
- Introduction to Business Law
- Importance in Commerce
- Contracts in Business Law
- Company Law Basics
- Employment and Labor Law
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Consumer Protection Law
- Competition Law
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
- Business Ethics and Law
- Recent Developments in Business Law
- Conclusion
Introduction to Business Law
What Is Business Law it refers to the laws that govern the rights, relationships, and conduct of individuals and businesses engaged in commerce, trade, and sales. It encompasses a wide range of legal disciplines including contracts, torts, property, employment, and intellectual property. Business law is integral to the operation and success of any business as it provides the legal framework for conducting business, ensuring that all parties in a business transaction are treated fairly and that their rights are protected. What Is Business Law and can be divided into various sub-categories, each governing specific aspects of commercial activities. Whether a business is large or small, it must comply with a broad spectrum of rules and regulations. Understanding business law helps entrepreneurs, managers, and employees navigate legal challenges and make informed decisions that ensure the smooth functioning of their business. Moreover, knowledge of business law can prevent costly disputes and litigation.
Importance in Commerce
In the world of commerce, business law serves as the backbone for all commercial activities. It ensures that businesses operate within a framework that promotes fairness, transparency, and accountability. By establishing legal rights and responsibilities, business law helps to maintain order in the marketplace and provides a foundation for businesses to operate confidently, knowing that their legal interests are protected.
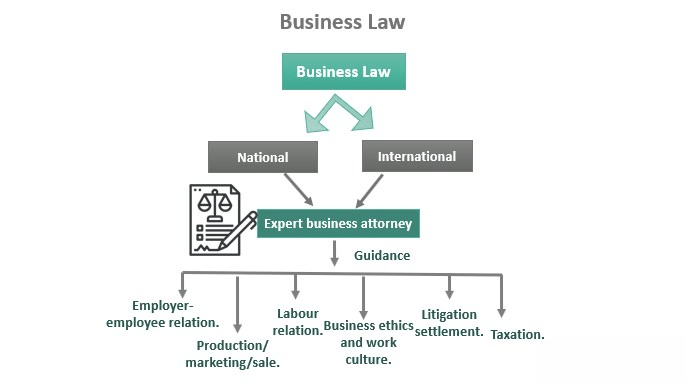
Additionally, business law provides businesses with the necessary tools to handle legal disputes, protect intellectual property, and negotiate contracts effectively. It also helps businesses to stay compliant with government regulations and minimize legal risks that could potentially harm their operations. The importance of business law cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the stability, growth, and success of commercial enterprises.
Contracts in Business Law
- A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties that is enforceable by law. In business law, contracts play a pivotal role in the relationship between businesses, suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders. Contracts govern a wide range of transactions, from purchasing goods to providing services, and they serve to establish clear expectations and obligations for all parties involved.
- Key elements of a contract include mutual consent, consideration (something of value exchanged), legal capacity, and a lawful purpose. Contracts can be written or oral, although written contracts provide greater clarity and are easier to enforce in case of a dispute. In business law, some common types of contracts include sales agreements, employment contracts, partnership agreements, and non-disclosure agreements.
Company Law Basics
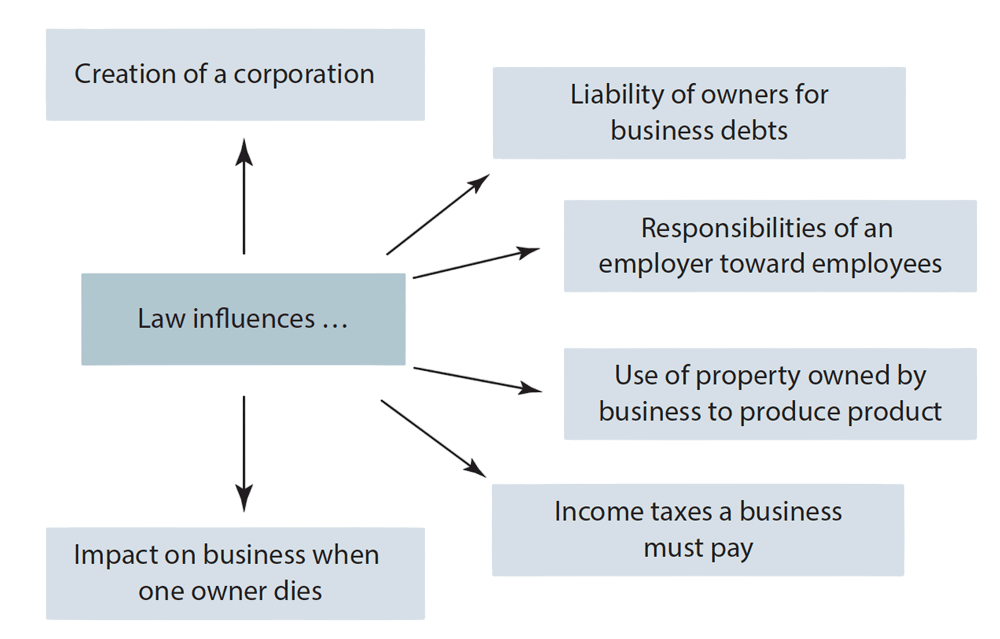
- Company law refers to the laws and regulations that govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies. It covers various aspects such as company formation, governance, rights and responsibilities of shareholders and directors, mergers and acquisitions, and the liquidation process. Company law is vital for businesses that operate as corporate entities, such as limited liability companies (LLCs), corporations, and partnerships.
- One of the main components of company law is corporate governance, which ensures that companies are managed in the best interests of their shareholders and stakeholders. This includes the establishment of a board of directors, the distribution of dividends, and the resolution of disputes between stakeholders.
- Company law also governs the financial reporting and transparency requirements for businesses, ensuring that companies maintain accurate financial records and provide shareholders with regular updates on the financial health of the organization. Failure to comply with company law regulations can result in fines, penalties, and legal consequences.
Employment and Labor Law
Employment and labor law governs the relationship between employers and employees. It addresses issues related to hiring, firing, workplace safety, wages, benefits, and employee rights. Employment law ensures that employees are treated fairly, receive their entitled compensation, and work in safe and non-discriminatory environments. This area of law is crucial for businesses as it helps prevent workplace disputes and ensures compliance with labor regulations. Key aspects of employment and labor law include wage and hour laws, anti-discrimination laws, workers’ compensation, and employee privacy rights. Businesses must adhere to these laws to avoid lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage. Moreover, labor law provides protections for unionized workers, including collective bargaining rights and dispute resolution processes. Understanding employment and labor law is essential for both employers and employees to ensure fair treatment in the workplace.
Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind such as inventions, designs, logos, trademarks, and original works of authorship. Intellectual property law protects the ownership and usage rights of these creations, allowing creators to profit from their innovations while preventing others from using them without permission. In business law, IP plays a critical role in ensuring that businesses protect their innovations and brands. Intellectual property rights include patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Each type of IP protection serves a different purpose. For example, patents protect inventions, while trademarks protect brand names and logos. Businesses that fail to protect their intellectual property risk losing their competitive edge, facing imitation, or having their brand diluted. As such, businesses must understand the importance of IP protection and how to secure their rights through registrations and legal enforcement.
Consumer Protection Law
- Consumer protection law ensures that businesses treat consumers fairly and protect their interests in commercial transactions. This area of law includes regulations regarding the quality of goods and services, advertising practices, product labeling, warranties, and consumer rights in case of fraud or unfair practices.
- Consumer protection laws aim to prevent businesses from taking advantage of consumers through deceptive advertising, unsafe products, or unfair business practices. These laws are particularly important in industries such as food, healthcare, and finance, where consumer safety and well-being are paramount.
- In addition to regulatory requirements, consumer protection laws provide consumers with avenues for redress when their rights are violated, such as through refund claims, product recalls, or lawsuits for damages. Understanding consumer protection laws helps businesses build trust with customers and avoid costly legal issues.
Competition Law
- Competition law, also known as antitrust law, regulates business practices that may restrict competition in the market. The goal of competition law is to promote fair competition by preventing monopolies, cartels, and other anti-competitive practices that could harm consumers or stifle innovation.
- Competition law covers areas such as price-fixing, market allocation, predatory pricing, and mergers and acquisitions. It ensures that businesses compete fairly, which leads to lower prices, better products, and improved services for consumers.
- Governments around the world have regulatory bodies responsible for enforcing competition laws, and businesses that violate these laws can face significant penalties, including fines and forced divestitures. Companies must understand competition law to avoid engaging in practices that may be deemed anti-competitive.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Disputes are inevitable in business, and resolving conflicts effectively is critical for maintaining relationships and minimizing losses. Dispute resolution mechanisms in business law include various processes such as negotiation, mediation, arbitration, and litigation. Negotiation is often the first step in resolving a dispute, where the parties attempt to reach a mutually agreeable solution. Mediation involves a neutral third party who helps facilitate a resolution but does not impose a binding decision. Arbitration is a more formal process where a third party makes a binding decision on the dispute. Litigation, or going to court, is the final step and is typically used when other forms of dispute resolution fail. Litigation can be time-consuming, costly, and damaging to relationships, making alternative dispute resolution mechanisms like mediation and arbitration preferable for many businesses.
Business Ethics and Law
Business ethics refers to the moral principles and standards that guide business behavior. While business law provides a legal framework, business ethics involves adhering to values such as honesty, integrity, and fairness in all aspects of business operations. Business ethics plays a vital role in shaping the culture of an organization and ensuring that businesses operate in a socially responsible manner. Many businesses implement ethical codes of conduct to guide their employees and ensure that their operations align with societal values. In some cases, ethical behavior in business may overlap with legal requirements. For instance, environmental regulations, fair labor practices, and anti-corruption laws all serve to align business practices with ethical standards.
Recent Developments in Business Law
- Business law is a dynamic field that continuously evolves to address new challenges and opportunities in the marketplace. Recent developments in business law include the rise of data protection laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which has reshaped how businesses collect, process, and store personal data.
- Additionally, the growing importance of e-commerce and digital transactions has led to the development of new regulations governing online businesses, cybersecurity, and electronic contracts. The global nature of business has also resulted in the creation of international trade agreements and laws that govern cross-border transactions.
- The rise of emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, has also prompted changes in business law. Legal professionals must keep pace with these developments to ensure that businesses are compliant with new regulations and can take advantage of technological advancements while mitigating potential legal risks.
Conclusion
What Is Business Law answer is a vital component of the commercial world, providing a legal framework that governs business activities, ensures fair competition, and protects the rights of individuals and companies. From contracts and intellectual property to employment law and dispute resolution, business law covers a broad range of topics that impact businesses daily. As commerce continues to evolve, businesses must stay informed about changes in the legal landscape and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. By understanding business law, companies can protect their interests, avoid costly disputes, and create a foundation for sustainable growth and success.





