
If you’re looking for IBM Rational Build Forge Interview Questions for Experienced or Freshers, you are in right place. There are a lot of opportunities from many reputed companies in the world. According to research IBM, Rational Build Forge has a market share of about 0.1%. So, You still have the opportunity to move ahead in your career in IBM Rational Build Forge Development. ACTE offers Advanced IBM Rational Build Forge Interview Questions that help you in cracking your interview & acquire a dream career as IBM Rational Build Forge Developer.
1. What is IBM Rational Build Forge?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge is a comprehensive build and release management tool designed to automate and streamline the software development lifecycle. It provides a centralized platform for managing the build process, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and reliability in delivering software applications.
2. What are the key features of IBM Rational Build Forge?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge encompasses many features, including automated builds, continuous integration, release management, and multi-platform support. It facilitates collaboration among development and operations teams by providing a centralized dashboard for monitoring and managing the entire build and release pipeline.
3. How does IBM Rational Build Forge facilitate automation in software development?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge excels in automation by orchestrating code compilation, testing, and packaging tasks. This automation reduces manual errors, accelerates development cycles, and ensures that the software delivery process is consistent and repeatable.
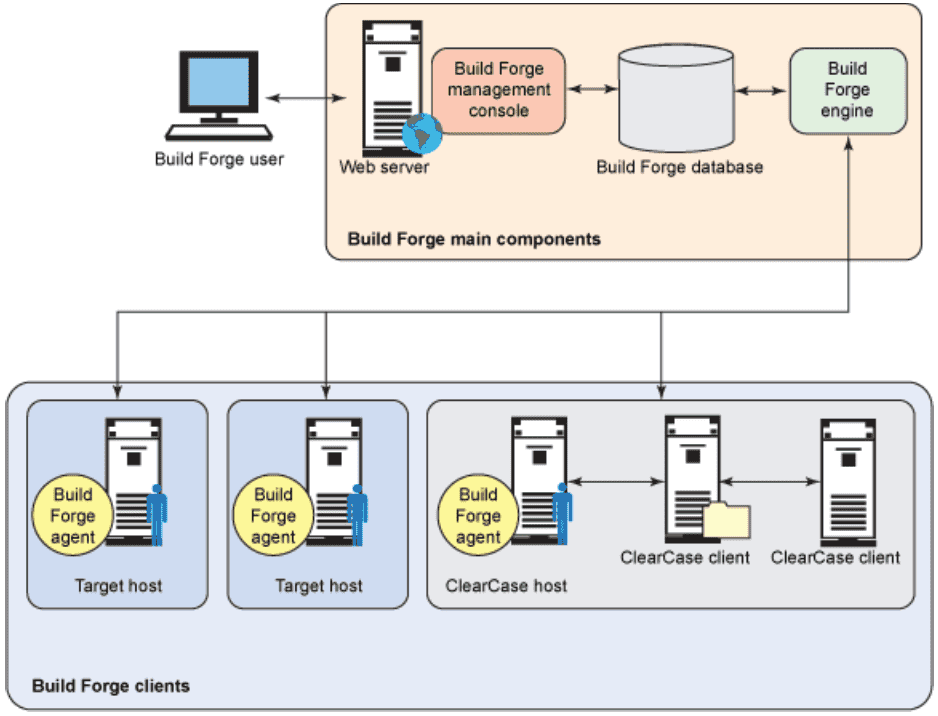
4. What are the benefits of using IBM Rational Build Forge for build and release management?
Ans:
The benefits of IBM Rational Build Forge include increased efficiency, faster time-to-market, reduced errors, and improved collaboration. Its centralized build and release management approach enhances traceability and enables teams to deliver high-quality software consistently.
5. Can IBM Rational Build Forge integrate with other development tools?
Ans:
Yes, IBM Rational Build Forge is designed to integrate seamlessly with various version control systems, issue-tracking tools, and other components of the software development lifecycle. This integration ensures that it can fit into existing development environments and workflows.
6. Explain the “Build Forge Agents” concept in IBM Rational Build Forge.
Ans:
Build Forge Agents are essential components that enable the distributed execution of build and deployment processes. These agents operate on remote machines, allowing for parallel execution of tasks across different environments, contributing to improved scalability and efficiency in the development process.
7. How do it dependencies between different build and deployment tasks?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge manages dependencies through a defined workflow mechanism. This ensures that tasks are executed in the correct order, with all prerequisites satisfied. This approach enhances the reliability and predictability of the entire build and deployment process.
8. What role does the Build Forge Repository play in the build process?
Ans:
The Build Forge Repository is a centralized storage for artefacts, scripts, and configuration files essential for the build process. Centralizing Centralizing resources promotes consistency, reduces redundancy, and ensures that builds are conducted with the correct and up-to-date components.
9. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support versioning of build scripts?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge provides version control for build scripts, allowing developers to track changes, roll back to previous configurations, and maintain a history of build configurations. This versioning capability ensures reproducibility and auditability in the build process.
10. What security features are offered for protecting sensitive information in the build process?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge incorporates robust security features, including authentication, authorization, and encryption. These features safeguard access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized individuals can modify build configurations, repositories, and other critical information.
11. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle exceptions during the build process?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge logs detailed information about build processes, making it easier for developers to identify and troubleshoot errors. Additionally, it supports notifications for failed builds, enabling rapid response and resolution of issues to maintain the integrity of the development pipeline.
12. Can IBM Rational Build Forge be used for continuous integration (CI)?
Ans:
Yes, IBM Rational Build Forge supports continuous integration by automating the integration of code changes and triggering builds based on events such as code commits. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement, early detection of integration issues, and faster feedback loops for development teams.
13. How does IBM Rational Build Forge help manage and optimize build resources?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge dynamically allocates and manages build resources, optimizing their usage based on demand. This ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, leading to faster building times and improved overall productivity in the software development process.
14. What languages are supported for defining build and deployment processes?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge offers flexibility in defining build configurations by supporting various scripting languages, including Ant, Maven, and Shell scripts. This flexibility allows development teams to use the scripting language best suits their project requirements.
15.Explain the role of the Build Forge Dashboard in monitoring the build and release process.
Ans:
The Build Forge Dashboard is a centralized hub for monitoring the entire build and release pipeline. It provides real-time visibility into build status, logs, and metrics, empowering teams to identify bottlenecks, track progress, and make informed decisions for continuous improvement.
16.How does IBM Rational Build Forge support the deployment of applications?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge facilitates the creation of deployment configurations tailored for various environments, including development, testing, and production. This ensures consistency in the deployment process, reducing the risk of configuration errors and enhancing the reliability of application deployments.
17. Can IBM Rational Build Forge be integrated with continuous delivery (CD) pipelines?
Ans:
Yes, IBM Rational Build Forge is designed to integrate seamlessly into continuous delivery pipelines. Automating the entire software delivery lifecycle, including testing and deployment, supports continuous delivery principles, allowing teams to deliver high-quality software faster.
18. Explain the “Build Forge Modules” concept and their role in the build process.
Ans:
Build Forge Modules are reusable IBM Rational Build Forge components that encapsulate specific build tasks. Promoting modularity enables development teams to create efficient and standardized build configurations, fostering reusability and maintainability in the build process.
19. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle versioning of artefacts and binaries?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge supports the versioning of artefacts, ensuring that developers can track changes and use the correct versions of dependencies in the build process. This versioning capability is crucial for maintaining consistency and reliability in software builds.
20.What role does Scheduler play in managing and scheduling build jobs?
Ans:
The Build Forge Scheduler automates the scheduling of build and deployment jobs, allowing teams to define specific times or trigger tasks in response to events. This automation enhances efficiency, ensures timely execution, and contributes to the overall reliability of the software development process.
21. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support build acceleration and optimization?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge employs various techniques, such as parallelization and incremental builds, to accelerate the build process. Optimizing resource usage and minimizing redundant tasks significantly reduces the time required for software delivery, promoting faster time-to-market.
22. How is IBM Rational Build Forge used to deploy cloud applications?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge can seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms, allowing development teams to build and deploy applications in cloud environments. This flexibility in deployment options is valuable for organizations embracing cloud technologies in their software development lifecycle.
23.What role does the Build Forge CLI (Command Line Interface) play in the build process?
Ans:
The Build Forge CLI provides a command-line interface for users to interact with IBM Rational Build Forge programmatically. This interface is instrumental in automating tasks, integrating with other tools, and incorporating Build Forge into custom workflows, enhancing the overall automation capabilities of the platform.
24. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support the rollback of deployments in case of errors or issues?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge provides mechanisms for rolling back deployments to previous versions, offering an essential feature for managing errors or issues. This capability enables development teams to quickly recover from problems and maintain system stability in production environments.
25. Explain the “Build Forge Templates” concept and their significance.
Ans:
Build Forge Templates are predefined configurations within IBM Rational Build Forge that serve as starting points for creating consistent and standardized build and deployment processes. They streamline the process of defining configurations, ensuring that teams adhere to best practices and maintain a level of standardization.
26. How does IBM Rational Build Forge generate reports related to the build and release process?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge offers reporting features that provide valuable insights into the build and release process. These reports include information on build status, execution times, and other metrics, enabling development teams to analyze performance and make data-driven improvements.
27. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support audit requirements in the software development process?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge addresses compliance and audit requirements by logging and tracking build activities. The platform incorporates access controls and permissions, ensuring only authorized individuals have the necessary privileges. This helps organizations meet regulatory standards and maintain a secure and auditable development process.
28. What is the role of the Build Forge REST API in integrating with other tools and systems?
Ans:
The Build Forge REST API is a powerful tool for integrating IBM Rational Build Forge with external systems and tools. It allows for programmatic communication, enabling seamless integration into existing workflows, custom scripts, and third-party tools, expanding the capabilities of the build and release management process.
29. How does IBM Build Forge handle deployment environment variations?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge accommodates environmental configurations by allowing the creation of environment-specific configurations. This flexibility ensures that builds and deployments adapt to the unique requirements of each environment, promoting consistency and reliability across development, testing, and production stages.
30. When is IBM Build Forge most beneficial in a development lifecycle?
Ans:
Development teams involved in complex and multi-faceted software projects, especially those operating in distributed environments, would benefit significantly from implementing IBM Rational Build Forge. Its automation, integration capabilities, and support for various scripting languages make it an ideal solution for organizations aiming to optimize their build and release management processes. The platform’s features cater to teams seeking efficiency, reliability, and consistency in their software development lifecycle.
31. What is the primary purpose of IBM Rational Build Forge?
Ans:
- Automate build and release processes
- Streamline software development lifecycle
- Enhance collaboration among teams
- Ensure consistency in builds
- Support multi-platform environments
- Provide centralized monitoring and management
32. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle parallel execution of tasks?
Ans:
- Utilizes Build Forge Agents
- Distributes tasks across remote machines
- Enables efficient parallelization
- Enhances scalability
- Accelerates overall build process
- Reduces build times
33. What languages does IBM Rational Build Forge support for scripting build processes?
Ans:
- Ant
- Maven
- Shell scripts
- Python
- Perl
- JavaScript
34. Explain the role of the Build Forge Repository in the build process.
Ans:
- Centralized storage for artefacts
- Houses scripts and configuration files
- Promotes consistency in builds
- Reduces redundancy
- Ensures correct and up-to-date components
- Enhances traceability
35. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support continuous integration (CI)?
Ans:
- Automates integration of code changes
- Triggers build on code commits
- Detects integration issues early
- Fosters a culture of continuous improvement
- Enables faster feedback loops
- Enhances collaboration among developers
36. What is the significance of Build Forge Modules in the build process?
Ans:
- Encapsulates specific build tasks
- Promotes modularity
- Enhances reusability
- Facilitates standardized configurations
- Streamlines build process definition
- Supports efficient maintenance
37. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support deployment to different environments?
Ans:
- Creates environment-specific configurations
- Ensures consistency in deployments
- Reduces risk of configuration errors
- Supports development, testing, and production environments
- Enhances reliability of deployments
- Streamlines deployment process
38. Can IBM Rational Build Forge integrate with cloud environments?
Ans:
- Yes, it seamlessly integrates with cloud platforms
- Allows building and deploying in the cloud
- Provides flexibility in deployment options
- Supports cloud-based development
- Enables scalability in the cloud
- Optimizes cloud resources
39. What role does the Build Forge Dashboard play in the software development lifecycle?
Ans:
- Provides centralized monitoring
- Offers real-time visibility into build status
- Displays logs and metrics
- Identifies bottlenecks in the pipeline
- Facilitates informed decision-making
- Enhances overall pipeline management
40. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle versioning of artefacts and binaries?
Ans:
- Supports version control for artefacts
- Tracks change in dependencies
- Maintains a history of build configurations
- Ensures reproducibility in builds
- Facilitates auditing and compliance
- Enhances traceability of artefacts
41. What is the significance of Build Forge Templates in the build process?
Ans:
- Predefined configurations for consistency
- Serve as starting points for builds
- Ensure adherence to best practices
- Streamline configuration definition
- Promote standardization in processes
- Facilitate efficient configuration creation
42. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support build acceleration and optimization?
Ans:
- Utilizes parallelization techniques
- Implements incremental builds
- Reduces redundant tasks
- Accelerates overall build process
- Optimizes resource usage
- Minimizes time required for software delivery
43. What security features does IBM Rational Build Forge offer?
Ans:
- Authentication mechanisms
- Authorization controls
- Encryption for sensitive data
- Role-based access
- Protects build configurations and repositories
- Ensures secure and controlled access
44. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle errors and exceptions during builds??
Ans:
- Logs detailed information on build processes
- Facilitates quick identification of errors
- Supports notifications for failed builds
- Enhances troubleshooting capabilities
- Enables rapid response to issues
- Maintains the integrity of the development pipeline
45. Can IBM Rational Build Forge be integrated into continuous delivery pipelines?
Ans:
- Yes, it seamlessly integrates into CD pipelines
- Automates entire software delivery lifecycle
- Supports testing and deployment automation
- Ensures continuous delivery principles
- Facilitates rapid and reliable software releases
- Enhances efficiency in delivery processes
46. How does IBM Rational Build Forge support compliance and audit requirements?
Ans:
- Logs and tracks build activities
- Provides an audit trail for compliance
- Implements access controls and permissions
- Ensures secure and auditable development
- Meets regulatory standards
- Enhances transparency and accountability
47. What is the role of the Build Forge CLI in the build process?
Ans:
- Provides a command-line interface
- Allows users to interact programmatically
- Supports automation of tasks
- Facilitates integration with other tools
- Enables customization and scripting
- Expands automation capabilities
48. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle environmental configurations?
Ans:
- Allows creation of environment-specific configurations
- Ensures adaptability to different environments
- Promotes consistency across environments
- Facilitates customization for specific needs
- Supports development, testing, and production
- Enhances flexibility in deployment
49. Can IBM Rational Build Forge generate reports and metrics?
Ans:
- Yes, it provides reporting features
- Offers insights into build status
- Presents execution times and metrics
- Enables performance analysis
- Supports data-driven improvements
- Enhances visibility and decision-making
50. What is the role of the Build Forge REST API in integration?
Ans:
- Allows programmatic communication
- Facilitates integration with external systems
- Supports custom workflows
- Enables seamless interaction with other tools
- Expands automation possibilities
- Enhances extensibility and integration capabilities
51. How does IBM Rational Build Forge optimize the dynamic building of resources?
Ans:
- Allocates and manages resources dynamically
- Optimizes resource usage based on demand
- Ensures efficient utilization of build resources
- Reduces idle time for resources
- Enhances scalability in resource allocation
- Contributes to building times faster
52. What are the key benefits of IBM Rational Build Forge in a development environment?
Ans:
- Increases efficiency in building processes
- Accelerates time-to-market
- Reduces errors in software releases
- Enhances collaboration among teams
- Provides centralized monitoring and management
- Supports consistent and repeatable builds
53. How does IBM Rational Build Forge handle variations in deployment configurations?
Ans:
- Allows creation of environment-specific configurations
- Accommodates variations across environments
- Facilitates customization for specific deployment needs
- Ensures consistency in deployment processes
- Promotes reliability in different deployment scenarios
54. What role does Build Forge Scheduler play in the management of build jobs?
Ans:
- Automates scheduling of build and deployment jobs
- Allows definition of specific execution times
- Triggers tasks in response to events
- Enhances efficiency in task execution
- Ensures timely completion of build jobs
55.How does IBM Rational Build Forge support rollback of deployments?
Ans:
- Provides mechanisms for rolling back deployments
- Enables quick recovery from errors or issues
- Supports reverting to previous versions
- Ensures stability in production environments
- Facilitates efficient management of deployment errors
56.What role does Build Forge Repository play in promoting build consistency?
Ans:
- Centralized storage for building artefacts
- Houses scripts and configuration files
- Eliminates redundancy in building resources
- Ensures all builds use correct and up-to-date components
- Enhances traceability and audibility
57. How does IBM Rational Build Forge contribute to a culture of continuous improvement?
Ans:
- Supports continuous integration practices
- Automates integration of code changes
- Triggers build on code commits
- Identifies integration issues early in the process
- Enables faster feedback loops for development teams
58. Can IBM Rational Build Forge be tailored for specific project needs?
Ans:
- Yes, it supports environment-specific configurations
- Facilitates customization for different project requirements
- Allows the creation of specific deployment scenarios
- Promotes adaptability to project-specific needs
- Enhances flexibility in configuring build processes
59. How does IBM Rational Build Forge address the challenges of distributed development environments?
Ans:
- Utilizes Build Forge Agents for distributed execution
- Ensures consistency across development locations
- Facilitates collaboration among geographically dispersed teams
- Supports parallel execution for efficient development
- Centralizes monitoring for streamlined management
60. In what scenarios is most beneficial for software development teams?
Ans:
- Complex and multi-faceted software projects
- Distributed development environments
- Environments with a need for efficient build automation
- Organizations embracing continuous integration practices
- Projects with diverse deployment requirements
- Teams aiming for consistency, reliability, and efficiency in the software development lifecycle
61. What is the collaboration between development and operations teams?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge facilitates collaboration by providing a centralized build and release management platform. Development and operations teams can share a common view through the Build Forge Dashboard, allowing them to monitor progress, identify issues, and coordinate efforts efficiently. The tool streamlines communication, ensuring that both teams work seamlessly toward common goals, leading to faster and more reliable software delivery.
62. How can IBM Rational Build Forge be integrated with version control systems?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge supports integration with various version control systems like Git, SVN, and CVS. This integration ensures that the build process is synchronized with the latest.
Code changes promote consistency between source code and build configurations. Developers can trigger builds automatically upon code commits, fostering continuous integration practices.
63. How does the management of large-scale and complex software projects?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge is well-suited for large-scale and complex projects as it offers features like parallel execution, modular build configurations, and support for multiple scripting languages. These capabilities enable the tool to efficiently manage the intricacies of large projects, reduce build times, and maintain a high level of organization and consistency in the development pipeline.
64.What advantages does IBM Rational Build Forge offer regarding build reproducibility?
Ans:
Build reproducibility is a key strength of IBM Rational Build Forge. The tool supports versioning of build scripts and configurations, ensuring developers can recreate specific builds reliably. This capability is crucial for debugging, testing, and auditing purposes, allowing teams to maintain consistency across different stages of the software development lifecycle.
65. How does IBM Rational Build Forge enhance the security of build processes?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge addresses security concerns by implementing robust authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms. Access controls and permissions restrict access to sensitive build configurations and repositories. This ensures that only authorized personnel can modify or execute critical build processes, safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of the software delivery pipeline.
66. How does IBM Build Forge reduce manual errors in the build process?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge significantly reduces manual errors by automating the build and release processes. Automation ensures that repetitive and error-prone tasks, such as code compilation and packaging, are executed consistently. This reduces the likelihood of human errors, enhances the reliability of builds, and allows development teams to focus on higher-value tasks.
67. Can IBM Build Forge adapt to various programming languages and frameworks?
Ans:
Yes, IBM Rational Build Forge is versatile and can adapt to different programming languages and frameworks. It supports various scripting languages, including Ant, Maven, and Shell. This flexibility allows development teams to use the languages and frameworks that best suit their project requirements, making IBM Rational Build Forge adaptable to diverse technology stacks.
68. How does IBM support organizations in meeting regulatory compliance standards?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge aids organizations in meeting regulatory compliance standards by providing comprehensive logging and tracking of build activities. This audit trail is essential for demonstrating compliance with industry regulations. Access controls and permissions ensure that only authorized users have the necessary privileges, contributing to a secure and compliant development process.
69. What role does the Build Forge Scheduler play in optimizing build processes?
Ans:
The Build Forge Scheduler is crucial in optimizing build processes by automating the scheduling of build and deployment jobs. It allows teams to define specific execution times, trigger tasks in response to events, and efficiently manage resource allocation. This automation ensures the timely execution of tasks, minimizes idle time and contributes to the overall efficiency of the software development lifecycle.
70. How do IBM dependencies between different components in a software project?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge manages dependencies by enforcing a defined workflow for build and deployment processes. Tasks are executed in a specified order, ensuring that prerequisites are met. This systematic approach enhances the reliability of builds, prevents issues related to missing dependencies, and contributes to a smooth and consistent development pipeline.
71. What advantages do you offer regarding monitoring and reporting capabilities?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge provides extensive monitoring and reporting capabilities through its centralized Build Forge Dashboard. This dashboard offers real-time visibility into build status, logs, and metrics. Teams can identify bottlenecks, track progress, and make informed decisions based on detailed reports, contributing to continuous improvement in the development process.
72. How does Build Forge support optimizing build resources in a dynamic environment?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge supports the dynamic allocation and management of build resources. By optimizing resource usage based on demand, it ensures that resources are efficiently utilized. This capability is particularly beneficial in dynamic and changing environments, where resource requirements may vary, contributing to building times and enhanced scalability faster.
75. Can IBM Build Forge be customized for specific organizational needs?
Ans:
Yes, IBM Rational Build Forge is designed to be extensible and customizable. It provides a Build Forge REST API that allows organizations to integrate it with other tools and systems. This flexibility enables the customization of workflows, the creation of tailored solutions, and the extension of its functionality to meet specific organizational requirements.
76. How does it support the rollback of deployments in case of errors?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge provides mechanisms for the rollback of deployments, allowing teams to revert to previous versions in case of errors or issues. This capability is crucial for maintaining system stability and reliability in production environments. Quick and efficient rollback procedures minimize downtime and ensure a robust deployment process.
77. How do Build Forge Agents contribute to parallel task execution in diverse environments?
Ans:
Build Forge Agents are essential for parallel execution as they operate on remote machines, enabling the simultaneous execution of tasks across different environments. This parallelization can increase the efficiency of the build process,
reduce overall build times and ensure that tasks are processed concurrently, improving scalability.
78. How does IBM Build Forge optimize tasks in optimized form environments?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge supports multi-platform environments by providing consistent and centralized platfocentralized build and deployment tasks. It is designed to adapt to diverse platforms, ensuring the build process remains consistent across different operating systems. This adaptability enhances flexibility in development and deployment scenarios.
79. What role do you play in ensuring standardized Build Forge Templates?
Ans:
provide starting points for creating consistent build and deployment configurations, enforcing best practices and reducing the likelihood of configuration errors. Templates streamline defining configurations, contributing to a more organized and individualized development pipeline.
80. How does IBM contribute to faster time-to-market for software releases?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge contributes faster time-to-market by automating and optimizing the development and delivery process. Automation reduces manual intervention, accelerates build times, and ensures consistency, allowing teams to release high-quality software rapidly. The streamlined and efficient processes supported by Build Forge contribute to quicker software delivery cycles.
81.What advantages do you offer in terms of modular build configurations?
Ans:
| Advantages of Modular Builds | Description | |
| Scalability |
Easily scale projects with the addition or modification of modules. |
|
| Reusability | Improve efficiency by reusing modular components across various projects. | |
| Maintenance | Simplify ongoing maintenance and updates through a modular structure. | |
| Flexibility | Adapt and customize projects more easily with a modular approach. | |
| Collaboration | Facilitate collaboration by allowing teams to work on different modules concurrently. |
82. How does IBM Build Forge aid in transitioning from continuous integration to continuous delivery?
Ans:
IBM Rational Build Forge facilitates a seamless transition from continuous integration to continuous delivery by automating the entire software delivery lifecycle. It supports continuous integration practices and extends automation to the testing and deployment phases. This end-to-end automation ensures a smooth and reliable transition from development to production, aligning with continuous delivery principles.
83. How does it handle dependency resolution in complex build processes?
Ans:
- Utilizes a defined workflow mechanism
- Manages dependencies through task execution order
- Ensures prerequisites are satisfied before task execution
- Supports parallel execution with consideration for dependencies
- Enhances reliability in managing complex software dependencies
84. What strategies does IBM Build Forge use to minimize bottlenecks in large-scale projects?
Ans:
- Implements parallelization techniques
- Optimizes resource allocation dynamically
- Utilizes Build Forge Agents for distributed execution
- Supports modular build configurations
- Provides detailed monitoring through the Build Forge Dashboard
85. How does it support blue-green deployments and canary releases?
Ans:
- Facilitates environment-specific configurations
- Allows creation of deployment scenarios for blue-green releases
- Supports versioning and rollback mechanisms
- Enables controlled release to a subset of users for canary releases
- Enhances flexibility and reliability in deployment strategies
86. How does IBM Build Forge address challenges in managing microservices build?
Ans:
- Supports modularity with Build Forge Modules
- Enables separate build configurations for microservices
- Facilitates version control for individual microservices
- Streamlines coordination through centralized monitoring
- Enhances adaptability to the dynamic nature of microservices development
87. How does IBM Build Forge integrate with Docker and Kubernetes?
Ans:
- Integrates seamlessly with Docker for containerization
- Supports Dockerized build environments
- Enables Kubernetes-compatible deployment configurations
- Enhances scalability and resource efficiency in containerized environments
- Streamlines the incorporation of container technologies into the build and deployment pipeline
88. Can Build Forge handle complex branching strategies in version control systems?
Ans:
- Supports integration with various version control systems
- Adapts to diverse branching strategies
- Enables automated builds based on branch commits
- Enhances traceability with versioned build configurations
- Facilitates consistent builds across different branches
89. How does it improve the traceability and auditability of build processes?
Ans:
- Maintains a comprehensive audit trail of build activities
- Logs detailed information about each build process
- Enforces access controls and permissions for security
- Supports versioning of build scripts and configurations
- Enhances transparency and accountability in the development lifecycle
90. How does IBM Build Forge manage and optimize build resources in cloud environments?
Ans:
- Seamless integration with cloud platforms
- Optimizes cloud resource usage dynamically
- Supports building and deploying applications in cloud environments
- Enhances scalability and efficiency in resource allocation
- Provides flexibility in deployment options for cloud-based projects
91. How does it cross-platform builds in heterogeneous development environments?
Ans:
- Ensures consistent builds across different operating systems
- Supports multi-platform build configurations
- Adapts to diverse development environments seamlessly
- Facilitates parallel execution of tasks on various platforms
- Enhances flexibility and efficiency in cross-platform development






