- Introduction
- What is inventory network the executives?
- How truly does store network the board work?
- Why is production network the board significant?
- Key elements of powerful inventory network the board
- Advancement of production network the executives
- Production network counseling
- Manual for store network the board
- Production network the board steps
- Store network the executives steps
- Levels of Activities in the Supply Chain
- Technology and Supply Chain Management
- Theories of Supply Chain Management
- Audience
- Prerequisites
- Conclusion
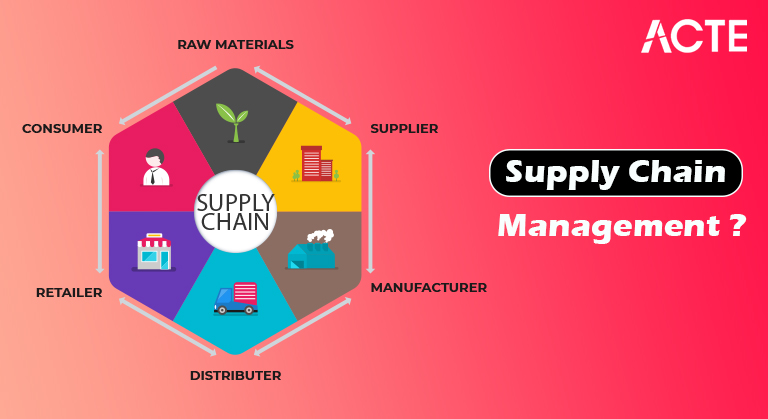
- Store network the executives can be characterized as the administration of stream of items and administrations, which starts from the beginning of items and finishes with the item’s utilization toward the end-client. This is a concise early on instructional exercise that clarifies the systems applied in the quickly developing area of Supply Chain Management in an association.
- In an association, assuming an item is made utilizing unrefined components from different providers and in the event that these items are offered to clients, a store network is made. Contingent upon the size of the association and the quantity of items that are made, an inventory network might be intricate or basic.
- Store network Management alludes to the administration of an interconnected organization of organizations associated with a definitive conveyance of labor and products to clients.It involves the capacity and transport of unrefined components, the course of stock and the capacity and transportation of the last products from the place of assembling to the mark of utilization.
- The expression “store network the board” was first instituted by Keith Oliver in 1982. Oliver characterized in 1982 the Supply Chain idea as follows: – “Store network the executives (SCM) is the most common way of arranging, carrying out, and controlling the tasks of the production network with the reason to fulfill client prerequisites as proficiently as could really be expected.
- Production network the board traverses all development and capacity of unrefined components, work-in-process stock, and completed merchandise from starting place to point-of-utilization”. From that point forward, practically all Supply Chain Book writers have fostered their own definitions.
- They accepted that the term was snappy and the I2M abbreviation would be generally welcomed, however everything changed during a key directing panel meeting with Dutch hardware monster Philips. At the gathering, he and his group discovered that their snappy expression was not excessively appealing, and Oliver was tested by one of the client’s chiefs: Mr. Van t’Hoff. Oliver clarified Mr. Van t’Hoff what he implied by I2M: “We’re discussing the administration of a chain of supply like it were a solitary element,” Mr. Oliver answered, ―not a gathering of dissimilar capacities.”
- “why don’t you call it that?” Mr. Van t’Hoff said. “Call it what?” Mr. Oliver inquired. “All out inventory network the executives.” Scott Stephens, Former Chair of the Supply-Chain Council (SCC) (1983-1997) and Former Chief Technology Officer of the SCC (1997-2005) states in his blog that in the wake of knowing the story, he was not entirely certain assuming it was Keith Oliver or Mr. Van t’Hoff who authored the term.
- In any case, as Oliver fostered the idea preceding the gathering and involved it first out in the open during the Financial Times interview, gives credit to Oliver’s story to be the Ring of Truth. Nonetheless, the idea of an inventory network in administration was critical well before, in the mid twentieth century, particularly with the production of the sequential construction system.
- The qualities of this time of inventory network the executives incorporate the requirement for huge scope changes, re-designing, scaling back driven by cost decrease programs, and far reaching regard for Japanese administration rehearses.
- Arranging: Plan and deal with all assets expected to fulfill client need for an organization’s item or administration. Whenever the production network is laid out, decide measurements to gauge whether the store network is proficient, viable, conveys worth to clients and meets organization objectives.
- Obtaining: Pick providers to give the labor and products expected to make the item. Then, at that point, lay out cycles to screen and oversee provider connections. Key cycles include: requesting, getting, overseeing stock and approving provider installments.
- Producing: Put together the exercises expected to acknowledge unrefined components, make the item, test for quality, bundle for transportation and timetable for conveyance.
- Conveyance and Logistics: Coordinate client orders, plan conveyances, dispatch loads, receipt clients and get installments.
- Returning: Make an organization or interaction to reclaim flawed, overabundance or undesirable items.
- Recognizing possible issues. At the point when a client arranges more item than the producer can convey, the purchaser can grumble of helpless assistance. Through information examination, makers might have the option to expect the lack before the purchaser is disheartened.
- Enhancing cost progressively. Occasional items have a restricted time span of usability. Toward the finish of the period, these items are ordinarily rejected or sold at profound limits. Carriers, inns and others with transitory “items” ordinarily change costs powerfully to satisfy need. By utilizing insightful programming, comparative determining procedures can further develop edges, in any event, for hard merchandise.
- Working on the portion of “accessible to guarantee” stock. Logical programming apparatuses help to powerfully distribute assets and timetable work in view of the business gauge, real orders and guaranteed conveyance of natural substances. Makers can affirm an item conveyance date when the request is put – altogether lessening erroneously took care of requests.
- Associated: Being ready to get to unstructured information from web-based media, organized information from the Internet of Things (IoT) and more customary informational collections accessible through conventional ERP and B2B mix apparatuses.
- Cooperative: Improving joint effort with providers progressively implies the utilization of cloud-based business organizations to empower multi-endeavor coordinated effort and commitment.
- Digital mindful: The production network should solidify its frameworks and safeguard them from digital interruptions and hacks, which should be an endeavor wide concern.
- Intellectually empowered: The AI stage turns into the advanced inventory network’s control tower by ordering, planning and leading choices and activities across the chain. The majority of the store network is mechanized and self-learning.
- Exhaustive: Analytics abilities should be scaled with information continuously. Bits of knowledge will be extensive and quick. Dormancy is inadmissible in the inventory network of things to come. Many stock chains have started this cycle, with cooperation in cloud-based business networks at an unsurpassed high and significant endeavors in progress to reinforce examination capacities.
- The SCM cycle begins with sorting out what items clients need. This stage includes the beginning phases of store network arranging, generally thought to be one of the two overall classes of SCM alongside store network execution.
- Inventory network arranging begins with request arranging, an interaction for social event chronicled information, for example, past deals, and applying investigation and factual displaying to provoke a gauge or interest plan that the outreach group and functional offices – – for instance, assembling and advertising – – can settle on. The conjecture decides the sorts and amounts of items to be made.
- Getting the conjecture right is basic for keeping away from exorbitant issues, for example, the bullwhip impact, in which little variances in retail request are amplified further up the production network, prompting extreme deficiencies or excesses of stock.
- A few organizations perform request arranging as a feature of a formalized interaction called deals and tasks arranging (S&OP), which envelops an iterative course of information gathering, conversation, accommodating of interest plans with creation plans, and the board endorsement.
- A few organizations remember S&OP for a more extensive cycle called coordinated business arranging (IBP) that joins other offices’ arrangements in a solitary company wide plan.
- In the following significant stage, creation arranging, the organization makes certain about the particulars of where and how the items called for in the interest plan will be made.
- (Creation arranging is likewise utilized in different enterprises, like agribusiness and oil and gas.) An all the more adjusted variety called timely arrangement and booking (APS; then again, APO for streamlining) looks to improve the assets that go into creation and make them more receptive to changes popular. It is ordinarily robotized in particular programming.
- MRP is a cycle tracing all the way back to the 1960s that most makers use to guarantee adequate materials and parts, like subassemblies, are accessible for use in the assembling system by taking stock of what’s close by, distinguishing holes, and purchasing or making the leftover things. The focal archive in both MRP and creation arranging is the bill of materials (BOM), a total rundown of the things expected to make an item.
- MRP is now and then done as a feature of assembling asset arranging (MRP II), which widens the MRP idea to different offices like HR and money.
- MRP and MRP II were the ancestors of big business asset arranging (ERP), which is intended to incorporate the significant business cycles of organizations in any industry. As you’ll see, ERP programming has become fundamental to SCM.
- Stock administration comprises of different strategies and equations for guaranteeing satisfactory stockpile – – from unrefined components in an assembling plant, maybe oversaw in a MRP framework, to bundled merchandise in a retail location for minimal use of time and assets.Makers are confronted with an assortment of stock administration issues.
- A considerable lot of which include organizing request arranging with stock at the two closures of the creation interaction. For instance, now and then MRP prompts more stock – – particularly when the framework is first carried out – – and the producer should attempt to synchronize MRP boundaries with the stock currently available.
- The SCM interaction begins with sorting out what items clients need. This stage includes the beginning phases of inventory network arranging, generally thought to be one of the two overall classes of SCM alongside store network execution.
- Production network arranging begins with request arranging, a cycle for get-together verifiable information, for example, past deals, and applying investigation and measurable displaying to spur a conjecture or interest plan that the outreach group and functional offices – – for instance, assembling and advertising – – can settle on. The conjecture decides the sorts and amounts of items to be fabricated.
- Getting the conjecture right is basic for staying away from exorbitant issues, for example, the bullwhip impact, in which little vacillations in retail request are amplified further up the store network, prompting extreme deficiencies or overflows of stock.
- A few organizations perform request arranging as a component of a formalized interaction called deals and activities arranging (S&OP), which incorporates an iterative course of information gathering, conversation, accommodating of interest plans with creation plans, and the board endorsement. A few organizations remember S&OP for a more extensive interaction called coordinated business arranging (IBP) that joins other offices’ arrangements in a solitary companywide plan.
- In the following significant stage, creation arranging, the organization makes certain about the particulars of where and how the items called for in the interest plan will be made.
- (Creation arranging is likewise utilized in different businesses, like agribusiness and oil and gas.) An all the more adjusted variety called early arrangement and planning (APS; then again, APO for advancement) tries to enhance the assets that go into creation and make them more receptive to changes popular. It is ordinarily mechanized in specific programming.
- MRP is an interaction tracing all the way back to the 1960s that most producers use to guarantee adequate materials and parts, like subassemblies, are accessible for use in the assembling system by taking stock of what’s close by, distinguishing holes, and purchasing or making the excess things.
- The focal record in both MRP and creation arranging is the bill of materials (BOM), a total rundown of the things expected to make an item.
- MRP is here and there done as a component of assembling asset arranging (MRP II), which widens the MRP idea to different divisions like HR and money.
- MRP and MRP II were the ancestors of big business asset arranging (ERP), which is intended to coordinate the significant business cycles of organizations in any industry. As you’ll see, ERP programming has become essential to SCM.
- Stock administration comprises of different procedures and equations for guaranteeing sufficient stockpile – – from natural substances in an assembling plant, maybe oversaw in a MRP framework, to bundled products in a retail location – – for minimal use of time and assets.
- Makers are confronted with an assortment of stock administration issues, a large number of which include organizing request arranging with stock at the two finishes of the creation interaction. For instance, in some cases MRP prompts more stock – – particularly when the framework is first carried out – – and the maker should attempt to synchronize MRP boundaries with the stock currently close by.
- At times called obtaining, acquirement is the most common way of tracking down providers for merchandise, dealing with those connections and getting the products financially – – alongside all the correspondence, like conveying demands for offers, and desk work, including buy requests and solicitations.
- It is a significant area of production network the board, considering how much is traded at all focuses along the chain. Most players in the production network – – providers, makers, merchants and retailers – – have committed obtainment staff.
- Vital obtaining is a raised and more modern sort of acquisition that expects to streamline an organization’s obtaining interaction by exploiting its combined buying power and adjusting it to business objectives.
- Provider relationship the board (SRM), interestingly, addresses obtaining issues by zeroing in on the providers the organization considers generally basic to progress and deliberately fortifying associations with them while cultivating ideal execution. Figure 2 shows the SRM interaction in a nutshell.
- Operations covers the moving and putting away of merchandise, from the conveyance of parts and unrefined components to makers or processors to the conveyance of completed items to stores or direct to customers, and even past for item adjusting, return and reusing – – a cycle called switch strategies.
- Stock administration is strung all through the strategies interaction.
- Client – The beginning of the inventory network is the client. The client chooses to buy an item and thus contacts the outreach group of an organization. A business request is finished with the date of conveyance and the amount of the item mentioned. It might likewise incorporate a portion for the creation office relying upon whether or not the item is accessible in stock.
- Arranging – Once the client has made his/her business request, the arranging division will make a creation intend to deliver the item sticking to the requirements of the client. At this stage, the arranging office will know about natural substances required.
- Buying – If unrefined components are required, the buying division will be informed and they thus send buying requests to the providers requesting the redemption of a particular amount of natural substances on the necessary date.
- Stock – Once the unrefined components have been conveyed, they are checked for quality and exactness and afterward put away in a distribution center till they are expected by the creation division.
- Creation – Raw materials are moved to the creation site, as per the particulars spread out in the creation plan. The items expected by the client are presently made utilizing the unrefined components provided by the providers. The finished items are then tried and moved back to the distribution center contingent upon the date of conveyance expected by the client.
- Transportation – When the completed item is moved into capacity, the delivery office or the transportation division decides when the item passes on the stockroom to arrive at the client on schedule.
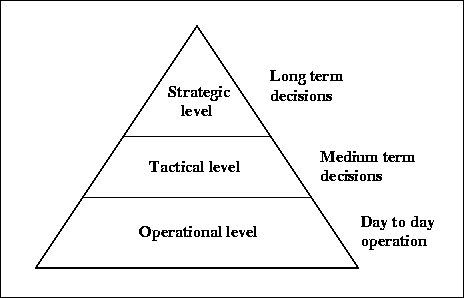
- Strategic – At this level, senior management is involved in the supply chain process and makes decisions that concern the entire organization. Decisions made at this level include the size and site of the production area, the collaborations with suppliers, and the type of that product that is going to be manufactured and so forth
- Tactical – Tactical level of activity focuses on achieving lowest costs for running the supply chain. Some of the ways this is done is by creating a purchasing plan with a preferred suppliers and working with transportation companies for cost effective transport.
- Operational – At the operational level, activity decisions are made on a day-to-day basis and these decisions affect how the product shifts along the supply chain. Some of the decisions taken at this level include taking customer orders and the movement of goods from the warehouse to the point of consumption.
- In order to maximize benefits from the supply chain management process, organizations need to invest in technology.
- For the optimal working of the supply chain management process, organizations mainly invest in Enterprise Resource Planning suites.
- Also, the advancement of Internet technologies allows organizations to adopt Web-based software and Internet communications.
- Resource-Based View (RBV)
- Transaction Cost Analysis (TCA)
- Knowledge-Based View (KBV)
- Strategic Choice Theory (SCT)
- Agency Theory (AT)
- Institutional theory (InT)
- Systems Theory (ST)
- Network Perspective (NP)
- Supply Chain Management is a branch of management that involves suppliers, manufacturers, logistic providers, and most importantly, the customers.
- The supply chain management process works through the implication of a strategic plan that ensures the desired end product leaving a customer with maximum satisfaction levels at the lowest possible cost.
- The activities or the functions involved in this type of management process are divided into three levels: the strategic level, the tactical level and the operational level.
Introduction :-
What is inventory network the executives?
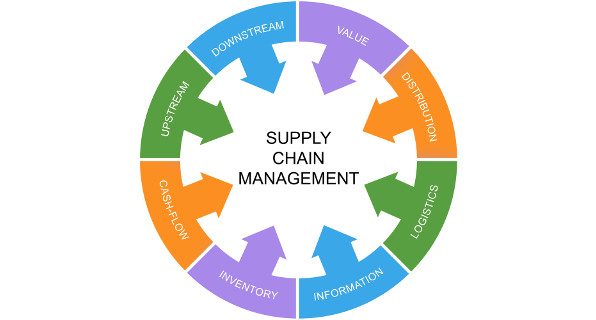
Store network the board is the treatment of the whole presentation stream of a decent or administration – beginning from the crude parts the entire way to conveying the end result to the shopper. An organization makes an organization of providers (“joins” in the chain) that move the item along from the providers of unrefined components to those associations that manage clients.
How truly does store network the board work?
As per CIO, there are five parts of customary store network the board frameworks:
Why is production network the board significant?
Powerful inventory network the board frameworks limit cost, burn through and time in the creation cycle. The business standard has turned into a without a moment to spare store network where retail deals consequently signal recharging requests to producers. Retail retires can then be restocked nearly as fast as item is sold. One method for facilitating develop this cycle is to break down the information from production network accomplices to see where further enhancements can be made.
By examining accomplice information, the CIO.com post recognizes three situations where successful store network the executives builds worth to the production network cycle:
Key elements of powerful inventory network the board :-
The production network is the clearest “face” of the business for clients and shoppers. The better and more compelling an organization’s store network the executives is, the better it safeguards its business notoriety and long haul supportability.
IDC’s Simon Ellis in The Path to a Thinking Supply Chain¹ characterizes what is production network the board by recognizing the five “Cs” of the powerful production network the executives of things to come:
Advancement of production network the executives :-
While the previous stock chains were centered around the accessibility, development and cost of actual resources, the present inventory chains are about the administration of information, administrations and items packaged into arrangements.
Present day inventory network the executives frameworks are about considerably more than exactly where and when. Inventory network the board influences item and administration quality, conveyance, costs, client experience and eventually, benefit.
As of late as 2017, a normal inventory network got to multiple times a bigger number of information than only five years sooner. Notwithstanding, under a fourth of this information is being dissected. That implies the worth of basic, time-delicate information – like data about climate, unexpected work deficiencies, political distress and microbursts sought after – can be lost.
Present day supply chains exploit enormous measures of information produced by the chain cycle and are organized by logical specialists and information researchers. Future production network pioneers and the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) frameworks they oversee will probably zero in on upgrading the handiness of this information – dissecting it continuously with insignificant inertness.
Production network counseling :-
With IBM Services, you can advance your inventory network processes into wise work processes, to arrive at new degrees of responsiveness and development.
Challenge siloed cycles to uncover efficiencies, empower your groups to execute and convey, and utilize arising innovations like AI and blockchain to open doors in each progression of the worth chain – from interest wanting to arrange organization and satisfaction.
Worldwide store network pioneers have been compelled to generally reevaluate customary approaches to working, where the best danger in exploring interruptions is acting with the previous rationale.
IBM inventory network counseling administrations can fortify inventory network the board, assisting clients with building strong, lithe and maintainable stockpile chains for what’s to come. Our results driven methodology, market-driving advancements and coordination capacities assist you with developing your inventory network work processes, hyperautomate direction, further develop productivity and engage your kin.
1. Request arranging :
2. Creation arranging :
3. Material necessities arranging (MRP) :
4. Stock administration :
Manual for store network the board :-
The pandemic showed what can happen when the inconceivable falls to pieces worldwide inventory chains and disturbs life as far as we might be concerned. Viable inventory network the executives can reestablish request. The items that help present day cultures are fabricated and disseminated by probably the most broad frameworks at any point assembled.
A worldwide organization of supply chains brings us everything from the produce and bundled products that fill grocery store racks to the chips that run our cell phones and the unrefined components of new development. It took an overall wellbeing emergency to cause us to acknowledge exactly the way that delicate these worldwide stock chains are.
Presently, two years after the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, economies are recuperating however supply chains stay drowsy and powerless. Manufacturing plants run at underneath limit since they can’t get natural substances or laborers. Containerships back up at ports, and there aren’t an adequate number of drivers to convey merchandise crosscountry. The disarray has made store network a family word and production network the board a first concern for some organizations.
Store network the board is an expansive field that incorporates every one of the cycles, frameworks and methodologies for improving an item’s creation and dispersion. Its numerous features incorporate interest arranging, stock administration, strategies, acquirement and provider the board.
Created as a manual paper process more than century prior, when mid twentieth century industrialists expected to upgrade producing, production network the board is presently tied inseparably to 21st-century innovation. Be that as it may, as the pandemic has uncovered, without worldwide reconciliation and exact information, innovation is as prone to cause inventory network disappointment all things considered to forestall it.
Reestablishing the worldwide inventory chains that have been overturned by the pandemic won’t be simple. This extensive manual for SCM clarifies the fundamental phrasing, cycles, patterns and difficulties you want to comprehend to guarantee that production network innovation adapts to the situation. As you read this outline, click on the hyperlinks for inside and out data and exhortation on the key subjects.
Production network the board steps :-
Each significant period of an item’s development through the inventory network, from materials to creation and dissemination (see Figure 1), has its own unmistakable business cycles and teaches. The majority of the cycles, which started as paper-based techniques, are presently generally dealt with in specific inventory network the executives programming. Here is a bit by bit depiction of what goes into store network the board.
1. Request arranging
2. Creation arranging
3. Material prerequisites arranging (MRP)
4. Stock administration
5. Acquirement
6. Operations
Store network the executives steps :-
Each significant period of an item’s development through the inventory network, from materials to creation and circulation (see Figure 1), has its own unmistakable business cycles and trains. A large portion of the cycles, which started as paper-based strategies, are presently typically taken care of in particular store network the board programming. Here is a bit by bit portrayal of what goes into store network the board. Various Links in the Supply Chain
Levels of Activities in the Supply Chain :-
In order to make sure that the above supply chain is running smoothly and also to ensure maximum customer satisfaction at the lowest possible cost, organizations adopt supply chain management processes and various technologies to assist in these processes.
There are three levels of activities Supply Chain Management in that different departments of an organization focus on to achieve the smooth running of the supply chain. They are:
Technology and Supply Chain Management :-
Theories of Supply Chain Management:-
A number of experts in the field of supply chain management have tried to provide theoretical foundations for some areas of supply chain management by adopting organizational theory.
Some of these theories are:
Audience :-
This tutorial will be useful for students from management streams who aspire to learn the basics of Supply Chain Management. Professionals, regardless of which sector or industry they belong to, can use this tutorial to learn how to apply the methods of Supply Chain Management in their respective project environments.
Prerequisites :-
The readers of this tutorial are expected to have a general idea of what supply chain management means and what place and importance it holds in an organization.





