
Microsoft’s Windows networking encompasses protocols, services, and technologies designed to enhance communication and facilitate resource sharing among Windows computers. Key features include file and printer sharing, network discovery, and group policies for streamlined resource management. It utilizes standard protocols like TCP/IP to accommodate various network types, including LANs and WANs. Active Directory consolidates resource management and user authentication, and user-friendly features like HomeGroup and Workgroup configurations simplify resource sharing among Windows devices. With compatibility for both wired and wireless connections, Windows networking plays a crucial role in establishing smooth and collaborative computing environments for users and organizations utilizing Microsoft Windows operating systems.
1. What is Link?
Ans:
A link refers to the connectivity between two devices. It includes the type of cables and protocols used for one device to be able to communicate with the other.
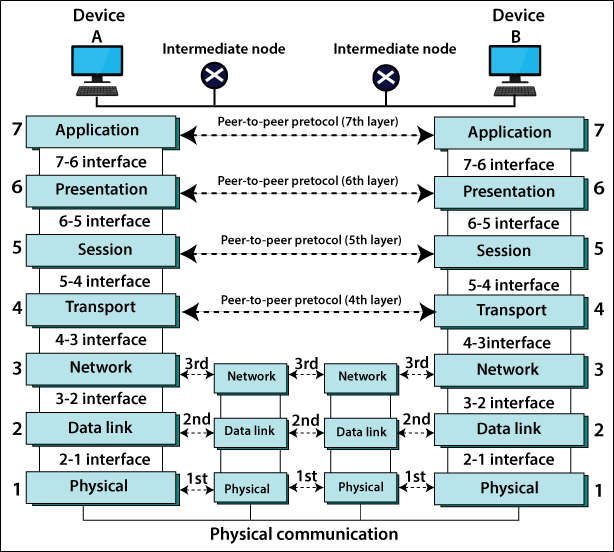
2. What are layers of OSI reference model?
Ans:
There are 7 OSI layers:
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer.
3. What is backbone network?
Ans:
A backbone network is the centralized infrastructure that is designed to distribute the different routes and data to the various networks. It also handles management of bandwidth and the various channels.
4. What is LAN?
Ans:
LAN is short for a Local Area Network. It refers to the connection between the computers and other network devices that are located within the small physical location.
5. What is node?
Ans:
A node refers to a point or joint where a connection takes place. It can be a computer or device that is part of a network. Two or more nodes are needed to form a network connection.
6. What are routers?
Ans:
Routers can connect the two or more network segments. These are intelligent network devices that store the information in its routing table such as paths, hops and bottlenecks. With this info, they are able to determine the best path for a data transfer. Routers operate at OSI Network Layer.
7. What is a point to point link?
Ans:
It refers to a direct connection between two computers on a network. A point to point connection does not need any other network devices other than connecting a cable to the NIC cards of both computers.
8. What is anonymous FTP?
Ans:
Anonymous FTP is a way of granting user access to files in public servers. Users that are allowed access to data in these servers do not need to identify themselves, but instead, log in as an anonymous guest.
9. What is subnet mask?
Ans:
A subnet mask is the combined with an IP address in order to identify the two parts:
- The extended network address and host address. Like IP address, a subnet mask is made up of 32 bits.
- Subnet mask is the mask used to determine what subnet IP address belongs to.
10. What is maximum length allowed for UTP cable?
Ans:
A single segment of UTP cable has allowable length of 90 to 100 meters. This limitation can be overcome by using the repeaters and switches.
11. What is data encapsulation?
Ans:
Data encapsulation is the process of breaking down the information into the smaller manageable chunks before it is transmitted across the network. It is also in this process that source and destination addresses are attached into headers, along with the parity checks.
12. Describe Network Topology?
Ans:
A Network Topology refers to the layout of the computer network. It shows how the devices and cables are physically laid out, as well as how they are connect to the one another.
13. What is VPN?
Ans:
VPN means Virtual Private Network, a technology that allows the secure tunnel to be created across a network such as Internet.
For example: VPNs allow to establish the secure dial-up connection to the remote server.
14. Describe NAT.
Ans:
NAT is Network Address Translation. This is the protocol that provides the way for multiple computers on the common network to share single connection to the Internet.
15. What is job of Network Layer under OSI reference model?
Ans:
The Network layer is the responsible for a data routing, packet switching and control of network congestion. The Routers can be operate under this layer.
16. How does network topology affect decision in setting up network?
Ans:
Network topology dictates what media must use to interconnect devices. It also serves as the basis on what materials, connector and terminations that is applicable for a setup.
17. What is RIP?
Ans:
RIP, short for the Routing Information Protocol is used by routers to send data from a one network to another. It efficiently manages routing data by broadcasting its routing table to all the other routers within the network. It determines a network distance in units of hops.
18. What are different ways of securing computer network?
Ans:
There are the several ways to do this. Install reliable and updated anti-virus program on all the computers. Make sure that firewalls are setup and configured properly. User authentication will also help the lot. All of these combined would make highly secured network.
19. What is NIC?
Ans:
NIC is short for a Network Interface Card. This is the peripheral card that is attached to a PC in order to the connect to a network. Every NIC has its own MAC address that identifies a PC on the network.
20. What is WAN?
Ans:
WAN stands for the Wide Area Network. It is the interconnection of computers and devices that are geographically dispersed. It connects the networks that are located in the different regions and countries.
21. What is the importance of the OSI Physical Layer?
Ans:
The physical layer does the conversion from the data bits to the electrical signal, and vice versa. This is where network devices and cable types are considered and set up.
22. How many layers are under TCP/IP?
Ans:
There are four layers:
- Network Layer
- Internet Layer
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
23. What are proxy servers ?
Ans:
Proxy servers primarily prevent the external users who identify the IP addresses of internal networks. Without knowledge of a correct IP address, even the physical location of the network cannot be identified. Proxy servers can make the network virtually invisible to the external users.
24. What is the function of the OSI Session Layer?
Ans:
This layer provides protocols and means for two devices on a network to communicate with each other by holding the session. This includes setting up the session, managing information exchange during session, and tear-down process upon termination of a session.
25. What is the importance of implementing a Fault Tolerance System?
Ans:
A fault tolerance system ensures the continuous data availability. This is done by eliminating a single point of a failure. However, this type of the system would not be able to protect data in some cases, such as in accidental deletions.
26. What does 10Base-T mean?
Ans:
The 10 refers to a data transfer rate, in this case 10Mbps. The word Base refers to the base band, as opposed to broadband. T means twisted pair, which is cable used for a network.
27. What is a private IP address?
Ans:
Private IP addresses are assigned for use on intranets. These addresses are used for internal networks and are not routable on external public networks. This ensures that no conflicts are present among internal networks while at the same time the same range of private IP addresses are reusable for the multiple intranets since they do not “see” each other.
28. What is NOS?
Ans:
NOS, or Network Operating System, is specialised software whose main task is to provide the network connectivity to the computer in order for it to be able to communicate with the other computers and connected devices.
29. What is DoS?
Ans:
DoS, or Denial-of-Service attack, is an attempt to prevent users from being able to access the internet or any other network services. Such attacks may come in different forms and are done by the group of perpetrators. One common method of doing this is to overload the system server so it cannot anymore process legitimate traffic and will be forced to reset.
30. What is OSI and what role plays in computer networks?
Ans:
OSI (Open Systems Interconnect) serves as the reference model for data communication. It is made up of the 7 layers, with each layer defining a particular aspect on how network devices connect and communicate with one another. One layer may deal with physical media used, while another layer dictates how data is actually transmitted across the network.
31. What are cables being shielded and having twisted pairs?
Ans:
The main purpose of this is to prevent crosstalk. Crosstalks are the electromagnetic interferences or noise that can affect data being transmitted across the cables.
32. What is the advantage of address sharing?
Ans:
By using the address translation instead of routing, address sharing provides the inherent security benefit. That’s because host PCs on the Internet can only see the public IP address of the external interface on a computer that provides address translation and not a private IP address on the internal network.
33. What are MAC addresses?
Ans:
MAC, or Media Access Control, uniquely identifies the device on the network. A MAC address is made up of the 6-byte parts.
34. How can I identify the IP class of a given IP address?
Ans:
By looking at a first octet of any given IP address, one can identify whether it’s Class A, B or C. If the first octet begins with the 0 bit, that address is Class A. If it begins with the bits 10 then that address is the Class B address. If it begins with 110, then it’s the Class C network.
35. What is the main purpose of OSPF?
Ans:
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First, is the link-state routing protocol that uses the routing tables to determine the best possible path for the data exchange.
36. What are firewalls?
Ans:
Firewalls serve to protect the internal network from external attacks. These external threats can be hackers who want to steal data or computer viruses that can wipe out data in an instant. It also prevents the other users from external networks from gaining access to a private network.
37. Describe star topology?
Ans:
Star topology consists of the central hub that connects to the nodes. This is one of the simplest to setup and maintain aslo.
38. What are gateways?
Ans:
Gateways provide the connectivity between the two or more network segments. It is usually the computer that runs the gateway software and provides translation services. This translation is the key in allowing the different systems to communicate on a network.
39. What is the disadvantage of star topology?
Ans:
One major disadvantage of the star topology is :
- Once the central hub or switch gets damaged, the entire network becomes unusable.
40. What is SLIP?
Ans:
SLIP, or Serial Line Interface Protocol, is actually an old protocol developed during the early UNIX days. This is one of the protocols that are used for remote access.
41. What is backbone network?
Ans:
A backbone network is the centralised infrastructure that is designed to distribute the different routes and data to the various networks. It also handles the management of bandwidth and the multiple channels.
42. What is tracert?
Ans:
Tracert is the Windows utility program that can be used to trace a route taken by data from a router to the destination network. It also shows the number of hops taken during an entire transmission route.
43. What are the functions of a network administrator?
Ans:
A network administrator has more responsibilities that can be summarised into the 3 key functions:
- Installation of a network
- Configuration of a network settings
- Maintenance /troubleshooting of the networks.
44. What is DHCP?
Ans:
DHCP is short for a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Its main task is to automatically assign an IP address to devices across the network. It first checks for a next available address not yet taken by any device, then assigns this to the network device.
45. What is TCP/IP?
Ans:
TCP/IP is short for the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. This is a set of protocol layers that is designed to make a data exchange possible on different types of the computer networks, also known as a heterogeneous network.
46. How can I manage the network using a router?
Ans:
Routers have a built-in console that lets you configure different settings, like security and data logging. can assign restrictions to the computers, such as what resources it is allowed access to, or what particular time of a day they can browse the internet. can even put restrictions on what websites are not viewable across the entire network.
47. What protocol applied for transfer files between different platforms?
Ans:
Use FTP (File Transfer Protocol) applied for the file transfers between such various servers. This is possible because FTP is a platform independent.
48. What is the use of the default gateway?
Ans:
Default gateways provide the means for a local network to connect to an external network. The default gateway for connecting to an external network is usually the address of an external router port.
49. What can be considered as good passwords?
Ans:
Good passwords are made up of not just letters, but by combining the letters and numbers. A password that combines the uppercase and lowercase letters is more favourable than one that uses all the uppercase or all lowercase letters. Passwords must not be words that can easily be guessed by the hackers, such as dates, names, favourites, etc. Longer passwords are also better than short ones.
50. What is the number of network IDs in a Class C network?
Ans:
For Class C networks, the number of usable Network ID bits is 21. The number of possible network IDs is 2 raised to 21 or 2,097,152. The number of the host IDs per network ID is 2 raised to 8 minus 2, or 254.
51. What common software problems lead to network defects?
Ans:
Software related problems can be any or combination of following:
- Client server problems
- Application conflicts
- Error in configuration
- Protocol mismatch
- Security issues
- User policy and rights issues
52. What is ICMP?
Ans:
ICMP is Internet Control Message Protocol. It provides the messaging and communication for protocols within the TCP/IP stack. This is also a protocol that manages error messages that are used by network tools such as PING.
53. What is Ping?
Ans:
Ping is the utility program that allows to check connectivity between the network devices on the network can ping a device by using its IP address or device name, such as the computer name.
54. What advantages do fibre optics have over other media?
Ans:
One major advantage of the fibre optics is that it is less susceptible to electrical interference. It also supports a higher bandwidth, meaning more data can be transmitted and received. Signal degradation is very minimal over long distances.
55. What is the difference between hub and switch?
Ans:
A hub acts as the multiport repeater. However, as more and more devices connect to it, it would not be able to efficiently manage the volume of traffic that passes through it. A switch provides a better alternative that can improve the performance especially when a high traffic volume is expected across all the ports.
56. What are different network protocols supported by Windows RRAS services?
Ans:
There are the three main network protocols are supported:
- NetBEUI
- TCP/IP
- IPX
57. What are maximum networks and hosts in class A, B and C networks?
Ans:
For Class A, there are 126 possible networks and 16,777,214 hosts For Class B, there are 16,384 possible networks and 65,534 hosts For Class C, there are 2,097,152 possible networks and 254 hosts.
58. What is the standard colour sequence of straight-through cable?
Ans:
Standard colour sequence of the straight-through the cable is:
- Orange /white,
- Orange, green/white,
- Blue, blue/white,
- Green, brown/white, brown
59. What protocols fall under the Application layer of TCP/IP stack?
Ans:
The following are protocols under the TCP/IP Application layer:
- FTP
- TFTP
- Telnet
- SMTP
60. Can connect two computers for file sharing?
Ans:
Yes, I can connect two computers together using only one cable. In this setup, the data transmit pin of one cable is connected to a data receive pin of another cable, and vice versa.
62. What is ipconfig?
Ans:
Ipconfig is the utility program that is commonly used to identify the address information of the computer on a network. It can show a physical address as well as the IP address.
63. What is the difference between straight-through and crossover cable?
Ans:
- A straight-through cable is used to connect computers to the switch, hub or router.
- A crossover cable is used to connect the two similar devices together, like a PC to PC or Hub to hub.
64. What is client/server?
Ans:
- Client/server is the type of network wherein one or more computers act as servers.
- Servers provide a centralised repository of resources such as printers and files.
- Client refers to the workstation that accesses the server.
65. Describe networking.?
Ans:
Networking refers to an inter connection between the computers and peripherals for data communication. Networking can be done using the wired cabling or through the wireless link.
66. Does the MAC address get transferred as well?
Ans:
Yes, that’s because MAC addresses are the hard-wired into the NIC circuitry, not a PC. This also means that PC can have the different MAC address when the NIC card was replaced by the another one.
67. Explain clustering support?
Ans:
Clustering support refers to the ability of the network operating system to connect the multiple servers in a fault-tolerant group. The main purpose of this is that in the event that one server fails, all processing will continue on with the next server in a cluster.
68. Where is the best place to install an Anti-virus program?
Ans:
An anti-virus program must be installed on all the servers and workstations to ensure protection. That’s because individual users can access any workstation and introduce the computer virus when plugging in removable hard drives or the flash drives.
69. Describe Ethernet.
Ans:
Ethernet is one of the popular networking technologies used nowadays. It was developed during the early 1970s and is based on the specifications as stated in the IEEE. Ethernet is used in the local area networks.
70. What are the drawbacks of implementing ring topology?
Ans:
In case one workstation on a network suffers a malfunction, it can bring down an entire network. Another drawback is that when there are the adjustments and reconfigurations needed to be performed on the particular part of the network, the entire network has to be temporarily brought down as well.
71. Difference between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA?
Ans:
| Feature | CSMA/CD | CSMA/CA | |
| Collision Handling |
Detects collisions and attempts resolution. |
Aims to prevent collisions by using a reservation-based approach. | |
| Ethernet Usage | Historically used in traditional Ethernet networks. | Commonly employed in wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi. | |
| Mechanism | Listens for ongoing transmissions, starts if medium is clear. | Listens, waits for a clear channel, and uses RTS/CTS for reservation. | |
| Efficiency |
Efficiency declines with increased traffic and collisions. |
More efficient in collision avoidance, especially in high contention. | |
| Backoff Mechanism |
Applies binary exponential backoff after a collision. |
Utilizes random backoff time to minimize simultaneous transmissions after a collision. | |
| Cable Type |
Typically used in shared coaxial cable networks. |
Often used in wireless networks where medium control is challenging. | |
| Standardization |
Defined in IEEE 802.3 standard for Ethernet. |
Defined in IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless LANs. |
72. What is SMTP?
Ans:
SMTP is short for a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. This protocol deals with all Internal mail, and provides the necessary mail delivery services on a TCP/IP protocol stack.
73. What is multicast routing?
Ans:
Multicast routing is the targeted form of broadcasting that sends the message to the selected group of users. Instead of sending it to all the users on the subnet.
74. What is the importance of Encryption on a network?
Ans:
Encryption is a process of translating information into the code that is unreadable by the user. It is then translated back or decrypted back to normal readable format using the secret key or password. Encryption helps ensure that information that is intercepted halfway would remain unreadable because the user has to have a correct password or key for it.
75. How are IP addresses arranged and displayed?
Ans:
IP addresses are displayed as a series of four decimal numbers that are separated by a period or dots. Another term for this arrangement is a dotted decimal format.
An example is 192.168.101.2
76. Explain the importance of authentication.?
Ans:
Authentication is a process of verifying a user’s credentials before he can log into a network. It is normally performed using the username and password. This provides the secure means of limiting the access from the unwanted intruders on a network.
77. What is tunnel mode?
Ans:
This is the mode of data exchange wherein two communicating computers do not use IPSec themselves. Instead, the gateway that is connecting LANs to the transit network creates the virtual tunnel that uses an IPSec protocol to secure all the communication that passes through it.
78. What are different technologies involved in establishing WAN links?
Ans:
Analog connections – using the conventional telephone lines; Digital connections – using the digital-grade telephone lines; switched connections – using the multiple sets of links between a sender and receiver to move data.
79. What is one advantage of mesh topology?
Ans:
In the event that one link fails, there will always be another available. Mesh topology is one of the most fault-tolerant network topologies.
80. When troubleshooting computer network problems, what hardware-related problems can occur?
Ans:
A large percentage of the network is made up of hardware. Problems in these areas can range from malfunctioning hard drives, broken NICs and even hardware startups. Incorrect hardware configuration is also one of those culprits to be looked into.
81. What can be done to fix signal attenuation problems?
Ans:
A common way of dealing with such a problem is to use the repeaters and hub, because it will help regenerate a signal and therefore prevent a signal loss. Checking if cables are properly terminated is also the must.
82. How does dynamic host configuration protocol aid in network administration?
Ans:
Instead of having to visit every client computer to configure the static IP address, the network administrator can apply the dynamic host configuration protocol to create the pool of IP addresses known as scopes that can be dynamically assigned to clients.
83. Explain profile in terms of networking concept?
Ans:
Profiles are the configuration settings made for each user. A profile may be created that puts the user in a group.
84. What is the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
Ans:
The primary differences between 2.4 GHz and 5GHz wireless frequencies are the range and bandwidth.
5GHz provides the faster data rates at shorter distance, whereas 2.4GHz offers coverage for a farther distances, but may perform at a slower speeds
85. What is IEEE in computer networking?
Ans:
IEEE, or Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, is an organisation composed of engineers that issues and manages standards for electrical and electronic devices. This includes the networking devices, network interfaces, cables and connectors.
86. What protocols fall under TCP/IP Internet Layer?
Ans:
There are the four protocols that are being managed by this layer.
These are:
- ICMP
- IGMP
- IP
- ARP
87. When it comes to networking, what are rights?
Ans:
Rights refer to authorised permission to perform a specific action on the network. Each user on a network can be assigned individual rights, depending on what must be allowed for that user.
88. What is one basic requirement for establishing VLANs?
Ans:
A VLAN is required because at switch level there is only one broadcast domain, which means whenever a new user is connected to switch this information is spread throughout the network. VLAN on switch helps to create a separate broadcast domain at switch level. It is used for security purposes.
89. What is IPv6?
Ans:
IPv6 , or Internet Protocol version 6, was developed to replace IPv4. At present, IPv4 is being used to control internet traffic, butis expected to get saturated in the near future. IPv6 was designed to overcome this limitation.
90. What is Socket?
Ans:
A socket is a one endpoint of a two-way communication link between the two programs running on a network. A socket is bound to the port number so that the TCP layer can identify the application that data is destined to be sent to.






