
- Who is a Line Manager?
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Skills Required for Line Managers
- Importance of Line Managers
- Line Manager vs Staff Manager
- Relationship with Team Members
- Challenges Faced by Line Managers
- Conclusion
Who is a Line Manager?
A line manager is a key figure within an organization who directly oversees employees and is accountable for their performance and output. Positioned between upper management and operational staff, line managers act as a vital link that ensures the smooth flow of communication skills and coordination throughout the company. They typically manage specific departments or teams and are responsible for making sure that the daily activities of their team align with the organization’s overall strategic goals. Unlike middle or upper-level managers who may focus primarily on long-term planning and high-level decision-making, line managers are deeply involved in the execution of these plans. Their role requires a hands-on approach to managing both people and processes, making them crucial for translating strategic objectives into actionable tasks. This dual responsibility means they must be effective supervisors and functional leaders, guiding their teams to meet performance targets while also managing workflows and resources efficiently. What Is a Line Manager serves as the first point of contact for employees, playing a critical role in addressing questions, resolving issues, and supporting team members to maintain productivity. They help create a work environment where employees feel supported and motivated, fostering engagement and collaboration. Additionally, line managers often provide feedback and report on team performance to higher management, ensuring transparency and alignment within the organization. Overall, line managers bridge the gap between strategy and execution, making them essential for achieving organizational success. Their ability to manage people and processes on the frontline helps drive operational teams efficiency and contributes significantly to meeting the company’s objectives.
Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of a line manager are varied and can differ depending on the size, structure, and sector of the organization. However, certain core duties remain consistent across most industries. One of the primary responsibilities is team supervision, where the line manager oversees the daily tasks of their team, ensuring that work is completed on time and meets the required quality standards. This hands-on approach helps maintain productivity and keeps operations running smoothly. Another important role is goal setting. Line managers work closely with their teams to establish individual and group objectives that align with the broader company goals. Clear goal setting motivates employees and provides a roadmap for success, helping the team focus their efforts effectively. Performance management is also a key responsibility. Line managers continuously monitor employee performance, provide constructive feedback, and conduct formal appraisals. This ongoing evaluation process helps identify strengths, address weaknesses, and recognize achievements, which boosts morale and improves results. Effective resource allocation is essential. Line managers ensure that the right people are assigned to the right tasks based on skills and availability, optimizing team efficiency. Additionally, they focus on training and development by identifying skill gaps and arranging necessary training sessions to help employees grow professionally and keep up with evolving job demands.
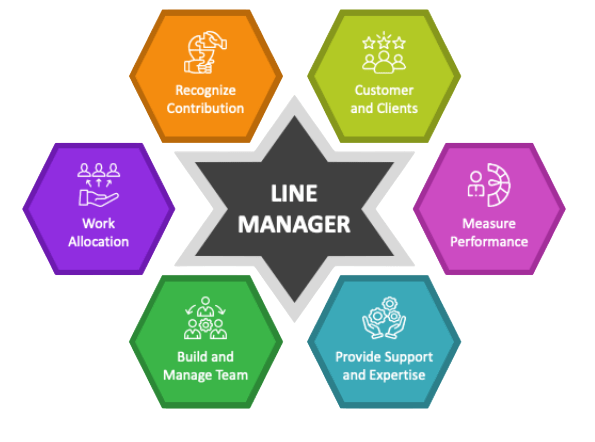
Line managers also handle conflict resolution, mediating disputes and maintaining a positive and collaborative work environment. Lastly, they are responsible for ensuring compliance with organizational policies and legal regulations, safeguarding the company from risks and maintaining ethical standards. These diverse roles make line managers indispensable for operational success.
Skills Required for Line Managers
- Leadership Skills: Line managers must effectively lead and motivate their teams, fostering trust, boosting morale, and driving productivity to meet organizational goal setting.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication is essential for conveying instructions, listening to employee concerns, and ensuring smooth coordination between upper management and team members.
- Decision-Making Ability: Line managers are responsible for making timely, effective decisions related to daily operations, problem-solving, and resource allocation to keep work on track.
- Technical Knowledge: Having relevant technical expertise allows line managers to understand tasks, guide employees accurately, and maintain quality standards within their department.
- Time Management: Managing multiple priorities, meeting deadlines, and organizing tasks efficiently help line managers maximize team productivity and align efforts with business objectives.
- Conflict Resolution: Strong interpersonal skills enable line managers to address and resolve workplace conflicts quickly, ensuring a harmonious and focused work environment.
- Performance Management: Line managers must monitor employee performance, provide constructive feedback, conduct evaluations, and encourage continuous development to improve overall team effectiveness.
- Direct Supervision: Line managers oversee the day-to-day activities of employees, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently and according to organizational standards.
- Communication Bridge: They act as a vital link between upper management and frontline employees, facilitating clear communication and ensuring that company goals and policies are understood and implemented.
- Performance Monitoring: Line managers regularly assess employee performance, provide feedback, and identify areas for improvement, which helps boost individual and team productivity.
- Employee Motivation: By supporting and motivating their teams, line managers enhance job satisfaction, reduce turnover, and promote a positive work environment.
- Problem Solving: Line managers address operational issues promptly, resolving conflicts, managing crises, and adapting to changing circumstances to maintain workflow continuity.
- Training and Development: They identify skill gaps and facilitate training or coaching to help employees grow, ensuring the workforce remains competent and competitive.
- Implementation of Policies: Line managers ensure that organizational policies, procedures, and strategic plans are effectively executed at the operational level, aligning daily work with broader business objectives.
- Building Trust: A strong relationship starts with trust. Team members need to feel confident that their leader is honest, reliable, and supportive, which fosters open communication and collaboration.
- Effective Communication: Maintaining clear, consistent, and two-way communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures everyone is aligned with goals and expectations.
- Empathy and Support: Understanding team members’ challenges and showing genuine care boosts morale and creates a positive work environment where employees feel valued.
- Encouraging Collaboration: Good leaders promote teamwork by encouraging sharing of ideas and human resources, which enhances creativity and problem-solving within the group.
- Providing Feedback: Constructive feedback helps team members grow professionally and improve performance, while also reinforcing positive behaviors.
- Respect and Recognition: Showing respect for individual differences and recognizing achievements motivates employees and strengthens their commitment to the team.
- Conflict Resolution: A healthy relationship requires addressing conflicts quickly and fairly to maintain harmony and productivity, preventing small issues from escalating.
Importance of Line Managers
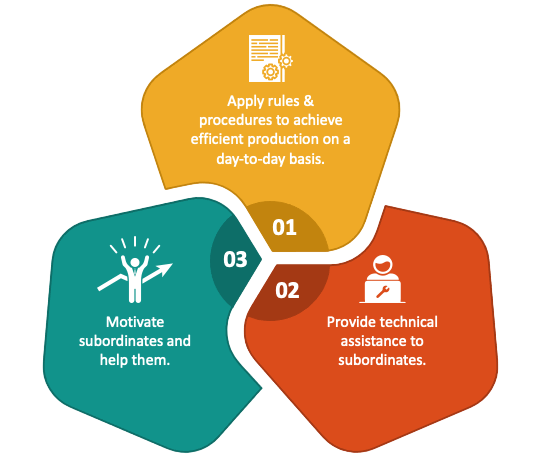
Line Manager vs Staff Manager
Line managers and staff managers play distinct yet complementary roles within an organization, often working closely together to ensure smooth operations and strategic alignment. Line managers hold direct authority over production or operational activities. They are responsible for supervising employees who perform core business functions, enforcing company policies, and ensuring that work output meets quality and quantity standards. Line managers focus on the day-to-day execution of tasks, directly managing teams or departments involved in creating products or delivering services. Their role is hands-on, emphasizing operational efficiency and meeting short-term goals. In contrast, staff managers serve a more advisory and supportive function. They provide specialized expertise and guidance that help line managers perform their roles more effectively. Departments such as human resources, information technology, finance, and legal services typically fall under staff management. Staff managers do not have direct control over the production process but design policies, develop best practices, and offer essential services that enable operational departments to function smoothly. Their focus is often on long-term planning, compliance, and ensuring the overall health of the organization’s infrastructure. While line managers are responsible for implementing strategies and overseeing operations, staff managers create the frameworks and support systems that empower line managers to succeed. This division of labor allows organizations to balance effective execution with strategic oversight. The collaboration between line and staff managers is crucial, as staff functions enhance operational capabilities and help address challenges, while line management ensures that day-to-day activities align with the organization’s goals. Together, they create a dynamic partnership that drives organizational success.
Relationship with Team Members
Challenges Faced by Line Managers
Line managers often operate in high-pressure environments where they must balance multiple responsibilities and face a range of challenges. One major challenge is workload management. Line managers are tasked with juggling both managerial duties and operational tasks, which can be overwhelming, especially in fast-paced settings. This requires excellent time workload management and prioritization skills to ensure that neither aspect is neglected. Another common issue is the lack of training. Many line managers are promoted from technical or specialist roles without receiving adequate managerial training. This gap can make it difficult for them to effectively lead teams, handle conflicts, or make strategic decisions, impacting overall performance. Employee resistance is also a frequent challenge. Managing difficult team members or overcoming resistance to change demands strong interpersonal and communication skills. Line managers must find ways to motivate employees and foster a positive work environment despite these obstacles. Often, line managers face ambiguity in their roles, as they must balance strategic directives from upper management with the practical realities of day-to-day execution. This dual responsibility can lead to conflicting priorities and stress. Performance issues among team members also require careful handling. Line managers must address underperformance fairly while maintaining motivation and morale. This can be a delicate balance, requiring emotional intelligence and coaching skills. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological change means line managers must continuously adapt to new tools and platforms, which can be challenging without adequate support. Addressing these challenges successfully requires resilience, ongoing skill development, and strong support from senior workload management. With the right human resources and training, line managers can overcome these hurdles and contribute significantly to organizational success.
Conclusion
Line managers play a crucial role in the smooth functioning and success of any organization. They serve as the vital link between the strategic plans developed by senior leadership and the practical execution carried out by operational teams. By managing day-to-day activities, supervising employees, and ensuring that tasks align with the organization’s goals, line managers directly influence productivity and quality outcomes. When equipped with the right skills, tools, and mindset, they can effectively drive team performance, foster collaboration, and create a positive work environment that motivates employees to excel. In today’s fast-changing business landscape, where organizations are increasingly focused on agility and employee engagement, the importance of line managers continues to grow. Their ability to adapt quickly, support diverse teams, and communicate effectively makes them indispensable in maintaining operational teams efficiency and implementing change initiatives. Line managers also play a key role in employee development by identifying skill gaps, providing feedback, and encouraging continuous learning. Recognizing this, forward-thinking organizations are investing heavily in the training and development of line managers. Providing them with leadership programs, coaching, and resources is no longer optional but essential for sustained business success. Empowered line managers not only boost productivity and employee engagement but also contribute to innovation and long-term growth. In essence, nurturing strong line managers is a strategic investment that yields significant returns, enabling companies to remain competitive and responsive in an ever-evolving marketplace.





