
- Energy Source Comparison
- Vehicle Components
- Efficiency Analysis
- Environmental Impact
- Maintenance Differences
- Performance Metrics
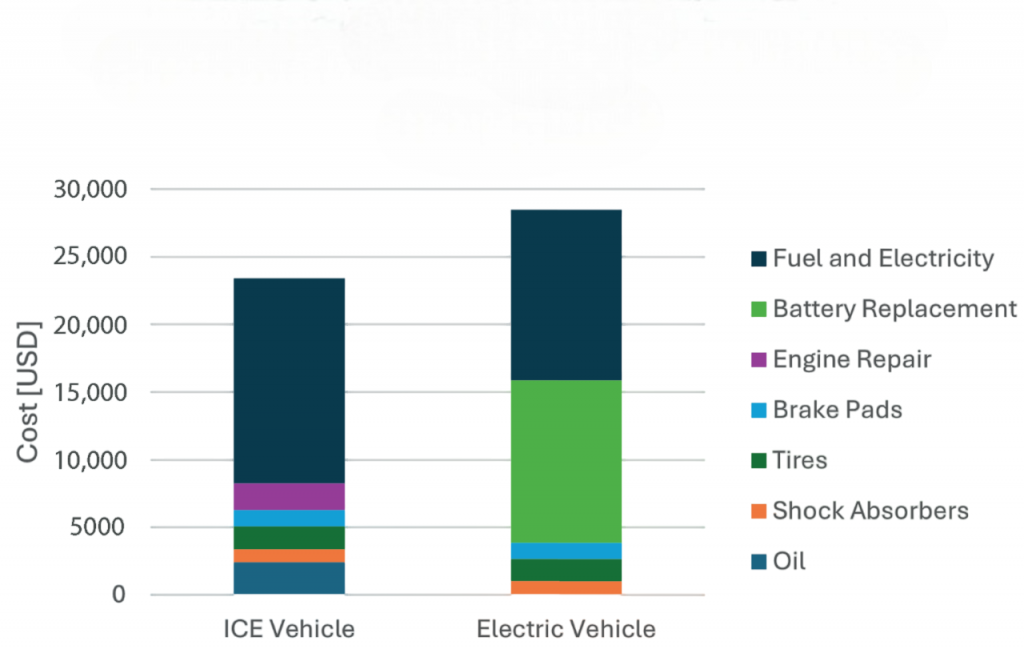
- Operating Costs
- Refueling vs Charging
- Range Considerations
- Government Support
- Resale and Lifespan
- Conclusion
Energy Source Comparison
As the global push towards sustainable transportation gains momentum, the debate between Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles intensifies. Each technology has its distinct advantages and challenges, influencing consumer choices, government policies, Artificial Intelligence Training and the future of mobility. This article provides an in-depth comparison of EVs and ICE vehicles across multiple critical dimensions to help readers understand their differences and what the future holds. The argument between internal combustion engine (ICE) and electric vehicles (EVs) is more important than ever as the world’s drive towards sustainable transportation picks up speed. Both technologies have particular benefits and drawbacks that influence government regulations, customer preferences, and the direction of future mobility. Anyone thinking about how their transportation choices will affect the environment, the economy, and technology must be aware of these distinctions.
Ready to Get Certified in Artificial Intelligence ? Explore the Program Now Artificial Intelligence Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Vehicle Components
ICE vehicles consist of complex mechanical components including the engine, transmission, fuel injection system, exhaust system, and numerous moving parts subject to wear and tear.
- These components require precise engineering and regular maintenance to ensure optimal operation.
- In contrast, EVs feature a simpler drivetrain with fewer moving parts. The primary components include the electric motor, battery pack, power electronics, and a simpler transmission system or direct-drive mechanism.
- The absence of components like the multi-speed transmission, fuel injectors, and exhaust systems reduces mechanical complexity.
This simplified architecture not only lowers manufacturing complexity but also contributes to reduced maintenance requirements and potentially longer vehicle lifespans for EVs. The reduced number of components decreases the likelihood of mechanical failure and the need for frequent repairs.
Efficiency Analysis
When analyzing efficiency, EVs clearly outperform ICE vehicles. Internal combustion engines convert only about 20-30% of the chemical energy in fuel into useful mechanical energy, with the rest lost as heat and friction. Additionally, energy losses occur during fuel refining, transportation, and idling.
Electric motors, by comparison, convert over 85-90% of electrical energy into mechanical power. Moreover, regenerative braking in EVs recaptures kinetic energy during deceleration, further enhancing overall efficiency. This makes EVs much more energy-efficient from source to wheel. Overall, EVs use energy more effectively, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. The superior efficiency of electric motors is a key reason why many experts view EVs as the future of sustainable transportation.
Environmental Impact
Environmental concerns are a major factor driving the shift towards electric mobility. ICE vehicles emit significant amounts of CO2, nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and other pollutants during fuel combustion.
- These emissions contribute to climate change, urban air pollution, and health issues. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, dramatically reducing localized air pollution.
- However, the overall environmental impact depends on the electricity generation mix. When charged with fossil fuel-generated electricity, EVs still have a carbon footprint, although generally lower than ICE vehicles.
- Battery production for EVs involves resource-intensive mining of lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which raises concerns about environmental degradation and ethical sourcing.
Nevertheless, advances in battery recycling, sustainable mining practices, and second-life battery applications are helping to mitigate these challenges. In sum, EVs offer a pathway to significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and urban pollution, particularly as the electricity grid becomes greener.
Maintenance Differences
ICE vehicles require regular maintenance including oil changes, fuel filter replacements, spark plug servicing, and exhaust system repairs. The complexity of the internal combustion engine means that wear and tear on components can lead to frequent repairs and downtime. EVs have simpler drivetrains with no oil, fewer fluids, and no exhaust systems, leading to reduced maintenance needs. Typical maintenance tasks for EVs involve battery health monitoring, tire rotations, brake system checks (which last longer due to regenerative braking), and cooling system maintenance. While EVs generally cost less to maintain over their lifetime, battery degradation and eventual replacement remain significant considerations. Manufacturers typically offer warranties on batteries to cover performance for 8-10 years or more.
Performance Metrics
Performance is an area where EVs excel due to the characteristics of electric motors. EVs provide instant torque from zero RPM, resulting in rapid acceleration and smooth, quiet operation. This leads to a responsive driving experience often superior to ICE vehicles.
- ICE vehicles, however, have historically had the advantage in top speed and driving range.
- Modern advancements have improved EV range substantially, and high-performance EV models can match or exceed the acceleration and top speed of many gasoline-powered cars.
EVs also benefit from a lower center of gravity due to battery placement, improving handling and stability. However, the heavier battery packs can affect agility compared to lighter ICE vehicles.
Operating Costs
Operating costs for EVs are generally lower than for ICE vehicles. Electricity is often cheaper than gasoline or diesel on a per-mile basis, and EVs require less maintenance. The reduced need for oil changes, fewer brake replacements, and simpler drivetrains contribute to cost savings, especially as Artificial Intelligence Training enhances predictive maintenance and vehicle efficiency. ICE vehicles, by contrast, face higher fuel costs, more frequent maintenance, and more potential repairs over their lifecycle. Additionally, fluctuating fuel prices can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. While upfront costs for EVs tend to be higher, the lower operating costs and incentives such as tax rebates can balance this over time, making EVs economically attractive for many buyers.
Refueling vs Charging
Refueling an ICE vehicle is a quick process, typically taking 5 to 10 minutes at a gas station, with extensive fueling infrastructure widely available. This convenience is a major factor influencing consumer preference.
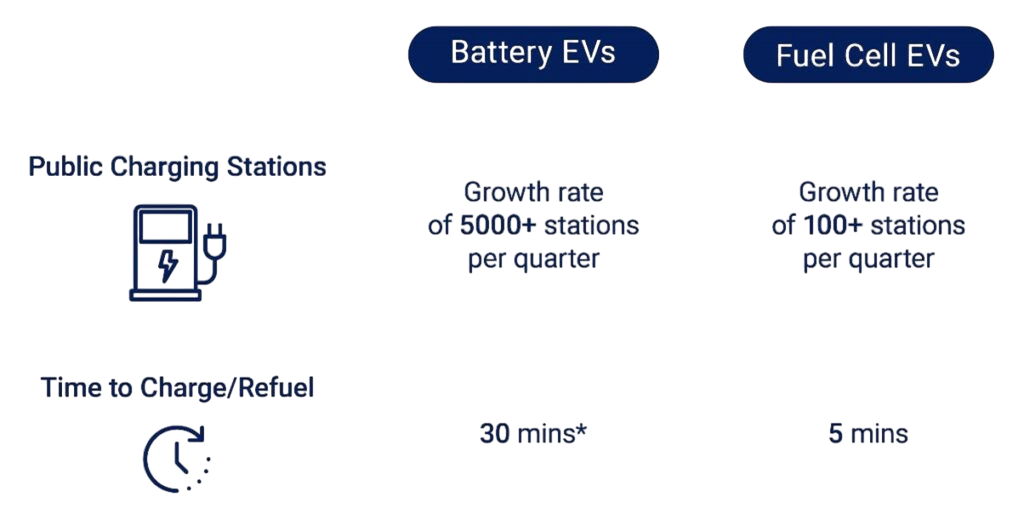
Charging EVs, however, requires more time. Charging speed depends on the type of charger: Level 1 (120V) chargers take the longest (up to 24 hours for a full charge), Level 2 (240V) chargers require 4-8 hours, and DC fast chargers can provide an 80% charge in 20-40 minutes. While home charging is convenient for many EV owners, public charging infrastructure is still expanding. As charging technology improves and networks grow denser, refueling times and convenience for EVs will continue to improve.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Artificial Intelligence Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Range Considerations
Range anxiety remains a concern for some potential EV buyers. ICE vehicles typically offer ranges of 300-400 miles per tank, with refueling stations readily available nationwide.
- EV ranges vary widely depending on the battery capacity, model, and driving conditions. Current mainstream EVs offer ranges between 150 and 370 miles, with premium models exceeding 400 miles on a full charge.
- Continuous improvements in battery technology are steadily increasing range capabilities.
Range considerations influence vehicle choice based on driving habits. For urban commuting, where daily distances are relatively short, EVs are ideal. For long-distance travel, some consumers still prefer ICE vehicles or hybrid solutions until charging infrastructure matures.
Government Support
Governments worldwide are incentivizing EV adoption to meet climate goals. Incentives include tax credits, rebates, reduced registration fees, and access to carpool lanes. Some cities offer free or discounted parking for EVs. In contrast, ICE vehicles are increasingly subject to stricter emissions regulations, fuel economy standards, and in some regions, bans or restrictions on sales of new fossil fuel vehicles in the coming decades. These government policies play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics and accelerating the transition towards electric mobility.
Preparing for Artificial Intelligence Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Resale and Lifespan
Resale value is an important consideration for vehicle buyers. Historically, ICE vehicles have had predictable depreciation patterns influenced by brand, mileage, and condition.
- EVs have faced uncertainty in resale value due to battery degradation concerns and evolving technology.
- However, as battery reliability improves and demand for used EVs increases, resale values are stabilizing.
Lifespan-wise, EVs may have an advantage due to fewer moving parts and less mechanical wear. Batteries typically retain good capacity for 8-10 years, after which replacement or repurposing can extend vehicle life.
Conclusion
The comparison between Electric Vehicles and Internal Combustion Engine vehicles reveals clear advantages for EVs in terms of efficiency, environmental impact, maintenance, and operating costs. However, challenges remain around charging infrastructure, range, and upfront costs, where Artificial Intelligence Training can play a vital role in optimizing battery performance and charging efficiency. With supportive government policies and rapid technological progress, EVs are positioned to dominate the future of personal and commercial transportation, marking a transformative shift towards cleaner, smarter mobility. In conclusion, the emergence of EVs signifies a paradigm shift in transportation philosophy rather than merely a change in technology. EVs are changing how we drive today and opening the door for a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable transportation future by fusing technological innovation, economic efficiency, and environmental responsibility.



