
- Introduction to SAP MM
- Audience
- Prerequisites
- Features of SAP MM
- Screen Navigation
- Special Procurement
- SAP Implementation Guide
- Menu path for MM Configuration
- Procurement cycle
- Configurations
- Conclusion
- SAP is an enterprise resource planning software that was designed to manage resources, information, and activities that are required to finish business processes like procurement and managing orders, billing of orders, and management of human resources. SAP applications work with real-time data.
- It’s the power to be configured consistent with the requirements of the business. It allows a business to form rapid changes in its requirements through a standard set of programs. This tutorial adopts a step-by-step approach to acquaint the readers with the SAP MM environment and the way to form good use of its features. it’ll also help learners to perform procurement of stock materials in SAP.
- SAP MM is one of the modules of SAP that contracts with material management and stock management.
- Material Management as a process provides no need for materials or any gaps within the store chain process of the community. SAP MM revs the procurement and material management activities, making the business run smoothly with the whole time and cost-efficiency.
- It bargains with collecting the materials (products and/or services) and resources of a company to rev productivity and lower costs. At an equivalent time, SAP MM is sort of adaptable to adopt changes that are regular in any enterprise environment.
- It bargains with the Procurement Process, Master Data (Material & Vendor Master), Account Resolution & Valuation of fabric, Inventory Management, Invoice Verification, Material Requirement Planning, etc.
- When a client purchases SAP, it comes during a CD within the sort of software. When SAP is first installed, it’s its standard setup that must be configured consistent with the requirements of the client, i.e., organization.
- Configuration of SAP is completed with the assistance of an implementation guide, referred to as IMG. it’s wont to add fields, to vary field names, to switch dropdown lists, etc. to regulate consistent with the functionality of a corporation. IMG is where we define the enterprise structure and other settings that are required for the functioning of SAP consistent with the wants of a corporation.
- SAP Customizing Implementation Guide (IMG) ⇒ Enterprise Structure ⇒ Definition
- SAP Customizing Implementation Guide (IMG) ⇒ Enterprise Structure ⇒ Assignment
- SAP Customizing Implementation Guide (IMG) ⇒ General ⇒ Material Master
- SAP Customizing Implementation Guide (IMG) ⇒ Materials Management
- Determination of Requirement
- Creating order
- Posting Goods Receipt
- Posting Invoice
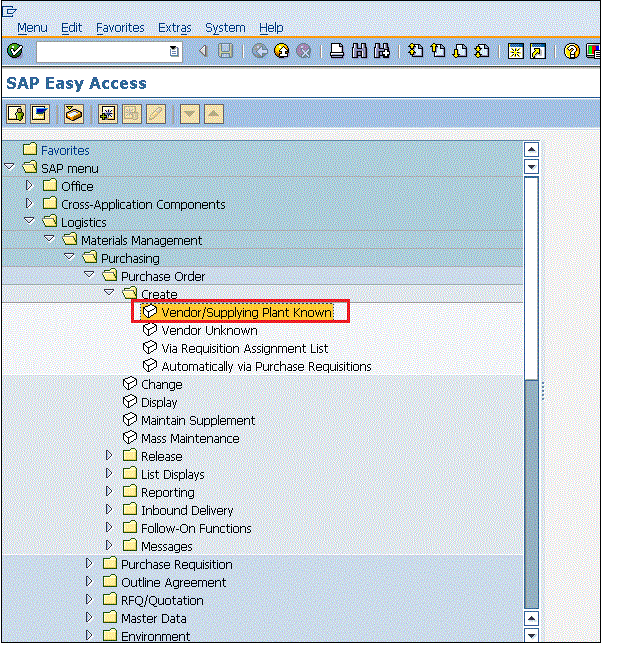
- Logistics ⇒ Materials Management ⇒ Purchasing ⇒ order ⇒ Create ⇒ Vendor/ Supplying Plant Known
- TCode: ME21N
- Invoice/Delivery Tab (Provide the tax code, Payment terms and conditions, and incoterms)
- Assignment Tab (Provide a legitimate G/L code, business area, and WBS element)
- Click on Save. a replacement order is going to be created.
- IMG ⇒ Logistic General ⇒ Material Master ⇒ Field Selection ⇒ Assign Fields to Field Selection Groups
- TCode: OMSR
- Step 1 − On the Show IMG screen, choose Assign Fields to Field Selection Groups by observing the overhead path.
- Step 2 − Select the entry during which you would like to form the changes.
- Step 3 − Here you’ll change the properties of the fields as hidden, display, required entry, or optional entry. Click on Save. Field Groups are now set with the specified field entries.
- IMG ⇒ Logistic General ⇒ Material Master ⇒ Field Selection ⇒ Maintain Field Selection for Data Screens
- TCode: OMS9
- IMG ⇒ Logistic General ⇒ Material Master ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Maintain Company Codes for Materials Management
- TCode: OMSY
- IMG ⇒ Logistic General ⇒ Material Master ⇒ Basic Settings ⇒ Define Attributes of System Messages
- TCode: OMT4
Introduction to SAP MM:
Audience:
This tutorial has been designed for beginners without prior exposure to materials management. With the customer demands changing rapidly, this tutorial is going to be especially useful for those that want to find out the way to manage the availability chain management side of the business using SAP so that market demands are often met within the shortest possible time.
Prerequisites:
Basic knowledge of ERP concepts will assist you in understanding the concepts of the SAP Material Management System described during this tutorial.
Features of SAP MM:
The features of an SAP MM system are as follows −

Screen Navigation:
The first step to knowing SAP is to possess a basic knowledge of its various screens. the subsequent sections describe the way to navigate through the screens available in SAP and the way to use the functionalities of the quality toolbar.
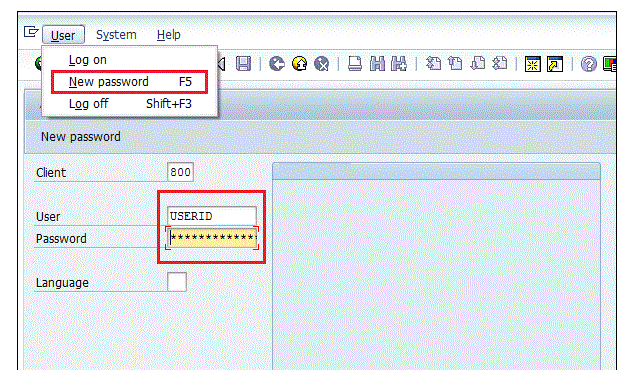
Login Screen
Log on to the SAP ERP server. The SAP login screen will prompt you for the User ID and therefore the Password. Provide a legitimate user ID and password and press enter. The user id and password are provided by the supervisor. The login mesh seems as follows −
Standard Toolbar Icon
The subsequent screenshot displays the toolbars unrestricted on the SAP screen. −
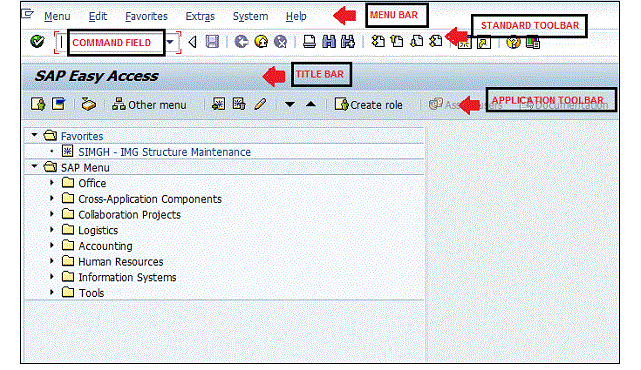
Menu Bar − The menu bar is the top line of the dialog window within the SAP system.
Standard Toolbar − This toolbar includes standard functions like save, top of the page, end of the page, page up, page down, print, etc.
Title Bar − The title bar displays the name of the application/business process you’re currently in.
Application Toolbar − Application-specific menu choices are open on this toolbar.
Command Field − to start a business application without steering through menu transactions, some logical codes are given to the business processes. Transaction codes are documented within the command field to create an application now.
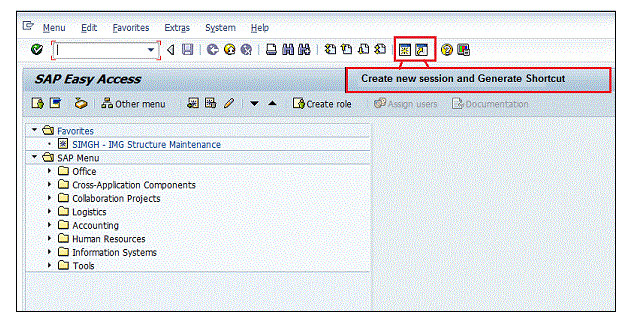
New Session Icon
For creating a replacement session, we use the subsequent keys shown within the screenshot below −
Log Off
It is an honest practice to sign off from the SAP system once you finish your work. There are several ways to sign off from the system, but they are often done using the subsequent instructions as shown within the screenshot below −
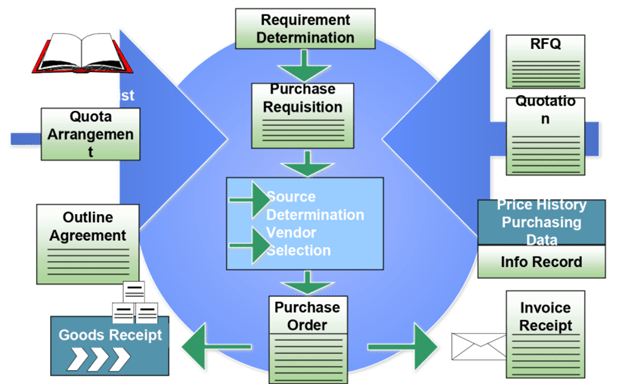
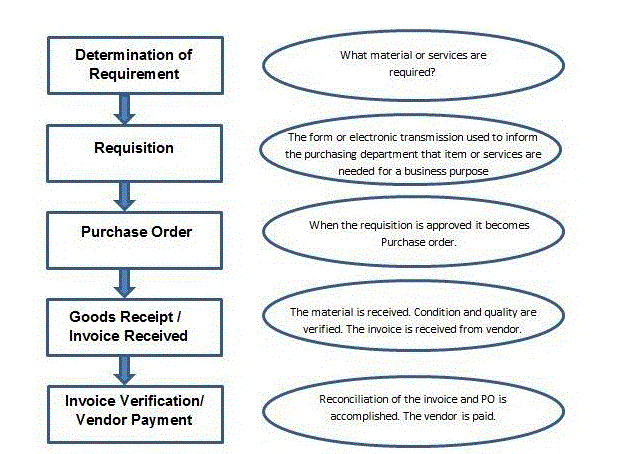
Basic Procurement Activities
The next figure shows the flow of necessary procurement actions −

Special Procurement:
Special products are the products that are handled differently, as these stocks don’t belong to the corporate. Special stocks stand kept at some special location. Special procurement and special stock types are split into the subsequent categories −
Consignment Stocks
Consignment stocks are that material that’s available at our store premises, however, it still belongs to the seller (seller) of the fabric. If you utilize the fabric from consignment stocks, then you’ve got to pay the seller.
Third-party Processing
In third-party processing, a corporation passes on a sales order to the associate external vendor (seller) who sends the products on to the customer. The sales order isn’t processed by the corporate, but by the seller (seller). Third-party items are often entered in purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and sales orders.
Pipeline Handling
In pipeline handling, the corporate needn’t order or store the fabric involved. it’s obtainable as and when required via a pipeline (for example, oil or water), or another sort of cable (such as electricity). the fabric that’s consumed is settled with the seller (seller) daily.
Returnable Transport Stock
The company orders goods from a vendor (seller). the products are delivered with returnable transport packaging (pallets, containers) that belongs to the seller (seller) and is stored at the customer’s premises until they return it to the corporate.
Subcontracting
The vendor (the subcontractor) receives components from the ordering party with the assistance of which it produces a product. the merchandise is ordered by your company through a sale order. The components required by the seller (seller) to manufacture the ordered product are listed within the order and provided to the subcontractor.
Stock Transfer Using Stock Transport Order
Goods are procured and supplied within a corporation. One plant orders the products internally from another plant (receiving plant/issuing plant). the products are procured with a special sort of order – the stock transport order. you will be ready to request and monitor the transfer of products with a stock transport order.
SAP Implementation Guide:
Menu path for MM Configuration:
The main menu paths for the MM area are as follows −
Procurement cycle:
Every organization acquires material or services to finish its business needs. the method of shopping for materials and obtaining services from vendors or dealers is named procurement. The steps required to acquire material from the procurement cycle. Every organization performs some common sequential steps to acquire material within the right quantity at the proper price. The important steps during a procurement cycle are as follows −
Determination of Requirement
This is the primary step during a procurement cycle. it’s the logical subdivision, where it’s determined what material or services are required by the corporate, and which supplier can fulfill the need. an inventory of requirements is formed then it’s approved by a senior authority within the organization. After approval, a proper list is formed that’s referred to as the acquisition order with another level of approval which is shipped to the seller.
Creating order
A purchase order is the formal and final confirmation of the wants that are sent to the seller to provide material or services. a sale order includes important information like the name of the fabric with its corresponding plant, details of buying organization with its company code, name of the vendor, and date of delivery. sale order is often created by following the steps given below −
Path to make an order
Step 1 − On the SAP Menu screen, choose Start Vendor/Supplying Plant Known by observing the overhead track.
Step 2 − Fill altogether the required details like the name of the seller, purchasing organization, purchasing group, company code, and details of the fabric, for instance, material number, price, currency, and plant.
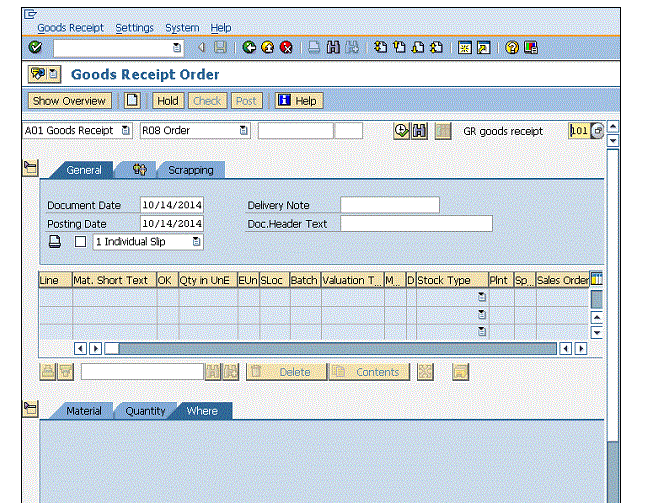
Step 3 − Fill altogether the required details under Item, by selecting the tabs as shown within the following screenshot −
Configurations:
SAP MM is flexible enough to permit its configurations to be modified within the background to suit the business requirements of a corporation. Configurations help in making custom enhancements within the structure. This chapter describes a number of the important configurations in SAP MM.
Assign Fields to Field Selection Groups
This configuration allows one to form some fields optional, hidden, or mandatory within the master record. Follow the steps given below to line this configuration.
Path to Assign Fields to Field Selection Groups
Maintain Field Selection for Data Screens
This configuration allows one to form some data screens within the master data as optional, hidden, or mandatory. Follow the steps given below to line this configuration.
Path to take care of Field Selection for Data Screens
Step 1 − On the Display IMG screen, choose Maintain Field Selection for Data Screens by observing the overhead path.
Step 2 − Select the sector selection group during which you would like to form changes. Here you’ll make changes within the field reference as hidden, display, required entry, or optional entry. Click on Save. The field section for data nets is now supported.
Maintain Company Codes for Materials Management
This configuration allows one to take care of company codes with a period alongside the financial year. Follow the steps given below to line this configuration.
Way to take consideration of Company Codes for Materials Management
Step 1 − On the Display IMG screen, choose Maintain Company Codes for Materials Management by obeying the overhead track.
Step 2 − Supply details like name, company code, alongside the economic year and therefore the time for that. Click on Save. Company code is now sustained for materials management.
Define Attributes of System Messages
Sometimes the system doesn’t allow us to save lots of a document when its information is incomplete. In such cases, the system issues some messages to point the evidence of the error. These system messages are often found out by following the steps given below.
Path to Define Attributes of System Messages
Step 1 Follow the above path to select Define Attributes of System Messages on the Display IMG screen.
Step 2 Here you can keep track of the type of message (warning or error), the message number, and the message description. Save the file. System messages are now kept.
Conclusions:
The SAP MM (Material Management) Module is an SAP ERP component that aids organizations in material management, inventory management, and warehouse management throughout the supply chain process. In SAP, a transaction is the processing of specific information to complete business process requirements.






