
- Introduction to Performance Management
- Objectives of Performance Management
- Key Components of Performance Management
- Performance Planning
- Performance Monitoring
- Employee Development
- Performance Appraisal Systems
- Conclusion
Introduction to Performance Management
Performance management is an ongoing process designed to enhance the effectiveness and productivity of employees within an organization. Its main purpose is to align individual goals with the broader objectives of the company, ensuring that every employee understands their role and contributes meaningfully toward organizational growth. The process typically involves setting clear performance expectations, regularly monitoring progress, providing constructive feedback, and identifying areas where employees can improve or develop new skills. This continuous cycle aims to promote growth, increase efficiency, and maintain high levels of employee engagement. In today’s modern workplace, performance management extends far beyond traditional annual appraisals. It has evolved into an integrated and dynamic process that focuses on continuous improvement. Regular feedback sessions allow employees to understand how they are performing in real time and offer opportunities for immediate adjustments. Coaching plays a critical role in guiding employees through challenges and helping them develop professionally. Goal-setting is collaborative and aligned with both personal career aspirations and company needs, creating a shared sense of purpose. By adopting this comprehensive approach, organizations not only improve overall performance but also enhance employee satisfaction and retention. Employees feel valued and supported when they receive ongoing recognition and development opportunities. Ultimately, effective performance management builds a culture of accountability, continuous learning, and motivation. This culture contributes directly to organizational success by fostering a workforce that is skilled, engaged, and aligned with the company’s vision and goals.
Objectives of Performance Management
The primary objectives of performance management focus on both individual and organizational goals, creating a balanced approach that drives success at all levels. One of the main objectives is enhancing employee performance. This is achieved by clearly defining job expectations and offering continuous support and feedback, helping employees perform to the best of their abilities. When employees understand what is expected and receive guidance, their productivity and quality of work improve significantly. Another important goal is aligning individual goals with the broader organizational objectives. This alignment ensures that every employee is working toward a common purpose, which helps the organization achieve its strategic targets efficiently. Performance management acts as a bridge, connecting personal achievements with company success. Employee development is also a key focus. The process identifies areas where employees need improvement and provides necessary resources, such as training and mentoring, to support their growth. This continuous development helps employees enhance their skills and prepares them for future challenges. Improving organizational efficiency is another critical objective. By addressing performance gaps and streamlining processes, performance management helps reduce inefficiencies and ensures that efforts are directed toward the organization’s strategic goals.
Recognition and reward play an essential role in motivating employees. Acknowledging hard work and achievements boosts morale and encourages employees to maintain high performance levels. Lastly, performance management helps identify high-potential employees who can take on greater responsibilities and leadership roles, supporting succession planning and long-term organizational growth. Together, these objectives create a comprehensive framework that benefits both employees and the organization.
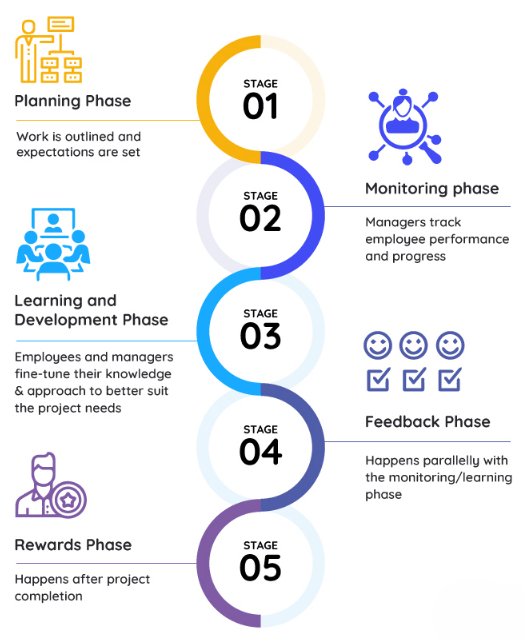
Key Components of Performance Management
- Goal Setting: Setting clear, measurable, and achievable goals is one of the first steps in performance management. These goals should be specific, aligned with organizational priorities, and mutually agreed upon between the employee and manager.
- Continuous Feedback: Performance management is not a one-time activity. Regular feedback, both positive and constructive, is crucial in guiding employees and making them aware of areas for improvement.
- Employee Development: An essential part of performance management is ensuring that employees receive adequate training, mentorship, and opportunities for skill enhancement to help them grow professionally.
- Performance Review: A formal review typically takes place annually or semi-annually, but this should not be the only point of feedback. It summarizes the employee’s performance review and provides a broader view of their contributions.
- Recognition and Reward: Recognizing employees for meeting or exceeding their goals is key to motivating continued high performance. This can take the form of promotions, bonuses, public acknowledgment, or other rewards.
- Action Plans: When performance falls short of expectations, action plans are created. These plans identify specific areas for improvement and outline the steps that need to be taken.
- First Phase of Performance Management: Performance planning is the initial stage of the performance management cycle, setting the foundation for employee success.
- Setting Clear Expectations: It involves defining the employee’s roles, responsibilities, and expected behaviors to ensure clarity in what is required.
- Defining Specific Goals: Managers and employees work together to establish goals that focus on key priorities and guide employee efforts.
- Using SMART Goals: Goals must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound to ensure they are clear and trackable.
- Agreeing on Performance Criteria: Both parties agree on how performance will be measured through key indicators and standards.
- Identifying Resources and Support: Employees should have access to necessary tools, training, and support to help them achieve their goals effectively.
- Establishing Feedback Mechanisms: Regular feedback channels are set up to help employees understand their progress and improve continuously during the performance period.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Employee development emphasizes ongoing growth, helping employees enhance their skills and capabilities over time.
- Training and Skill Development: Providing employees with necessary training and resources equips them to improve their current job performance.
- Career Development Plans: Creating clear career development paths aligns employees’ personal goals with the company’s future needs, encouraging long-term commitment.
- Mentoring and Coaching: Pairing employees with experienced mentors or coaches offers personalized guidance, support, and advice to help employees grow professionally.
- Workshops and Seminars: Organizing workshops and seminars provides opportunities for employees to learn new skills and expand their knowledge relevant to their roles.
- Preparation for Future Roles: Employee development prepares staff for upcoming challenges and potential promotions, ensuring the organization has a ready pool of talent.
- Improving Employee Engagement: Investing in development increases motivation, job satisfaction, and loyalty, which benefits both employees and the organization.
Performance Planning
Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is a continuous process that involves tracking employee progress to ensure that individual and organizational goals are being met. It is an essential part of performance management, helping managers and employees stay aligned and focused on achieving desired outcomes. Performance monitoring can include tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), observing workplace behavior, and collecting feedback from multiple sources such as peers, supervisors, and even customers. By regularly assessing performance, organizations can identify strengths, address challenges, and support employee development more effectively. One important aspect of effective performance monitoring is regular check-ins. Managers should meet frequently with employees to discuss their progress, any challenges they are facing, and potential obstacles that might hinder their work. These conversations provide opportunities to offer guidance, adjust goals if needed, and keep employees motivated and engaged. Another critical component is the use of performance metrics. Tracking employee performance against established metrics or key performance indicators helps ensure that work aligns with the organization’s objectives. These measurable indicators provide clear benchmarks for success and make it easier to identify areas needing improvement. Real-time feedback is also vital in effective performance monitoring. Instead of waiting for formal annual reviews, providing immediate feedback allows employees to make timely corrections and improve their performance continuously. This approach encourages a culture of open communication and ongoing development. Overall, performance monitoring helps maintain focus, encourages accountability, and fosters a proactive environment where employees can succeed and contribute to organizational growth.
Employee Development
Performance Appraisal Systems
Performance appraisals are formal evaluations of an employee’s performance over a specific period, usually conducted annually or semi-annually. These evaluations are based on pre-established goals and objectives and serve as an important tool for providing feedback on an employee’s strengths and areas for improvement. Performance appraisals help both employees and managers understand how well expectations are being met and identify opportunities for development and growth. There are several types of performance appraisal systems used by organizations, each with its own approach. The traditional appraisal system follows a top-down model where managers evaluate employees based on predefined criteria. This method focuses on the manager’s perspective and often emphasizes goal achievement and job performance. Self-assessment is another type of appraisal where employees evaluate their own performance. This encourages self-reflection and personal accountability. The employee’s self-assessment is then compared with the manager’s evaluation to identify any differences in perception and foster a meaningful discussion. The 360-degree feedback system collects input from multiple sources including peers, subordinates, supervisors, and sometimes even clients. This comprehensive feedback provides a well-rounded view of an employee’s performance, highlighting different strengths and potential blind spots. Finally, continuous appraisal is an ongoing process where employees receive regular feedback throughout the year rather than during a single formal review. This approach promotes continuous improvement, allowing employees to address issues promptly and stay aligned with organizational goals. Overall, these various appraisal methods help organizations manage performance effectively and support employee development.
Conclusion
Performance management is a comprehensive and continuous process that is essential for enhancing employee performance, aligning individual efforts with organizational goals, and promoting employee development. It involves setting clear expectations, regularly monitoring progress, providing timely feedback, and supporting employees in improving their skills. When effectively implemented, a performance management system helps organizations reach their strategic objectives while creating a positive and motivating work environment. A well-structured performance management system benefits both the organization and its employees. For the organization, it ensures that resources are used efficiently and that all employees are contributing to key business priorities. For employees, it provides clarity about their roles, recognition for their achievements, and opportunities for growth and development. This dual focus helps boost employee engagement, satisfaction, and retention. However, performance management also comes with challenges. These can include bias in evaluations, lack of clear communication, or insufficient training for managers in providing constructive feedback. Overcoming these challenges requires adopting best practices such as continuous feedback, objective performance metrics, and training programs for both managers and employees. By addressing these challenges and committing to a transparent and fair performance management process, organizations can build a system that drives excellence. This system encourages accountability, supports career development, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, effective performance management leads to sustained business growth and a motivated, high-performing workforce prepared to meet future challenges.





