- Introduction to Green Supply Chain Management (GSCM)
- Evolution of Supply Chains and the Need for Greening
- Key Components of Green Supply Chain Management
- Benefits of Implementing GSCM
- Challenges in Adopting GSCM Practices
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- Technologies Enabling Green Supply Chains
- Conclusion
Introduction to Green Supply Chain Management (GSCM)
Green Supply Chain Management, or GSCM, is an innovative and comprehensive approach that integrates environmental considerations into every aspect of supply chain management. This approach covers the entire life cycle of a product, starting from the initial stages of product design and raw material sourcing, through manufacturing and distribution, and continuing all the way to the final disposal or recycling of the product. The primary goal of GSCM is to reduce the ecological footprint of a company’s operations while still maintaining competitiveness and profitability in the marketplace. Unlike traditional supply chains, which often overlook environmental impacts, GSCM places sustainability at the core of business strategy. This means companies actively work to reduce waste generation, conserve natural resources, minimize harmful emissions, incorporate PMP Training, and ensure that sourcing practices are responsible and ethical. Implementing green supply chain practices involves many different initiatives. For example, companies may choose suppliers who use renewable materials or operate with environmentally friendly processes. Manufacturers might adopt energy-efficient technologies and optimize production methods to reduce pollution and energy consumption. Distribution networks can be redesigned to minimize transportation emissions by using alternative fuels or optimizing delivery routes. Additionally, companies focus on product end-of-life management by promoting recycling and reusing materials, reducing landfill waste. As awareness of environmental issues grows, businesses face increasing pressure from regulators, consumers, investors, and other stakeholders to demonstrate sustainable practices. This shift has made GSCM not just a choice but a necessity for companies that want to remain relevant and competitive in today’s market. By embracing green supply chain management, businesses can reduce their environmental impact, comply with evolving regulations, enhance brand reputation, and meet the rising demand for sustainable products.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Evolution of Supply Chains and the Need for Greening
Historically, supply chains were designed primarily with a focus on efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The main concerns were speed, volume, and maintaining competitive prices. During this time, environmental costs such as carbon emissions, pollution, and waste were often overlooked or treated as external factors that did not directly impact business decisions. This approach allowed companies to prioritize short-term gains without accounting for the long-term consequences of their operations on the environment. However, over the past few decades, growing awareness of global environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, pollution, and biodiversity loss began to change the way supply chains were viewed, raising questions like Why Do Scrum Masters Get Paid so Much as agile roles gained prominence in driving sustainable and adaptive practices. International agreements like the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Climate Agreement brought environmental sustainability to the forefront of global policy discussions. These efforts encouraged countries and businesses alike to take responsibility for their environmental impact and to reduce their carbon footprints. At the same time, consumers became increasingly eco-conscious, demanding products that are not only affordable but also sustainable and ethically produced. Governments responded by imposing stricter environmental regulations, which compelled companies to comply with new standards to avoid penalties and protect their reputations.
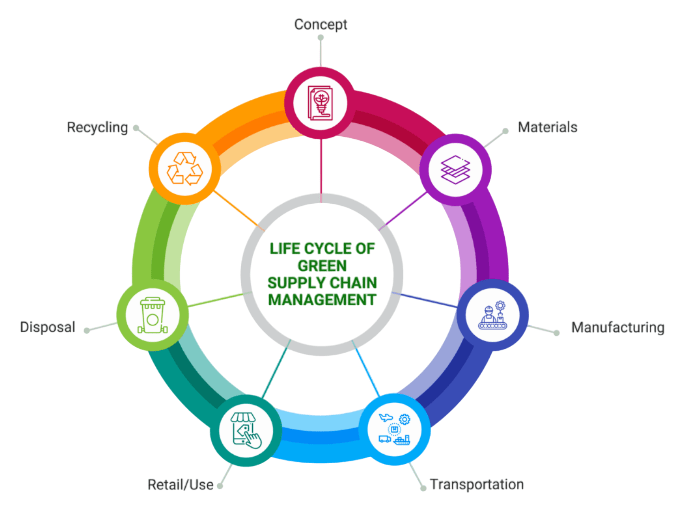
These trends pushed organizations to rethink their supply chains and evaluate every stage of the process from an environmental perspective. This shift led to the rise of Green Supply Chains, which integrates sustainability as a key business objective rather than an afterthought. It represents a strategic pivot from focusing solely on economic goals to adopting a triple bottom line approach that balances people, planet, and profit. By embracing this holistic mindset, companies can build resilient, responsible supply chains that support long-term success in a rapidly changing world.
Key Components of Green Supply Chain Management
- Green Procurement: This involves sourcing raw materials and products that are environmentally friendly, recyclable, or produced through sustainable practices. It emphasizes choosing suppliers who follow green standards and minimize harmful environmental impact.
- Eco-Friendly Design: Also known as design for the environment (DfE), this focuses on creating products with minimal environmental impact throughout their lifecycle, a concept increasingly valued alongside rising trends like the Project Manager Salary in India .
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Green manufacturing processes aim to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and limit emissions. This involves using cleaner production techniques, renewable energy sources, and waste-reduction strategies during production.
- Green Distribution and Logistics: This component focuses on optimizing transportation and distribution to reduce carbon emissions. Strategies include route optimization, using fuel-efficient or electric vehicles, and consolidating shipments to lower environmental impact.
- Reverse Logistics: Reverse logistics involves the return, reuse, recycling, or proper disposal of products and materials. It helps companies manage product take-backs, reduce waste, and recover value from used goods.
- Waste Management: Efficient waste management practices focus on reducing, reusing, and recycling waste materials throughout the supply chain. This minimizes landfill use and supports circular economy principles.
- Performance Monitoring and Compliance: Companies must track and assess environmental performance regularly. This includes setting measurable goals, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and continuously improving sustainability practices through audits and reporting.
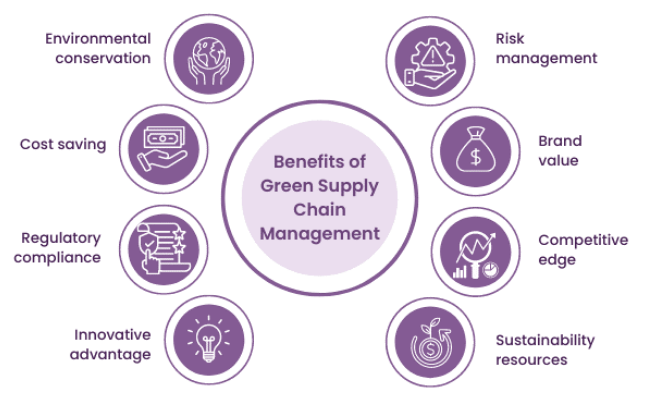
- Environmental Conservation: At its core, Green Supply Chain Management (GSCM) promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental harm.
- Resilience Against Climate Risks: GSCM helps companies become more resilient to environmental disruptions such as floods, wildfires, and extreme weather events.
- Cost Savings Through Efficiency: Green practices often lead to operational efficiencies. Reducing waste, optimizing energy use, integrating PMP Training, and improving logistics can lower production.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Sustainability efforts strengthen corporate image. Companies with environmentally responsible supply chains are often viewed more favorably by stakeholders, media, and the general public.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Modern consumers prefer brands that reflect their environmental and social values. A green supply chain builds trust, encouraging long-term loyalty and higher customer retention.
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Reduction: Adopting GSCM helps businesses stay ahead of evolving environmental regulations. This reduces the risk of legal penalties and ensures smooth operations in global markets with strict compliance standards.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: GSCM encourages innovation in product design, packaging, and processes. Companies that lead in sustainability often differentiate themselves in the market and gain a competitive edge.
- Patagonia – Recycled Materials & Product Longevity: Patagonia is a leading example of sustainable supply chain practices. The company uses recycled fabrics and promotes product longevity by encouraging customers to repair, reuse, and recycle clothing instead of buying new items.
- Patagonia – Transparent and Ethical Sourcing: Patagonia maintains a transparent supply chain, sharing detailed sourcing information with the public. It emphasizes ethical labor practices and high environmental standards across its suppliers and production facilities.
- IKEA – Sustainable Sourcing of Raw Materials: IKEA sources wood, cotton, and other raw materials from sustainable and certified sources, aligning with agile principles similar to those in What Is Scrum XP.
- Unilever – Waste Reduction and Circular Economy: Unilever has committed to making all of its plastic packaging reusable, recyclable, or compostable. The company’s supply chain integrates circular economy principles, reducing landfill waste and improving resource efficiency.
- Apple – Carbon-Neutral Supply Chain Goals: Apple has committed to making its entire supply chain carbon neutral by 2030. This involves partnering with suppliers to use 100% renewable energy and improve energy efficiency in manufacturing.
- Nike – Environmentally Friendly Manufacturing: Nike integrates sustainable design and manufacturing by reducing water usage, eliminating harmful chemicals, and increasing the use of recycled materials in its products.
- Toyota – Green Logistics: Toyota incorporates green logistics through fuel-efficient transport, hybrid delivery trucks, and optimized routes to reduce emissions and energy use in its supply chain operations.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Benefits of Implementing GSCM
Challenges in Adopting GSCM Practices
Despite the many advantages of Green Supply Chain Management, implementing it effectively presents several challenges and complexities. One major difficulty lies in distinguishing genuine sustainability efforts from superficial marketing tactics, often referred to as “greenwashing.” Some companies may exaggerate or misrepresent their environmental initiatives to appeal to eco-conscious consumers without making meaningful changes to their operations. This can damage a company’s credibility and trustworthiness when customers and stakeholders discover the truth. Moreover, misleading environmental claims can lead to legal consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and regulatory scrutiny, which can harm a company’s reputation and financial standing. Another challenge in adopting GSCM is the potential increase in costs associated with sustainable sourcing, production methods, and transportation, which must be carefully managed across the different Phases of Project Management. Environmentally friendly materials and processes can sometimes be more expensive than conventional alternatives, especially during the initial transition phase. Companies may also face difficulties in identifying and verifying suppliers that meet strict environmental and ethical standards. Supply chain transparency can be limited, particularly when dealing with multiple tiers of suppliers across different countries and regulatory environments. Furthermore, integrating sustainability into complex global supply chains requires significant changes in strategy, culture, and operations. It demands collaboration across departments and with external partners, along with investments in new technologies and training. Measuring and reporting environmental performance accurately is another challenge, as companies need reliable data and standardized metrics to assess progress and demonstrate accountability. Despite these hurdles, companies that commit to authentic and transparent GSCM Practices can gain a competitive edge by building stronger customer loyalty, complying with evolving regulations, and contributing positively to the environment. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, clear communication, and a long-term commitment to sustainability as a core business value.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Technologies Enabling Green Supply Chains
The adoption of digital and clean technologies plays a critical role in the success of Green Supply Chain Management. These advanced tools provide companies with the ability to evaluate the environmental impact of a product at every stage of its life cycle, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing, distribution, use, and eventual disposal or recycling. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify opportunities to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize emissions, ultimately supporting more sustainable product design and development. This process, often referred to as eco-design, focuses on creating products that are environmentally friendly throughout their entire life span while maintaining functionality and profitability. Digital technologies also enhance sustainability reporting by enabling companies to collect accurate, real-time information on environmental performance, similar to how teams can Learn Burndown Charts With Jira for better project tracking. This transparency is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and demonstrating accountability to consumers, investors, and other stakeholders who increasingly demand proof of sustainable practices. Tools such as life cycle assessment software, carbon footprint calculators, and environmental management systems provide a comprehensive view of the ecological impact, helping companies set measurable goals and track progress over time. Clean technologies complement digital tools by offering practical solutions to reduce environmental harm. For example, renewable energy sources, energy-efficient machinery, and waste reduction techniques lower the carbon footprint of supply chain operations. The integration of digital and clean technologies enables companies to optimize their processes, reduce operational costs, and comply with environmental regulations more effectively. In summary, the combination of digital and clean technologies empowers organizations to build greener, more resilient supply chains. These tools not only improve environmental outcomes but also enhance competitiveness by meeting the growing market demand for sustainable products and responsible business practices.
Preparing for a PMP Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
Green Supply Chain Management has evolved from being a niche or optional practice into a critical business imperative for organizations worldwide. In today’s environment, companies face rising expectations from customers who increasingly prefer eco-friendly products, regulators who enforce stricter environmental standards, and investors who prioritize sustainability in their decision-making. As a result, incorporating environmental sustainability into supply chain operations is no longer a choice but a necessity. GSCM helps organizations conserve valuable natural resources, reduce waste and emissions, and protect the environment while simultaneously improving operational efficiency. By adopting sustainable practices throughout the supply chain and applying PMP Training, companies can lower costs through energy savings, waste reduction, and optimized resource use. These improvements not only benefit the planet but also contribute to a stronger brand reputation, helping businesses attract loyal customers and differentiate themselves in competitive markets. Successfully implementing Green Supply Chain Management requires a firm commitment from leadership and a willingness to innovate. It involves collaboration and coordination across the entire value chain, from suppliers and manufacturers to logistics providers and distributors. Every stakeholder must align on sustainability goals and actively contribute to achieving them. This often means investing in new technologies, redesigning processes, and continuously monitoring environmental performance. While the transition to GSCM can be challenging, companies that embrace this approach stand to gain immense rewards. Financial benefits arise from cost savings, risk mitigation, and improved market positioning. Environmental gains support global efforts to combat climate change and preserve ecosystems for future generations. Ultimately, Green Supply Chain Management represents a powerful strategy for businesses committed to long-term success and responsible corporate citizenship.