
- Git is an open-source distributed version control system. It is designed to handle minor to major projects with high speed and efficiency. It is developed to co-ordinate the work among the developers. The version control allows us to track and work together with our team members at the same workspace.
- Git is foundation of many services like GitHub and GitLab, but we can use Git without using any other Git services. Git can be used privately and publicly.
Install Git
- To install Git on Windows you will need to download the installer from the Git website:
- Download the most current version for your operating system by double clicking on the package name
- Select Run to begin the installation:
- Click Yes to continue:
- Click Next to continue:
- If you need to change the installation folder, click Browse and select a new location. To accept the default location click on Next:
- To accept the default components to be installed click Next. Otherwise, select the additional components to be installed before clicking the Next button:
- Accept the default Start Menu folder by clicking Next, or use Browse to select a new folder location:
- Select the default text editor for Git, then click Next:
- Adjust your PATH environment, then click Next:
- Choose which SSL/TLS library you’ll use for HTTPS. Then, click Next:
- Keep the default line ending conversion by clicking Next. To change the default, choose one of the two other choices before clicking Next:
- Choose the terminal emulator you’ll use, and then click Next:
- Configure the extra options, and then click Next:
- Check Launch Git Bash and complete the setup by selecting Finish:
- You can launch the Git GUI from the bash shell. Type git gui at the command line and hit enter:
- Once you open Git you can select either Create New, Clone Existing or Open Existing Repository. In this example, we create new repository. Enter a directory name or click on Browse to navigate to a directory:
- A blank repository is created:
Features
Some remarkable features of Git are as follows:
- Open SourceGit is an open-source tool. It is released under the GPL (General Public License) license.
- ScalableGit is scalable, which means when the number of users increases, the Git can easily handle such situations.
- DistributedOne of Git’s great features is that it is distributed. Distributed means that instead of switching the project to another machine, we can create a “clone” of the entire repository. Also, instead of just having one central repository that you send changes to, every user has their own repository that contains the entire commit history of the project. We do not need to connect to the remote repository; the change is just stored on our local repository. If necessary, we can push these changes to a remote repository.
- SecurityGit is secure. It uses the SHA1 (Secure Hash Function) to name and identify objects within its repository. Files and commits are checked and retrieved by its checksum at the time of checkout. It stores its history in such a way that the ID of particular commits depends upon the complete development history leading up to that commit. Once it is published, one cannot make changes to its old version.
- SpeedGit is very fast, so it can complete all the tasks in a while. Most of the git operations are done on the local repository, so it provides a huge speed. Also, a centralized version control system continually communicates with a server somewhere.Performance tests conducted by Mozilla showed that it was extremely fast compared to other VCSs. Fetching version history from a locally stored repository is much faster than fetching it from the remote server. The core part of Git is written in C, which ignores runtime overheads associated with other high-level languages.Git was developed to work on the Linux kernel; therefore, it is capable enough to handle large repositories effectively. From the beginning, speed and performance have been Git’s primary goals.
- Supports non-linear developmentGit supports seamless branching and merging, which helps in visualizing and navigating a non-linear development. A branch in Git represents a single commit. We can construct the full branch structure with the help of its parental commit.
- Branching and MergingBranching and merging are the great features of Git, which makes it different from the other SCM tools. Git allows the creation of multiple branches without affecting each other. We can perform tasks like creation, deletion, and merging on branches, and these tasks take a few seconds only. Below are some features that can be achieved by branching:
- We can create a separate branch for a new module of the project, commit and delete it whenever we want.
- We can have a production branch, which always has what goes into production and can be merged for testing in the test branch.
- We can create a demo branch for the experiment and check if it is working. We can also remove it if needed.
- The core benefit of branching is if we want to push something to a remote repository, we do not have to push all of our branches. We can select a few of our branches, or all of them together.
- Data AssuranceThe Git data model ensures the cryptographic integrity of every unit of our project. It provides a unique commit ID to every commit through a SHA algorithm. We can retrieve and update the commit by commit ID. Most of the centralized version control systems do not provide such integrity by default.
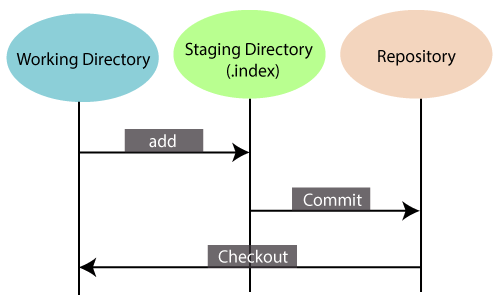
- Staging AreaThe Staging area is also a unique functionality of Git. It can be considered as a preview of our next commit, moreover, an intermediate area where commits can be formatted and reviewed before completion. When you make a commit, Git takes changes that are in the staging area and make them as a new commit. We are allowed to add and remove changes from the staging area. The staging area can be considered as a place where Git stores the changes.Although, Git doesn’t have a dedicated staging directory where it can store some objects representing file changes (blobs). Instead of this, it uses a file called index.
- Another feature of Git that makes it apart from other SCM tools is that it is possible to quickly stage some of our files and commit them without committing other modified files in our working directory. Maintain teh clean historyGit facilitates with Git Rebase; It is one of the most helpful features of Git. It fetches the latest commits from the master branch and puts our code on top of dat. Thus, it maintains a clean history of the project.
Benefits
- A version control application allows us to keep track of all the changes that we make in the files of our project. Every time we make changes in files of an existing project, we can push those changes to a repository. Other developers are allowed to pull your changes from the repository and continue to work with the updates that you added to the project files.
- Some significant benefits of using Git are as follows:
- Saves TimeGit is lightning fast technology. Each command takes only a few seconds to execute so we can save a lot of time as compared to login to a GitHub account and find out its features.
- Offline WorkingOne of the most important benefits of Git is that it supports offline working. If we are facing internet connectivity issues, it will not affect our work. In Git, we can do almost everything locally. Comparatively, other CVS like SVN is limited and prefer the connection with the central repository.
- Undo MistakesOne additional benefit of Git is we can Undo mistakes. Sometimes the undo can be a savior option for us. Git provides the undo option for almost everything.
- Track the ChangesGit facilitates with some exciting features such as Diff, Log, and Status, which allows us to track changes so we can check the status, compare our files or branches.
Devops Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers!
Download
Advantages
- Good distributed model as each developer gets a local repository with a full history of commits which makes git fast compared to other VCs.
- Branching capabilities and merging are easy (as they are cheap), good data integrity.
- They are free and open-source we can easily download the source code and performs changes to it. They can handle larger projects efficiently.
- The push/pull operations are faster with a simple They save time and developers can fetch and create pull requests without switching.
- Data redundancy and replications. Add ons can be written in many languages.
- They have good and faster network performance and superior disk utilization and they think about its data like a sequence of snapshots.
- The object model is very simple and minimizes push/pull data transfers.





