
A Product Manager oversees the development of a product from initial concept to launch. They work closely with cross-functional teams, including engineering, marketing, and design, to establish the product’s vision and strategy. By analyzing market trends and customer feedback, Product Managers prioritize features to ensure the product meets user needs and aligns with business objectives. Their role is essential for achieving success in the marketplace.
1. What is a product manager?
Ans:
A product manager manages a product from its conceptualization to its launch date into the market but ensures the development is in line with the customers’ identified needs and the business’s objectives. PMs collaborate with multiple cross-functional teams, such as engineering, design, and marketing, to provide one vision for a product. They also gather and analyze research market information, prioritize features, and create a product roadmap.
2. What makes a good product?
Ans:
A good product effectively solves a customer problem, responds well to market needs, and delivers a hassle-free user experience. These are all measured by factors such as customer satisfaction, market share, profitability, and whether or not the revenue can be sustained or continued to grow. A good product should be scalable and adaptable as needs or market conditions change. Of necessity, it must be distinctive in providing value that is different from that of its competitors.
3. Which of the following are common product management frameworks?
Ans:
- Common product management frameworks include Lean, Agile, and Scrum. The Lean approach aims to minimize waste and maximize efficiency in product development.
- Agile focuses on iterative development when the teams deliver small improvements.
- Within these setups, a form of Agile is Scrum, where work is broken into sprint time boxes, with an appraisal at the end of each sprint to make changes to the product as they were given feedback.
- JTBD theory is another widely utilized framework to help PMs focus on the user’s actual needs and goals.
4. Define the product development process.
Ans:
- Product development typically starts with identifying a market opportunity or customer need. During the ideation phase, possible solutions are brainstormed.
- Once a concept is chosen, the PM collaborates with the design and engineering teams to create a prototype. The development follows, where the product is built and tested for functionality, usability, and market fit.
- The launch is then followed by monitoring of the product and iteration after it is launched.
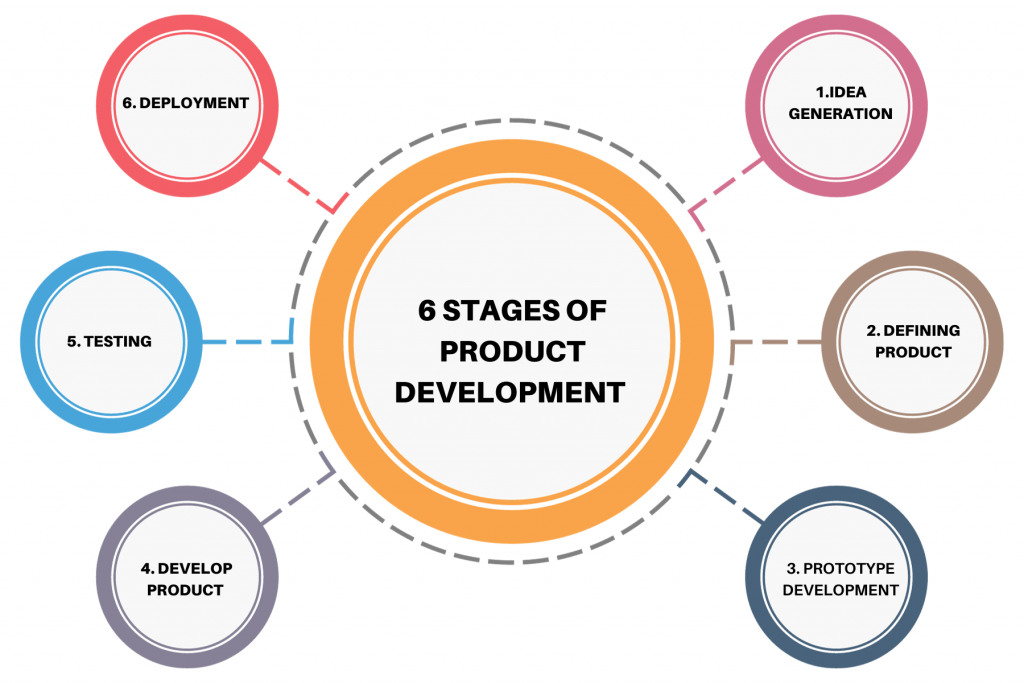
5. What criteria are used for feature prioritization for product road mapping?
Ans:
Customer needs, business impact, and feasibility drive feature prioritization. The PM determines whether it solves critical user pain points and business goals and fits into the revenue generation or growth dimension. The final aspect is customer satisfaction and retention. In addition, cost, the complexity of implementation, and resource availability, among other factors, determine which features will be developed first. Techniques such as the RICE scoring model help quantify and compare features for prioritization.
6. How is a product vision developed?
Ans:
Developing a product vision would require understanding the core problem it looks to solve and establishing long-term impact potential. It starts from extensive market research, customer insight, and competitor analysis towards areas of unmet needs. Collaborate with key stakeholders such as leadership, engineering, and marketing teams to align strategic business goals. The product vision should be inspirational and concise as well as actionable. It gives direction to the team.
7. What is the approach to product goals?
Ans:
- Product goal-setting involves outlining measurable outcomes or results that should be achieved. These goals must align with the company’s larger objectives.
- They must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART).
- PMs frequently use frameworks such as Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) to set challenging but achievable goals for product growth, user engagement, or market share.
- Goals must be grounded in data, and some, such as customer feedback, competitive analysis, and market trends, would have to be the most important determinants.
8. What methods does it employ to gather market information?
Ans:
- The best market research techniques require conducting qualitative and quantitative methods. PMs survey, interview, and even conduct focus groups to gather primary customer feedback by identifying their pain points, needs, and preferences.
- Conducting competitor analysis: Here, PMs analyze the strengths, weaknesses, and market position of any competitor. PMs can use data-driven techniques like analytics tools to understand industry behaviour, market trends, and broader industry shifts that can inform product decisions.
9. How are market needs and customer pain points assessed?
Ans:
Market needs and customer pain points are determined from primary sources like through direct user feedback, surveys, interviews, assessing customer support tickets, and online reviews. Another way is to do secondary source research, such as Net Promoter Score, as an indirect metric for measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty. The competitive analysis will help identify market gaps the product can fill. Data from user analytics provides insights into how the customers interact with the product, illustrating areas where users may struggle or fall off.
10. What qualities differentiate between a good PM and a great one?
Ans:
| Quality | Good PM | Great PM |
|---|---|---|
| Vision | Understands the product vision | Creates and inspires a compelling product vision |
| Communication | Communicates effectively with teams | Builds strong relationships and influences stakeholders |
| Decision-Making | Makes informed decisions | Anticipates outcomes and embraces calculated risks |
| Customer Focus | Listens to customer feedback | Proactively seeks customer insights and advocates for their needs |
| Analytical Skills | Analyzes data to inform decisions | Uses data-driven insights to drive strategy and innovation |
11. Which methodologies are used when taking user feedback into the product development phase?
Ans:
- Methods to enforce feedback in the product development process Mostly, many of the key techniques are involved in product development: Traditional User Surveys, Interviews, and Feedback Forms can gather users’ opinions regarding the product’s features.
- Analytics tools for tracking user behaviour make the areas of pain or areas that need improvement quite visible. Beta testing can also be very useful; users test pre-release product versions.
12. What is the purpose of a user persona in the product strategy?
Ans:
Personas allow teams to concentrate on designing for the target audience and assist in prioritizing features based on user needs. By aligning a product with user expectations, personas help improve user satisfaction and engagement. They are also helpful for maintaining a shared understanding across cross-functional teams of who the product is for.
13. What are the experiences with A/B testing?
Ans:
A/B testing creates two versions of a product or feature that help to find which version is better for the users. In this way, it helps with data-driven decision-making by comparing one variation versus the other based on metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and even user engagement. To experience A/B testing firsthand when optimizing the layouts of a user interface: one version had simplified navigation, while the other had more detailed menus.
14. What are some procedures for ensuring a product is user-friendly?
Ans:
- Ensuring a user-friendly product involves multiple steps, including understanding user needs through research and persona development.
- The intuitive design extends beyond a product that’s intuitive by design, including a product with simple navigation and workflows to promote little or no learning curves.
- Usability testing with real users may be scheduled to reveal more issues. Iteration based on the feedback continues to refine the experience. Finally, accessibility allows people with different ability levels to use the product.
15. Describe an occasion when a design trade-off had to be made.
Ans:
- Product development creates design trade-offs due to time, budget, or technical feasibility constraints.
- For instance, when working on one project, a decision was made between a highly customizable interface and performance efficiency.
- Considered multiple factors and after discussions with several stakeholders and engineers, finalized a less customizable but simpler interface, more responsive and faster as the trade-off to meet the deadline and ensuring it has no jerks in the user experience at the cost of performance.
16. How is collaboration with cross-functional teams managed?
Ans:
Collaboration with cross-functional teams requires effective communication and alignment of goals. One of the most effective strategies is regular meetings among all teams, such as design, engineering, and marketing teams, where those teams can share updates and discuss challenges. Each team’s proper role and responsibility have been ensured by making them answerable to one another. Collaborative tools, such as project management software, help keep everyone aligned with the goals.
17. Can an example be provided of a disagreement with engineers or designers?
Ans:
Sometimes, opinion differences between engineers and designers can lead to disagreement over priorities. One such situation that comes to mind is when the designers wanted an additional complex feature, and the engineers objected because it would cause performance degradation. Had to call for a meeting to weigh both aspects from both parties. After weighing the needs against technical limitations, I compromised to make the design simple enough without making significant losses on the look and feel.
18. Describe an instance of stakeholder persuasion.
Ans:
- Engaging stakeholders sometimes calls for combining data with stories and their concerns. One specific instance occurred when stakeholders needed to be persuaded to invest in a feature that was popular among users.
- Initially, it was of little interest to anyone from the stakeholders’ side. Here, data from the users’ surveys were used to propose the probable effect on customer retention and create a development plan that would not severely affect the accounts.
19. How are product updates communicated to the team and stakeholders?
Ans:
- Product updates must be communicated according to a process. Regular sprint reviews or even product demos allow real-time sharing of progress.
- Verbal or paper-based record: like on a product roadmap, in release notes, or email updates. Details are written down. Reports are concise for stakeholders and focused on ‘outcomes that really matter and timelines,’ and unnecessary details are avoided, especially when using visual reminders, like dashboards or charts that can deliver progress.
20. What tools are used for project management and collaboration?
Ans:
This can be done by multiple tools used to manage projects and align teams in a way that aids collaboration. Some very common project management tools include Jira, Trello, and Asana, through which all tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities can be tracked. Tools such as Slack or Microsoft Teams support real-time discussions with various departments. Much collaborative work in documents and presentations goes through Google Workspace or Microsoft 365.
21. What KPIs are tracked for a product?
Ans:
This again varies with the product and what it needs to achieve, but some common KPIs that would be tracked in general include customer acquisition rate, user retention rate, CLTV, and many more. Other significant KPIs include MAU, churn rate, and feature adoption rate. Digital products track other performance metrics like uptime, response time, and error rates. These are revenue KPIs, such as recurring revenue or profit margins, that let us know how well a product is doing.
22. How is data used in product decision-making?
Ans:
- Data provides irreplaceable insight into customers’ product use, behaviour, and market trends, helping them make informed decisions.
- Analyzing user interactions and following feature performance would help product teams understand how customers relate to a product. A/B test data enables PMs to check the effects of new features or changes in design on the product.
- Moreover, customer support ticket data and reviews could hint at the pain points that may be outdated or bug fixes. Therefore, data is generally useful for prioritizing features, improving the user experience, and validating the fit between the product and the market.
23. Can an example of how data analytics influenced product strategy be provided?
Ans:
- Through data analysis, a streaming service may learn that users are bailing on certain genres or dropping at a given point in a show.
- This can inform strategic choices, such as concentrating more on highly engaging content and redesigning the user interface to help better users find content.
- By changing the product based on this outcome, the company could also improve engagement rates, reduce churn, and increase user satisfaction, thereby positively impacting its growth strategy.
24. What metrics define product success, and how are they measured?
Ans:
Product success metrics include customer satisfaction scores, user retention, and product adoption rates. Financial metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, and return on investment (ROI) are also very important. The usage metrics of user engagement indicate how well the product receives people. This includes time spent on the product, active user rates, and usage of features. The Net Promoter Score is another measure of customer loyalty and the chances of people recommending the product.
25. Which analytics tools are commonly employed?
Ans:
The most commonly used analytics tools in product management include Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Amplitude. These analytics tools help track user behaviour, engagement, and product performance. Tools like Hotjar are designed to supply the researcher or business owner with heatmaps and session recordings of user interaction on websites or apps. To understand complex data, business intelligence tools like Tableau or Power BI are generally utilized to place that information into a visual perspective.
26. How is customer feedback collected and processed?
Ans:
- Customer opinion might be collected through a survey, interview, focus group, or product review.
- In-app interactive mechanisms for providing feedback and live chat through services such as Intercom facilitate instant collection of customer opinion.
- Customer support tickets and social media mentions also reveal common pain points. After gathering the customers’ opinions, we usually group them according to common themes or use sentiment analysis tools to measure user satisfaction.
27. What customer feedback has led to changes in a product?
Ans:
- Feedback from customers may eventually reach a software company about the problem of navigation complexity faced by some users.
- When complaints about the same problem reach multiple ones about the same problem, the product team might redesign the user interface to make that feature easy to navigate.
- This change will be based on customer feedback, making the software easier to use and likely to improve customer satisfaction and fewer questions within support and retention.
28. How is the validation of a product as meeting customer needs to be conducted?
Ans:
Validations of whether the product meets customers’ needs include constant usability testing, continuous feedback, and insights from usage data. Customer journey mapping typically helps the PM grasp how users interact with the product and helps identify friction points. Finally, A/B testing goes in-step validation of changes before going fully live. Customer personas and user stories are also key to guiding feature development.
29. What experiences have been had with an unhappy customer?
Ans:
An unhappy customer might have experienced a bug against the positive experience. So, here, one needs to hear him out, empathize and provide an urgent solution. For instance, they can contact support if a customer’s feature fails. The PM may follow up directly to ensure the problem gets escalated for a fix and could keep the customer in the loop about the entire process. Sometimes, a response, and often more importantly, acknowledgement of the issue, quickly will transform an unhappy customer into a customer for life.
30. How is the balance maintained between customer requests and business goals?
Ans:
- Prioritize based on value, impact, and feasibility. Only some customer requests can be implemented; a PM must review each, considering whether it aligns with the product vision and business strategy.
- Thus, requests that provide significant value to most users or generate revenue become key; others must wait or be deprioritized.
- Since communication with customers remains paramount, justifying the thought process behind decisions helps them manage expectations without deviating from long-term business objectives.
31. Describe a challenging product problem and the resolution.
Ans:
- Recently, encountered a tough problem-a feature that slowed down the application’s performance with an increasing user base. However, it is a core experience feature that is resource-intensive; it indeed results in a degraded user experience.
- To address this problem, I collaborated with the engineering team to identify inefficient parts of the code and implemented optimizations, including caching frequently accessed data and making fewer requests to the server.
- As such, we monitored the effectiveness of this solution through user feedback and its analytics performance, ensuring that the problem would not return.
32. What approaches are taken for risk management in product development?
Ans:
Early identification of potential risks and corresponding mitigating strategies are implemented in the product development cycle. A proactive approach to managing risk includes regular assessment, contingency plans, and prioritization based on the ratio of risk-reward associated with features. Iterative development, such as Agile methodologies, reduces risks because this approach occasionally allows for changes in a project’s priorities, along with user feedback during beta testing to detect possible issues before release.
33. Describe a decision that significantly affected a product.
Ans:
An important decision made was the transition from using a monolithic architecture to a microservices-based solution for a scaling SaaS platform. This was because the monolithic structure resulted in slow feature releases. After consulting with the engineering team and stakeholders, I established that decomposing a system into smaller, independent microservices was a change that further improved scalability, made development faster, and enabled teams to be more independent.
34. Which of the criteria applies to the assessment of potential features?
Ans:
- Many criteria apply when evaluating potential features. Most importantly, the value it will bring to the user is often determined by assessing the user’s feedback or consideration via surveys and market research.
- The technical feasibility of incorporating the feature into the system and the human resources required for its development are also considered.
- Even the ROI determination, such as in user engagement or revenue generation, is conducted.
- Other factors include whether this feature aligns well with the overall product strategy or could be released within the given timeline without compromising quality.
35. How is scope creep handled on a project?
Ans:
- Transparent communication, defined requirements, and tight change control manage scope creep. A clearly defined scope at the outset with specific deliverables will keep the team on track.
- Regularly reviewing stakeholders ensures everyone is on board and additional requests are scrutinized and evaluated based on priority and impact.
- If changes are required, the team will determine the resources and time needed through a formal change request process. Agile methodologies can avoid scope creep by introducing incremental changes in a controlled manner.
36. What experience exists with Agile and Scrum methodologies?
Ans:
With vast experience in Agile and Scrum practices, there has been active involvement in sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and sprint retrospectives to implement continuous improvement. In Scrum practices, clear definitions of user stories, frequent updating of backlogs, and regular sprint reviews helped deliver features iteratively. With flexibility in adjustment according to customer feedback, this methodology allowed for quick adjustment according to its feedback.
37. How are technical requirements defined in cooperation with engineering teams?
Ans:
The process usually involves discussions and clarifications to define technical requirements in partnership with the engineering teams. This begins with clearly understanding business and user needs, which is then translated into technical specifications. In such discussions, collaborate with engineers to ensure the requirements are feasible within time and resources. User stories or detailed requirement documents are prepared, usually with participation from both the product and engineering teams.
38. What is the awareness of APIs and integrations?
Ans:
- Both of these, API and integration, nowadays are the spine of modern product development.
- Experience includes integrating third-party services, such as payment gateways and social media platforms, and developing internal APIs for microservices architecture.
- In brief, knowing how APIs work is a good thing. I’ve used RESTful APIs to exchange data between different systems, including services like CRM platforms or analytics tools that help enhance product functionality.
39. What methods are used to stay updated about industry trends and technology?
Ans:
- It’s a mixture of continuous learning and engagement with the community. Regularly follow industry-leading blogs, attend webinars, and participate in professional forums and LinkedIn groups, where the latest trends are discussed.
- Staying up-to-date on newsletters and reading reports from research firms, such as Gartner or McKinsey, may give one an idea of new technologies under development.
- Attending conferences and networking with peers provides real-time information about the industry’s direction.
40. What are the tools for wireframing and prototyping?
Ans:
Figma, Sketch, and Adobe XD are typically used for wireframing and prototyping. These platforms offer user-friendly interfaces to create interactive wireframes and high-fidelity prototypes. Figma is particularly helpful for team collaboration, allowing real-time comments and feedback. Balsamiq is another low-fidelity wireframing tool used. InVision is beneficial for linking prototypes to workflows, enabling usability testing before actual development.
41. What does a company do to prepare for a product launch?
Ans:
It encompasses several stages, such as finalizing product features, testing for bugs, and ensuring the product is market-ready. There is a detailed preparation plan set for a launch; this comprises timelines, marketing activities, and distribution strategies. It is cross-functional, so teams like sales, marketing, and customer support are apprised and enabled. As such, pricing strategy and product positioning are defined, and beta testing or soft launches are done to attain preliminary feedback.
42. How is a go-to-market strategy developed?
Ans:
- A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is developed by defining the product’s target audience and market. Market research is performed to understand customer needs, the competitive landscape, and positioning opportunities.
- Next, clear messaging is established, pointing out the product’s unique value proposition. Distribution channels, pricing, and promotion tactics are also outlined to maximize reach and engagement.
- GTM strategy also coordinates with sales and customer success teams to prepare them to efficiently support the launch of a new product and onboard new customers.
43. What is an example of a successful product launch that was managed?
Ans:
- A high-level success would be the full launch of a completely new feature in the SaaS product, which greatly improves user engagement.
- An example scenario would be a team launching an AI-based data analytics tool after sufficient deep market research and beta testing.
- The product will take off very soon if, at its launch, the marketing campaigns are strong enough, the key customers are engaged via webinars, and incentives are presented to early adopters.
44. Which of the following metrics can be used to measure the success of a product launch?
Ans:
Customer acquisition rate, sales revenues, and engagement level through the first days of users are key indicators used to measure the success of a product launch. Other important indicators include active users, product adoption rate, and customer feedback or satisfaction scores. Within weeks of launching, a retention level also tells much about long-term successes. Moreover, tracking media coverage, social media engagement, and website traffic might measure the effectiveness of the launching campaign.
45. What is the role of marketing in the context of product strategy?
Ans:
Marketing plays a critical role in product strategy, enabling it to define target audiences, position the product within the market, and create messaging that inspires attention and action and delivers unique value propositions to potential users. Marketing teams generate awareness and demand and facilitate and drive the adoption of the product through through campaigns, content, and other promotional means.
46. How do they mentor junior product managers or team members?
Ans:
- She develops her junior product managers by periodically giving them feedback and encouraging them to speak openly-honestly.
- It guides them through such key aspects of product management as prioritization, market research, and stakeholder management.
- She keeps them engaged with smaller projects or features they own as a hands-on experience, so there is less chance of doing something wrong.
- It is useful to help them build their confidence and skill set through best practices, one-to-one coaching, and participation in important decision-making processes.
47. How is a culture of innovation promoted within a team?
Ans:
- Encourage the innovation culture through creative thinking and risk-taking with the team. The leader then creates a friendly atmosphere that allows people to have room for free discussion, welcoming all ideas.
- Brainstorming sessions and sessions on new technologies or market trends are frequent and meant to stimulate creativity. Recognizing and rewarding innovative ideas also motivates team members to continue thinking outside the box.
- Opening channels for experimenting, such as hackathons or side projects, takes the innovation culture to a whole new level.
48. Describe leading an organization through significant change.
Ans:
Leading a team through significant change requires clear communication, empathy, and flexibility. For example, if an organization changes its product development lifecycle from traditional to a new development lifecycle- for example, transitioning from Waterfall to Agile- a PM might have to train and induct a team in Agile. The process should start by spelling out expectations followed by continuous support and giving it time to settle.
49. What are the biggest trends in the industry?
Ans:
Some of the most important trends in the product management industry include the increased use of AI and ML to enhance products and provide a customized experience. This also consists of the growing influence of customer-centricity as product managers focus on deep customer insights to drive decisions. Agile and Lean methodologies continue dominating, and data-driven decision-making becomes more important.
50. How does product strategy adapt to the changes in the market?
Ans:
- Adapting the product strategy to new market conditions involves agility and responsiveness to new information.
- PMs should continually monitor market trends, competitor actions, and customer feedback to identify emerging opportunities or threats.
- For instance, if a new competitor enters the market, a company can change its strategy by improving key features, reducing prices, or focusing on another type of customer segment.
- Data analytics and market research can inform the decision-making process, and flexibility in product development allows for quick pivots when necessary.
51. Which competitor’s product is admired, and what are the reasons for this admiration?
Ans:
- Slack is an admired competitor’s product as it transformed how teams communicate. Its intuitive interface, integration with other tools, and focus on real-time collaboration set it apart.
- What contributes to admiring Slack is that it combines simplicity with powerful functionalities.
- This product has effectively solved a critical pain point: the awfulness of team communications while remaining flexible to different industries.
- Moreover, Slack’s bots and automation simplify workflows, and its API ecosystem lets businesses customize the platform to their needs.
52. What criteria guide decisions when considering potential collaborations or partnerships?
Ans:
Several factors are considered when assessing partnerships, beginning with strategic alignment. The potential partner needs to complement the company’s goals and values. Key considerations in this regard are the partner’s reputation, market presence, and customer base for mutual growth. The technical or operational feasibility of systems and processes is also considered. Shared revenue models and risks regarding potential financial implications are carefully weighed. Last but not least, continual innovation is critical to ensuring sustainable success.
53. How important is sustainability in product strategy?
Ans:
For example, considering their environment’s growing concern amongst consumers, sustainability is now becoming an integral part of product strategy. Material sourcing, energy efficiency in production or reducing waste in manufacturing can constitute sustainability in a product. Ethical sourcing and fair labour are also included under sustainable practices. Strategically speaking, such products are built to meet regulatory requirements while creating an added veneer to the brand’s reputation.
54. What is the future of product management?
Ans:
- The future of product management will be even starker, with even more data-driven decision-making, AI-driven insights, and automation.
- More sophisticated data analytics tools have become available for product managers, allowing them to gain deeper insights into user behaviour and market trends and, thus, make more informed decisions.
- Agile and lean methodologies will be taken further to deliver more rapid and flexible product development.
- Product managers will also need to collaborate more closely with AI and machine learning teams to ensure these technologies are applied optimally within their products.
55. What skills will future product managers need?
Ans:
- Technical, analytical, and soft skills are all essential for a future product manager. A deep grasp of data analytics and machine learning will become crucial to making the right, data-driven decisions.
- Good leadership and communication skills will be needed to work through cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
- Anticipating and being very adaptable to new tools and frameworks will thus prove important, especially in Agile and Lean environments.
- Product managers would need very high EQ in terms of understanding, in advance, the customer’s needs and requirements and could convert the business goals into technical requirements.
56. How will customer expectations shift in the next few years?
Ans:
Customers will expect far more personalized products and services, where AI and data analytics will take centre stage in offering the required experience. Speed will also be of the essence, as users will anticipate faster delivery and quicker customer support than ever before. Interactions across all platforms should be seamless and continuous; consumers will demand more transparency from businesses on privacy and sustainability issues. Convenience and high ethical and social responsibility will determine what customers will choose in the future.
57. What are some innovative ideas for product development?
Ans:
One innovative idea for product development is AI-facilitated self-adaptive interfaces that learn user behaviour over time and can adapt to individual users’ requirements. Another idea involves AR features for upgrading user interaction, especially in retail or education-oriented products. Design products with modular structures so that their components are easily upgradeable and can be repaired without creating waste. Second, blockchain-based systems intend to make supply chains more transparent to build trust and gain competitive advantage in certain industries.
58. How would a new feature be approached for launch?
Ans:
- Developing a new feature begins with intensive market research and testing in real user scenarios to determine whether the feature solves a problem.
- Thus, the process begins with a stringent roadmap, defining success metrics, and testing the feature in beta with a select set of users. A soft launch then ensues to get the first feedback and make the refinements before widening the rollout.
- It would also start a campaign of intense marketing and communication to users about the new feature. This campaign would aim to discuss the benefits and urge them to use it through tutorials, demos, or special promotions.
59. Describe how one can develop improvements for an existing product.
Ans:
- Improving an existing product starts with gathering opinions and information from the users through surveys and interviews and analyzing customer support data to assess where the problem lies.
- With that, the team directs its improvements toward aspects relevant to user experience, technical feasibility, and business success. An in-depth analysis of the product’s analytics would reveal what points users fail or drop off.
- Prototyping possible solutions and A/B testing may determine which improvements work. Finally, continuous monitoring after the changes are made guarantees that the updates bring about the desired results in solving the problems and improving the product’s performance.
60. What is the decision-making process if available data is sparse?
Ans:
In such a case, a formal decision-making process is required when data is scarce. General insights may first be sought through customer interviews or opinions from authorities. Past experiences or similar cases would also contribute to developing a hypothesis. Cross-functional teams, in brainstorming sessions, also provide ideas. Small-scale experiments or pilot tests may be run to gather more information if time allows. Then, risk analysis may be conducted to conclude the likely positive impact with manageable risk for something to be decided.
61. What post-launch actions would be taken if a product does not meet users’ expectations?
Ans:
If a product doesn’t meet the expectations of its users post-launch, collect very detailed feedback from surveys, feedback through customer support channels and interviews with users to highlight specific pain areas. Then analyze usage data and analytics to understand how users interact with the product. A root-cause analysis will uncover the causes of issues in terms of whether they are due to product design, usability, or missing features.
62. How can a product roadmap be developed for a new product in the industry?
Ans:
- For a hypothetical AI-driven content management tool, the product roadmap could be initial feature development that enhances text editing recommends AI-driven content and integrates it into extant systems.
- Enhancement of onboarding features, add collaboration functionality to edit in teams, and release the mobile app version.
- End- Advanced features: multilingual support, AI-driven content performance analytics, and social media site links. Improvements in user experience: fixing bugs based on user complaints and preparing for international expansion.
63. How is a similar product from a competitor reacted to?
Ans:
- If a competitor launches a similar product, a quick evaluation is required to understand the competitor’s strengths and weaknesses and the market’s reception.
- Marketing messages describing the unique value propositions must be used. The roadmap may be changed to speed up the launch of key differentiating features. Engage customers now through surveys or interviews.
- This might give insight into unmet needs that can be addressed, and promotional activities such as discounts, loyalty programs, or partnerships that can help reinforce customer retention and loyalty.
64. What if a critical feature is delayed?
Ans:
Partly, clear communication should be kept with stakeholders- the customers- on what has been delayed, the causes, and the changes being made. Meanwhile, interim solutions or workarounds can be offered to users, minimizing their impact. Internally, teams may decide to re-prioritize other features or releases to recover momentum and allocate some resources to finish the delayed feature’s development without affecting quality.
65. If customer feedback is a major concern over the product, what actions are taken?
Ans:
When large issues come through with customer feedback, the problem is recognized first, and the customers are assured that it’s under consideration. A rapid assessment is performed to confirm the scope and impact of the issue. The development team would focus on a fix, and regular updates on progress would be shared with the customers. Compensations such as discounts, among others, can be offered to the customers in case the issue significantly affects them to mitigate dissatisfaction.
66. What are the strategies for launching a meagre budget product?
Ans:
- Since the budget is minimal, product launch strategies depend heavily on organic and grassroots marketing. Some ways to generate word of mouth are social media, content marketing, such as a blog or video, and email marketing.
- Influencer or industry leader product reviews and testimonials can be done very cheaply. The strategy may be to create a viral referral program where customers are encouraged to share a product.
- Partnering with complementary brands or platforms also adds scope without a significant expense.
67. How does customer segmentation influence product development?
Ans:
- Customer segmentation is how product managers know which features and functionality to include in a product. Features will attract certain user groups based on demographics, behaviour, or needs.
- The more PMs understand their various customer personas, the better they prioritize feature development to provide the most value to key segments.
- It also helps personalize the product experience, target marketing messages, and create differentiated pricing models.
- For instance, a product may have a “pro” version for power users and a simplified version for casual users, depending on the specific needs and use cases.
68. What experience exists with user journey mapping?
Ans:
User journey mapping is creating an illustrated representation of the activities a customer undertakes while moving forward to interact with a product from initial awareness all through post-purchase support. Mapping in previous projects helped identify areas needing more clarity onboarding and more discoverability. Understanding these touchpoints allowed the product team to get over-priority improvements, streamline the user experience, and increase customer satisfaction.
69. How does it ensure the product and business strategy are aligned?
Ans:
This happens due to continuous communication and coordination between product managers and leadership, where systematic strategic planning ensures that the product roadmap reflects business objectives, like revenue targets, market expansion, or customer satisfaction goals. Established KPIs measure how product performance supports overall business outcomes. Focusing on short-term and longer-term goals assures development efforts align with the company’s overall vision and priorities.
70. Why is product lifecycle management important?
Ans:
- Product lifecycle management is critical to ensuring that the product evolves with the changing conditions of the marketplace and concerning its target users’ needs over time.
- It encompasses managing a product throughout its life cycle-the introduction and growth phases up to maturity and eventually decline.
- PLM helps teams decide when to market the product’s next version, scale it, and withdraw it from the market.
- In this regard, constant customer performance and feedback analysis can stretch the product’s life cycle, maximize profitability within its lifecycle, and minimize the risks of out-of-date or underperforming offerings.
71. How do ethical considerations get included in product management?
Ans:
- Data privacy should be approached transparently regarding the collection, storage, and uses of user data and its accessibility to all users, regardless of ability.
- It also includes caring for the product’s environmental impact, ensuring sustainability in sourcing, and ensuring sustainability during manufacturing.
- Algorithmic or design biases, representation concerns in marketing, and regulatory compliance are important aspects of responsible product management that directly affect user trust and brand reputation.
72. What are the methods applied for competitor analysis?
Ans:
Competitor analysis uses many methods to derive insights into the competitive landscape. SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is a common tool for evaluating competitors’ positioning. Surveys and focus groups are market research tools that can help collect data on customer perceptions of existing competitors. The competitors’ online presence was analyzed using web traffic, social media engagement, and SEO performance to help understand the extent of reach and effectiveness.
73. To what extent do market trends influence product strategy?
Ans:
Market trends are a strong influencer of product strategy because they influence how users behave and what they prefer in certain ways. For instance, a rise in demand for green may encourage an emphasis on green materials or features. Technological advancement, like AI or IoT, requires adding newer product features to cope with the competition. Changes in consumer demographics or economic considerations require a product’s redesign to align with new market focuses or alter pricing models.
74. What criteria determine whether to enter a new market?
Ans:
- Several criteria guide the decision to enter a new market, starting with market potential and demand. These include the size, growth rate, and customer demographics of a market that should be studied with a heightened awareness of the competitive landscape.
- Existing players and barriers to entry are also considered. Regulated considerations, including compliance requirements and local laws, can be a great driver in determining how feasible entry into a market may be.
- Allowing evaluation of internal capabilities, including resources and expertise, can ensure an organization has what it takes to be strong enough for successful market penetration.
75. What is the role of pricing strategy in product management?
Ans:
- Pricing strategy will be vital in product management and affect revenue, market positioning, and customer perception.
- Moreover, the chosen pricing strategy must coincide with the broader business goals, such as target markets for that specific product.
- Value-based pricing, cost-plus pricing, or competitive pricing could be used to address a product’s unique value proposition.
- A defined and effective pricing strategy will communicate the product’s value to the consumer, leading to adoption or loyalty.
76. Which techniques are effective for improving customer retention?
Ans:
Customer retention is multi-dimensional: the initial process of ensuring that quality service is afforded to the customer. However, communication would be much stronger if more personalization is a part of loyalty programs. Regular interaction through focused email marketing campaigns and feature updates keeps customers interested. Customer feedback solicitation and follow-through make the users feel that their opinions matter, creating a sense of loyalty.
77. How would customer engagement be measured and counted?
Ans:
Quantitative and qualitative metrics may be used to track and measure customer engagement. NPS, CSAT scores, and CES comprise key performance indicators allowing insight into user sentiment. Engagement analytics such as active users, session duration, and feature usage rates help evaluate the user frequency and depth of interaction with the product. In addition, using social media mentions and feedback can give a qualitative view of customer engagement.
78. What is the role of community building in product management?
Ans:
- Building a community is an important part of product management because it increases users’ loyalty and makes them part of the community.
- Discussions with users on forums, social media groups, or events can directly lead to feedback and enhance the product development process.
- A great community is also very resourceful regarding customer support, as people solve most issues on their own to improve at that issue or best practices.
- Communities also create brand advocates who can naturally promote the product. A community can help product managers create and strengthen customer relationships, improving the product experience.
79. What strategies encourage innovation in product development?
Ans:
- Creating an environment that encourages creativity and experimentation fosters innovation in product development. This can be done mainly through cross-functional teams, where all functions contribute to brainstorming and problem-solving.
- Ideas for regular ideation sessions and hackathons can be very inspirational. Creating a learning culture that recognizes failures and encourages learning from them will enable teams to take more calculated risks.
- Open lines of communication with customers and an ear for market trends will also provide valuable knowledge for innovation.
80. What are some recent trends in technology impacting product management?
Ans:
The latest technology trends significantly impact product management, with AI and machine learning leading the way. They enhance data analytics, enabling better decision-making regarding user behavior and preferences. Increased automation tools streamline development, resulting in faster time-to-market. Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on secure coding practices due to heightened concerns around data privacy and cybersecurity.
81. What product failure occurred, and what lessons were learned?
Ans:
The most high-profile product failure is Google Glass, which promised to bring augmented reality to everyday experience. It was initially exciting, but by the end, it became known for its invasion of privacy, social acceptability, and usability issues. One of the lessons learned from that failure was that there should be a good understanding of market readiness and behaviour before introducing innovation. In addition, effective user testing and premature resolution of ethical concerns can help prevent a backlash.
82. How are conflicting interests of key stakeholders over a product feature addressed?
Ans:
- Suppose key stakeholders cannot agree on a particular product feature. In that case, this is probably where the need to go into discussion would be to ensure each party gets to voice their opinion and worries.
- Data collection in pursuit of user feedback about the feature may suggest how to proceed. Therefore, end user needs must be placed at the forefront but in conjunction with broader business needs.
- If this is not possible, compromises or phased implementations should be considered. Effective disagreement resolution will ultimately depend on good communication and shared objectives.
83. What happens when user testing produces unexpected results?
Ans:
- When user testing produces unexpected results, the data should first be analyzed to understand what caused the outcome.
- Qualitative user feedback can even explain why the results are different from expectations. More testing or interviews can also increase clarity.
- Having some findings, the product team might pivot, which could mean redoing features, changing user interfaces, or solving specific issues. Knowing the insights and iterating faster is the way to align a product to the users’ needs.
84. How do the sales and support teams provide feedback on the product development process?
Ans:
The input from the sales and support teams is channelled into product development through structured communication through regular meetings and specific interfaces. Sales teams usually have information about customer pain points and objections made during the sale. Support teams may pass on typical problems or requests requested by the users. This feedback is captured and ranked based on its influence on customer satisfaction and corporate objectives.
85. What is the most difficult challenge encountered in product management?
Ans:
The most difficult thing as a product manager is balancing the competing interests of stakeholders, users, and market demands. One of the pressures that product managers face, therefore, is the pressure to make quick decisions where results are yielded with the quality of work done within aligning perspectives of long-term strategic goals. Making data-driven decisions where information may be limited requires strong willpower.
86. What drives a passion for product management?
Ans:
- A passion for product management is often fueled by the need to create impactful solutions that solve real user problems.
- The dynamic aspects of the work, often spanning multiple teams and impacting different aspects of a product, make it extremely appealing.
- The ability to interact with customers to understand their needs and iterate based on feedback provides meaning.
- Moreover, the excitement of watching a product go from concept to launch and overcoming adversity in the process can be highly rewarding for anyone working in the field.
87. What are the essential skills for a Product Manager to develop?
Ans:
- Critical skills for a Product Manager include good communication and interpersonal skills, which are necessary to work closely with cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
- Analytical skills help interpret data to make decisions and understand what users want to know and do. Problem-solving skills help when difficulties arise in product development.
- Moreover, project management allows PMs to prioritize tasks, handle timelines, and arrive on time.
88. What sources are used to remain abreast of best practices in product management?
Ans:
Knowledge of best practices in product management is brought about through online sources, professional networks, and further education. Great website resources, such as Mind the Product, Product Coalition, and other individual blogs on product management, contribute to insights and even case studies. For depth and the latest trends in information, one should read books on product management and listen to or watch podcasts and webinars of industry coverage.
89. Can a time be described when a pivot in product strategy was necessary?
Ans:
A product strategy needs to pivot when market conditions change, customer needs change, or when initial assumptions are proven incorrect. For example, a firm might start with a product targeting small businesses but pivot to serve enterprise clients to realize better demand in the latter market. That pivot would require updating the product’s core features, pricing approach, and marketing effort to align with the targeted new customers.
90. What questions are still unanswered about the company and product vision?
Ans:
Remaining questions about the company and product vision include how the product aligns with the organization’s mission and long-term goals. Clarity on measuring success through key metrics is essential, along with understanding the target market and how the product meets their evolving needs. Additional questions may address future refinements, potential pivots based on market feedback, and responses to competitive forces.






