
- Definition and Purpose
- Importance in Product Development
- Key Components
- Target Audience
- Gathering Requirements
- Prioritizing Features
- Writing Guidelines
- Conclusion
Definition and Purpose
A Product Requirement Document (PRD) is a detailed and formalized document that defines both the functional and non-functional requirements of a product or a specific feature. It serves as a foundational reference point for development teams, product managers, designers, and other stakeholders involved in the product lifecycle. The PRD ensures that everyone is aligned with the product’s vision, objectives, and intended outcomes. By clearly outlining what needs to be built and why it is needed, the PRD helps prevent miscommunication, manage expectations, and streamline the development process. The primary purpose of a PRD is to articulate the “what” and “why” behind a product or feature. It takes broad business goals or user needs and translates them into specific, actionable items that can guide the work of cross-functional teams. This includes detailed descriptions of features, user flows, acceptance criteria, and any technical or design constraints. It may also include information on performance expectations, usability requirements, and potential risks or dependencies. A well-crafted PRD not only supports the efficient execution of development tasks but also serves as a tool for prioritization and scope management. It enables teams to stay focused on delivering the most valuable aspects of the product while ensuring that all requirements are properly documented and understood. By serving as a single source of truth, the PRD contributes to consistent decision-making, timely delivery, and alignment across all stakeholders involved in the product development effort.
Importance in Product Development
The importance of a Product Requirement Document (PRD) in product development cannot be overstated. A well-written PRD lays the groundwork for a successful product by clearly defining what needs to be built and why. It serves as a central point of reference for all team members, including developers, designers, product managers, and stakeholders. By documenting detailed functional and non-functional requirements, the PRD helps ensure that everyone involved is aligned with the product’s vision, objectives, and scope. One of the key benefits of a PRD is clarity and alignment. It minimizes misunderstandings and miscommunication by outlining product features, user needs, and project goals in a structured format. This shared understanding helps prevent conflicting assumptions and keeps all contributors on the same page throughout the development process. A PRD also supports focused decision-making by giving decision-makers a clear understanding of priorities, constraints, and dependencies. This allows them to make informed choices about what features to build first, how to manage timelines, and where to allocate resources. Efficient resource allocation is another advantage, as well-defined requirements help teams focus their time and effort on the most valuable aspects of the product.
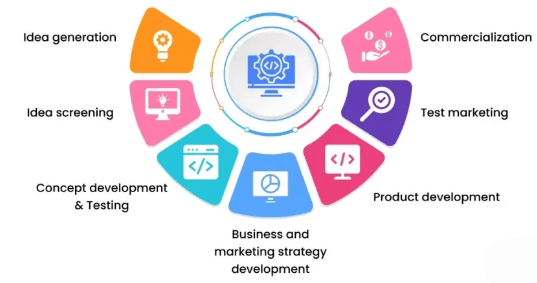
Additionally, a PRD aids in measuring success by setting clear expectations and defining criteria for evaluating the final product. It also plays a crucial role in risk management. With precise requirements in place, the risk of scope creep, feature bloat, and costly delays is significantly reduced. Overall, a strong PRD enhances collaboration, improves planning, and increases the likelihood of delivering a successful product.
Key Components
- Title and Introduction: The title should clearly define the product or feature, while the introduction provides a brief overview of the document’s purpose.
- Objectives and Goals: What is the product or feature aiming to achieve? These goals should align with the business strategy and address user needs.
- Scope: This section defines what is included and what is excluded from the product’s development. It ensures that there are no misunderstandings regarding the product boundaries.
- User Stories/Use Cases: Describe the user flow in terms of who the end-users are and what actions they will take. This will help teams design with the user in mind.
- Functional Requirements: These are the core technical and functional specifications of the product. What features must the product have to meet the goals?
- Non-Functional Requirements: This covers aspects like performance, security, scalability, and usability requirements that aren’t immediately visible but affect the product’s functionality.
- Design and UX Guidelines: This section should include design elements, user interface expectations, and user experience guidelines.
- Timeline: Include deadlines, milestones, and delivery schedules to ensure the product is delivered on time.
- Success Metrics: Define how the product’s success will be measured post-launch, including KPIs, usage metrics, and any other relevant data.
- Stakeholders: Identify the key stakeholders (product managers, engineers, designers, etc.) and their roles in the development process.
- Product Managers: Product managers are responsible for defining the product vision and ensuring that the development team follows the requirements specified in the Product Requirements Document (PRD). They act as the bridge between stakeholders and the development team, guiding the product’s direction.
- Development Teams (Engineers and Developers): The development teams use the PRD as a blueprint to build and implement the product. They rely on the detailed requirements to write code and develop features that align with the product goals.
- Designers (UI/UX): Designers refer to the PRD to understand both the functional needs and aesthetic expectations of the product. This helps them create user interfaces and experiences that meet the goals outlined, ensuring the product is user-friendly and visually appealing.
- Quality Assurance (QA): The QA team leverages the PRD to design test cases that verify the product meets the defined standards. By using the PRD, they ensure that every feature works as intended and that the product is reliable and bug-free.
- Executives: Executives use the PRD to grasp the product’s overall goals and how it fits within the company’s strategic objectives. This understanding helps them make informed decisions regarding funding and resource allocation.
- Marketing Teams: Marketing professionals rely on the PRD to understand the product’s features and benefits, enabling them to create effective campaigns and messaging tailored to target audiences.
- Sales and Support Teams: These teams use the PRD to familiarize themselves with product functionalities and customer benefits, allowing them to better sell the product and provide quality customer support.
- MoSCoW Method: This technique categorizes features into four priority groups: Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, and Won’t-have. This method helps teams focus on what is most important.
- Kano Model: The Kano Model classifies features based on how they impact customer satisfaction. Understanding these categories helps prioritize features that improve user happiness.
- Value vs. Effort Matrix: This approach plots features on a matrix comparing their business value against the effort required for development.
- Customer Feedback: Prioritizing features based on direct input from customers ensures that development focuses on solving real user problems.
- Market Trends Analysis: Monitoring industry trends and competitor offerings helps identify features that keep the product competitive and relevant in the marketplace.
- Stakeholder Input: Engaging internal stakeholders such as sales, marketing, and support teams provides insights into market demands and operational feasibility for feature prioritization.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential risks associated with implementing certain features, including technical complexity or market uncertainty, aids in making informed prioritization decisions.
Target Audience
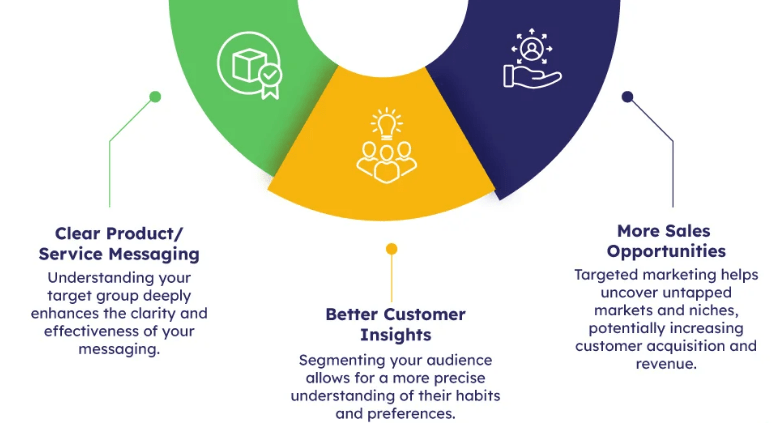
Gathering Requirements
Gathering requirements is a critical first step in creating an effective Product Requirement Document (PRD). This phase involves close collaboration with a variety of stakeholders and users to identify their needs, pain points, and expectations for the product. By thoroughly understanding these factors early on, product teams can ensure that the development efforts are focused on delivering real value. One key activity during this phase is conducting stakeholder interviews. These conversations involve engaging with business leaders, customers, and end-users to gather qualitative insights into their challenges, goals, and desired features. This direct feedback helps uncover important needs that might not be obvious from surface-level observations. User research is another essential component. Techniques such as surveys, focus groups, and usability testing provide quantitative and qualitative data on user behaviors and preferences. This information helps teams better understand how users interact with current solutions and what improvements or new functionalities are needed. Market research also plays an important role. By analyzing competitors and industry trends, product teams can ensure that the new product remains relevant and offers unique advantages that meet market demands. Additionally, analyzing existing data from current products or services, such as usage analytics and customer feedback, can reveal areas for improvement and identify new opportunities. Finally, collaboration and consensus-building among cross-functional teams, including design, engineering, and marketing, help refine and validate requirements. This collective input ensures the PRD is comprehensive, balanced, and supported by all key contributors, setting a strong foundation for successful product development.
Prioritizing Features
Writing Guidelines
Writing a clear and actionable Product Requirement Document (PRD) is essential for successful product development. To achieve this, several key guidelines should be followed. First, clarity is paramount. The document should avoid jargon or overly technical language to ensure it is easily understood by all stakeholders, including both technical teams and non-technical business leaders. Clear communication helps prevent misunderstandings and keeps everyone aligned on the product vision. Brevity is also important. The PRD should be concise, including only the information necessary for teams to grasp the product’s scope and how to execute it effectively. Avoiding unnecessary details helps maintain focus and makes the document easier to navigate and use as a reference throughout the development process. Each requirement must be actionable. This means specifications should be precise and unambiguous, enabling development teams to implement features without confusion. Clear, well-defined requirements reduce the risk of errors and rework, saving time and resources. The PRD should be user-focused. Writing requirements from the user’s perspective ensures that the product development remains centered on meeting real user needs and improving their experience. This approach helps prioritize features that provide genuine value rather than focusing solely on technical capabilities. Finally, traceability is critical. Every requirement should be linked back to a specific business goal or user need. This connection ensures that the development work aligns with strategic objectives and makes it easier to measure success once the product is launched. Following these guidelines helps create a PRD that guides teams effectively and contributes to delivering a successful product.
Conclusion
A well-crafted Product Requirement Document (PRD) is a vital tool for successful product development. It acts as the single source of truth, providing a clear and shared understanding of the product’s vision, scope, and goals. By aligning all teams including product management, development, design, and marketing a good PRD helps ensure that everyone is working toward the same objectives, reducing confusion and conflicting priorities throughout the project. An effective PRD guides the development process to be more efficient by clearly outlining requirements, which helps teams focus on building features that meet user expectations and align with overall business goals. This clarity supports better decision-making, prioritization, and resource allocation, ultimately leading to higher-quality products delivered on time and within scope. Gathering detailed requirements, prioritizing key features, and maintaining continuous collaboration between cross-functional teams throughout the product lifecycle are critical to achieving these outcomes. This collaborative approach encourages early feedback and adjustments, reducing costly changes late in development. By following structured guidelines when writing the PRD, avoiding common pitfalls such as unclear or overly complex requirements, and keeping the document updated as the project evolves, teams can minimize risks and misunderstandings. This proactive management creates a smoother development process and increases the likelihood of delivering a product that satisfies user needs. In summary, a well-maintained PRD provides the foundation for a well-planned and coordinated product development effort. It ensures that every step, from initial concept to final release, supports the goal of creating a successful product that drives business growth and customer satisfaction.





