
What Is DataStage?
Datastage is an ETL tool which extracts data, transform and load data from source to the target. The data sources might include sequential files, indexed files, relational databases, external data sources, archives, enterprise applications, etc. DataStage facilitates business analysis by providing quality data to help in gaining business intelligence.
Datastage is used in a large organization as an interface between different systems. It takes care of extraction, translation, and loading of data from source to the target destination. It was first launched by VMark in mid-90’s. With IBM acquiring DataStage in 2005, it was renamed to IBM WebSphere DataStage and later to IBM InfoSphere.
Various version of Datastage available in the market so far was Enterprise Edition (PX), Server Edition, MVS Edition, DataStage for PeopleSoft and so on.
Datastage is used in a large organization as an interface between different systems. It takes care of extraction, translation, and loading of data from source to the target destination. It was first launched by VMark in mid-90’s. With IBM acquiring DataStage in 2005, it was renamed to IBM WebSphere DataStage and later to IBM InfoSphere.
Various version of Datastage available in the market so far was Enterprise Edition (PX), Server Edition, MVS Edition, DataStage for PeopleSoft and so on. The latest edition is IBM InfoSphere DataStage
IBM Information Server Includes Following Products,
- IBM InfoSphere DataStage
- IBM InfoSphere QualityStage
- IBM InfoSphere Information Services Director
- IBM InfoSphere Information Analyzer
- IBM Information Server FastTrack
- IBM InfoSphere Business Glossary
DataStage Overview
Datastage has following Capabilities.
- It can integrate data from the widest range of enterprise and external data sources
- Implements data validation rules
- It is useful in processing and transforming large amounts of data
- It uses scalable parallel processing approach
- It can handle complex transformations and manage multiple integration processes
- Leverage direct connectivity to enterprise applications as sources or targets
- Leverage metadata for analysis and maintenance
- Operates in batch, real time, or as a Web service
DataStage Architecture:
DataStage follows the client-server architecture. The different versions of DataStage have different types of client-server architecture. Now I am going to explain the architecture of DataStage7.5. Data Stage 7.5 version is a standalone version in which DataStage engine, repository (metadata) and service all is installed in server and client is installed in local PC. These access the servers by the ds-client. The users are created in Windows or Unix DataStage server. One has to create new Windows or UNIX user in the DS server to give them the access permission. Then need to add them to Data Stage group. It will give them access to the DataStage server from the client. Dsadm is the Data Stage server and dstage is the group of DataStage.
DataStage is divided into two components – Client components and Server components.
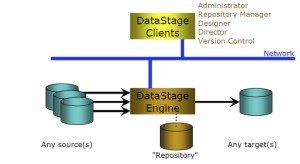
Client Components:
- DataStage Administrator – The DataStage administrator is answerable for creating and deleting projects and also setting the environment variable.
- DataStage Designer – DataStage Designer is used for designing the job.
- DataStage Director – It is responsible for run, scheduling and validate the jobs.
- DataStage Manager – DataStage Manager is used for export and import the projects.
Server Components:
- DS Server – DS Server remains answerable to run executable server tasks
- DS Package Installer–It is used to install packaged DS jobs
- Repository or project–It is a central store, which is containing all the information.
Metadata Services• Execution Services• Design Services
Common Repository: As a result It provides the following types of metadata required to support DataStage:
Project metadata: In all project level metadata components include reusable subcomponents, table definitions; routines organized into folders and built in stages.
Design metadata: It consists design time metadata is created through the DataStage and QualityStage Designer and information Analyzer.
Operational metadata: In addition It contains metadata for the operational history of integration process to run the time and date of events and parameter are used.
Common Parallel Processing Engine: Engine use parallelism and pipelining for quickly handle high volumes of work and runs executable jobs to extract, load data on several setting, and transform.
Common Connectors: Generally It provides connectivity for a large number of external resources to access the common repository from processing engine, and the data source supported by InfoSphere information Server used for input or output.
What are DataStage Components?
DataStage contains four main components They are:
Manager: The main interface for the Repository of DataStage used for storage and management of reusable Metadata by the DataStage Manager. He will observe and edit the content on Repository.
Designer: In the designer, the interface used to create the DataStage applications or jobs and specifies the data source for required transformation to destination of data jobs. Simultaneously they created executable to compile by the schedule through the director and run by the server.
Administrator: Administrator is used for to perform tasks and includes DataStage users for setting up creating and moving projects.
Director: Generally It consists of executing and monitoring Datastage server jobs and parallel jobs.Get in touch with OnlineItguru and mastering in Datastage and it is a online training.
What Would Be The Future On DataStage?
Fact DataStage has a bright future. But high versions in DataStage are more expensive on maintainer to a process of extracting, transforming. And loading meaningful data into the data warehouse. At the same time known as significant since this data processed in further. And analyzed for considerable business intelligence to determine success in business purpose.
Therefore ETL tools getting more popular and previously used for mostly on data warehousing. Now also used for several other types of data-intensive tasks like data export, data migration. As a result Rules-based data processing and this trend continued to increase the business by using an ETL tool.
Scope To DataStage:
Recommended Audience:
Specifically It is a basic course for ETL developers and project administrator’s responsible for transformation and data extractions.
Prerequisites:
One should have basic fundamental knowledge of SQL will be enough to understand the concepts in DataStage, for learning and it helps in utilizing the functions in DataStage to their full potential and also must have basic knowledge of Windows operating system.
Duties And Responsibilities Of A DataStage Developer:
- Provide professional support to the team and also evaluate all codes
- Develops and also executes tests on all data stage jobs
- Monitor whole DataStage jobs also contribute production support
- ELT job versions are designed and also analyzed by Datastage developers
- Examine work and fulfil all business laws
- Plan and schedule all the tasks of Datastage jobs
- Review all functional business specifications and applications
- Plan different block diagrams and also logic flowcharts
- Develop different computer software designs
- Documenting all user-level processes and program levels
- Examine performance and also monitor work including capacity planning
- Design and manage the multiple data warehouses
- Correlate with crew members
- Administrate every offshore and also onsite work packages
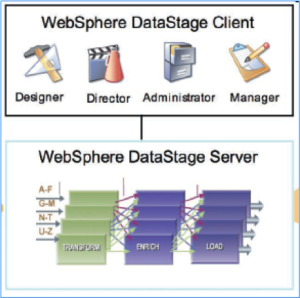
DataStage Components
- Administrator – Administers DataStage projects, manages global settings and interacts with the system. Administrator is used to specify general server defaults, add and delete projects, set up project properties and provides a command interface to the datastage repository.With Datastage Administrator users can set job monitoring limits, user privileges, job scheduling options and parallel jobs default.
- Manager – it’s a main interface to the Datastage Repository, allows its browsing and editing. It displays tables and files layouts, routines, transforms and jobs defined in the project. It is mainly used to store and manage reusable metadata.
- Designer – used to create DataStage jobs which are compiled into executable programs. It is a graphical, user-friendly application which applies visual data flow method to develop job flows for extracting, cleansing, transforming, integrating and loading data. This module is mainly used by Datastage developers.
- Director – manages running, validating, scheduling and monitoring DataStage jobs. It’s mainly used by operators and testers.
Database Stages
- Oracle Enterprise allows reading data from and writing data to an Oracle database (database version from 9.x to 10g are supported).
- ODBC Enterprise permits reading data from and writing data to a database defined as an ODBC source. In most cases it is used for processing data from or to Microsoft Access databases and Microsoft Excel spreadsheets.
- DB2/UDB Enterprise permits reading data from and writing data to a DB2 database.
- Teradata permits reading data from and writing data to a Teradata data warehouse. Three Teradata stages are available: Teradata connector, Teradata Enterprise and Teradata Multiload
- SQLServer Enterprise permits reading data from and writing data to Microsoft SQLl Server 2005 amd 2008 database.
- Sybase permits reading data from and writing data to Sybase databases.
- Stored procedure stage supports Oracle, DB2, Sybase, Teradata and Microsoft SQL Server. The Stored Procedure stage can be used as a source (returns a rowset), as a target (pass a row to a stored procedure to write) or a transform (to invoke procedure processing within the database).
- MS OLEDB helps retrieve information from any type of information repository, such as a relational source, an ISAM file, a personal database, or a spreadsheet.
- Dynamic Relational Stage (Dynamic DBMS, DRS stage) is used for reading from or writing to a number of different supported relational DB engines using native interfaces, such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, DB2, Informix and Sybase.
- Informix (CLI or Load)
- DB2 UDB (API or Load)
- Classic federation
- RedBrick Load
- Netezza Enterpise
- iWay Enterprise
Datastage Stages Palette – ETL Tools
Datastage and QualityStage stages are sorted into the below logical sections:
- General Objects
- Stages of Data Quality
- Development and Debug Stages
- Database connectors
- Restructure stages
- Real-time stages
- Debug and Development stages
- Sequence activities
Looking for top jobs in Business Intelligence ? This blog post gives you all the information you need !
The widely and popular stages used in DataStage and Quality Stage are discussed below and specific major features are explained below
- General Elements

- A Link indicates the flow of the data. Reference, stream and lookup are the main types of links.
- The container can be shared or private; the main role is to visually make it simple so that the complex database job design and letting the design for ease of usage and recognition.
- Annotation is basically used for adding floating Datastage descriptions and notes on job posts. This provides a way to document ETL process and used in understanding the given job.
2. Debug And Development Stages
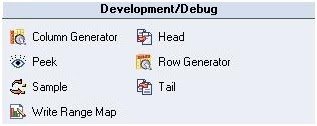
- Row generator replicates a set of data which sticks to the appropriate metadata (cycled or randomized). Useful for development and testing.
- Column generator can add one or more column to the flow and can generate test data for the column.
- Peek The column values are recorded and could be viewed in the director. It can have multiple output link, but single input link.
- Sample operates on an input data set and has two modes:- percent mode and period mode.
- Head occupies first N rows at each partition and copies them to an output data set from an input data set
- A Tail is same as the head stage. From each of the partitions, last N rows are selected.
- Write Range Map writes a form where the dataset is usable by the range partitioning method.
3. Processing Stages
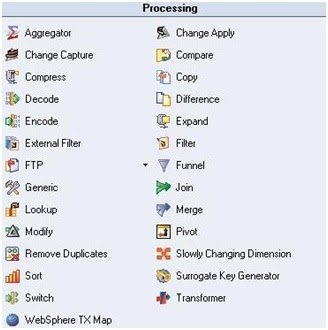
- Aggregator joins data vertically from grouping the incoming data stream and calculating brief about a min, count, max etc.; for each team. The data could be sorted using two methods: pre-sort and hash table.
- Copy copies the input data to single or more output data flows.
- FTP stage implements the FTP protocol to transfer data to a remote machine
- Filter filters records that don’t meet relevant requirements.
- Funnel converts multiple streams into a single one.
- Join combines more than one input according to the values of a key column/s.
- Lookup includes two or more inputs based on values of key column/s. It should have a 1 source, but can have multiple lookup tables
- Merge includes one master input with multiple updates inputs related to the values of a key column/s. The inputs need to be sorted and unmatched secondary entries can be caught using multiple reject links.
- Modify stage alters the dataset record. Useful for renaming columns, not default data type conversion and null handling.
- Remove duplicates wants input to be single sorted data set.
- Removes all duplicate content and writes into a single output.
- Slowly changing Dimension computerizes the revised process of dimension tables where data frequently change.
- Sort sorts the input columns
- Transformer stage handles validation of data, extracted data and lookups.
- Change Capture catches the before and the after states of 2 data which are inputted and are converted into a single data set that shows the differences made.
- Change apply will apply changes to the operation to the previous dataset so as to compute after dataset. It retrieves data from the change capture stage.
- Difference stage executes a record-by-record comparison of 2 input data and outputs the record which is the difference between records.
- Checksum produces checksum from the specific columns in a row and gets added to the stream. Also able to differentiate between records.
- Compare does a searching comparison on column-column of pre-sorted records. It can have one output and two input link.
- Encode encodes data, such as gzip with encoding command
- Decode decodes the previously encoded data in the previous stage.
- External Filter allows specifying an OS command that filters the processed data.
- Generic stage permits users to provoke OSH operator from DataStage stage having options.
- Pivot Enterprise is used for horizontal pivoting. It maps or assigns multiple columns in the input row to a single column over multiple output rows.
- Surrogate Key Generator manages key source by generating to a column, the surrogate key.
- Switch stage matches each input row to an output link on the basis of the value of a selector field. The concept is similar to switch statement in most programming languages.
- Compress combines data set using the GZIP utility (or can be done using LINUX/UNIX command)
- Expand extracts previous compressed data set into raw binary data.
4. File Stage Types
- The Sequential file is used to see data from or write into one or more flat (sequential) files.
- Data Set stage allows users to see data from or write data to a file set. File sets are OS files, each of which has .ds extension and one or more data files.
- File Set stage allows users to read data from or write data to a file set. Unlike datasets, file sets conserve formatting and are readable by other apps.
- The complex flat file allows reading on a mainframe machine similar to a header, MVS data sets, and trailer structured files from complex file structures.
- External Source allows reading data from multiple source programs to output.
- Lookup File Set is similar to File set Stage. Partitioned hashed file can be used for lookups.
5. Database Stages
- Oracle Enterprise permits reading data to an Oracle database.
- ODBC Enterprise permits looking data from and writing it to a database called as ODBC source. It is used in the processing of data in Microsoft Access and Excel spreadsheets.
- DB2/UDB Enterprise allows writing, reading data to a DB2 Database.
- Teradata allows writing, reading data to a Teradata data warehouse. Three Teradata stages are present; Teradata connector, Enterprise and Multiload.
- SQL Server Enterprise allows writing, reading data to Microsoft SQLI Server 2005 and 2008 database.
- Sybase allows into Sybase Databases, reading and writing data.
- Stored procedure stage chains DB2, Oracle, Sybase, Teradata and Microsoft SQL Server.
- MS OLEDB is used to retrieve information from all types of the information repositories, such as an ISAM file, relational Source or a spreadsheet.
- Dynamic Relational Stage is reading from and writing into a different supported relational DB using interfaces such as Microsoft SQL, DB2, Oracle, Sybase and Informix.
- Informix (CLI or Load)
- DB2 UDB (API or Load)
6. Real Time Stages

- XML Input stage makes it possible to convert hierarchical XML data to flat relational data sets.
- XML Output writes on to XML structures.
- XML Transformer converts XML documents by XSLT stylesheet.
- Websphere MQ stages give a collection of connectivity menu to access IBM WebSphere MQ enterprise messaging systems. Two MQ stages available in Datastage and in QualityStage;they are Websphere MQ connector and plug-in stage.
- Java Client stage could be useful as a target and lookup too. The package contains 3 public classes.
- Java Transformer level helps in the following three links: input, output and reject
- WISD Input: Defined as Information Services Input stage
- WISD Output: Defined as Information Services Output stage
7. Restructure Stages
- Column export, export data onto a single column of datatype binary or string from numerous columns of different data types. It can have a single output, input and a reject link.
- Column imports corresponding to the Column Export stage. Characteristically used to divide data inward bound in a single column into numerous columns.
- Combine records stage group rows which have exact same keys, over vectors of sub-records.
- Make sub-records merge particular input vectors into a vector of sub-records whose columns have the same names and data types as the original vectors.
- Make vector combines specified input vectors into a vector of columns
- Promote sub-records supports input sub-records columns to columns top level.
- Split sub-records splits an input sub-records field into a set of top level vector columns.
- Split vector supports the elements of a fixed length vector over the set of top level columns.
8. Data Quality Stages
- Investigate stage predicts data module of appropriate columns of all records from the source file. Offers word and character investigation methods.
- Match frequency stage obtains input from a file, a database or processing stages and generates an occurrence distribution report.
- MNS: Refers to Multinational address standardization
- WAVES: Refers to worldwide address verification and enhancement system.
9. Sequence Types Of Activity Stages
- Job Activity indicates Datastage server or else similar job to execute.
- Notification Activity used to move the emails to client described recipients by Datastage.
- Sequencer used for synchronization of the control flow of numerous actions in a job progression.
- Terminator Activity allows shutting down the entire progression once certain circumstances persist.
- Wait for file Activity waits for an exact file to emerge or fade away and launches the dispensation.
Major business and technical advantages and disadvantages of using DataStage ETL tool:
Business Advantages Of Using DataStage As An ETL Tool:
- Significant ROI (return of investment) over hand-coding Learning curve – quick development and reduced maintenance with GUI tool
- Development Partnerships – easy integration with top market products interfaced with the datawarehouse, such as SAP, Cognos, Oracle, Teradata, SAS
- Single vendor solution for bulk data transfer and complex transformations (DataStage versus DataStage TX)
- Transparent and wide range of licensing options
Technical Advantages Of Using DataStage Tool To Implement The ETL ProcessesSingle interface to integrate heterogeneous applications
- Flexible development environment – it enables developers to work in their desired style, reduces training needs and enhances reuse. ETL developers can follow data integrations quickly through a graphical work-as-you-think solution which comes by default with a wide range of extensible objects and functions
- Team communication and documentation of the jobs is supported by data flows and transformations self-documenting engine in HTML format.
- Ability to join data both at the source, and at the integration server and to apply any business rule from within a single interface without having to write any procedural code.
- Common data infrastructure for data movement and data quality (metadata repository, parallel processing framework, development environment)
- With Datastage Enterprise Edition users can use the parallel processing engine which provides unlimited performance and scalability. It helps get most out of hardware investment and resources.
- The datastage server performs very well on both Windows and unix servers.
Major Datastage Weaknesses And Disadvantages
- Big architectural differences in the Server and Enterprise edition which results in the fact that migration from server to enterprise edition may require vast time and resources effort.
- There is no automated error handling and recovery mechanism – for example no way to automatically time out zombie jobs or kill locking processes. However, on the operator level, these errors can be easily resolved.
- No Unix Datastage client – the Client software available only under Windows and there are different clients for different datastage versions. The good thing is that they still can be installed on the same windows pc and switched with the Multi-Client Manager program.
- Might be expensive as a solution for a small or mid-sized company.






