
- Introduction to Fixed Income Securities
- Types of Fixed Income Securities
- Bond Terminology: Par, Coupon, Yield, Maturity
- Interest Rate Risk and Duration
- Credit Risk and Ratings
- Yield Curve and Economic Indicators
- Pricing and Valuation of Fixed Income Instruments
- Tax Implications and Regulations
- Fixed Income Portfolios and Investment Strategies
- Role in Diversification and Capital Preservation
- Trading and Market Infrastructure
- Trends in the Global Fixed Income Market
Introduction to Fixed Income Securities
Fixed income securities are a type of investment that provides a steady income. They pay investors regular interest, often at a fixed rate, over a set time. When these securities mature, investors get their original money back, known as the principal. Governments, like federal, state, or local authorities, and companies of all sizes usually issue these financial instruments. Companies use fixed income securities to raise money for expansion, projects, or daily operations. Governments use them to fund public works or infrastructure projects, which helps communities grow. Due to their structure, fixed income securities are seen as less risky than stocks. Stocks can fluctuate significantly, making their values unpredictable. On the other hand, fixed income securities usually offer more stable returns. Investors often choose them when they want to protect their money or earn a steady income, especially during uncertain times. For instance, a retiree might prefer bonds or treasury bills for income instead of risking it in stocks.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Types of Fixed Income Securities
Bonds are debt instruments where the issuer borrows funds from investors and agrees to pay back the principal along with periodic interest payments (coupons). In the world of fixed-income investments, different types of bonds offer unique chances for financial growth and managing risk. Government bonds, like U.S. Treasuries and Indian Government Securities, serve as a basic investment option backed by national governments. Municipal bonds are localized debt instruments issued by city or regional authorities. Corporate bonds form another important category, allowing companies to raise funds for expanding operations and strategic projects.
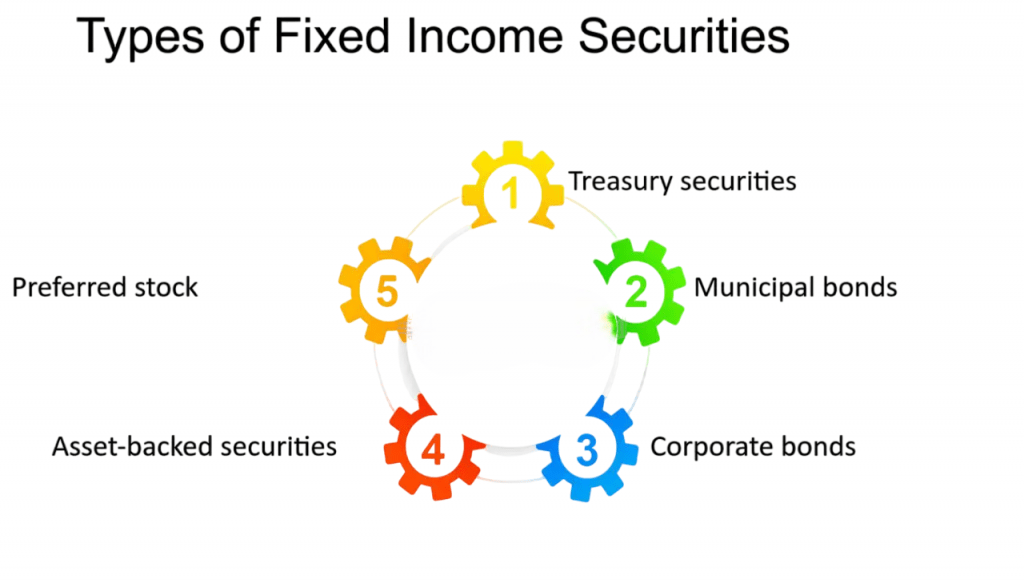
Debentures are unsecured debt instruments that depend on an issuer’s creditworthiness. They often offer higher yields to balance out risks. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) provide short-term government securities with maturities from a few days to one year. They are sold at a discount and do not pay periodic interest. Medium-term notes, which usually mature between one and ten years, give investors regular interest payments and the return of principal. Together, these investment vehicles support different financial goals and risk levels.
Bond Terminology: Par, Coupon, Yield, Maturity
- Par Value (Face Value): The amount the issuer agrees to repay at maturity, usually $1,000 per bond.
- Coupon Rate: The annual interest rate paid on the bond’s face value.
- Yield: The return an investor earns on a bond, which can vary based on the purchase price and market interest rates.
- Maturity: The date on which the bond’s principal is repaid to investors.
- Interest rate risk: The possibility that bond prices will drop when interest rates increase.
- Duration: Measures how sensitive a bond is to changes in interest rates.
- Longer duration: Bonds with a longer duration are more affected by changes in interest rates.
- Managing risk: Knowing about duration helps investors manage and lower interest rate risk.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM): The total return anticipated if the bond is held until maturity.
- Current Yield: Annual coupon payment divided by the bond’s current price.
- Discount and Premium: Bonds trading below par are at a discount; those above par are at a premium.
- Interest Income: Generally taxed as ordinary income.
- Capital Gains: Profits from selling bonds may be subject to capital gains tax.
- Tax-Exempt Bonds: Certain municipal bonds offer tax-free interest income.
- Providing Steady Income: Regular interest payments offer predictable cash flow.
- Preserving Capital: High-quality bonds can protect principal investment.
- Reducing Volatility: Bonds often have lower price fluctuations compared to equities.
- Diversifying Risk: Including bonds can reduce overall portfolio risk due to their low correlation with stocks.
- Primary Market: New issues are sold directly to investors
- Secondary Market: Existing securities are bought and sold among investors
- Trading: Can occur over-the-counter (OTC) or through exchanges, depending on the security type
- Market Participants: Institutional investors, banks, brokers, and individual investors
- Market Characteristics: Liquidity and transparency vary across different segments of the fixed income market
- Interest Rate Movements: Central bank policies impact bond yields and prices
- Inflation Expectations: Rising inflation can erode real returns on fixed income investments
- Economic Growth: Stronger economies may lead to higher interest rates, affecting bond valuations
- Regulatory Changes: New regulations can alter market dynamics and investor behavior
- Technological Advancements: Automation and electronic trading platforms are increasing market efficiency
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Interest Rate Risk and Duration
Credit Risk and Ratings
Credit risk is an important factor in bond investments. It shows the likelihood that an issuer may fail to pay interest or principal. Credit rating agencies like Moody’s, S&P, and Fitch play a key role in assessing an issuer’s creditworthiness. They provide standardized ratings to help investors understand potential risks. These ratings fall into two main categories: Investment Grade and Non-Investment Grade, or Junk status. Investment Grade ranges from AAA to BBB- for S&P and Fitch, or Aaa to Baa3 for Moody’s. Non-Investment Grade starts at BB+ and below for S&P and Fitch, or Ba1 and below for Moody’s. Higher-rated bonds are usually seen as safer investments but offer lower yields. In contrast, lower-rated bonds come with more risk but can lead to better returns. This creates a complex risk-reward balance that investors need to consider carefully.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Yield Curve and Economic Indicators
The yield curve is an important economic tool that shows bond yields for different maturities. It provides investors and economists with useful insights into market trends and possible economic changes. The curve usually appears in three main shapes: a normal yield curve, which rises and indicates economic growth; an inverted yield curve, which slopes downwards and is often seen as a sign of a possible recession; and a flat yield curve, which points to economic uncertainty. By closely examining these shapes, investors can make better decisions about bond investments and understand the overall economic situation. The yield curve’s ability to turn complex financial data into a simple visual tool makes it essential for evaluating current market conditions and predicting future economic developments.
Pricing and Valuation of Fixed Income Instruments
The price of a bond is determined by discounting its future cash flows (coupon payments and principal repayment) to the present value using the market interest rate.
Understanding these concepts helps investors assess whether a bond is appropriately priced relative to market conditions.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Tax Implications and Regulations
Tax treatment of fixed income securities varies by jurisdiction and type.
Investors should consider the after-tax return when evaluating fixed income investments and consult tax professionals for personalized advice.
Fixed Income Portfolios and Investment Strategies
Building a strong fixed income portfolio requires careful planning to balance risk and return. Investors can manage their bond investments effectively with techniques like laddering. This involves choosing securities with staggered maturities to reduce reinvestment risk. The barbell strategy provides another method. It combines short-term and long-term bonds to improve yield and keep the portfolio flexible. Alternatively, the bullet strategy focuses on bonds that mature at the same time, which allows for precise timing with specific future financial needs. Successful fixed income investing depends on broad diversification across different issuers, sectors, and maturity dates. This approach helps reduce potential risks while possibly improving overall portfolio performance. By using these thoughtful strategies, investors can build a strong fixed income portfolio that meets their specific financial goals with more confidence and clarity.
Role in Diversification and Capital Preservation
Fixed income securities play a crucial role in investment portfolios by:
These attributes make fixed income securities essential for conservative investors and those nearing retirement.
Trading and Market Infrastructure
Absolutely. Here’s the exact same content you gave me, now restructured using only the tags you specified no change to wording, just layout:
Let me know when you’re ready for another batch I’ll keep the format locked in just how you like it.
Trends in the Global Fixed Income Market
The fixed income market is influenced by various global trends:
Staying informed about these trends is vital for making strategic investment decisions in the fixed income space.



