
- Introduction to IoT
- Evolution and Growth of IoT
- Key Industries Benefiting from IoT
- Emerging Technologies in IoT
- AI and Machine Learning Integration in IoT
- Security Challenges in IoT
- Smart Cities and IoT Adoption
- IoT in Healthcare, Agriculture, and Manufacturing
- IoT and 5G: Future Trends
- Job Opportunities in IoT
- Key IoT Certifications for Career Growth
- Conclusion
Introduction to IoT
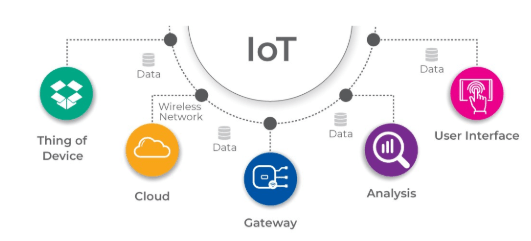
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity that allow them to collect, exchange, and process data. These devices can range from everyday household items to industrial machines, and they interact through the internet, enabling automation, optimization, and more intelligent decision-making. Cloud Computing Training plays a pivotal role in transforming various industries by offering real-time data insights, improving operational efficiency, and reducing costs. For instance, in healthcare, IoT devices enable remote patient monitoring, while in manufacturing, they enable predictive maintenance and process optimization. IoT also enhances consumer experiences by enabling smart homes with connected appliances, lighting, and security systems. As the number of connected devices grows, IoT is expected to revolutionize sectors such as transportation, agriculture, and energy management. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, IoT devices can analyze data and make autonomous decisions, paving the way for more advanced automation. However, challenges like data privacy, security concerns, and interoperability still need to be addressed for IoT to reach its full potential. The future of IoT looks promising, with advancements in 5G networks and edge computing expected to accelerate its growth and capabilities.
Evolution and Growth of IoT
IoT has evolved significantly over the last few decades, from the early days of connected devices in the 1980s with basic sensor technology to the sophisticated systems we see today. The rise of broadband internet, low-cost sensors, and powerful computing devices has contributed to the rapid growth of IoT. These advancements have enabled the development of smarter, more efficient systems capable of handling massive amounts of data and providing real-time insights. Now, billions of connected devices are in use globally, spanning various industries such as healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and agriculture. The integration of IoT with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and edge computing is unlocking new possibilities for automation and Cloud Security Service. As more devices become interconnected, IoT is driving innovations that improve decision-making, enhance user experiences, and optimize operations. The market for IoT is expected to continue expanding, with future trends focusing on increased automation, smarter cities, and the advancement of 5G networks to support the growing number of connected devices. This rapid growth brings both opportunities and challenges, such as ensuring robust security, managing data privacy, and achieving interoperability across diverse devices and platforms.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
Key Industries Benefiting from IoT
Several industries are reaping the benefits of IoT, including:
- Manufacturing: IoT enables predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring of production lines, and better resource management.
- Healthcare: IoT allows for remote monitoring, telemedicine, and personalized care, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Agriculture: IoT applications help Salesforce Commerce Cloud with crop monitoring, soil condition tracking, and optimizing irrigation, leading to better yield and resource efficiency.
- Retail: Through IoT, retailers can track inventory, enhance customer experience, and offer personalized shopping experiences.
- Transportation: IoT transforms logistics with real-time vehicle tracking, route optimization, and fleet management.
- Smart Homes: IoT is at the heart of smart homes, enabling automation for lighting, heating, security systems, and appliances.
- Edge Computing: Data processing closer to where the data is generated, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements.
- Blockchain: Ensuring data integrity and enhancing security in IoT networks by offering decentralized, tamper-proof records.
- Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN): Enabling long-range communication with minimal power consumption, ideal for IoT devices in remote locations.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Integrating IoT data with AR to provide immersive experiences, especially in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Lack of standardization: Different manufacturers use different protocols, making it difficult to secure devices uniformly.
- Data privacy: IoT devices collect massive amounts of personal data, which can be exploited if not appropriately protected.
- Limited device security: Many IoT devices are resource-constrained and may not support advanced encryption or regular software updates.
- Traffic management: Real-time traffic monitoring and bright traffic lights to reduce congestion.
- Energy management: Smart grids and energy-efficient street lighting.
- Public safety: Surveillance cameras, environmental sensors, and emergency response systems.
- Waste management: IoT-enabled bins that notify when they need to be emptied.
- Healthcare: IoT devices like wearable health trackers, remote patient monitoring systems, and connected medical equipment transform healthcare by providing real-time data and improving patient care.
- Agriculture: IoT devices help farmers monitor crops, weather conditions, soil moisture, and livestock, improving productivity and sustainability.
- Manufacturing: IoT enables predictive maintenance, real-time asset tracking, and production optimization, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Autonomous vehicles: Real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
- Smart cities: Managing vast networks of connected devices more efficiently. Industrial IoT: Real-time data processing and decision-making at scale.
- IoT Developer: Designing and building IoT systems and applications.
- IoT Architect: Overseeing the design and implementation of complex IoT networks.
- Data Scientist/Analyst: Analyzing data generated by IoT devices to derive actionable insights.
- Security Expert: Ensuring the security of IoT networks and devices.
- IoT Project Manager: Leading the development and deployment of IoT projects.
- Certified IoT Professional (CIoTP): A comprehensive certification covering IoT architecture, design, and security.
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA): Focuses on networking skills, including IoT applications.
- CompTIA IT Fundamentals (ITF+): Provides knowledge of foundational IT and IoT concepts.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure IoT Developer Specialty: Focuses on developing IoT solutions on the Microsoft Azure platform.
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Emerging Technologies in IoT
Several emerging technologies are shaping the future of IoT:
AI and Machine Learning Integration in IoT
Integrating AI and Machine Learning (ML) with IoT enhances devices’ ability to make intelligent decisions based on data analysis. AI enables IoT systems to predict outcomes, optimize processes, and automate operations without human intervention, making them more efficient and responsive. For instance, smart thermostats can learn user preferences over time and adjust heating or cooling automatically, ensuring comfort while conserving energy. Similarly, autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI to process real-time data processing from sensors, enabling them to navigate, detect obstacles, and make split-second decisions, all without human input. Cloud Computing Training synergy between AI, ML, and IoT opens up vast possibilities in industries like healthcare, where wearable devices can predict health risks, or in manufacturing, where predictive maintenance can anticipate equipment failure before it occurs. With AI and ML, IoT devices not only react to data but also learn from it, making them more adaptive and capable of continuously improving their performance. This fusion of technologies is driving the next generation of intelligent automation, transforming everything from everyday tasks to complex business operations.
Security Challenges in IoT
As IoT devices increase, so do the risks associated with them. Security is a significant challenge in IOT Architecture, as many devices are vulnerable to cyberattacks, data processing breaches, and privacy violations. Challenges include:
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
Smart Cities and IoT Adoption
IoT is pivotal in developing smart cities, where infrastructure, services, and systems are interconnected and optimized for better urban living. IoT applications in smart cities include:
IoT in Healthcare, Agriculture, and Manufacturing
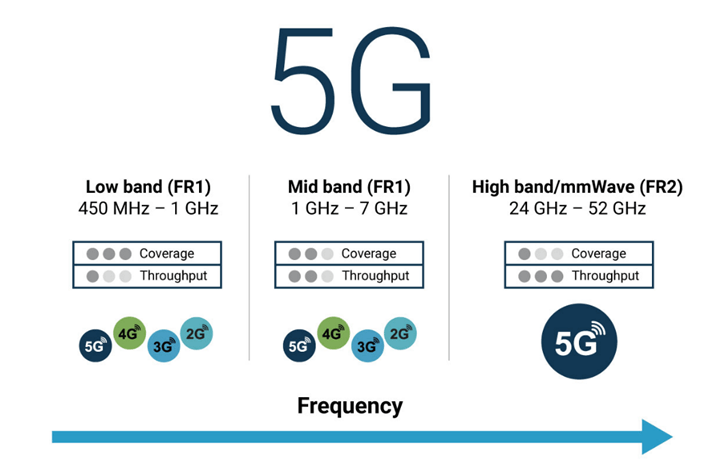
IoT and 5G: Future Trends
The combination of IoT and 5G networks is poised to accelerate IoT innovation, opening up new possibilities for connectivity and data processing. 5G offers faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, all of which are essential for handling the massive volume of data generated by billions of connected devices. With its ability to support a higher density of devices per square kilometer, 5G enables seamless communication between IoT devices in real-time, which is crucial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation. The ultra-low latency of 5G networks ensures that IOT Projects for Shaping the future can be transmitted almost instantaneously, allowing for faster decision-making and immediate action in critical applications like healthcare monitoring and disaster response.
Job Opportunities in IoT
The growing IOT Architecture ecosystem is creating a wide range of job opportunities, including:
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Key IoT Certifications for Career Growth
Several certifications can help professionals advance in the IoT field:
Conclusion
IoT rapidly transforms industries and our daily lives, creating brighter environments and offering solutions to complex challenges. As IoT continues to grow, it brings immense opportunities for innovation, improved efficiencies, and new job roles. However, it also presents challenges, particularly regarding security and privacy, which need to be addressed for its continued success. The future of IoT, especially with emerging technologies like AI, 5G networks, and edge computing, promises exciting developments and new possibilities. As Cloud Computing Training technologies converge, they will enable even smarter and more responsive systems. The integration of IoT with advanced analytics will drive further advancements in automation and decision-making.





