
- Understanding Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- EV Market Overview in India
- Government Policies & FAME
- Growth Drivers
- Local Manufacturing Trends
- Infrastructure Development
- Role of Startups
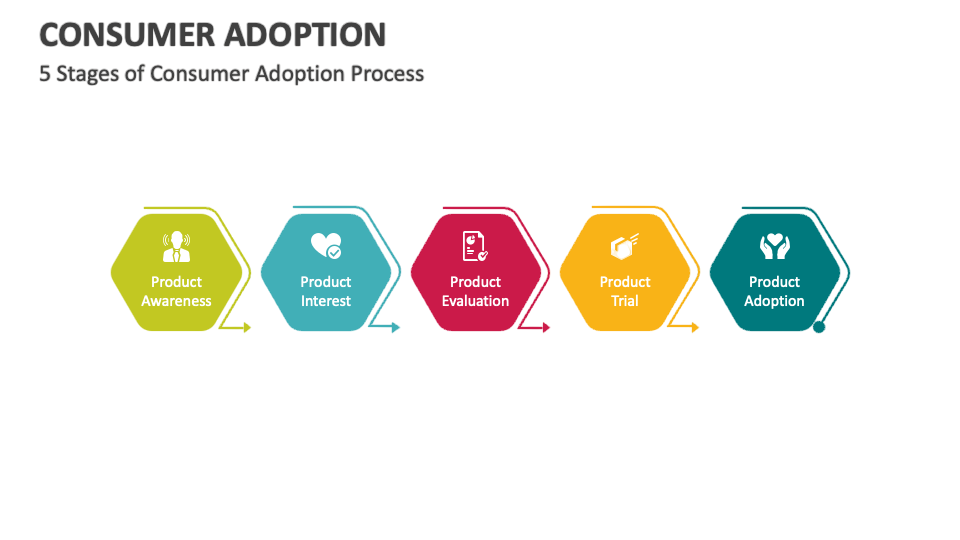
- Consumer Adoption Trends
- EV Financing Options
- Environmental Impact in India
- Challenges and Roadblocks
- Vision 2030 and Beyond
- Conclusion
Understanding Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) are changing our approach to transportation. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that depend on petrol or diesel, EVs are mainly powered by electric motors using energy stored in rechargeable batteries. This shift is more than just a technological change; it marks a significant move towards sustainability and energy independence. Worldwide, EVs play a crucial role in fighting climate change, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and reducing urban air pollution. They come in various types, including Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), which run only on battery technology; Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), which mix a battery-powered motor with a traditional engine; and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), which recharge on their own through regenerative braking. BEVs are especially popular because of their simplicity and zero-emission operation. India, with its growing urban population and rising energy needs, is at a pivotal point in adopting sustainable transportation solutions. Moving to Artificial Intelligence Training EVs is not just an environmental necessity; it is also a strategic chance to boost domestic manufacturing, create jobs, and lessen reliance on imported oil.
EV Market Overview in India
The Indian EV market has evolved from a small niche to a rapidly expanding industry with a national impact. Industry estimates suggest that the EV sector in India could draw over $20 billion in investments by 2030. The market now features a diverse mix of two-wheelers, three-wheelers, passenger cars, and electric buses, with two-wheelers and e-rickshaws leading due to their affordability and suitability for urban areas.
- Urban Leaders: Delhi, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune are driving EV startups in India adoption through incentives and investments.
- Diverse Ecosystem: Includes manufacturers, battery technology producers, charging stations developers, financiers, and mobility software firms.
- Investment Potential: Over $20 billion projected by 2030, signaling strong national and global interest.
- Segment Growth: Two-wheelers and e-rickshaws dominate due to cost-effectiveness and urban compatibility.
- Cross-Sector Collaboration: Unified efforts are transforming EVs into a mainstream transportation solution across ev startups in india.
Government Policies & FAME
Government involvement has been key to EV startups in India growth. The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, launched in 2015, has been crucial for boosting demand. Now in its second phase, FAME II aims to encourage electric buses, three-wheelers, and two-wheelers while also developing public charging stations infrastructure.
- Tax Incentives: GST on EVs reduced to 5%, compared to 28% on traditional vehicles.
- State Policies: Many states offer road tax exemptions, registration fee waivers, and government subsidies for electric cars for charging stations infrastructure.
- PLI Scheme: Supports domestic production of lithium-ion and advanced batteries to reduce import dependency.
Growth Drivers
- Environmental Awareness: Rising air pollution has increased demand for sustainable transport solutions.
- Fuel Cost Savings: EVs offer running costs as low as one-tenth of petrol vehicles.
- Urbanization and Congestion: Compact, low-maintenance EVs suit short urban trips and crowded streets.
- Technological Advancement: battery technology, motor, and energy system improvements are boosting range and reliability.
- Digital Ecosystem: Apps simplify charging station discovery, booking, and payment for EV users.
Ready to Get Certified in Artificial Intelligence ? Explore the Program Now Artificial Intelligence Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Local Manufacturing Trends
EV startups in India sector is benefiting from the “Make in India” initiative. Domestic production of EVs, batteries, and power electronics has picked up, fueled by cost pressures and policy incentives. Major automakers such as Tata Motors, Mahindra Electric, and Hero government subsidies for government subsidies for electric cars are increasing their production capabilities and developing locally sourced parts.
- Startup Momentum: Ola Electric has established large-scale facilities for e-scooter and battery assembly.
- Gigafactory Growth: Large battery plants signal a move toward technological self-reliance.
- Supply Chain Localization: Boosts job creation and keeps manufacturing costs competitive.
- Academic Collaboration: Universities and research bodies are developing lithium-ion alternatives like sodium-ion and solid-state batteries.
- Innovation Focus: Homegrown technologies aim to enhance safety and reduce battery costs.
Infrastructure Development
Charging infrastructure remains both a challenge and an opportunity. For EV adoption to succeed Artificial Intelligence Training, a reliable network of charging stations is essential. ev startups in india is seeing rapid growth in this area, with state electricity boards, oil companies like IOCL and BPCL, and private firms such as Tata Power, Statiq, and ChargeZone leading the way.
- Level 1 (120V): Basic home outlets suitable for overnight charging.
- Level 2 (240V): Common in residential areas and at public stations.
- DC Fast Charging: Enables rapid recharging, ideal for highways and fleet operations.
- Battery Swapping: Gaining traction for commercial and last-mile delivery vehicles.
- Key Players: SUN Mobility and Battery Smart offer quick battery replacement networks to reduce downtime.
- Ather Energy: Adds smart connectivity features to scooters, enabling real-time diagnostics and navigation.
- BluSmart: Operates India’s first all-electric ride-hailing fleet, reducing urban transport emissions.
- Yulu: Specializes in micro-mobility with shared electric bicycles and scooters for last-mile travel.
- Market Impact: Startups enhance consumer experience, attract foreign investment, and promote local entrepreneurship.
- Business innovation: Models like subscription access, energy-as-a-service, and shared ownership are reshaping vehicle markets.
- Two-Wheeler Dominance: Over 60% of EV sales are electric scooters and bikes, driven by affordability and incentives.
- Urban Shift: government subsidies for government subsidies for electric cars are gaining popularity among professionals due to improved range and charging access.
- Fleet Adoption: Logistics and ride-hailing operators are switching to EVs to reduce costs and meet sustainability targets.
- Flexible Models: Leasing, battery-as-a-service (BaaS), and pay-per-use options reduce upfront costs.
- Fintech Innovation: Startups use data analytics to assess residual values and streamline loan approvals.
- Banking Shift: Traditional lenders now offer tailored EV loans with favorable interest rates.
- Market Accessibility: Financial solutions are expanding EV access beyond premium buyers to mass-market consumers.
- Battery Recycling: Focused on minimizing waste and recovering valuable metals for reuse.
- Smart Charging: Systems that integrate with the power grid to optimize load management and efficiency.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Technology that allows EVs to return energy to the grid during peak demand periods.
- IoT and Telematics: Enable real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance through connected systems.
- Lightweight Materials: Enhance energy efficiency without compromising structural safety.
- Localized Innovation: Indian research institutions and automakers are co-developing solutions tailored to tropical climates and diverse terrains.
- Cleaner Air: EVs eliminate tailpipe emissions, reducing NOx and particulate matter in urban environments.
- Renewable Integration: As India’s grid adopts solar and wind, EVs become even more carbon-efficient.
- Public Transport Impact: Cities like Pune and Delhi report better air quality and quieter streets with electric buses.
- Energy Security: Reduced oil imports strengthen national economic resilience and conserve foreign exchange.
- High Upfront Costs: EV prices are still higher than traditional vehicles, despite ongoing reductions.
- charging Accessibility: Infrastructure gaps persist in rural and Tier-II cities, limiting adoption.
- Battery Supply Chain: Heavy reliance on imported lithium and cobalt exposes the industry to global volatility.
- Skill Gaps: India requires trained professionals for EV servicing, battery management, and recycling operations.
- Consumer Hesitation: Range anxiety and limited model availability continue to influence buyer decisions.
- Collaborative Action: government subsidies for electric cars, industry, and academia must work together to build a sustainable EV ecosystem.
- Job Creation: The EV sector could generate over 10 million direct and indirect jobs by 2030.
- Circular Economy: Post-2030 focus includes battery recycling, energy storage reuse, and renewable grid integration.
- Smart Mobility: Autonomous EVs, AI-driven traffic systems, and smart grids will redefine urban transportation.
- State Leadership: Delhi, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu are setting ambitious electrification targets for public transport.
To Explore Artificial Intelligence in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Artificial Intelligence Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Role of Startups
Startups are essential to India’s EV ecosystem. Companies like Ather Energy, BluSmart, Yulu, and Revolt Motors are leading EV innovation in vehicle design, mobility platforms, and charging technology.
Consumer Adoption Trends
Consumer views of EVs in India are changing rapidly. Initially seen as expensive and limited in range, EVs are now appreciated for their low running costs, convenience, and environmental advantages.
EV Financing Options
Financing has been one of the initial obstacles in EV adoption, as traditional banks were wary of lending for relatively new technology. This is changing. Major banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) now provide specialized EV loans with competitive interest rates.
Innovations in the Indian EV Space
The Indian EV landscape is becoming a hub for EV innovation. Key areas of rapid growth include:
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Artificial Intelligence Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Environmental Impact in India
EVs have the potential to significantly improve India’s environmental health. With no tailpipe emissions, they greatly reduce urban air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, which contribute to respiratory illnesses.
Preparing for Artificial Intelligence Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite the progress, several obstacles remain:
Vision 2030 and Beyond
India’s Vision 2030 aims for 30% of its vehicle fleet to be electric. Some state policies, particularly those in Delhi, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu, aim for up to 80% electrification for public and commercial transport.
Conclusion
The future of electric vehicles in India is not a distant vision; it is already taking shape. What started as an environmental need has turned into a technological and economic transformation. With the support of policies, EV innovation, and consumer interest, India is on track to become one of the largest EV markets globally. The journey ahead will require determination, collaboration, and creativity, but it promises a cleaner, quieter, and more sustainable transportation landscape for Artificial Intelligence Training future generations. India’s government subsidies for electric cars revolution has just begun, and its success will redefine not only how we drive but how we power our future.




