
- Introduction to How Internet Works
- How does the web function at home?
- How is the Internet associated?
- How the Web Works
- In Short
- Where to Begin? Web Addresses
- Understanding The Differences Between Internet Connections
- Who oversees the Internet?
- Computer Networks
- Associating with the Internet
- The Internet
- Making Contact
- Conveying the genuine idea
- Protocal Stacks and Packets
- Application Protocols: HTTP and the World Wide Web
- Why do we utilize the Internet?
- Utilizations of Internet
- Conclusion
- Whenever you enter something like Google.com the solicitation goes to one of the numerous exceptional PCs on the Internet known as Domain Name Servers (DNS). This large number of solicitations are steered through different switches and switches. The area name waiters keep tables of machine names and their IP addresses, so when you type in Google.com it gets converted into a number, which distinguishes the PCs that serve the Google Website to you.
- Whenever you need to see any page on the Web, you should start the movement by mentioning a page utilizing your program. The program asks a space name server to interpret the area name you mentioned into an IP address. The program then, at that point, sends a solicitation to that server for the page you need, utilizing a standard called Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP.
- The server ought to continually be associated with the Internet, prepared to serve pages to guests. Whenever it gets a solicitation, it searches for the mentioned archive and returns it to the Web program. At the point when a solicitation is made, the server for the most part logs the client’s IP address, the record mentioned, and the date and time it was mentioned. This data differs from server to server.
- A normal Web page requires the Web program to demand more than one record from the Web server and in addition to the HTML/XHTML page, yet additionally any pictures, templates, and different assets utilized in the page. Every one of these documents including the primary page needs a URL to recognize everything. Then, at that point, everything is sent by the Web server to the Web program and the Web program gathers this data and showcases them as a Web page.
- A client enters a URL into a program (for instance, Google.com. This solicitation is passed to an area name server.
- The area name server returns an IP address for the server that has the Website (for instance, 68.178.157.132).
- The program demands the page from the Web server utilizing the IP address indicated by the area name server.
- The Web server returns the page to the IP address determined by the program mentioning the page. The page may likewise contain connections to different records on a similar server, for example, pictures, which the program will likewise ask for.
- The program gathers all the data and showcases it to your PC as a Web page.
- Since the Internet is a worldwide organization of PCs every PC associated with the Internet should have an interesting location. Web addresses are in the structure nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn where nnn should be a number from 0 – 255. This address is known as an IP address. (IP represents Internet Protocol; to a greater degree toward this later.)
- If you interface with the Internet through an Internet Service Provider (ISP), you are normally allowed a brief IP address for the term of your dial-in meeting. Assuming that you associate with the Internet from a neighborhood (LAN) your PC may have a long-lasting IP address or it may get a transitory one from a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. Regardless, assuming that you are associated with the Internet, your PC has a one-of-a-kind IP address.
- ISOC delegates the IAB-Internet Architecture Board. They satisfy routinely to survey guidelines and allot assets, similar to addresses.
- IETF-Internet Engineering Task Force. Another volunteer association meets routinely to talk about functional and specialized issues.
- Also, what’s a PC organization? A PC network is only at least two PCs associated together to such an extent that they might send messages between one another. In bigger organizations, PCs are associated together in complex plans, where some go-between PCs have more than one association with different PCs, to such an extent that each PC can arrive at some other PC in the organization using ways through a portion of those go-between PCs.
- PCs aren’t the main things that utilization organizations – the street and rail networks are the same as PC organizations, simply those organizations transport individuals rather than data.
- Trains on a rail network work on a specific sort of track – such a show is required because generally, the organization couldn’t work. Similarly, streets are intended to suit vehicles that match a sort of example – vigorous vehicles of a specific size range that movement inside a specific sensible speed range. PCs in an organization have shown as well, and we generally call these shows ‘conventions’.
- There are numerous sorts of famous PC networks today. The most regular by a wide margin is the supposed ‘Ethernet’ network that associates PCs together in homes, schools, and workplaces. Nonetheless, WiFi is turning out to be progressively famous for interfacing together gadgets so that links aren’t needed in any way.
- Whenever you interface with the Internet, you’re utilizing organizing innovation, however, things are generally significantly muddier. There’s a well-suited expression, “Rome wasn’t inherent a day” because nor was the Internet. The main explanation the Internet could jump up so rapidly and inexpensively for individuals was because one more sort of organization previously existed all through the world – the telephone organization!
- The pre-presence of the telephone network gave a medium to customary PCs in conventional people groups homes to be associated with the incredible innovative military and exploration network that had been created in years prior. It just required some innovative authority as ‘modems’. Modems permit telephone lines to be transformed into a small-scale network association between a home and an extraordinary organization (an ‘ISP’) that as of now is associated up to the Internet. It resembles an extension signing up the street networks on an island and the central area – the street networks become one, because of a unique sort of association between them.
- Quick Internet associations that are done using ‘(A)DSL’ and ‘Link’ are indistinguishable to telephone line associations truly – there’s as yet a joining interaction or some likeness thereof happening in the background. As Arthur C. Clarke once said, ‘any adequately cutting edge innovation is unclear from wizardry’.
- The truly astounding thing about the Internet isn’t innovation. We’ve had enormous Internet-like PC networks previously, and ‘The Internet’ existed sometime before ordinary individuals knew the term. Interestingly, such a monstrous PC organization could exist without being assembled or represented in any sort of truly coordinated manner. The main association that truly has a hold on the center PC organization of the Internet is a US-government-upheld non-benefit organization called ‘ICANN’, yet no one could guarantee they ‘controlled’ the Internet, as their command and exercises are very restricted.
- The Internet is a confirmation both at the same time because of how technologists collaborated and by how businesspeople took up the errand, unmanaged, to utilize the shows of the technologists to attach ordinary individuals and organizations. The Internet didn’t create on the Microsoft Windows ‘working framework’ – Internet innovation was worked around a lot more established specialized working frameworks; all things considered, the innovation could be applied to normal PCs by essentially assembling support for the important systems administration shows on top of Windows. It was never arranged, yet great establishments and an absence of bottlenecks (like controlling bodies) regularly lead to unanticipated extraordinary ascents – like the phone network previously, or even the overall spread of the human populace and society.
- A PC 116
- in a little area 115
- in a bigger area 60
- constrained by an ISP 69
- (on the Internet)
- Since we can convey messages the crucial step is finished. All we want to do is to placed stuff in our messages with a specific goal in mind to such an extent that it seems OK at the opposite end.
- Letters we send in reality generally share stuff practically speaking – they are composed on paper and in a language comprehended by both source and beneficiary. I’ve talked about before how shows are significant for organizations to work, and this significant idea stays valid for our messages.
- All pieces of the Internet move messages written in things called ‘Bundles’, and the format and substance of those ‘parcels’ are finished by the ‘Web Protocol’ (IP). You don’t have to know these terms, however, you really do have to realize that these straightforward messages are mistake inclined and shortsighted.
- You can consider ‘bundles’ the Internet comparability of a sentence – for a continuous discussion, there would be a large number of them sent in the two bearings of correspondence.
- Every one of those who’ve played ‘Chinese murmurs’ will realize how screwed up (‘undermined’) messages can get when they are sent between numerous specialists to get from their starting point to their objective. PC networks aren’t that awful; however, things truly do turn out badly, and it’s important to have the option to consequently identify and address issues when they do.
- Envision you’re attempting to address spelling mistakes in a letter. It’s typically simple to do because there are far fewer words than there are conceivable word-length blends of letters. You can see when letter blends don’t explain words (‘mistakes’), and afterward effectively think about what the right word ought to have been. It does work.
- Mistakes in messages on the Internet are rectified fundamentally the same way. The messages that are sent are just made longer than they should be, and the additional room is utilized to “summarize” the message as it were – if the “summarizing” doesn’t match the message a blunder has been viewed and the message will require as despise.
- In undeniable reality, it is generally expected conceivable to consistently appraise with sensible precision what wasn’t right with a message without requiring resending.
- Blunder identification and remedy can never be awesome, as the message and “summarizing” part could be unintentionally screwed up with the goal that they erroneously demonstrate nothing turned out badly. The hypothesis is based on putting away a large enough “summarizing” part so this lamentable chance is far-fetched that it very well may be securely overlooked.
- Solid message move on the Internet is done through ‘TCP’. You might have heard the term ‘TCP/IP’: this is only the typical mix of ‘IP’ and ‘TCP’ and is utilized for practically all Internet correspondence. IP is essential to the Internet, yet TCP isn’t – there are indeed other ‘conventions’ that might be utilized that I will not be covering.
- Each PC on the Internet knows how to contact the PCs (the ‘root’ ‘DNS servers’) liable for things like com, organization, net, and the UK. There are a couple of such PCs and one is preached indiscriminately. The DNS server PC is inquired as to whether they know www.example.com and will react saying they know which server PC is liable for com.
- The com server PC is asked it knows www.example.com and will react saying they know which server PC is liable for example.com.
- ‘The ‘example.com’ server PC is inquired as to whether it knows www.example.com and will react saying that it knows the relating server PC to be 69.60.115.116.
- Let’s say your IP address is 1.2.3.4 and you need to make an impression on the PC 5.6.7.8. The message you need to send is “Hi PC 5.6.7.8!”. The message should be sent over anything that sort of wire associates your PC to the Internet.
- Suppose you’ve dialed into your ISP from home and the message should be communicated via a telephone line. Along these lines the message should be interpreted from an alphabetic message into electronic signs, communicated over the Internet, then, at that point, interpreted back into an alphabetic message.
- How could this be refined? Using a convention stack. Each PC needs one to convey on the Internet and it is typically incorporated into the PC’s working framework (for example Windows, Unix, and so forth)
- The convention stack utilized on the Internet is referred to as the TCP/IP convention stack on account of the two significant correspondence conventions utilized. The TCP/IP stack resembles this:
- Look for data on anything across the globe consistently.
- Impart, work together with others.
- Work from home to the workplace or work from home.
- Do exchanges with business substances.
- Download records from a remote.
- Get taught and engaged.
- Complete social.
- Do a bunch of exercises.
- Gather functional information from distant hardware (fixed as well as moving).
- Process information while it is spilled to the focal server.
- Get continuous information on the encompassing gadgets, frameworks, climate to mechanize exercises.
- Plan a choice accepting framework as against the choice emotionally supportive network.
- Associate individuals, partners, machines, and everything
- Availability. An Internet is worldwide assistance and available to all.
- Simple to Use.
- Communication with Other Media.
- Minimal expense.
- Expansion of Existing IT Technology.
- Adaptability of Communication.
- Security.
- How PCs can be associated together, much under non-ideal conditions, (for example, not being actually associated, or just with having a telephone line as an association with the world)
- How an Internet can be fabricated with the end goal that every one of the PCs on it can reach one another
- How messages can be sent between PCs on the Internet
- How messages can encode solicitations and reactions that mean significant human applications
- How human-justifiable URLs, based upon human reasonable space names, permit the internet to work
- How records can encode pages
- How the Internet can be made free from any harm
Introduction to How Internet Works:
How does the Internet function? Great inquiry! The Internet’s development has become touchy and it appears to be difficult to get away from the assault of www.com’s seen continually on TV, heard on the radio, and found in magazines. Since the Internet has become such a huge piece of our lives, a decent agreement is expected to utilize this new instrument most actually.
This whitepaper clarifies the fundamental foundation and innovations that make the Internet work. It doesn’t go into extraordinary profundity, yet covers enough of every area to give a fundamental comprehension of the ideas in question. For any unanswered inquiries, a rundown of assets is given toward the finish of the paper. Any remarks, ideas, questions, and so forth are supported and might be coordinated to the creator at rshuler@gobcg.com.
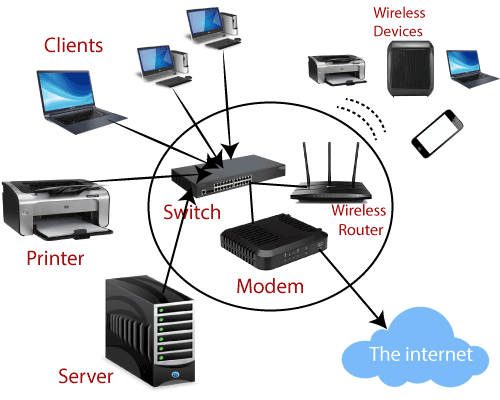
How does the web function at home?
A remote switch interfaces straightforwardly to a modem by a link. This permits it to get data from – and communicate data to – the web. The switch then, at that point, makes and speaks with your home Wi-Fi network utilizing worked-in radio wires. Thus, each of the gadgets on your home organization has web access.
How is the Internet associated?
Switch. A switch is an equipment gadget that permits you to interface a few PCs and different gadgets to a solitary Internet association, which is known as a home organization. Numerous switches are remote, which permits you to make a home remote organization, ordinarily known as a Wi-Fi organization.
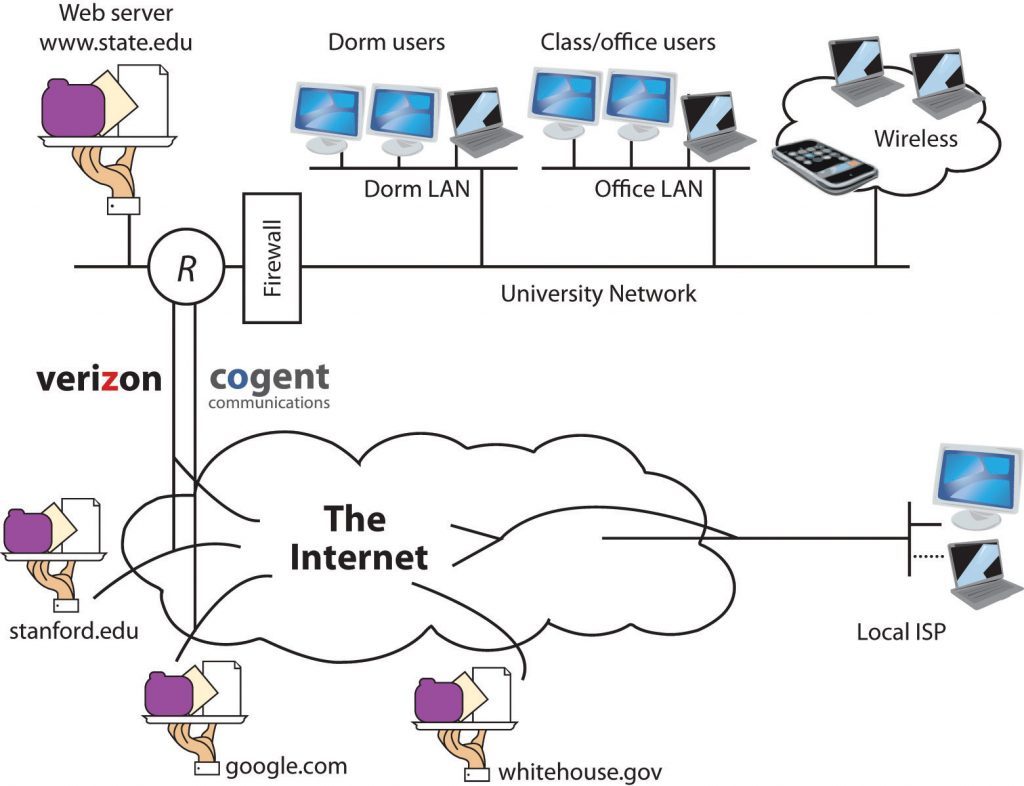
On the easiest level, the Web genuinely comprises of the accompanying parts −
Your PC − This is the PC at which you sit to see the web.
A Web program − A product introduced on your PC which assists you with perusing the Web.
A web association − This is given by an ISP and interfaces you to the web to reach any Website.
A Web server − This is the PC on which a site is facilitated.
Switches and Switches − They are the blend of programming and equipment that take your solicitation and pass to fit Web server.
The Web is known as a client- server framework. Your PC is the client and the far-off PCs that store electronic records are the servers.
How the Web Works:
In Short:
We have perceived how a Web client-server cooperation occurs. We can sum up these means as follows −
Where to Begin? Web Addresses:
Understanding The Differences Between Internet Connections:
While figuring out which kind of Internet speed and Internet association type is ideal for you or your family, it’s vital to comprehend the differentiation between every association. In the present age, there are various ways of associating PCs, work areas, cell phones, gaming consoles, tablets, and tablets to the Internet. Probably the most broadly utilized Internet associations are depicted underneath.
Mobile: Numerous PDA and cell phone suppliers offer voice plans with Internet access. Versatile Internet associations give great paces and permit you to get to the Internet.
Wifi hotspots: Wifi Hotspots are destinations that offer Internet access over a remote neighborhood (WLAN) via a switch that then, at that point, associates with an Internet specialist co-op. Areas of interest use WiFi innovation, which permits electronic gadgets to interface with the Internet or trade information remotely through radio waves. Areas of interest can be telephone-based or unsupported, business or free to the general population.
Dial-up: Dial-up associations expect clients to connect their telephone line to a PC to get to the Internet. This specific sort of association likewise alluded to as simple doesn’t allow clients to settle on or get telephone decisions through their home telephone administration while utilizing the Internet. Presently more obsolete, a dial-up association used to be among the most widely recognized Internet association type.
Broadband: This fast Internet association is given through one or the other link or phone organizations. Perhaps the quickest choice accessible, broadband Internet utilizes various information channels to send huge amounts of data. The term broadband is shorthand for wide data transfer capacity. Broadband Internet associations, for example, DSL and link are viewed as high-data transfer capacity associations. Albeit numerous DSL associations can be viewed as broadband, not all broadband associations are DSL.
Dsl: DSL, which represents Digital Subscriber Line, utilizes an existing 2-wire copper phone line associated with one’s home so the administration is conveyed simultaneously as a landline telephone utility. Clients can in any case make phone calls while riding the Internet.
Link: Satellite Internet association is a type of broadband access. Through the utilization of a link modem, clients can get to the Internet over digital TV lines. Link modems can give incredibly quick admittance to the Internet, making a link association a feasible choice for some.
Isdn: ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) permits clients to send information, voice, and video content over advanced phone lines or standard phone wires. The establishment of an ISDN connector is expected at the two closures of the transmission-with respect to the client as well as the Internet access give
Who oversees the Internet?
The Internet isn’t administered and has no single power figure. A definitive expert for where the Internet is going reprieves with the Internet Society, or ISOC. ISOC is a deliberate participation association whose intention is to advance worldwide data trade through Internet innovation.
This model partitions strategies into a layered arrangement of conventions. These layers are as per the following:
Application layer (most elevated) – worried about the data(URL, type, and so forth) This is the place where HTTP, HTTPS, and so on, comes in.
2Transport layer – liable for start to finish correspondence over an organization.
Network layer – gives information course.
Computer Networks:
Associating with the Internet:
The Internet:
Making Contact:
I’ve laid out how the Internet is a PC organization: presently I will clarify how two PCs that could be on different sides of the world can send messages to one another.
Envision you were composing a letter and expected to send it to somebody. Assuming you just composed a name on the front, it could never show up, except if maybe you lived in a little town. A name is seldom sufficiently explicit. Thusly, we use locations to contact somebody, regularly utilizing: the name, the house number, the street name, the town name, the province name, and now and again, the nation name. This permit sending of messages on one more sort of organization – the postal organization. Whenever you send a letter, normally it will be passed between postal arranging workplaces beginning from the arranging office closest to the beginning, then, at that point, up to progressively enormous arranging workplaces until it’s taken care of by an arranging office covering districts for both the beginning and the objective, then, at that point, down to progressively little arranging workplaces until it’s at the arranging office closest the objective – and afterward, it’s conveyed. A model’s IP address is 69.60.115.116.
They are only a series of digit bunches where the digit bunches towards the right are progressively neighborhood. Every digit bunch is a number somewhere in the range of 0 and 255. This is only an estimate; however, you could imagine this address meaning:
The little area, the bigger area, the ISP, and the Internet, could all be considered PC networks by their own doing. Hence, for a message to the equivalent ‘bigger area’, the message would be missed towards one of those go-between PCs in the bigger area and afterward back down to the right more modest area, and afterward to the right PC.
Conveying the idea:
Conveying the genuine idea:
Names, not Numbers:
Whenever a great many people consider a ‘Web Address’ they consider something like www.example.com rather than 12.34.156.78. Individuals connect with names without breaking a sweat other than numbers, so exceptional PCs that people need to get to are commonly appointed names (‘space names’) utilizing a framework known as ‘DNS’ (the ‘area name framework’). All Internet correspondence is as yet done utilizing IP addresses (review 69.60.115.116 is an IP address). The ‘area names’ are along these lines meant IP addresses in the background, before the principle correspondence begins.
Profoundly, the method involved with looking into an area name is very straightforward – it’s a course of ‘homing in’ by moving leftwards through the name, following a cross-examination way. This is best shown as a visual demonstration – www.example.com would be turned upward as follows:
Note that contrast between a server PC is being ‘answerable’ for a space name and the area name relating to that PC. For instance, the example.com capable DNS server may not be simply similar to example.com.
Protocal Stacks and Packets:
So your PC is associated with the Internet and has a novel location. How can it ‘converse with’ different PCs associated with the Internet? A model should serve here:
Application Protocols: HTTP and the World Wide Web:
One of the most regularly utilized administrations on the Internet is the World Wide Web (WWW). The application convention that makes the web work is Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP. Try not to mistake this for the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). HTML is the language used to compose website pages. HTTP is the convention that internet browsers and web servers use to speak with one another over the Internet. It is an application-level convention since it sits on top of the TCP layer in the convention stack and is utilized by explicit applications to converse with each other. For this situation, the applications are internet browsers and web servers.
HTTP is a connectionless text-based convention. Clients (internet browsers) send solicitations to web servers for web components, for example, pages and pictures. After the solicitation is overhauled by a server, the association between client and server across the Internet is detached. Another association should be made for each solicitation. Most conventions are association arranged. This implies that the two PCs speaking with one another keep the association open over the Internet. HTTP doesn’t be that as it may be. Before an HTTP solicitation can be made by a client, another association should be made to the server.
Why do we utilize the Internet?
This is the essential employments of the web which are as per the following:
Utilizations of Internet:
With the advancement of IOT, Artificial Intelligence advances, upheld by processing assets in the cloud, an ever-increasing number of new applications are being created over the web layer, and a couple of them are:
1. Tracking the Vehicle – Fleet Management framework
2. Monitoring the wellbeing of the moving vehicle – Telematics
3. Autonomous and Driverless vehicle – 5G organizations
4. Remote diagnostics and setting off preventive upkeep of hardware
5. Monitoring Children in the home from outside
6. Online gushing of occasions
7. Entertainment – Contents sharing stage (OTT), Internet TV, Web Serials
8. Connected Machines – Manufacturing
Features of Internet:
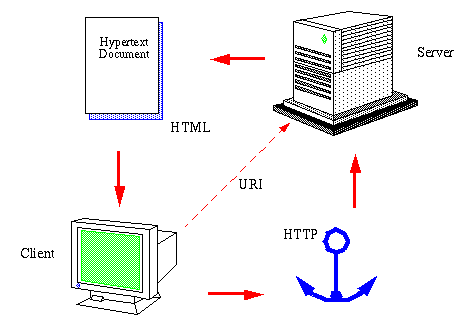
At the point when you type a URL into an internet browser, this occurs:
1. If the URL contains a space name, the program initially interfaces with an area name server and recovers the comparing IP address for the webserver.
2. The internet browser associates with the webserver and sends an HTTP demand (through the convention stack) for the ideal website page.
3. The web server gets the solicitation and checks for the ideal page. Assuming the page exists, the webserver sends it. On the off chance that the server can’t observe the mentioned page, it will send an HTTP 404 blunder message. (404 signifies ‘Page Not Found’ as any individual who has ridden the web likely knows.)
4. The internet browser gets the page back and the association is shut.
5. The program then, at that point, parses through the page and searches for other page components it needs to finish the site page. These generally incorporate pictures, applets, and so on
6. For every component required, the program makes extra associations and HTTP solicitations to the server for every component.
7. When the program has wrapped up stacking all pictures, applets, and so forth the page will be stacked in the program window.






