
Microsoft Dynamics CRM is a customer relationship management software package developed by Microsoft, focusing on enhancing customer relationships for any organization. It is one of the leading industry-standard CRM software available in market. The product focuses mainly on Sales, Marketing, and Customer Service sectors, however Microsoft has been marketing Dynamics CRM as an XRM platform and has been encouraging partners to use its proprietary (.NET based) framework to customize it.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a system for managing a company’s interactions with current and future customers. It often involves using technology to organize, automate, and synchronize sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support. CRM can help reduce costs and increase profitability by organizing and automating business processes that nurture customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Microsoft Dynamics CRM
Microsoft Dynamics CRM is a customer relationship management software package developed by Microsoft focused on enhancing the customer relationship for any organization. Out of the box, the product focuses mainly on Sales, Marketing, and Customer Service sectors, though Microsoft has been marketing Dynamics CRM as an XRM platform and has been encouraging partners to use its proprietary (.NET based) framework to customize it. In recent years, it has also grown as an Analytics platform driven by CRM.
The CRM Solution can be used to drive the sales productivity and marketing effectiveness for an organization, handle the complete customer support chain, and provide social insights, business intelligence, and a lot of other out-of-the-box functionalities and features. As a product, Microsoft Dynamics CRM also offers full mobile support for using CRM apps on mobiles and tablets.
As of writing this tutorial, the latest version of CRM is CRM 2016. However, in this tutorial we will be using CRM 2015 Online version as it is the latest stable version as well as frequently used in many organizations. Nevertheless, even if you are using any other versions of CRM, all the concepts in the tutorial will still hold true.
Product Offerings
Microsoft Dynamics CRM is offered in two categories :
CRM Online: CRM Online is a cloud-based offering of Microsoft Dynamics CRM where all the backend processes (such as application servers, setups, deployments, databases, licensing, etc.) are managed on Microsoft servers. CRM Online is a subscription-based offering which is preferred for organizations who may not want to manage all the technicalities involved in a CRM implementation. You can get started with setting up your system in a few days (not weeks, months or years) and access it on web via your browser.
CRM On-Premise:
CRM on-premise is a more customized and robust offering of Microsoft Dynamics CRM, where the CRM application and databases will be deployed on your servers. This offering allows you to control all your databases, customization, deployments, backups, licensing and other network and hardware setups. Generally, organizations who want to go for a customized CRM solution prefer on-premise deployment as it offers better integration and customization capabilities.
Setting Up Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online Account
Step 1 :
Navigate to the following URL
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamics365/home
In case you do not see the options of Trial version via this link in future, just try searching “Microsoft Dynamics CRM Free Trial” on Google.
Step 2 :
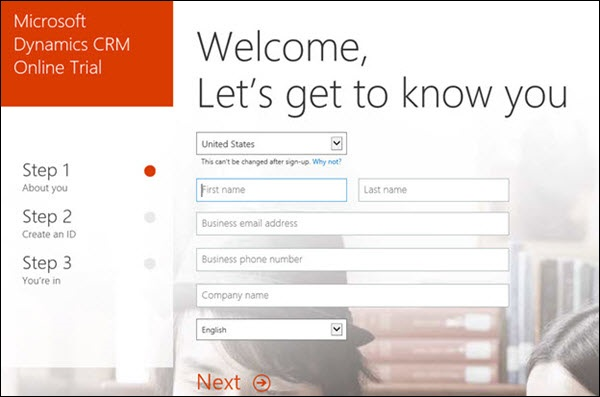
Click the Try it free button. This will start a 3-step registration process as shown in the following screenshot. In Step 1 of 3-step registration, fill in the mandatory details such as name, email, and language.
Step 3 :
Click the Try it free button. This will start a 3-step registration process as shown in the following screenshot. In Step 1 of 3-step registration, fill in the mandatory details such as name, email, and language.
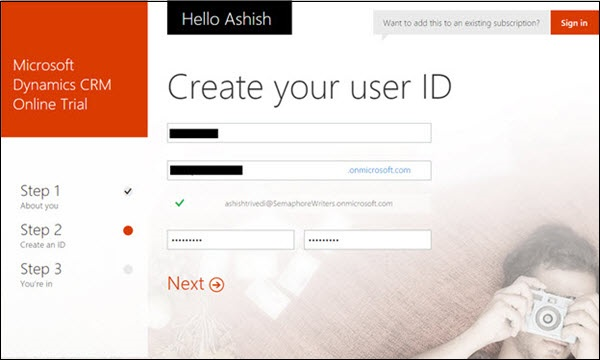
Step 4:
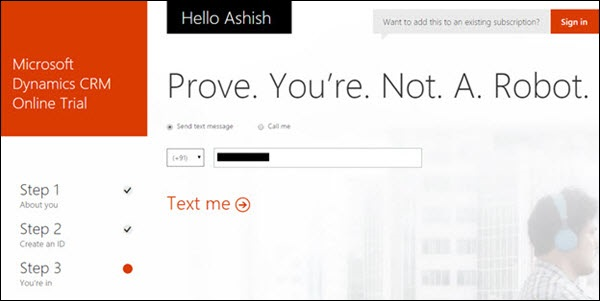
In Step 3 of 3-step registration, Microsoft will validate the mobile number that you have specified. For this, you can provide your mobile number and click Text me. It will then send an OTP to your mobile using which you will be able to proceed further with the setup.
Step 5:
Your Office 365 user ID will be created. You can save this user ID information for later access.
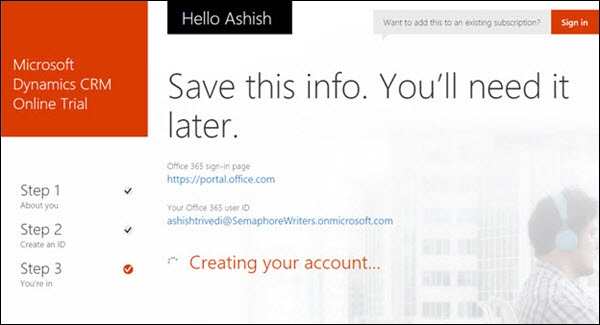
After setting up the account, it will now open your CRM Dashboard which will look something like the following.
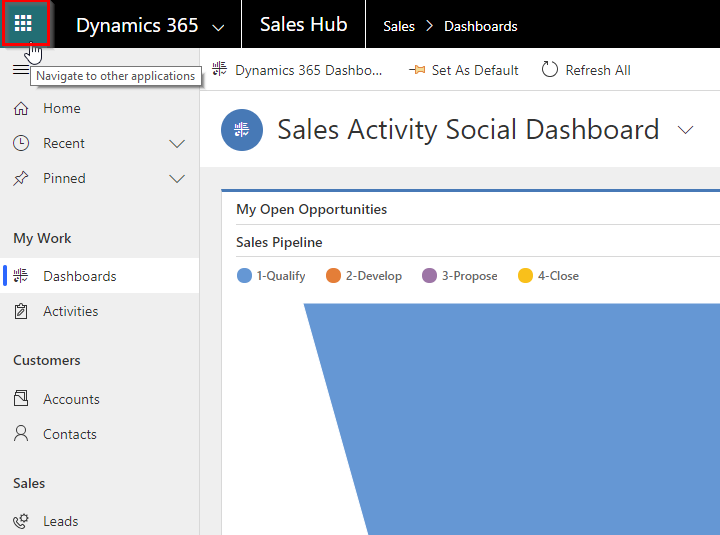
Just to emphasize again, the screenshots above may change with a future version, however setting up the environment will be a pretty simple process.
functional modules
The entire Microsoft Dynamics CRM is designed around the following functional modules.
- Sales
- Marketing
- Service Management
These functional modules are often called Work Areas.
Understanding CRM Functional Modules
The entire CRM application is divided functionally for different types of users and teams. Hence, if an organization is using CRM to manage its processes, the users from the Sales team would use the functionalities that come under the Sales module, while the users from the Marketing team would use functionalities that fall under the Marketing module.
All these three functional modules come together to drive the entire life cycle of gaining a new customer (Marketing), selling them the services (Sales) and maintaining the existing customers (Service Management).
To understand this flow in a better way, consider a bank which sells credit cards to its customers. The typical life cycle of selling a credit card to a customer would be as follows. In each step of this lifecycle, you will see how the Sales, Marketing and Service modules perform their role.
Sales & Marketing
The bank’s call center office executive receives data of potential customers; often called as Leads in CRM. These Leads are captured in the CRM system via marketing campaigns, sales drives, referrals, etc.
Sales
The call center executive communicates with these Leads either through phone calls/emails/etc. If the customer is interested in the credit card offering, the Lead record will be converted to an Opportunity record (won Lead).
Service
Once a customer becomes a part of the system, the company would assist him/her with payments, billing, refunds, etc. Whenever the customer has any queries or concerns, they will make a call to the call center and raise incidents. The executive will followup to resolve the case with the aim to provide quality service to the customer. These tasks fall under CRM Service Management.
Navigating CRM Work Areas
Step 1: Open CRM Home Page.
Step 2: By default, you will see the Sales work area as selected.
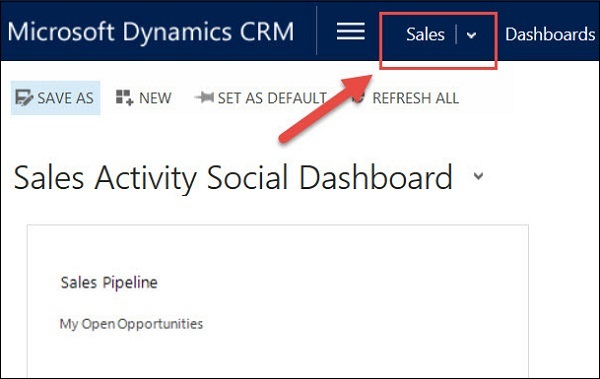
Step 3: To change the work area, click the Show work areas option. You will see the options for selecting Sales, Service, and Marketing.
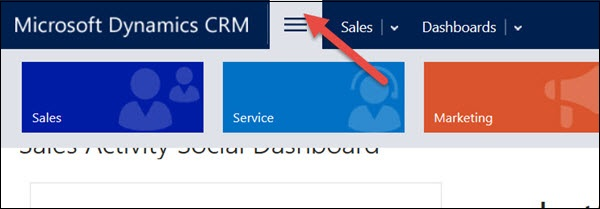
Step 4 : Click Sales. This will show you all the entities which fall under Sales such as Accounts, Contacts, Leads, Opportunities, Competitors, etc. Each of these entities are categorized by their business process such as My Work, Customers, Sales, Collateral, etc.
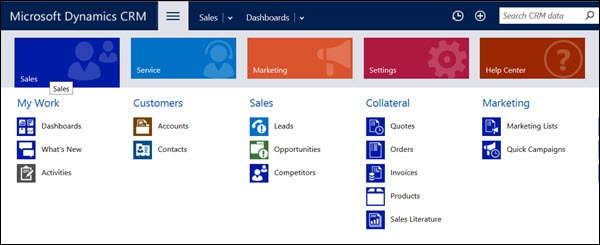
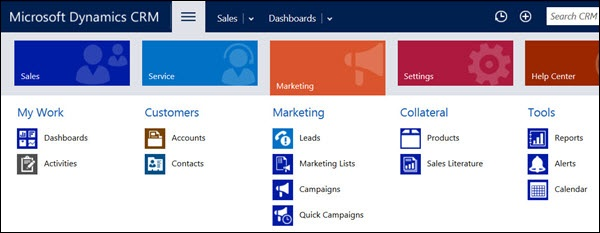
Step 5: Similarly, if you click the Marketing work area, you will see all the entities related to Marketing business functionalities.
Sales Module
The Sales module of CRM is designed to drive the entire sales life cycle of a new customer. The Sales module consists of the following sub-modules.
Leads
Represents a person or an organization that can be a potential customer to the company in future. This is the first step towards getting a potential customer in the system.
Opportunities
Represents a potential sale to the customer. Once a Lead shows interest in the offering, it gets converted to an Opportunity. An Opportunity will either be won or lost.
Accounts
Represents a company with which the organization has relations. Once an Opportunity wins, it gets converted to either an Account or Contacts.
Contacts
Represents a person, or any individual with whom the organization has relations. Mostly these Contacts are the customers of the organizations (e.g. all credit card customers of a bank). Once an Opportunity wins, it gets converted to either an Account or Contacts.
Competitors
Manages all the market competitors of the organization.
Products
Manages all the products offered by the organization to its customers (Example, all the credit card plans).
Quotes
A formal offer for products or services proposed at specific prices sent to a prospective customer (Example, yearly pricing of a certain credit card plan sent to the customer).
Orders
A quote that gets accepted by the customer turns into an Order (Example, out of all the plans that the organization offers you, you may go for a 6-month subscription).
Invoices
A billed order generates an invoice.
Marketing Module
The Marketing module of CRM is designed to drive the entire marketing process of an organization for its existing and potential customers. The Marketing module consists of the following sub-modules.
Marketing Lists
Provides a way to group your Contacts, Accounts, and Leads and interact with them via sending promotional emails, event details, newsletters and other updates relevant to the target customers. You can define the criteria to create your marketing lists.
Campaigns
Campaigns are designed to measure the effectiveness and accomplish a specific result, such as introducing a new product or increasing the market share and may include various communication channels such as email, newspaper ads, YouTube ads, etc.
Quick Campaigns
A Quick Campaign is similar to Campaign however it can be related to only one type of activity.All the above Marketing modules work in close co-ordination with the Sales module.
Service Management Module
The Service Management module of CRM is designed to focus, manage, and track the customer service operations of an organization such as supporting the incident-based services, supporting the customers using service scheduling, etc.
The Service Management module covers the following sub-modules:
Cases (Incidents)
Supports any customer requests, issues, or complaints to be tracked via incidents/cases. A case follows various stages of an issue resolution process and then finally gets resolved and is closed.
Knowledge Base
Maintains a master repository for all the common questions and answers that the customer frequently asks.
Contracts
Contracts work with Cases indicating all the active contracts that the customer has.
Resources/Resource Groups
Represents the people, tools, rooms, or pieces of equipment that are used to deliver a service. These resources can be used to solve a specific customer issue.
Services
Represents all the services that the organization offers to the customers.
Service Calendar
Used to schedule work timings and schedules of the users who work in the organization.
Activity Management
All the modules explained above use the Activity Management module of CRM. An Activity represents any kind of interaction with the customer such as a Phone Call, Email, Letter, etc. These activities can be related to any of the entities explained earlier such as Account, Contact, Lead, Case, etc. By default, CRM provides following types of activities out-of-the-box −
- Phone Call
- Task
- Appointment
- Recurring Appointment
- Letter
- Fax
- Campaign Response
- Campaign Activities
- Service Activity
- Custom Activities
Entity
An entity is used to model and manage business data in CRM. Contacts, Cases, Accounts, Leads, Opportunities, Activities, etc. are all entities which hold data records. Conceptually, a CRM entity is equivalent to a database table. For example, Contacts entity would hold Contact records, Cases entity would hold Cases records, and so on.
Field Types
Out-of-the-box, CRM provides 11 types of data fields that can be placed on forms:
- Single Line of Text
- Option Set (Dropdown)
- Two Options (Radio Button)
- Image
- Whole Number
- Floating Point Number
- Decimal Number
- Currency
- Multiple Lines of Text
- Date and Time
- Lookup
The following table lists each with a brief description:
Single Line of Text
This field stores up to 4000 characters of text. You can also specify the format as one of these: Email, Text, Text Area, URL, Ticker Symbol, and Phone. You can set the maximum length and IME mode for each of these.
Option Set (Dropdown)
This field stores a set of options each having a number value and label. In other words, it is a drop down field in CRM. You can also define Global Option Sets which can be used across multiple forms.
Two Options (Radio Button)
This field provides two options for the user to select (0 or 1). In other words, it is a radio button field.
Image
When an entity has an image field, it can be configured to display the image for the record in the application.
Whole Number
This field stores integer values between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647. It supports the specifying formats as None, Duration, Time Zone, and Language. You can set the minimum and maximum values too.
Floating Point Number
This field stores the floating point numbers up to 5 decimal points of precision between 0.00 and 1,000,000,000.00. You can set the minimum and maximum values too.
Decimal Number
This field stores up to 10 decimal points with values ranging from -100,000,000,000.00 and 100,000,000,000.00.
Currency
This field is used to store any currency values in the range of 922,337,203,685,477.0000 to 922,337,203,685,477.0000. You can also specify the Precision as Pricing Decimal, Currency Precision or any value between 0 to 4.
Multiple Lines of Text
This is a scrolling text box. You can set the maximum number of characters for this field.
Date and Time
This field is used to store date-related data in CRM with two supported formats: Date Only, and Date and Time. You can also specify the behavior as User Local, Date Only and Time-Zone Independent.
Lookup
You can create a lookup field using an entity relationship that has already been created, but not yet used with another lookup field. If you create a lookup field in an entity form, the relationship is automatically generated. A lookup field is created as a relationship field.
Workflows
Workflows in CRM allow you to automate simple and complex business processes within CRM. You can either create workflows using CRM out-of-the-box functionalities or write custom workflows with .NET code for implementing complex workflows. Workflow processes run in the background or in real-time and can optionally require a user input.
Workflows can be triggered based on specific conditions or can even be started manually by the users. Internally, CRM workflows are implemented using Windows Workflow Foundation. In this chapter, we will be learning about configuring workflows.
Configuring a workflow has the following major parts (in sequence):
- Configure the entity on which the workflow will run
- Configure whether the workflow will run synchronously or asynchronously
- Configure the message (event) on which the workflow will run
- Configure the scope in which the workflow will run
- Configure the stages and steps (actions) of the workflow
Synchronous/Asynchronous Workflow
When you create a workflow, you will see the option of Run this workflow in the background (recommended) which determines whether the workflow will run in real-time (synchronously) or in background (asynchronously).
Generally, the recommended approach is to run the workflows in the background since they use system resources as and when available. However, you can always switch back from a real-time workflow to background workflow and vice versa.
Workflow Messages
Workflows can be registered on specific events as follows:
- When a record is created
- When a record status changes
- When a record is assigned
- When a record field value changes
- When a record is deleted
Workflow Scope
Workflows allow you to set the scope in which the workflow will run. Following are the supported workflow scopes.
| User | Workflow will run only on the records owned by the same user as the workflow user. | |
| Business Unit | Workflow will run on the records owned by the users of the business unit same as the workflow user. | |
| Parent Child Business Units | Workflow will run on the records owned by the users of the business unit same as the workflow user as well as any child business units. | |
| Organization | Workflow will run on records owned by any user in CRM. |
Conclusion
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a mature product that has a proven track record in the market world-wide. It is among the leaders in its magic quadrant. Due to its completeness, its rich set of comprehensive features, and continuous support from the Microsoft product team (with strong endorsement from Microsoft’s CEO, Satya Nadella and direction from Microsoft Executive Vice President Scott Guthrie), the platform receives a lot of attention and is a breeze to work with.
Every year, as part of my MVP privileges, I get to meet the Dynamics 365 product team at Microsoft in Redmond, Washington. With no exception, every team member is energetic and enthusiastic about the product; they are eager to improve on it and to listen to any issues .






