
- SAS is a leader in business analytics. Through innovative analytics it caters to business intelligence and data management software and services. SAS transforms data into insight which can give a fresh perspective on business.
- Unlike other BI tools available in the market, SAS takes an extensive programming approach to data transformation and analysis rather than a pure drag drop and connect approach. That makes it stand out from the crowd as it gives much finer control over data manipulation. SAS has a very large number of components customized for specific industries and data analysis tasks.
What is SAS?
- SAS (Statistical analysis system) is one of the most popular software for data analysis. It is widely used for various purposes such as data management, data mining, report writing, statistical analysis, business modeling, applications development and data warehousing. Knowing SAS is an asset in many job markets. It is tagged ‘leader’ in Advanced Analytics Platforms as per Gartner 2019 Magic Quadrant for Data Science & Machine Learning Platforms.
Why SAS is popular in job market?
SAS has over 40,000 customers worldwide and holds largest market share in advanced analytics. It has been tagged ‘leader’ consistently for last 6 consecutive years in advanced analytics platforms. In finance (BFSI) industry, SAS retains No. 1 spot and is being used as a primary tool for data manipulation and predictive modeling.
- Data Security – Because of unparalleled data security provided by SAS software, it is leading the analytics software industry in BFSI sector.
- Tech Customer Support – SAS provides one of the best tech support. If you are stuck in anything related to SAS whether it is installation related issue or clarity in any of SAS functions and procedures, they have both online and offline community to support you.
- Detailed Documentation – SAS documentation is very detailed as compared to open source software like R and Python.
- Memory Management – SAS can store datasets on hard drive and process bigger data set than size of your RAM.
- Stable Software more important than cost of software license : All the functions and procedures of previous software version are supported in new SAS versions. Cost of software license is a peanut to a bank or pharmaceutical company.
- Legacy System – Many banks have been using SAS for last 20-30 years and they have automated the whole process of analysis and have written millions of lines of working code. To convert all the stable reporting system from SAS to R/Python, it may require significant additional cost.
SAS Modules
When you install SAS software, it has several in-built modules which are designed for various analytics and reporting purposes. See some of the common SAS modules or components.
- Base SAS – It is the most common SAS module. It is used for data manipulation such as filtering data, selecting, renaming or removing columns, reshaping data etc.
- SAS/STAT – It runs popular statistical techniques such as Hypothesis Testing, Linear and Logistic Regression, Principal Component Analysis etc.
- SAS/ACCESS – It lets you to read data from databases such as Teradata, SQL Server, Oracle DB2 etc.
- SAS/GRAPH – You can create simple and complex graphs using this component.
- SAS/ETS – You can perform time series forecasting such as ARIMA, Exponential Smoothing, Moving Average etc. using this module.
How to download and install SAS Software
SAS Software is available for free. It’s not a trial version but a complete software with almost all the functionalities of paid enterprise version of SAS. There are following two ways you can access SAS software.
1. SAS University Edition
- Installation Required
- Run on local machine (laptop / Desktop)
- No Internet Required
2. SAS OnDemand for Academics
- No Installation Required. Set up your account by registering yourself
- You can access it from anywhere as it is run on cloud
- Internet Required
- Don’t go by software name ‘Academics’. It is available for everyone not just college students
These two lessons provides step by step detailed documentation on how to download and install SAS software .
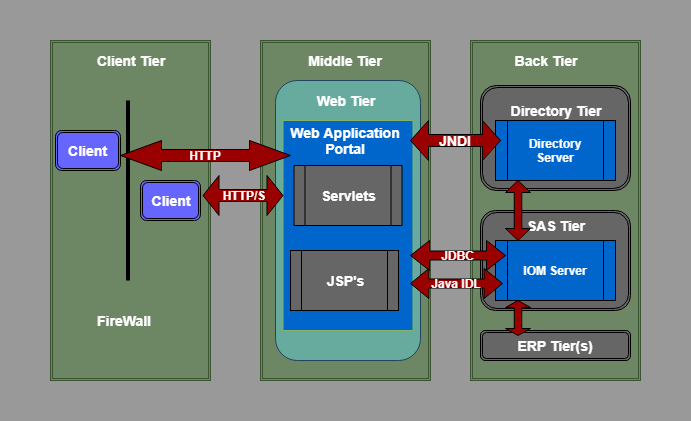
SAS Intelligence Platform ArchitectureSAS Intelligence Platform Architecture is designed to access large numbers of data efficiently, as well as provides timely intelligence to a great number of users simultaneously.The platform follows a three-tier architecture that enables you to distribute functionality in computer resources so that each type of work can be done by those resources that are most suitable for the job.You can easily examine the architecture to determine whether it meets the demands of your workload or not. For a large company, tiers can be installed in several machines with different operating systems, and for demonstrations, prototyping or very small enterprises, all the tires can be installed on a single machine.
- As shown in the following SAS Architecture Diagram, the SAS Information Delivery Portal is implemented using a three-tier architecture. This architecture has proved to be highly effective for developing and deploying enterprise applications.
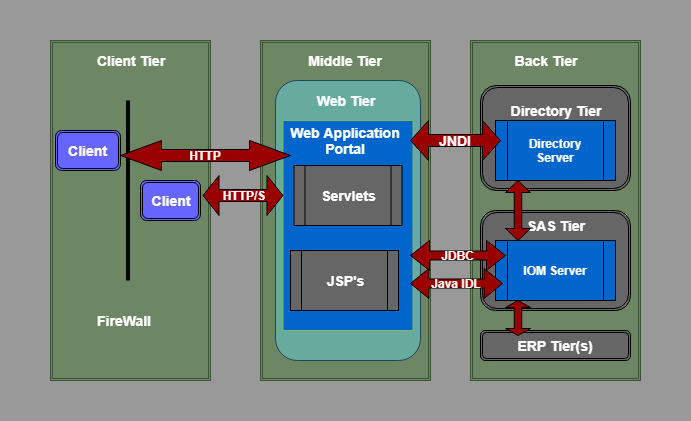
Architecture Components of SAS software are listed below.
Client Tier
- The client tier is used to view the portal and its content. It includes all the components that are used to view the portal and content. The client tier includes a web browser that is used to interact with the portal over HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) OR HTTP/S (HyperText Transmission Protocol, Secure). These HTTP or HTTP/S protocols makes the SAS Information Delivery Portal “firewall friendly.” The portal can be deployed anywhere on the network and users can access it from any internet connectivity like corporate intranet, extranet, or public internet.
- Depending on the content, the client can also use one or more standard desktop applications such as Adobe Acrobat Reader or Microsoft Excel. These applications are used in the process of view content. The content is streamed by the servlets in the middle tier of the portal.
- When the web browser receives such content that it does not know how to present it, it looks at the mime-type of content and tries to find a viewer that knows how to display it. Standard Web browser functionality redirects the stream of content to the appropriate viewer for displaying. Once the content comes under one of these applications, the user can process it locally or save it to disk.
- There is also another optional client application that is the SAS Package Reader. SAS Package Reader is part of the SAS Publishing Framework. The Package Reader enables the user to view and manage the contents of a SAS package off-line, independent of the portal Web application.
Middle Tier
- The middle tier is a center of SAS architecture which provides a centralized access point for enterprise information. All direct access to content is processed by the components that are operating in this tier. This design point offers several advantages.
- By separating business logic from display logic, you can use different clients to take advantage of logic at the middle tier. One more advantage is that the centralized point of access makes it easy to implement security rules, administer the portal and manage code changes.
The following functions are hosted by the middle tier:
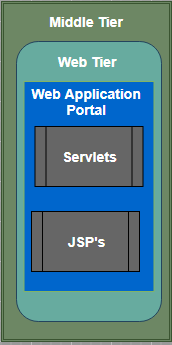
Web Tier
- The first part of the middle tier is the web tier that contain Web Application Portal for SAS Information Delivery.
Web Application Portal
- SAS Information Delivery Portal is a collection of web applications, Java Servlets, JSP, JavaBinx and other sections and resources. These components work together to access the information stored in the Enterprise Directory and present a customizable interface for the user.
Servlet container
- The servlet container or servlet engine is responsible for the management of the SAS Information Distribution Portal web application. Servlet Container or engine provides a runtime environment that supports deployment, concurrency, life-cycle management, and other services for Java components.
Web server
- The web server provides services for the servlet engine. For example, the servlet engine depends on the HTTP server so that it can provide HTTP message handling. Web servers can also be used to host web sites that can be accessed through the portal.
Back Tier
- The back tier is the third and last part of SAS architecture. This tier provides run time environment to Data Servers and Compute Servers. A compute server can also have business objects. For example, SAS IOM servers contain SAS stored processes that analyze the data and summarize the results. As shown in the above figure, the SAS Information Delivery Portal uses standard interfaces like JDBC and Java IDL to communicate and access data from IOM servers.
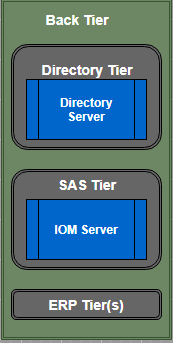
- Back tier contains two servers one is IOM Server that we have explained above, and another is the Enterprise Directory Server. According to the description of the Single Access Point for Enterprise Information, the Enterprise Directory Server stores metadata about the content that is located in the entire enterprise. The directory does not have content, and it contains only metadata that describes it. It contains the location of the information and how to access it, and how it relates to other content items. Web application portal uses JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) to access the enterprise directory server.
- Back Tier does not necessarily translate into additional hardware platforms. For small implementation, these servers can run on a machine similar to a web server. On the other hand, a large enterprise ca has many compute and data servers and can be an enterprise directory dat is distributed on many platforms. The architecture of the SAS Information Delivery Portal gives you the flexibility to distribute these functions as per the need.
Top 7 Features of SAS Programming
These are the 7 key features of SAS Programming Language:
1. Strong Data Analysis Abilities
- The first SAS feature is that SAS Programming has an ability of Strong Data analysis, as discussed below.
- It’s like a complete package for the stream of the data analysis. Its analysis acumen ranges from simple statistics to the advanced level. For instance, it plots bar graphs from the provided data to compute a correlation between complex SAS data sets.
- The best part about SAS is the inbuilt libraries. These contain all the necessary packages required for analyzing and reporting data.
2. Flexible 4 Generation Programming Language (4GL)
The important feature of SAS is that it is a 4GL programming language.
- SAS syntax is easy-to-learn. Teh code is like statements. These statements act as clear and concise instructions to teh systems.
- SAS has reduced coding for common application wif its inbuilt libraries. It provides an opportunity to modularize our job. It is user-friendly for non- programming users as well.
- SAS is an interactive language. Its log window is like a mirror that keeps instructing the user. It provides notes and marks error.
- It also has DS2, which helps in data manipulation. Complex data can be manipulated at its location in teh database.
3. SAS Studio
SAS Studio is unique among SAS features.
- It is easily accessible from any device with any web browser. There is no client installation required. All libraries and data files of the SAS program can be accessed through any web browser.
- It is very instructive in nature. Autocomplete feature prompts us various procedures as soon as one starts typing. Pop up syntax and parameter list is displayed for further guidance.
- It also helps you add and create individual code snippets and add it to the snippet library.
- We can point and click the interface; it guides us throughout the analysis process at various levels.
- Check out features of SAS Simulation Studio
4. Support for Various Types of Data Format
Support for the various data format is another feature of SAS.
- SAS language has the ability to read data from any kind of file, from any format and even from files with missing data.
- SAS provides support for SQL. It has a huge database of character encoding; there is full support for most widely used languages.
- It also maintains code singularity, so that SAS works with data in multiple languages.
5. Management
SAS Management is one of teh important features of SAS.
- SAS environment manager alerts, monitors and manages the analytics environment.
- Extended Java Graphical user interface administers SAS tasks in SAS Management Console.
- We can also completely execute a failed program in restart mode. It resumes from the same step where the program failed.
- The XML engine has a variety of functions like import and export of XML documents and creating XML Maps.
- Application Response Measurement interface looks into diverse applications and checks for the availability of transactions.
6. Report Output Format
SAS has the ability to display analytical results and number of reporting choices.
- High-quality graphics in Base SAS 9.4 are, ODS statistical graphics, ODS Graphics Designer and Editor etc.
- We can save and create reports in a standard format like RTF, PowerPoint, and pdf. We can also save them as ebook and I–book. It gives us the luxury of visual analytics.
- We can customize output according to the hierarchy of needs of the customers. The output can be ported to various places.
- Know more about SAS ODS (Output Delivery Systems)
7. Data Encryption Algorithms
- SAS makes sure that security maintains immaterial of how we grant access. SAS/SECURE is a security feature in SAS 9.4. We can also encrypt SAS data on disks through various algorithms.
- So, this was all about SAS features.
Features of SAS
- SAS is teh pioneer in data analytics because of its beneficial features. There are several key features that makes SAS superior in business analytics.
- We can transport SAS in the various computing environment, and it works exactly the same on all platforms, except for an interactive window.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SAS
Below we will discuss the benefits of learning SAS Softwares and limitations of SAS in detail.
Advantages of SAS
1. Easy to learn
- SAS syntax is very easy to learn. It can be learned easily by anyone without any programming skills. Coding is in teh form of simple statements. It’s like instructing a machine wat to do.
2. Ability to handle large database
SAS TEMPhas a strong ability to handle large database very easily.
3. Easy to debug
- SAS is a very comprehensible language. The process of debugging is easy. We can understand and correct the error that the log window clearly states.
4. Tested algorithms
- Developers thoroughly test and analyze the algorithm implemented in the SAS program. Every version of SAS is first tested in a controlled environment, before released. This is possible because SAS is a closed source language.
5. SAS Customer support
- SAS belonging to an organization performs proper monitoring. It is like a complete organization. It has very spontaneous customer support. As SAS is a closed source tool, it can only be edited by the SAS organization. No external adulteration is possible. SAS customer support handles all the problems.
6. Data Security
- Extending the above point, data in SAS is completely secured. We cannot extract, in case of office use wifout a license. Data security prevents it from manipulation. And dis is the reason for its popularity in the corporate world. SAS is a primary tool for many big companies. Being a close source, the company’s data is confidential here. Only freelancers use R. It is open source, theirfore, data security is not guaranteed. SAS is preferred professionally over any other language used for analysis.
7. SAS GUI
- SAS is one such language that has made statistical computing easier for non-programming users. It has an amazing Graphical User Interface (GUI). SAS user interface has various tools like graphs, plots, and a highly versatile library.
8. Nice Output
- SAS has evolved over a long period of time. It has a nice formatted output, one which is easily comprehensible.
9. Huge Job Prospects
- The fact why SAS is being used for a very long time in the industry is the huge job prospects. Professionals learn SAS as a prerequisite to enter the analytics industry. One who commands SAS can learn R and Python easily. It is the market leader in the analytics industry.
- Make a career in SAS technology – Explore SAS Careers Opportunities
b. Disadvantages of SAS
Below are some of the major limitations of SAS Programming:
1. Cost
- One major disadvantage of SAS is the cost. Being in a closed environment, it is complete software in itself. A person cannot use its all applications without a proper license.
2. SAS is not open source
- R has always implemented a new algorithm related to machine learning more quickly than SAS. The main reason is dat anyone can operate R as it is open source, but dis not true for SAS. SAS works in a closed environment.
- So, the algorithms dat are in SAS procedures are not for the common use of the public. They are available in the licensed version. They are not available openly for public research.
3. Lack of graphic representation
- R has a greater availability for advanced graphics. Its graphics presentation is far more vivid and compatible TEMPthan SAS. It has more descriptive plots, graphs, and diagrams.
- Learn about different types of Scatter Plots in SAS.
4. Difficult Text Mining
- Text mining is free in R, but in SAS, it uses SAS enterprise. Text mining means extracting information from text. It’s like deciphering a written code. It tells you what the written text can infer in terms of decision making. It is the process in which text converts to data for decision making and analysis.
5. Difficult than R
- SAS is more of a procedural language in comparison to R. It has more lines of codes TEMPthan R. We can more quickly apply new innovations like statistical learning and machine learning in R TEMPthan in SAS. Many packages that are free in R are chargeable in SAS. For example – Time series forecasting (SAS/ETS), Text mining, etc.
- So, this was all about SAS Advantages and Disadvantages. Hope you like our explanation.
SAS Program Structure – Steps Involved in a SAS Program
- In our last SAS Programming tutorial, we have seen SAS user interface and today we will talk about SAS program structure, steps involved in program structure of SAS Programming: SAS data step, PROC Step in SAS. Lastly, we will see some basic differences between SAS DATA and SAS PROC in brief.
Let’s now begin with the structure of SAS Program.
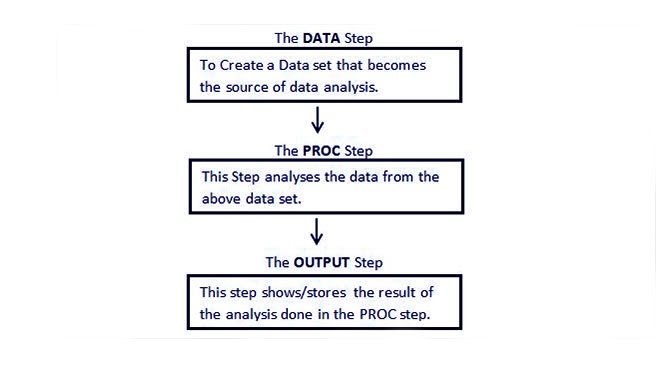
1. SAS Program Structure
- Before you run an analysis, write a report, before you do anything with your data, SAS must be able to read your data. For data to be analyzed by SAS, it first has to be in the form of a dataset. SAS DataSet is the organization of data values in a table in the form of rows and columns. The main components of a SAS program are the DATA step and the PROC step.
- Below is a diagrammatical representation of steps involved in the structure of the SAS Program.
- Here, is a simple program that converts kilometers to meters inside a SAS DATA step and prints the results in a SAS PROC step:
DATA distance;
kilometers = 23; <===== DATA STEP
meters = 1000*kilometers;
PROC PRINT DATA = distance;
Run; <====== PROC STEP
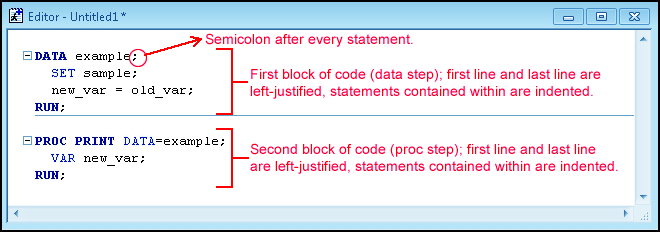
Let us examine each SAS component in detail.
i. SAS DATA Step
This step involves loading the required data set into SAS memory.
- A DATA step reads and modifies data and starts with the keyword DATA. This keyword is followed by a name that you make up for a SAS data set. The DATA step above produces a SAS data set named DISTANCE.
The SAS DATA Step is used for the following purposes:
- Getting input data into a SAS dataset.
- Editing- checking for any errors in the data and correcting them.
- Creating new SAS data sets from existing ones by merging and updating the old data sets.
- Data manipulation such as updating, modifying or rearranging data in a SAS dataset.
Syntax:
- DATA data_set_name; #Name of the data set.
- INPUT var1,var2,var3; #Defines the variables in this data set.
- NEW_VAR; #Creates a new variable.
- LABEL; #Assign labels to variables.
- DATALINES; #Enters the data.
- RUN;
ii. SAS PROC Step
- The beginning of all procedures in SAS starts with a PROC statement in which the keyword PROC is followed by the name of the procedure (MOD, PRINT, Proc SORT, or Proc MEANS, for example). In this step, a SAS built-in procedure is invoked for analyzing the data. Just like the recipe is followed in a sequential manner, in SAS we use basically the same statements every time.
Syntax:
- PROC procedure_name options; #The name of the proc.
- RUN;
iii. SAS OUTPUT Step
- An end of a step occurs when SAS comes across a new step which is marked by a DATA or PROC statement and a RUN statement. RUN statements tell SAS to run all the preceding lines. RUN statements, however, are not part of a DATA or PROC step.
- In the SAS program above, SAS comes to know that the SAS DATA step has ended when it comes to the PROC statement in the next line. The PROC step ends with a RUN statement, which means the program has ended.
Difference Between DATA Step and PROC Step
Here, are some basic differences between SAS DATA Step and PROC steps in SAS:
| DATA step | PROC step |
|---|---|
| They always Begin with DATA statements | They always begin with PROC statements |
| Read and modify data | Perform specific analysis on data |
| Create a SAS data set | Produce results or report |
Conclusion
- Hence, although a typical SAS program starts with a SAS DATA step to input data and then passes that data to a PROC step in SAS, it is not a hard and fast rule. Like you can stack building blocks in any order, you can arrange DATA and PROC steps in any order. The SAS program has the flexibility to contain either only DATA steps or only PROC steps.






