, ensuring that imaging data can be effectively incorporated into the clinical trial data set. This integration helps researchers and clinicians make informed decisions based on a comprehensive clinical and imaging data understanding.
88. How does SAS CDM manage the reconciliation of data collected through patient diaries and electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO)?
Ans:
- SAS CDM reconciles data from patient diaries and ePRO systems, ensuring consistency and accuracy in capturing patient-reported information.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) supports the reconciliation of data collected through patient diaries and electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO) by providing data validation and cross-checking tools.
- It allows data managers to compare information from different sources, identify discrepancies, and implement validation checks to ensure consistency. The system’s flexibility enables the customization of reconciliation processes to meet specific study requirements, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of patient-reported data in clinical trials.
89. Explain the role of CDISC Controlled Terminology in SAS CDM and its impact on data standardization.
Ans:
CDISC Controlled Terminology provides standardized definitions for clinical trial concepts, promoting data standardization and consistency in SAS CDM. The impact is significant in terms of data standardization. Using CDISC Controlled Terminology in SAS CDM helps maintain consistency, facilitates interoperability, and streamlines the submission process to regulatory authorities. It ensures that data collected in different studies align with established industry standards, enhancing the quality and comparability of clinical trial data.
90. How can SAS CDM handle integrating data from wearables and mobile health devices in clinical trials?
Ans:
- SAS CDM supports integrating data from wearables and mobile devices, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis of patient-generated health data.SAS Clinical Data Integration (CDM) can handle data integration from wearables and mobile health devices in clinical trials by providing a platform for data collection, transformation, and analysis.
- It supports various data formats and allows for harmonizing diverse data sources. Additionally, SAS CDM facilitates the creation of standardized datasets, ensuring consistency and compliance with regulatory requirements in clinical trials involving wearable and mobile health device data.
91. In what ways does SAS CDM contribute to the efficiency of clinical trial data review processes?
Ans:
SAS CDM enhances data review efficiency by providing tools for automated checks, facilitating quicker identification and resolution of data discrepancies during review processes. SAS CDM streamlines the clinical data review process by integrating, standardizing, and automating various aspects, leading to more efficient and reliable clinical trials.
92. How does SAS CDM handle the reconciliation of data collected from central and local laboratories in a multi-site trial?
Ans:
- SAS CDM reconciles data from central and local laboratories by implementing processes to ensure consistency and accuracy across diverse data sources.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) facilitates the reconciliation of data from central and local laboratories in multi-site trials by providing tools for data integration, validation, and consistency checks.
- It allows for mapping and standardizing data formats from various sources, ensuring uniformity. Additionally, SAS CDM supports the creation of reconciliation reports to identify and resolve discrepancies between central and local laboratory data, enhancing data quality and integrity in multi-site trials.
93 . Can SAS CDM automate data quality metrics generation for ongoing clinical trial data monitoring?
Ans:
Yes, SAS CDM includes features to automate the generation of data quality metrics, supporting ongoing monitoring and ensuring high-quality clinical trial data.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) can automate data quality metrics generation for constant clinical trial data monitoring. It provides features to define and set up data quality checks, allowing for automated validation against predefined criteria. SAS CDM can generate reports and metrics, helping to monitor data quality throughout the clinical trial, identify discrepancies, and facilitate timely corrective actions. This contributes to the overall integrity and reliability of the clinical trial data.
94. Explain the role of SDTM Synch in SAS CDM and its significance in data integration.
Ans:
SDTM Synch in SAS CDM facilitates data integration by harmonizing SDTM domains, ensuring compatibility and consistency in the representation of clinical trial data. In clinical data management, SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) is a standard for organizing and formatting data to facilitate regulatory submission. Suppose there have been updates or new features introduced. In that case, I recommend checking the latest SAS documentation or contacting SAS support for the most accurate and up-to-date information on any “SDTM Synch” feature in SAS CDM and its role in data integration.
95. In what ways does SAS CDM contribute to improving data quality in clinical trials?
Ans:
SAS CDM improves data quality by implementing robust validation checks, identifying discrepancies, and supporting data cleaning processes to ensure accurate and reliable results.SAS Clinical Data Management (CDM) improves data quality in clinical trials through robust data validation checks, standardized data formats, and efficient data cleaning processes. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and completeness of clinical trial data, ultimately enhancing the reliability of study results.

