Introduction to Internet of Things: IoT Tutorial with IoT Application
Describe the Internet of Things (IoT)
The phrase “Internet of Things” (IoT) refers to a network of actual physical things or gadgets that are linked to the Internet, frequently equipped with sensors, and have the ability to gather, share, and analyze data. These objects might include everything from wearable technology, commercial equipment, everyday home items, and buildings and automobiles to infrastructure.
IoT makes virtually everything “smart,” by improving aspects of our life with the power of data collection, AI algorithm, and networks. The thing in IoT can also be a person with a diabetes monitor implant, an animal with tracking devices, etc.
History of IOT
- 1970- The actual idea of connected devices was proposed
- 1990- John Romkey created a toaster which could be turned on/off over the Internet
- 1995- Siemens introduced the first cellular module built for M2M
- 1999- The term “Internet of Things” was used by Kevin Ashton during his work at P&G which became widely accepted
- 2004 – The term was mentioned in famous publications like the Guardian, Boston Globe, and Scientific American
- 2005-UN’s International Telecommunications Union (ITU) published its first report on this topic.
- 2008- The Internet of Things was born
- 2011- Gartner, the market research company, include “The Internet of Things” technology in their research
How IOT works?

The entire IOT process starts with the devices themselves like smartphones, smartwatches, electronic appliances like TV, Washing Machine which helps you to communicate with the IOT platform.
Four Fundamental Components of an IoT System
1) Sensors/Devices: These are the physical objects or gadgets that gather information from their surroundings.Sensors can measure various parameters like temperature, humidity, light, motion, and more. For the purpose of data collection and processing, these gadgets have sensors and processors incorporated.
2) Connectivity: Connectivity refers to the network that allows devices to communicate and transfer data. IoT devices may communicate data to the cloud or other connected devices via a variety of communication protocols, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks, and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN).
3) Data Processing and Storage: The collected data from IoT devices need to be processed and stored. Data processing can happen locally on the device (edge computing) or be sent to the cloud for more extensive analysis. The enormous volume of data produced by IoT devices is managed and stored using cloud platforms and databases.
4)User Interface and Applications: The user interface and applications provide a means for users or other systems to interact with the IoT system. Users may monitor and operate IoT devices, analyze data analytics, and make choices based on the gathered data using a mobile app, web-based dashboard, or other software tools.
- For example, if a user detects any changes in the temperature of the refrigerator, with the help of IOT technology the user should be able to adjust the temperature with the help of their mobile phone.
IoT Applications
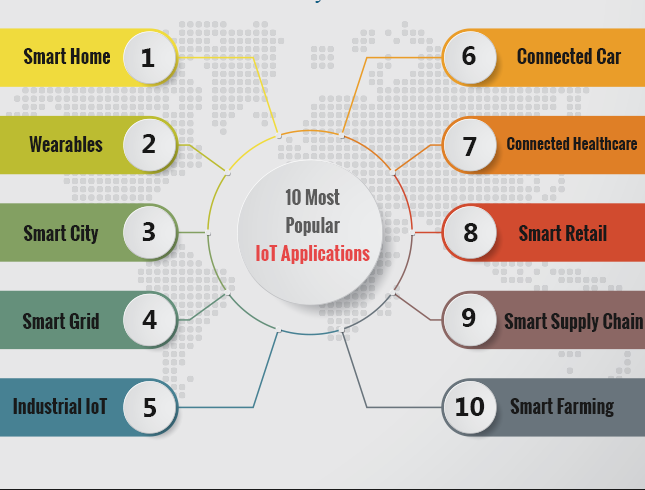
IoT Applications
IoT solutions are widely used in numerous companies across industries. Some most common IoT applications are given below:
The most common IoT applications are:
Smart Thermostats: Helps you to save resources on heating bills by knowing your usage patterns.
Connected Cars: IoT helps automobile companies handle billing, parking, insurance, and other related stuff automatically.
Activity Trackers: Helps you to capture heart rate patterns, calorie expenditure, activity levels, and skin temperature on your wrist.
Smart Outlets: Remotely turn any device on or off. It also allows you to track a device’s energy level and get custom notifications directly into your smartphone.
Parking Sensors: IoT technology helps users to identify the real-time availability of parking spaces on their phones.
Connect Health: The concept of a connected healthcare system facilitates real-time health monitoring and patient care. It helps in improved medical decision-making based on patient data.
Challenges of IoT
At present IoT is faced with many challenges, such as:
- Insufficient testing and updating
- Concern regarding data security and privacy
- Software complexity
- Data volumes and interpretation
- Integration with AI and automation
- Devices require a constant power supply which is difficult
- Interaction and short-range communication
The Advantages of IoT
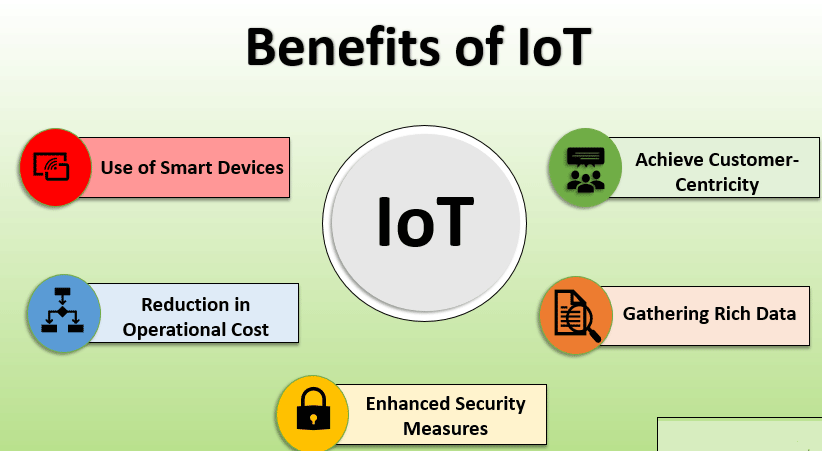
1) Increased Efficiency: IoT automates processes and tasks, reducing manual intervention and improving operational efficiency. Smart devices gather real-time data and trigger actions, streamlining operations.
2) Data-Driven Insights: IoT generates vast amounts of data, enabling data-driven decision-making. Businesses acquire a useful understanding of consumer behavior, operational trends, and performance indicators.
3) Enhanced Connectivity: IoT fosters seamless communication among devices, systems, and people. Real-time information sharing improves collaboration and coordination.
3) Improved Quality of Life: In the consumer space, IoT enhances convenience and comfort. Smart home devices and wearables offer personalized experiences and automate tasks, improving daily living.
Disadvantages IOT
Security:IoT technology creates an ecosystem of connected devices. However, during this process, the system may offer little authentication control despite sufficient security measures.
Privacy: The use of IOT, exposes a substantial amount of personal data, in extreme detail, without the user’s active participation. This creates lots of privacy issues.
Flexibility: There is a huge concern regarding the flexibility of an IoT system. It is mainly regarding integrating with another system as there are many diverse systems involved in the process.
Complexity: The design of the IOT system is also quite complicated. Moreover, it’s deployment and maintenance is also not very easy.
Compliance: IOT has its own set of rules and regulations. However, because of its complexity, the task of compliance is quite challenging.
IOT Best Practices
- Design products for reliability and security
- Use strong authentication and security protocols
- Disable non-essential services
- Ensure Internet-managed, and IoT management hubs & services are secured
- Energy efficient algorithms should be designed for the system to be active longer.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects or people called “things” that are embedded with software, electronics, network, and sensors which allows these objects to collect and exchange data.
- The actual idea of connected devices was proposed in 1970
- Four Key components of IoT framework are 1) Sensors/Devices, 2) Connectivity, 3) Data Processing, 4) User Interface
- Various applications of IoT are Smart Thermostats, Connected Cars, Activity Trackers, Smart Outlets, Connect Health, etc
- Technical Optimization, Improve Data Collection, Reduced Waste, Improved Customer Engagement are key benefits of IoT
- Security, Privacy, Complexity, Compliance, are key challenges of IoT
What is the difference between IoT and IIoT?
IOT:
- The full form of IoT is the Internet of Things
- A service model is human-centric.
- Communication transportation is done through wireless device
- The quality of data is medium to high.
- Criticality is not severe.
IIOT: The full form of IIoT is the Industrial Internet of Things
- A service model is machine-centric.
- It supports industry-oriented applications.
- Communication transportation is done through both wired and wireless devices.
- The quality of data is high to very high.
- Criticality is severe.
List layers of IoT protocol stack
Layers of IoT protocol stack are: 1) Sensing and information, 2) Network connectivity, 3) Information processing layer, 4) Application layer.
List mostly used sensors types in IoT
Mostly used sensor types in IoT are:
- Smoke sensor
- Temperature sensors
- Pressure sensor
- Motion detection sensors
- Gas sensor
- Proximity sensor
- IR sensors
Mention the basic difference between IoT and sensor businesses?
- A sensor business does not need an active internet connection to work. Internet of Things requires a control side to work.
How Does Bluetooth Low Energy Work?
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a low-power wireless communication technology for efficient data transmission between devices with low energy requirements, suitable for battery-operated devices like IoT sensors and wearables.
What is MicroPython?
- MicroPython is a lean implementation of the Python 3 programming language optimized for microcontrollers and embedded systems, providing a full Python environment with reduced memory footprint and execution speed.
List All of The Current Raspberry Pi models
- Raspberry Pi Model A
- Raspberry Pi Model A+
- Raspberry Pi Model B
- Raspberry Pi Model B+
- Raspberry Pi 2 Model B
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+
The Most Popular Water Sensors
Some of the most popular water sensors include:
- DHT11/DHT22 (temperature and humidity sensors)
- Soil Moisture Sensors
- Ultrasonic Water Level Sensors
- Float Switches
Distinguish Between Arduino and Raspberry Pi
Arduino:
- Arduino is a microcontroller-based platform ideal for simple, real-time tasks and hardware interfacing.
- It excels in low-power applications and is suitable for projects involving sensors and actuators.
Raspberry pi :
- Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer running on an OS like Linux.
- With a more powerful CPU, it is versatile, supporting general-purpose computing, multimedia tasks, and various programming languages.
What Are the Most Commonly Used Iot Protocols?
Some of the most commonly used IoT protocols are:
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
- AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)
- Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- Zigbee
- LoRaWAN
- Sigfox
List Some of the Wearable Arduino Boards
- Arduino LilyPad
- Arduino Gemma
- Adafruit FLORA
- Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense
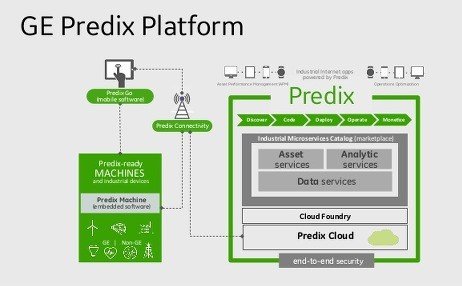
Describe Iot Ge-Predix:
GE Predix is an Industrial IoT platform by General Electric, designed for gathering and analyzing data from industrial machines and sensors to optimize performance and efficiency. It offers advanced analytics, edge computing, and cloud-based services for real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance.
Explain Iot Contiki
Contiki is an open-source OS made especially for resource-constrained IoT devices. It provides a lightweight and energy-efficient platform, enabling seamless connectivity, communication, and data exchange in IoT networks.
What Operating Systems Does the Raspberry Pi Support?
Here are the operating systems supported by Raspberry Pi :
- Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian)
- Ubuntu
- Fedora
- Arch Linux ARM
- Windows 10 IoT Core
- Kali Linux
What Distinguishes M2M From the Internet of Things?
Machine-to-Machine (M2M):
- Point-to-point communication between devices.
- Primarily used in industrial settings.
- Limited in scope and predefined interactions.
- Often relies on specific communication protocols tailored for the application.
Internet of Things (IoT): :
- A broader concept with interconnected devices.
- Diverse applications across industries.
- Emphasizes real-time data analytics and cloud connectivity.
- Utilizes standardized communication protocols for seamless interoperability.
- Embraces innovation and scalability, enabling the integration of new devices and technologies.
What Does IoT Testing Mean?
IoT testing refers to the process of evaluating and validating Internet of Things (IoT) devices, applications, and systems to ensure their functionality, security, and performance. It involves testing various aspects, such as device communication, data exchange, interoperability, and reliability, to deliver a reliable and secure IoT ecosystem.
What Varieties of Iot Are There?
Some of the key varieties of IoT include:
- Consumer IoT (smart home devices, wearables)
- Industrial IoT (automation, equipment monitoring)
- Healthcare IoT (connected medical devices)
- Smart Cities (traffic, waste management)
- Agriculture IoT (precision farming)
- Transportation and Logistics (fleet management)
- Energy and Utilities (smart grid)
What Are the Different Iot Testing Types?
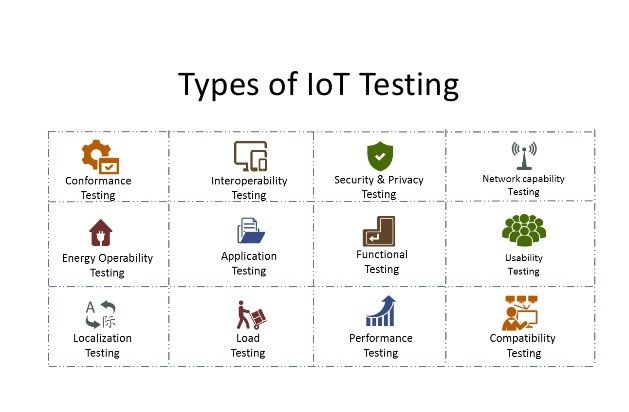
Some of the key IoT testing types are:
Functional Testing: Verifying that the IoT devices and applications perform their intended functions correctly and accurately.
Compatibility Testing: Ensuring that IoT devices and applications work seamlessly with different platforms, operating systems, and communication protocols.
Performance Testing: Evaluating the responsiveness, scalability, and efficiency of IoT systems under various load conditions.
Security Testing: Identifying and addressing potential security vulnerabilities to protect private information and prohibit unauthorised access.
Interoperability Testing: Validating the seamless communication and data exchange between different IoT devices and systems.
Reliability Testing: Ensuring that IoT systems perform consistently and reliably over an extended period, without unexpected failures.
What is the basic difference between the IoT network and Wireless Sensor Network?
Wireless Sensor Network things connected to the wireless network and gather some monitoring environment or data. IoT contains a combination of:
- WSN
- Internet
- Cloud Storage
- web or mobile application.
conclusion:
Internet of Things is the concept in which the virtual world of information technology connected to the real world of things. The technologies of the Internet of things such as RFID and Sensor make our life become better and more comfortable.Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.





