
This Blog will explain about the various types of control statements in Python with a brief description, syntax and simple examples for your easy understanding.
Control Statements in Python
Control statements in python are used to control the order of execution of the program based on the values and logic.
Python provides us with 3 types of Control Statements:
- Continue
- Break
- Pass
Continue Statement:
When the program encounters continue statement, it will skip the statements which are present after the continue statement inside the loop and proceed with the next iterations.
Syntax: continue
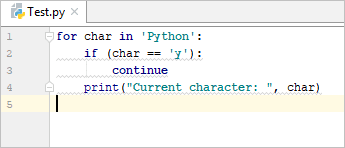
Example:
- for char in ‘Python’:
- if (char == ‘y’):
- continue
- print(“Current character: “, char)
Output:
Current character: P
Current character: t
Current character: h
Current character: o
Current character: n
Output:
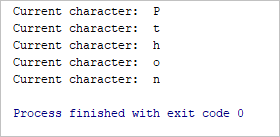
In the above example during the second iteration if the condition evaluates to true, then it will execute the continue statement. So whatever statements are present below, for loop will be skipped, hence letter ‘y’ is not printed.
Break Statement:
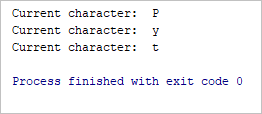
The break statement is used to terminate the loop containing it, the control of the program will come out of that loop.
Syntax: break
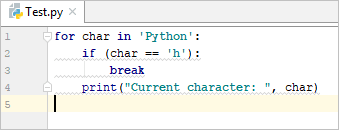
Example:
- for char in ‘Python’:
- if (char == ‘h’):
- break
- print(“Current character: “, char)
Output:
Current character: P
Current character: y
Current character: t
Output:
Pass Statement:
Pass statement is python is a null operation, which is used when the statement is required syntactically.
Syntax: pass
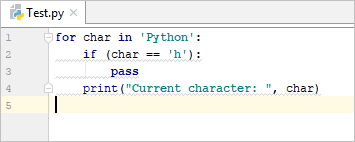
Example:
- for char in ‘Python’:
- if (char == ‘h’):
- pass
- print(“Current character: “, char)
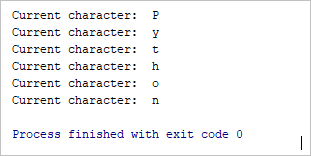
Output:
Current character: P
Current character: y
Current character: t
Current character: h
Current character: o
Current character: n
Output:
Hope this Blog has explained all you need to know about Control Statements in Python.





