What is Chef?
Chef is a configuration management technology developed by Opscode to manage infrastructure on physical or virtual machines. It is an open source developed using Ruby, which helps in managing complex infrastructure on the fly. This tutorial provides a basic understanding of the infrastructure and fundamental concepts of managing an infrastructure using Chef.
Why Chef?
Chef is a configuration management technology used to automate the infrastructure provisioning. It is developed on the basis of Ruby DSL language. It is used to streamline the task of configuration and managing the company’s server. It has the capability to get integrated with any of the cloud technology.In DevOps, we use Chef to deploy and manage servers and applications in-house and on the cloud.
Components of Chef
Before you embark on your journey any further towards Chef Tutorials, it is important that you first learn a few commonly used terms in Chef. Here is a Chef Tutorial step by step guide for beginners to know about the tool in-depth.

- The Chef Server: The Chef server is the essential method of correspondence between the workstations where your framework is coded, and the nodes where it is sent. All setup documents, cookbooks, metadata, and other data are put away on this server only. The Chef server additionally keeps data with respect to the condition of all hubs at the season of the last chef-client run.
- Workstations: Workstations are the place clients make, test, and keep up cookbooks and their desired cookbooks that will be pushed to chef nodes. Cookbooks made on workstations can be utilized privately by one association, or transferred to the Chef Supermarket for others to utilize. Also, workstations can be utilized to download cookbooks made by other Chef clients and can be found in the Supermarket.
- Bookshelf: The Bookshelf is a versioned storehouse where cookbooks are put away on the Chef server (for the most part situated at /var/pick/opscode/bookshelf extension ;). At the point when a cookbook is transferred to the Chef server, the new form is compared with the one which is already in the store, in case there are any changes, and another adaptation is stored.
- Cookbooks: Cookbooks are the principal segment of configuring nodes desirably on a Chef infrastructure. Cookbooks contain qualities and data about the coveted condition of a node, not how to get to that coveted state – Chef does all the work for that, through their broad libraries.
- Chef-repo: The chef-repo is a directory with the particular region of the workstation where cookbooks are authored and kept up. The chef-repo is dependably version-controlled, frequently using advantages of Git, and stores data and history that will be utilized on hubs, for example, cookbooks, data bags, etc.
- Chef-client: The role of the chef-client is to check the present design of the node against the formulas and arrangements already stored in the Chef server and convey the node right up to the match. The procedure starts with the chef-client checking the node’s run list, stacking the cookbooks required, then going on to checking and matching up the cookbooks with the present configuration of the node.
- Knife: The knife is a command that conveys between the chef-repo situated on a workstation and the Chef server. The knife command is configured with the knife.rb file extension, and is utilized from the workstation.
- Nodes: A node is a framework designed to run the chef-client. This can be any framework, as long as it is being kept up by Chef. Nodes are approved by the validator.pem and client.pem authentications that are made on the node itself right when it is bootstrapped. All nodes are required to be bootstrapped over SSH as either the root user or a client with raised benefits.
- Run Lists: Run lists characterize what cookbooks a node in Chef will utilize. The run list is an ordered list of all cookbooks and formulas that the chef-client requires to pull from the Chef server to keep running on a specific node. Run-lists are likewise used to characterize roles, which are utilized to characterize examples and traits crosswise over nodes.
- Environments: Chef environments exist to emulate a genuine work process, taking into consideration nodes that are to be composed into various “groups” that characterize the part the node plays in the fleet. This takes into consideration for a Chef user to join environments and versioned cookbooks to have diverse characteristics for various nodes at the same time.
- Recipes: Recipes are an essential part of the Chef cookbooks. Recipes are composed in Ruby and contain data with respect to everything that should be run, changed, or made on a node. Recipes fill in as an accumulation of assets that decide the arrangement or approach of a node, with resources being a design component of the recipe.
- Files: These are static documents that can be transferred to nodes. Files can be setup files or configuration files, contents, website files– anything that does not contain any different values on different nodes.
- Templates: Templates are installed Ruby files (.erb) that take into account content in view of the node itself and different variables that are produced when the chef-client is run and this template is utilized to make or update an existing file
Features of Chef:
Following are the most prominent features of Chef
- Chef uses popular Ruby language to create a domain-specific language.
- Chef does not make assumptions on the current status of a node. It uses its mechanisms to get the current status of the machine.
- Chef is ideal for deploying and managing the cloud server, storage, and software.
Advantages of Chef:
Chef offers the following advantages
- Lower barrier for entry − As Chef uses native Ruby language for configuration, a standard configuration language it can be easily picked up by anyone having some development experience.
- Excellent integration with cloud − Using the knife utility, it can be easily integrated with any of the cloud technologies. It is the best tool for an organization that wishes to distribute its infrastructure in a multi-cloud environment.
Disadvantages of Chef:
Some of the major drawbacks of Chef are as follows
- One of the huge disadvantages of Chef is the way cookbooks are controlled. It needs constant babying so that people who are working should not mess up with others cookbooks.
- Only Chef solo is available.
- In the current situation, it is only a good fit for AWS cloud.
- It is not very easy to learn if the person is not familiar with Ruby.
- Documentation is still lacking.
What are the Benefits from Chef?
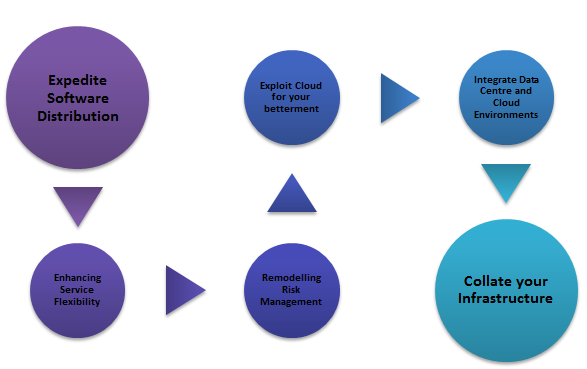
There are a few advantages associated with the usage of chefs. They are primarily associated with its innate nature to help you automate your infrastructure.
- Expedite Software Distribution: High-performing IT associations are the ones that can deploy their software product on request and inside one hour of another submit. Computerizing your IT infrastructure– assembling new conditions, testing and surveying changes to the code base, sending new programming adaptations etc. are the ones that are easily achievable via Chef.
- Enhancing Service Flexibility: Obviously, speed is not the only main essential factor. It’s insufficient to audit and deploy changes rapidly if these progressions additionally include bugs or make crashes a more probable event. By discovering those bugs and issues before they happen and close monitoring of issues, foundation robotization builds your framework’s strength in the same way as it increases your speed.
- Remodeling Risk Management: Chef’s infrastructure framework mechanization abilities can bring down the rate of risks and enhance compliance at all phases of improvement. Your compliance as well as security arrangements can be encoded as a major aspect of a Chef formula and can be tried consequently before sending.
- Exploit Cloud for your betterment: Via automating your cloud foundation and dealing with routine manual activities in a more streamlined way, Chef frees up some valuable time for your DevOps group to be more agile and proficient. Your applications and workloads can be moved rapidly and easily, while your servers and foundation are consequently introduced, designed, and provisioned by Chef formulas that you compose way ahead of time.
- Integrate Data Centre and Cloud Environments: Under the Chef umbrella, you can deal with all your cloud and on-premises conditions without a moment’s delay, including servers running the Windows, Linux, IBM AIX, and Solaris working frameworks. The chef is additionally a “cloud agnostic” arrangement, enabling you to continue utilizing it even as you change cloud suppliers.
- Collate your Infrastructure: The chef can easily slice through this many-sided organizational structures and data models to streamline your IT tasks and work process. From building and testing completely through conveyance, checking, and investigating, Chef gives a pipeline to nonstop deployment that you can use to accomplish progressively and settle on better choices.
Chef Certification
Certification is like a testimonial that no recruiter can ever ignore. With a shift to the cloud-based technologies and enhanced automation drives. Need for Chef professionals has increased so much so that organizations are paying up to $130,000 annually to the Chef professionals they are recruiting.
The Chef Certification program gives a chance to show and impart your computerization abilities wherever and at whatever point you pick. Chef utilizes a badge based appraisal approach just like DevOps that gives you a chance to modify your level of certification in a way that mirrors the aptitudes most applicable to your skill-set. Assessment badges reflect an authority of functional certifiable abilities you use to tackle issues with computerization. These individual identifications consolidate to meet pre-characterized levels of Chef Certification.
As we have already established that Chef certification comes in different badges and each badge display a different skill, here is a list of a few common badges that people opt for-
Chef Certification Exams
You will surely need expert help in this because Chef is still a nascent concept that many industry experts are not even aware of. You will need training and guidance. You can surely check out the website of ACTE Training, an online training platform that gives you training in a lot of contemporary courses.
Configuration Management
It is the collection of engineering practice that provides a systematic way to manage entities for efficient deployment. These entities include code, infrastructure, and people.
- Code: Code needs to be updated and stored.
- Infrastructure: Infrastructure needs to be configured.
- People: People need coordination.
You need to specify the configuration once on the central chef server and replicate that on thousands of nodes. Configuration management performs the following task-
- Find out which components to change when requirements change.
- Revert to a previous version of the component if you have replaced with a new version.
- Replace the wrong component.
- When requirement have changed redoing an implementation.
There are two types of configuration management.
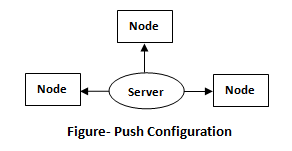
Push Configuration: Centralized server pushes configuration to the nodes.
Pull Configuration: Nodes checks with the server periodically and fetches the configuration from it. Chef follows pull configuration.
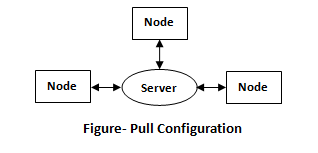
Key Building Blocks of Chef:
Recipe:
It can be defined as a collection of attributes which are used to manage the infrastructure. These attributes which are present in the recipe are used to change the existing state or setting a particular infrastructure node. They are loaded during Chef client run and compared with the existing attribute of the node (machine). It then gets to the status which is defined in the node resource of the recipe. It is the main workhorse of the cookbook.
Cookbook:
A cookbook is a collection of recipes. They are the basic building blocks which get uploaded to Chef server. When Chef run takes place, it ensures that the recipes present inside it get a given infrastructure to the desired state as listed in the recipe.
Resource:
It is the basic component of a recipe used to manage the infrastructure with different kinds of states. There can be multiple resources in a recipe, which will help in configuring and managing the infrastructure. For example
- package − Manages the packages on a node
- service − Manages the services on a node
- user − Manages the users on the node
- group − Manages groups
- template − Manages the files with embedded Ruby template
- cookbook_file − Transfers the files from the files subdirectory in the cookbook to a location on the node
- file − Manages the contents of a file on the node
- directory − Manages the directories on the node
- execute − Executes a command on the node
- cron − Edits an existing cron file on the node
Attribute:
They are basically settings. They can be thought of as a key value pair of anything which one wants to use in the cookbook. There are several different kinds of attributes that can be applied, with a different level of precedence over the final settings that the node operates under.
File:
It’s a subdirectory within the cookbook that contains any static file which will be placed on the nodes that uses the cookbooks. A recipe then can be declared as a resource that moves the files from that directory to the final node.
Templates:
They are similar to files, but they are not static. Template files end with the .ebr extension, which means they contain embedded Ruby. They are mainly used to substitute an attribute value into the files to create the final file version that will be placed on the node.
It is used to manage the metadata about the package. This includes details like the name and details of the package. It also includes things such as dependency information that tells which cookbooks this cookbook needs to operate. This allows the Chef server to build the run-list of the node correctly and ensures that all of the pieces are transferred correctly.
Chef − Related Technologies
Following is the list of Chef related technologies.
Puppet:
Puppet provides a standard way of delivering and operating software, no matter where it runs. It is an automated administrative engine for Linux, Unix, and Windows systems that performs administrative tasks based on centralized specification.
The primary features of Puppet are as follows
- Implementing new systems with a uniform configuration.
- Updating the systems and upgrading the security and software packages.
- Incorporating new features and adding dexterous capabilities.
- Customizing configurations for ensuring the availability of data sources.
- Optimizing the available resources and minimizing the cost.
- Simplifying the roles and enabling the team to focus on core and productive issues.
- Getting a bird’s eye view of the available infrastructure.
Ansible
Ansible is a radically simple IT automation platform that makes your applications and systems easier to deploy. Avoid writing scripts or custom code to deploy and update your applications — automate in a language that approaches plain English, using SSH, with no agents to install on remote systems.
The primary features of Ansible are as follows
- Simple and easy to learn
- Written in Python
- Agentless
- YAML-based Playbooks
- Ansible galaxy
SaltStack:
SaltStack is used for data-driven configuration. It is a new approach of infrastructure management built on a dynamic communication bus. It is used for data-driven orchestration, remote execution for any infrastructure, and configuration management for any app stack.
Fabric:
Fabric is a Python-based programming language, which is developed as an API of Python which needs to be imported in Python code in order to configure and manage an infrastructure.
Chef Architecture:
Chef works on a three-tier client server model wherein the working units such as cookbooks are developed on the Chef workstation. From the command line utilities such as knives, they are uploaded to the Chef server and all the nodes which are present in the architecture are registered with the Chef server.
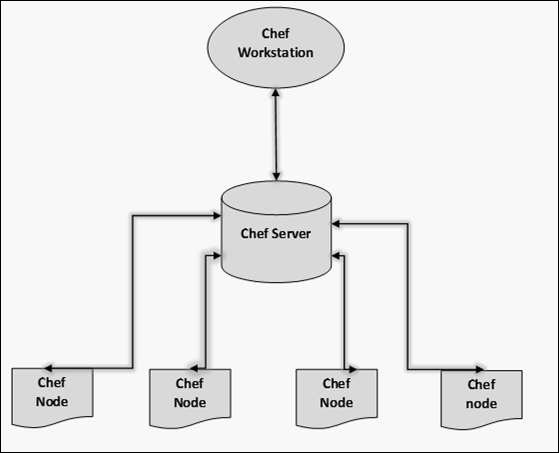
In order to get the working Chef infrastructure in place, we need to set up multiple things in sequence.
In the above setup, we have the following components.
Chef Workstation:
This is the location where all the configurations are developed. Chef workstation is installed on the local machine. Detailed configuration structure is discussed in the later chapters of this tutorial.
Chef Server:
This works as a centralized working unit of Chef setup, where all the configuration files are uploaded post development. There are different kinds of Chef server, some are hosted Chef servers whereas some are built-in premises.
Chef Nodes:
They are the actual machines which are going to be managed by the Chef server. All the nodes can have different kinds of setup as per requirement. Chef client is the key component of all the nodes, which helps in setting up the communication between the Chef server and Chef node. The other component of Chef node is Ohai, which helps in getting the current state of any node at a given point of time.
Conclusion:
Being a chef can be a good career. You won’t be rich, but you can be comfortable. You won’t always be home by 5 but a smart chef can still have a healthy life work balance.And don’t be a private chef, hotel chef, catering chef, cruise ship chef, golf course chef, food stylist, these are not real chef jobs.Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.






