SQL is a database language, used to update databases, execute queries, and manage permissions. It was designed for relational database management systems. It’s generally considered a declarative language. It’s been around in some form since the 70s and is just about as ubiquitous as data management itself.
The model was first introduced in a paper titled “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks” written by E. F. Codd. The language was at one point titled SEQUEL for Structured English Query Language; you may occasionally still hear SQL pronounced that way.
SQL-related products have been in commercial use since 1979, when they were introduced by a forerunner to Oracle. Does Oracle control SQL? No. IBM soon followed suit. Today SQL is used in many open source and commercial products. Often these include SQL in the name. PostgreSQL is among the best known.
There are two standards committees “guarding” SQL: the International Standards Organization and the American National Standards Institute. Still, SQL is not all the same. In order to access and use the data, you need a database program or server. The major vendors have their own servers for database applications. Oracle Database applications use the Oracle Database SQL. IBM’s server is DB2. There’s also the Microsoft SQL Server. Then there’s MySQL , an open source database program that is sometimes thought of as a light version of Microsoft SQL – a place to get started, but one your business may ultimately outgrow.
While multiple database programs use the SQL standard, they may eliminate portions or add to it. PL/SQL, for example, is oracle’s extension. Alterations make for some compatibility issues – this is an area of continued focus.
Uses of SQL
SQL is used in health care (cancer registries) business (inventories, trends analysis), and education. It even has applications in the defense industry.
Who works with SQL? Database developers and administrators and business analysts are among the better known users. But knowing at least a little SQL can be an asset for people in a lot of different roles, from the web developer to the PhD level scientist. The most basic task is the query — you specify “from” to tell the program what table(s) to retrieve data from and give additional clauses like “where” and “having” to narrow down what you want. A more advanced user will design and modify databases.
SQL Certifications
There are multiple SQL-related certifications that you can pursue. Certifications are usually vendor-specific — you’re getting certified in your expertise with particular solutions.
Microsoft recommends Certified Solutions Expert: Data Platform for those who build enterprise scale applications. SQL MCSE: Business Intelligence is for those who develop business solutions and Microsoft Certified Master: SQL 2008 for senior IT professionals who use SQL Server 2008.
IBM, meanwhile, offers the Certified Solutions Developer credential.
Then there’s Oracle. Oracle offers many SQL-related certifications for database administrators and developers. 10g and 11g administrators can be certified at the associate, professional, and master level. Some certifications require you to take particular courses.
As a database professional, you can also be certified in MySQL.
Be aware, though, that certifications change just about as frequently as technologies do.
Features of SQL
Here in this section of the SQL tutorial for beginners, we list some of the top features of SQL that make it so ubiquitous when it comes to managing relational databases.
- SQL is very simple and easy to learn language
- SQL is versatile as it works with database systems from Oracle, IBM, Microsoft, etc.
- SQL is an ANSI and ISO standard language for database creation and manipulation
- SQL has a well-defined structure as it uses long established standards
- SQL is very fast in retrieving large amounts of data very efficiently
- SQL lets you manage databases without knowing lot of coding.
Applications of SQL
Here in this section of the SQL tutorial we will learn SQL applications that make it so important in a data-driven world where managing huge databases is the norm of the day.
- SQL is used as a Data Definition Language (DDL) meaning you can independently create a database, define its structure, use it and then discard it when you are done with it
- SQL is also used as a Data Manipulation Language (DML) which means you can use it for maintaining an already existing database. SQL is a powerful language for entering data, modifying data and extracting data with regard to a database
- SQL is also deployed as a Data Control Language (DCL) which specifies how you can protect your database against corruption and misuse.
- SQL is extensively used as a Client/Server language to connect the front-end with the back-end thus supporting the client/server architecture
- SQL can also be used in the three-tier architecture of a client, an application server and a database which defines the Internet architecture.
Why should you learn SQL?
Today regardless of the relational databases systems by major corporations like Oracle, IBM, Microsoft and others, the one thing that is common to them is the Structured Query Language or SQL.
So if you learn SQL online then you will be able to pursue a very broad career spanning a lot of roles of responsibilities. Also if you are learning SQL then it is important for a data science career as well since a data scientist will also have to deal with relational databases and query it using the standard language SQL.
SQL Server Installation Step By Step Process
Here we will see how to install SQL in our system for that follow below steps. Here we are installing SQL in windows 8.1 OS.
Now go to your SQL Server installation files folder and double click on the setup file like as shown below.
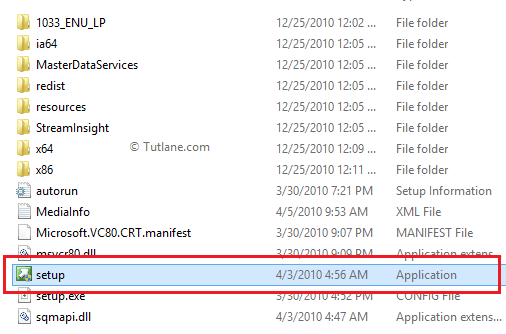
Whenever you click on the setup file, it will show the compatibility assistance window just ignore that message and click Run the program without getting help like as shown below.
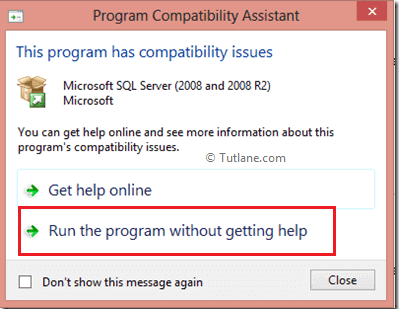
To setup SQL Server 2008 R2 it requires Microsoft .Net Framework and an updated windows installer that’s the reason it will show an alert window in that click OK to install required things like as shown below.
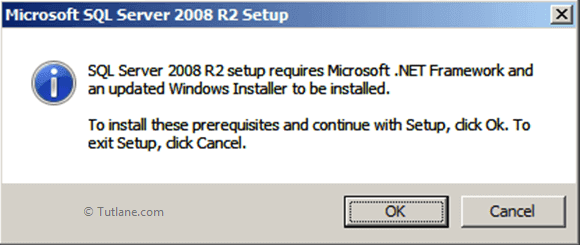
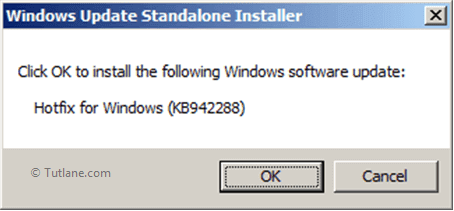
Once that is installed it will show the popup for Windows Update Standalone Installer, click OK button to install Windows Installer like as shown below.
Once we finish installation it will ask you to restart the system. Once we restarted now double click on setup button to install SQL Server it will open installation screen like as shown below in that select installation à under that select New installation or add features to an existing application like as shown below.
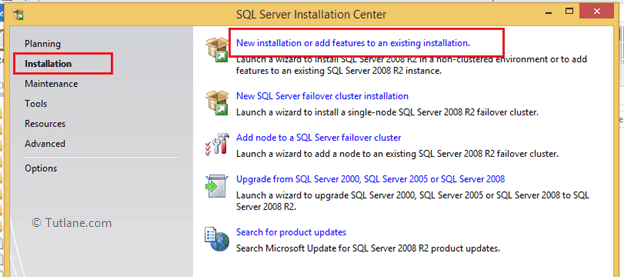
Once click on “New installation or add features to an existing application” it will open another window like as shown below.
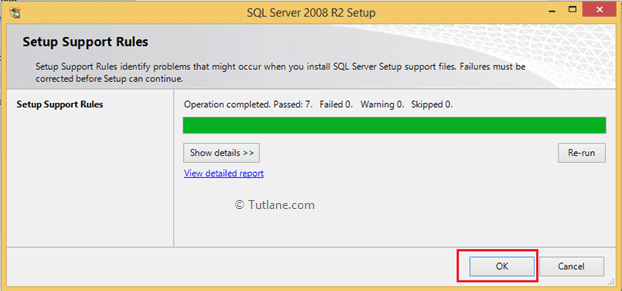
Here it will run Setup Support Rules like as shown above once done click OK. Now it will open another window to Setup Support Rules in this window click install button like as shown below.
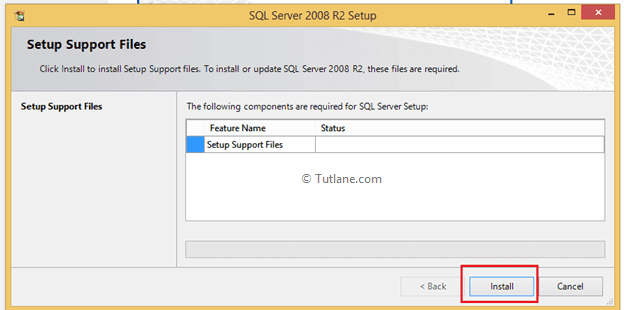
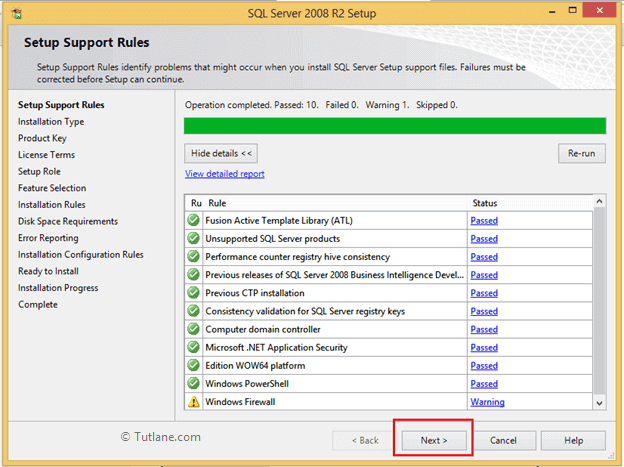
Once Setup Support Rules installation finished it will show tested result like as shown below in this if everything fine then click the install button.
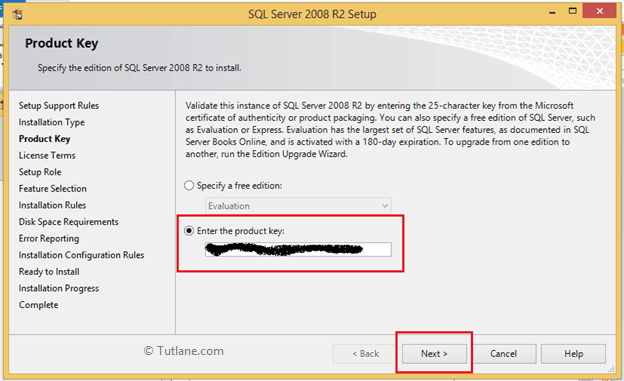
In the next screen, it will ask for the product key if you enter your key and click Next button like as shown below.
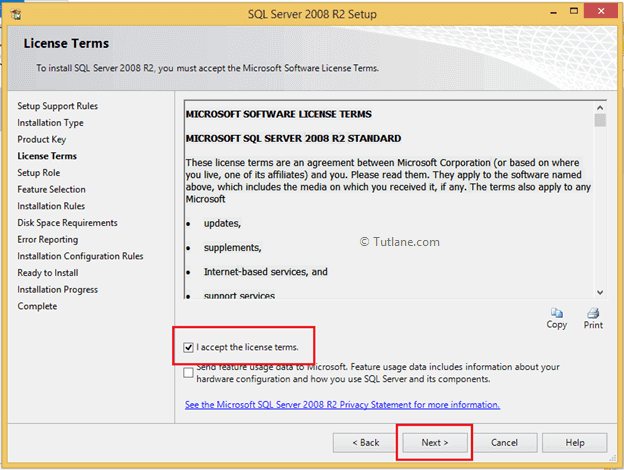
Now accept the terms and conditions and click the Next button.
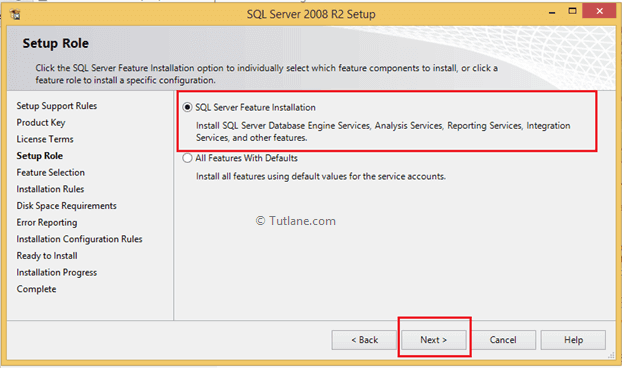
Now select SQL Server Feature Installation like as shown below and click the Next button.
Now click on Select All button to select all features to install and then click Next button like as shown below.
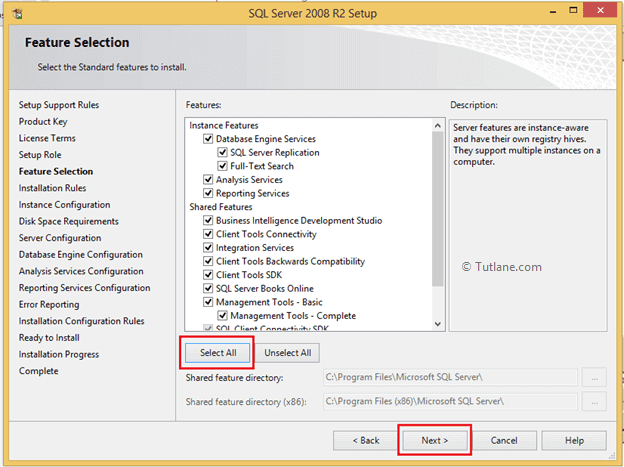
It will do the required tests once everything finished, click the Next button like as shown below.
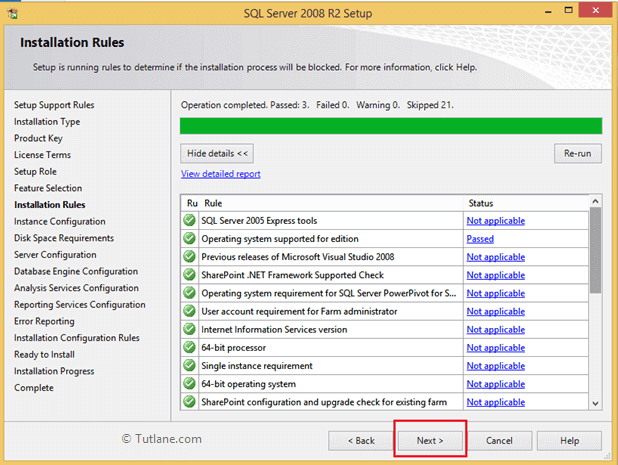
Now select Default Instance and click Next button like as shown below.
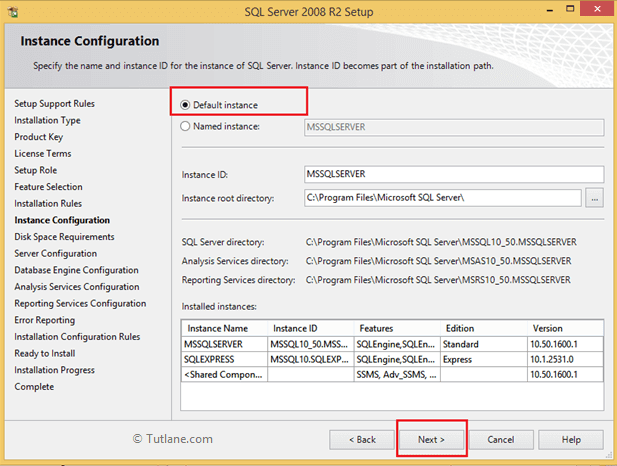
Now it will show required disk space to install all SQL Server features in that click Next like as shown below.
In the server configuration screen, you need to configure your accounts like as shown below and click Next button.
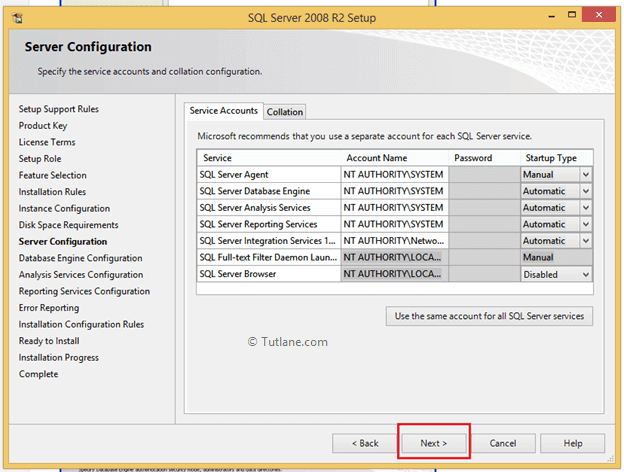
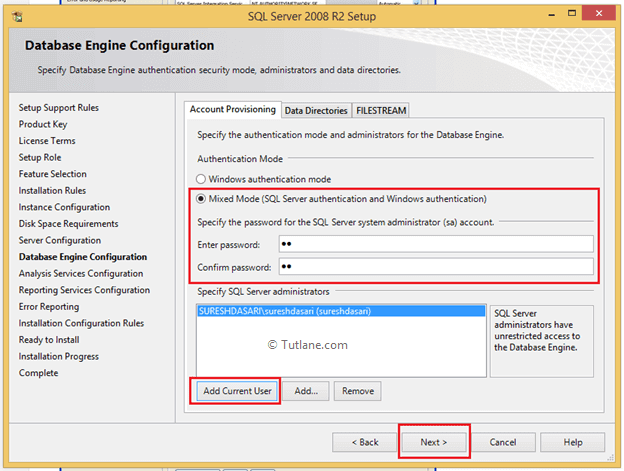
Now in database engine configuration window select Mixed mode authentication (It will allow you to login with windows and SQL authentication) then specify password for your account and also add SQL Server administrator account for that click on Add Current User button to add current user as administrator or click on Add button to add new user and click next like as shown below.
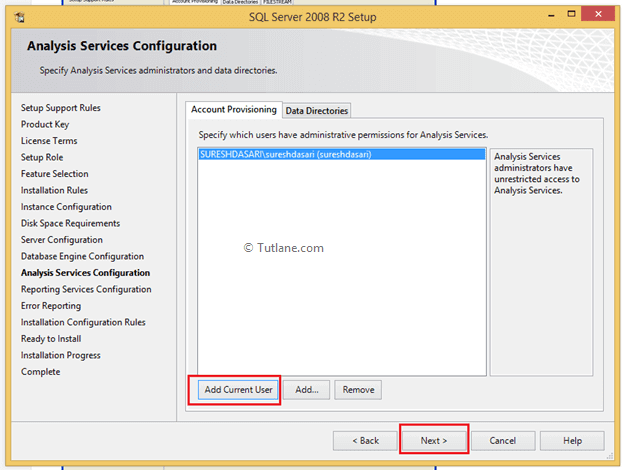
In Analysis services configuration window specify administrator by Click on Add Current User button or Add button to add a new user as administrator like as shown below.
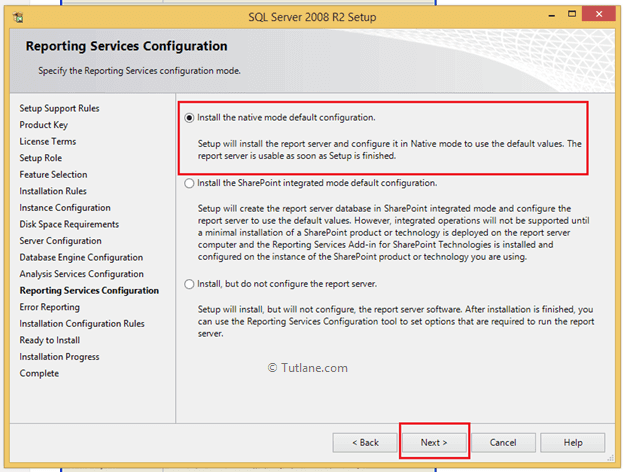
In reporting services configuration window select Install the native mode default configuration and click Next button like as shown below.
Now in Error Reporting window click Next button like as shown below.
In the installation configuration rules window, it will do some tests once everything is done click Next button like as shown below.
Now we are ready to install SQL Server so click on the install button like as shown below.
In the installation progress window, it will show installation progress once done click next button like as shown below.
Once everything installed correctly it will show a message like as shown below.
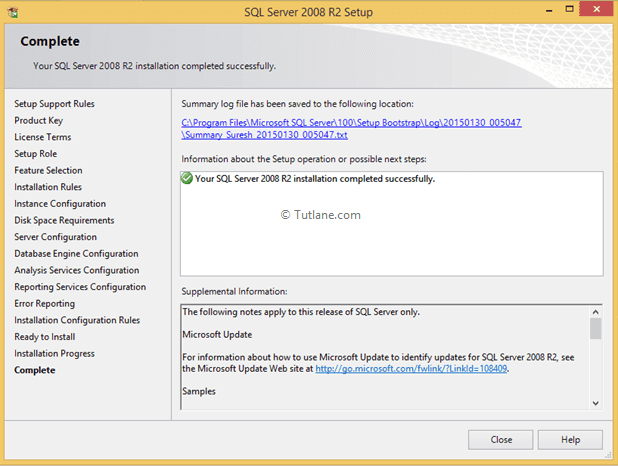
Now go to the start button of windows and open SQL Server Management Studio 2008 R2 like as shown below.
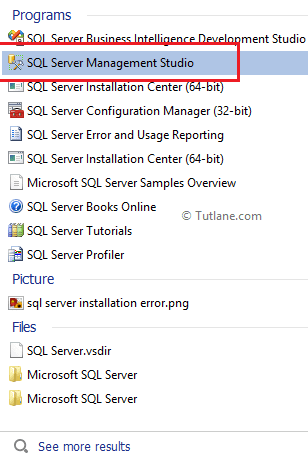
Now enter the server name and click Connect button like as shown below.
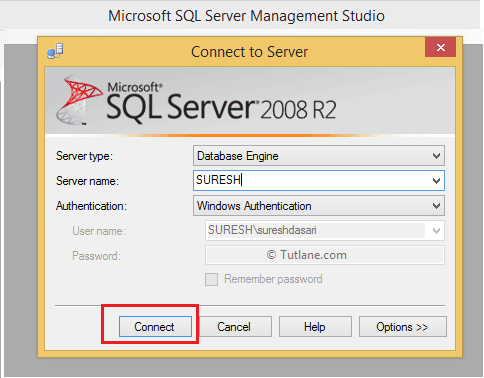
Now our SQL Server Management studio like as shown below.
Uses of SQL
SQL is used in health care (cancer registries) business (inventories, trends analysis), and education. It even has applications in the defense industry.
Who works with SQL? Database developers and administrators and business analysts are among the better known users. But knowing at least a little SQL can be an asset for people in a lot of different roles, from the web developer to the PhD level scientist. The most basic task is the query — you specify “from” to tell the program what table(s) to retrieve data from and give additional clauses like “where” and “having” to narrow down what you want. A more advanced user will design and modify databases.
SQL Certifications
There are multiple SQL-related certifications that you can pursue. Certifications are usually vendor-specific — you’re getting certified in your expertise with particular solutions.
Microsoft recommends Certified Solutions Expert: Data Platform for those who build enterprise scale applications. SQL MCSE: Business Intelligence is for those who develop business solutions and Microsoft Certified Master: SQL 2008 for senior IT professionals who use SQL Server 2008.
IBM, meanwhile, offers the Certified Solutions Developer credential.
Then there’s Oracle. Oracle offers many SQL-related certifications for database administrators and developers. 10g and 11g administrators can be certified at the associate, professional, and master level. Some certifications require you to take particular courses.
As a database professional, you can also be certified in MySQL.
Be aware, though, that certifications change just about as frequently as technologies do.