
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open source Continuous Integration server capable of orchestrating a chain of actions that help to achieve the Continuous Integration process (and not only) in an automated fashion. Jenkins is free and is entirely written in Java. Jenkins is a widely used application around the world that has around 300k installations and growing day by day. It is a server-based application and requires a web server like Apache Tomcat. The reason Jenkins became so popular is that of its monitoring of repeated tasks which arise during the development of a project. For example, if your team is developing a project, Jenkins will continuously test your project builds and show you the errors in early stages of your development.
By using Jenkins, software companies can accelerate their software development process, as Jenkins can automate build and test at a rapid rate. Jenkins supports the complete development lifecycle of software from building, testing, documenting the software, deploying and other stages of a software development lifecycle.
What is Continuous Integration?
Continuous integration is a software development method where members of the team can integrate their work at least once a day. In this method, every integration is checked by an automated build to search the error. The CI concept was first introduced over two decades ago to avoid “integration hell,” which happens when integration is put off till the end of a project.
In Continuous Integration after a code commit, the software is built and tested immediately. In a large project with many developers, commits are made many times during a day. With each commit code is built and tested. If the test is passed, the build is tested for deployment. If the deployment is a success, the code is pushed to Production. This commit, build, test, and deploy is a continuous process, and hence the name continuous integration/deployment.
Difference between Compilation and Continuous Integration
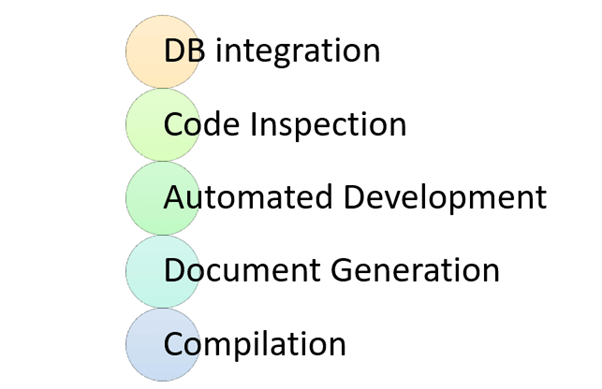
While compilation only compiles a code, CI does the following activities.
DB integration:
- Ensure DB and code in sync
- Automated creation of DB and test data.
Code Inspection:
- Ensures a healthy codebase
- Identifies problems early and applies best practices
Automated Deployment:
- Allows you to release product anytime
- Continually demo-able state and it is works on any machine
Document generation:
- Ensure documentation is current
- Removes burned from the developer
- Produces build reports and metrics
Compilation:
Compilation is the process the computer takes to convert a high-level programming language code into a machine language that the computer is able to understand. It ensures a code compiler on every target platform.
When do I build?
- At every check-in
- Every time a dependency changes
How do I build?
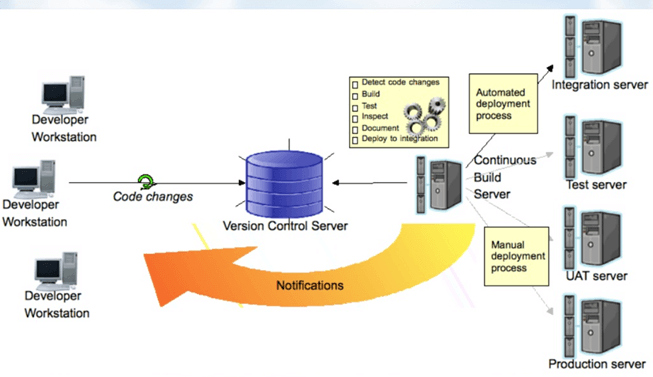
- Ideally, the build should from the command line and should not depend on IDE.come
- The build should happen continuously using a dedicated Cl server, not a cron job.
- CI built should be triggered on every check-in and not just at midnight
- The build should provide immediate feedback and Require no developer effort
- Identify key metrics and track them visually. More importantly, act on them immediately
What do you need to conduct the CI process?
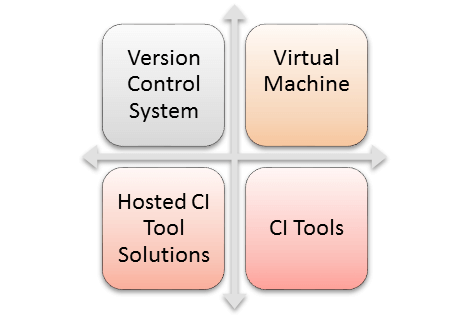
Here, are the key elements which you need to perform the entire CI process:
- Version Control System (VCS): It offers a reliable method to centralize and preserve changes made to your project over time.
- Virtual Machine: You should have a spare server or at least one virtual machine to build your system.
- Hosted CI Tool Solutions: To avoid servers or virtual machines, you should go for hosted CI tool solutions. This tool helps in the maintenance of the whole process and offers easier scalability.
- Tools: If you select a self-hosted variant, you will need to install one of the many CI tools like Jenkins, TeamCity, Bamboo, GitLab, etc.
How Continuous integration work?
You are surely aware of the old phone Nokia. Nokia used to implement a procedure called nightly build. After multiple commits from diverse developers during the day, the software built every night. Since the software was built only once in a day, it’s a huge pain to isolate, identify, and fix the errors in a large codebase.Later, they adopted the Continuous Integration approach. The software was built and tested as soon as a developer committed code. If any error is detected, the respective developer can quickly fix the defect.
Features of CI
Here, are important features of Continuous Integration
- Allows you to maintain just a single source repository
- You can test the clone of the production environment
- The built environment should be close to the production environment.
- Constant availability of a current build
- The complete process of build and testing and deployment should be visible to all the stakeholders.
Why Use CI?
Here are important reasons for using Continuous Integration:
- Helps you to build better quality software
- CI process helps to scale up headcount and delivery output of engineering teams.
- CI allows software developers to work independently on features in parallel.
- Helps you to conduct repeatable testing
- Increase visibility enabling greater communication
- Helps develop a potentially shippable product for fully automated build
- Helps you to reduced risks by making deployment faster and more predictable
- immediate feedback when issue arrives
- Avoid last-minute confusion at release date and timing
Best practices of using CI Systems
Here, are some important best practices while implementing
- Commit Early and Commit Often never Commit Broken Code
- Fix build failures immediately
- Act on metrics
- Build-in every target environment Create artifacts from every build
- The build of the software need to be carried out in a manner so that it can be automated
- Do not depend on an IDE
- Build and test everything when it changes
- The database schema counts as everything
- Helps you to find out key metrics and track them visually
- Check-in often and early
- Stronger source code control
- Continuous integration is running unit tests whenever you commit code
- Automate the build and test everyone
- Keep the build fast with automated deployment
Disadvantages of CI
Here, are cons/drawbacks of Continuous Integration process:
- Initial setup time and training is required to get acquainted with Cl server
- Development of suitable test procedures is essential
- Well-developed test-suite required many resources for Cl server
- Conversion of familiar processes
- Requires additional servers and environments
- Waiting times may occur when multiple developers want to integrate their code around the same time
Tools for CI process
Here, are some most essential CI tools:
Jenkins:

Jenkins is an open-source continuous integration tool. It is written using the Java programming language. It facilitates real-time testing and reporting on isolated changes in a more massive codebase. This software helps developers to quickly find and solve defects in their codebase & automate testing of their builds.
Bamboo:

Bamboo is a continuous integration build server that performs – automatic build, test, and releases in a single place. It works seamlessly with JIRA software and Bitbucket. Bamboo supports many languages and technologies such as CodeDeploy, Ducker, Git, SVN, Mercurial, AWS, and Amazon S3 buckets.
TeamCity:

TeamCity is a Continuous Integration server that supports many powerful features. It maintains a CI server healthy and stable even when no builds are running. It provides better code quality for any project
- Continuous integration is a software development method where members of the team can integrate their work at least once a day
- Development without CI creates lots of bugs whereas Development with CI offers Fewer bugs
- Important activities of Continuous Integration are 1)DB integration Code, 2)InspectionAutomatedDeployment,3)Document generation, and Compilation.
- The build should happen continuously using a dedicated Cl server, not a cron job.
- Important elements of CI are 1) Version Control System 2) Virtual Machine 3) Host CI Tool solutions 4) Tools
- Continuous Integration allows you to maintain just a single source repository
- CI process helps you to build better quality software.
- The most important best practices of Continuous Integration process is to Commit Early and Commit Often never Commit Broken Code
- The major drawback of the CI process is that well-developed test-suite required many resources for Cl server
- Jenkins, Bambook, and Teamcity are some useful Continuous Integration tools.
Jenkin History
- Kohsuke Kawaguchi, a Java developer, working at SUN Microsystems, was tired of building the code and fixing errors repetitively. In 2004, he created an automation server called Hudson that automates build and test tasks.
- In 2011, Oracle who owned Sun Microsystems had a dispute with Hudson open source community, so they forked Hudson and renamed it as Jenkins.
- Both Hudson and Jenkins continued to operate independently. But in a short span of time, Jenkins acquired a lot of projects and contributors while Hudson remained with only 32 projects. With time, Jenkins became more popular, and Hudson is not maintained anymore.
Why use Continuous Integration with Jenkins?
Some people might think that the old-fashioned way of developing the software is the better way. Let’s understand the advantages of CI with Jenkins with the following example
Let us imagine that there are around 10 developers who are working on a shared repository. Some developer completes their task in 25 days while others take 30 days to complete
Jenkins Plugins
By default, Jenkins comes with a limited set of features. If you want to integrate your Jenkins installation with version control tools like Git, then you need to install plugins related to Git. In fact, for integration with tools like Maven, Amazon EC2, you need to install respective plugins in your Jenkins.
Advantages of using Jenkins
- Jenkins is being managed by the community which is very open. Every month, they hold public meetings and take inputs from the public for the development of Jenkins projects.
- So far around 280 tickets are closed, and the project publishes a stable release every three months.
- As technology grows, so does Jenkins. So far Jenkins has around 320 plugins published in its plugins database. With plugins, Jenkins becomes even more powerful and feature rich.
- Jenkins also supports cloud-based architecture so that you can deploy Jenkins in cloud-based platforms.
- The reason why Jenkins became popular is that it was created by a developer for developers.
Disadvantages of using Jenkins
Though Jenkins is a very powerful tool, it has its flaws.
- Its interface is outdated and not user friendly compared to current UI trends.
- Though Jenkins is loved by many developers, it’s not that easy to maintain it because Jenkins runs on a server and requires some skills as server administrator to monitor its activity.
- One of the reasons why many people don’t implement Jenkins is due to its difficulty in installing and configuring Jenkins.
- Continuous integrations regularly break due to some small setting changes. Continuous integration will be paused and therefore requires some developer attention.
How to Download & Install Jenkins on Windows
Jenkins may be installed on either Windows or Unix platforms, but we will focus on Windows installation only.
Prerequisites:
Before you proceed to install Jenkins in your windows system, there are some prerequisites for Jenkins to install Jenkins in your computer.
Hardware requirements:
- You need minimum 256 MB of RAM in your computer or laptop to install Jenkins
- You need at least 1 GB of space in your hard drive for Jenkins.
Software Requirements:
- Since Jenkins runs on Java, you need either the latest version of Java Development Kit (JDK) or Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Release Types:
Jenkins releases two types of versions based on the organization needs.
- Long-term support release
- Weekly release
Long term support release (LTS) : Long-term support releases are available every 12 weeks. They are stable and are widely tested. This release is intended for end users.
Weekly release: Weekly releases are made available every week by fixing bugs in its earlier version. These releases are intended towards plugin developers.
We will use the LTS release though the process remains the same for Weekly release.
Conclusion:
- In Continuous Integration, after a code commit, the software is built and tested immediately
- Jenkins is an open source Continuous Integration server capable of orchestrating a chain of actions
- Before Jenkins when all Developers had completed their assigned coding tasks, they used to commit their code all at same time. Later, Build is tested and deployed.
- After Jenkins the code is built and tested as soon as Developer commits code. Jenkin will build and test code many times during the day
- By default, Jenkins comes with a limited set of features. If you want to integrate your Jenkins installation with version control tools like Git, then you need to install plugins related to Git
- The biggest pros of Jenkins is that it is managed by the community which holds public meetings and take inputs from the public for the development of Jenkins projects
- The biggest con of Jenkin is that Its interface is outdated and not user friendly compared to current UI trends.
- Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.






