
The Cisco Certified Network Associate, or CCNA, is a widely accepted certification that attests to one’s proficiency with networking principles. Network access, IP connectivity, IP services, security principles, automation, and programmability are just a few of the many areas it addresses. Getting certified as a CCNA verifies the knowledge and abilities needed for entry-level networking positions and acts as a springboard for additional Cisco certifications. Because it denotes expertise in setting up, running, and debugging small to medium-sized enterprise networks, it is highly esteemed in the industry.
1. What is the OSI model? Describe each stratum?
Ans:
The OSI model (Open Systems Interconnection model) is a conceptual framework used to understand and implement network protocols in seven layers.
- Physical: Deals with the hardware connection and transmission of raw binary data over a medium.
- Data Link: Manages error detection, correction, and framing of data packets.
- Network: Handles routing, forwarding, and addressing of data packets.
- Transport: Ensures reliable data transfer, error recovery, and flow control.
- Session: Manages sessions and controls dialogues between applications.
2. What are the differences between the TCP/IP model and the OSI model?
Ans:
The Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Interface layers make up the four layers of the TCP/IP model. Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, and Physical are the seven layers that make up the OSI model. The top three levels of the OSI model are combined into the Application layer of TCP/IP. Whereas OSI is more theoretical, TCP/IP is used in practice more frequently. The internet is built on TCP/IP, whereas OSI is more of a reference model.
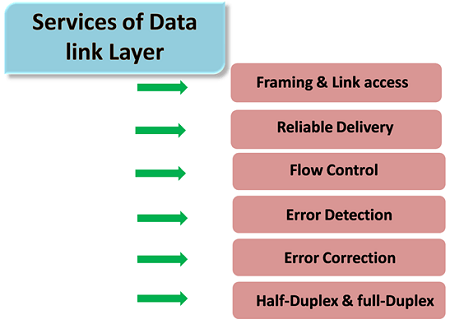
3. What is the purpose of the Data Link layer?
Ans:
- Framing: Divides the data into frames and provides proper formatting.
- Flow Control: Manages data flow to prevent congestion.
- Logical Link Control (LLC): Provides error and flow control and frames synchronization.
4. What are the distinctions between UDP and TCP?
Ans:
| Feature | UDP | TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connectionless | Connection-oriented |
| Reliability | Unreliable | Reliable |
| Flow control | No congestion control | Congestion control and flow control |
| Usage | Real-time applications | Applications requiring reliability |
| Examples | VoIP, streaming, online gaming | Web browsing, email, file transfer |
5. What is a subnet mask, and why is it used?
Ans:
- Network Segmentation: Dividing an extensive network into smaller, manageable sub-networks.
- Efficient IP Addressing: Reducing IP address wastage by allocating addresses based on need.
- Improved Security: Isolating network segments can improve security by controlling access.
- Optimized Performance: Smaller subnets reduce broadcast traffic and improve overall network performance.
6. How does a switch differ from a router?
Ans:
A switch connects multiple devices within the same local area network (LAN) and forwards data using MAC addresses. It typically features several Ethernet ports to accommodate these connections. In contrast, a router connects different networks, such as linking a LAN to a wide area network (WAN), and routes data based on IP addresses. Routers generally have fewer ports, which are used primarily for network connections rather than for connecting individual devices.
7. What is VLAN and why is it important?
Ans:
A virtual local area network, or VLAN, is a logical grouping of connected devices that, even though they are physically apart, enable communication as though they are on the same physical network. It’s significant because, by dividing traffic into distinct groups, it increases network security, lowers broadcast traffic, boosts network efficiency, and offers network managers more flexibility.
8. What is the process of ARP?
Ans:
In a local network, the Address Resolution mechanism (ARP) is a mechanism that maps an IP address to a physical MAC address. An ARP request broadcast with the IP address it want to reach is sent by a device when it needs to communicate with another device. In response, the IP-assigned device provides its MAC address. This mapping is then cached by the requesting device for later usage, enabling effective network connection.
9. What are the different types of network topologies?
Ans:
- Star Topology: All devices connect to a central hub or switch. Easy to manage but dependent on the central hub.
- Ring Topology: Devices form a closed loop. Data travels in one direction, reducing collisions, but failure in one device affects the whole network.
- Mesh Topology: Every device connects to every other device. It is highly redundant but complex and expensive.
10. What is a MAC address?
Ans:
A network interface card (NIC) is given a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address for Data Link layer communication. The address consists of forty-eight bits and is commonly expressed as 12 hexadecimal numbers (00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E, for example). On a local network, the MAC address guarantees that data packets are sent to the appropriate hardware device.
11. How does DNS work in a networking context?
Ans:
Human-readable domain names, like www.example.com, are translated into IP addresses, such as 192+.0.2.1, via the DNS (Domain Name System). Users can now visit websites without having to memorize IP addresses in numeric form. DNS also helps with load distribution, geographical load balancing, email routing, and service discovery. DNS resolvers, authoritative, root, and recursive DNS servers, and the domain name space are essential parts.
12. How does DHCP work?
Ans:
- DHCP Discover: The client broadcasts a discover message to find DHCP servers.
- DHCP Offer: Servers respond with an offer message containing an available IP address.
- DHCP Request: The client accepts one offer and requests that IP address.
- DHCP ACK: The server acknowledges and assigns the IP address to the client.
13. What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
Ans:
- Address Space: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses (4.3 billion addresses), while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses (340 undecillion addresses).
- Address Format: IPv4 uses dotted-decimal format (e.g., 192.0.2.1), and IPv6 uses hexadecimal (e.g., 2001:0db8::1).
- Header Complexity: IPv4 headers are 20-60 bytes; IPv6 headers are fixed 40 bytes.
- Configuration: IPv4 often requires manual configuration or DHCP; IPv6 supports automatic configuration (SLAAC).
14. What is the purpose of NAT?
Ans:
- Static NAT: a one-to-one mapping of IP addresses, private and public.
- Dynamic NAT: This method converts private IP addresses from a pool to public ones.
- PAT (NAT Overload): This protocol uses several ports to map several private IP addresses to a single public IP address.
15. What is the concept of a default gateway?
Ans:
A default gateway is a network node (typically a router) that serves as an access point for sending packets to destinations outside the local subnet. It enables communication with external networks when the destination IP is not within the same local subnet. Devices on a local network use the default gateway to route traffic to external networks. The gateway’s IP address is usually the first or last address in the subnet range and is configured manually or via DHCP.
16. What are private IP addresses? Give examples.
Ans:
IP addresses designated for private networks are known as private IP addresses, and they cannot be routed over the public Internet. Examples include:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (Class A)
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (Class B)
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 (Class C)
17. What is the routing process?
Ans:
Routing is the process of directing data packets from one network to another based on their destination IP addresses. Routers play a crucial role in this process by analyzing the destination address, consulting their routing tables, and selecting the optimal path for forwarding packets. The routing table contains routes and their associated metrics, while routing protocols, such as OSPF and EIGRP, determine the most efficient paths. Once the best route is identified, routers transmit packets to the next hop along that route.
18. What does a routing table do?
Ans:
A routing table is a data structure that stores a list of routes to various network destinations, maintained within a router or other network devices. This table includes several key components: the destination network, which indicates the target network address; the next hop, specifying the IP address to which packets should be forwarded; the metric, representing the cost associated with the route; and the interface, which indicates the outgoing interface used for that route.
19. What is the difference between static and dynamic routing?
Ans:
- Static Routing: Manually configured routes that do not change unless manually updated. Suitable for small, stable networks.
- Dynamic Routing: Automatically updates routes based on network changes using routing protocols (e.g., OSPF, EIGRP). Suitable for more extensive, dynamic networks.
20. What are link-state and distance-vector routing protocols?
Ans:
Link-state routing protocols, like OSPF, maintain a complete map of the network and use algorithms to compute the shortest path to each destination. Distance-vector protocols, like RIP, determine the best route to a destination based on distance (hop count) and direction (vector), sharing routing tables with immediate neighbours and relying on them for path information.
21. What is the EIGRP’s objective?
Ans:
Cisco created the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), a dynamic routing protocol, to let autonomous systems make scalable and effective routing decisions. It combines the benefits of distance-vector and link-state protocols, providing fast convergence, support for VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking), and reduced network traffic due to its use of incremental updates.
22. How does OSPF operate?
Ans:
The Dijkstra algorithm is used by Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), a link-state routing protocol, to find the shortest path to each network node. Each OSPF router maintains a map of the network topology, which it builds by exchanging link-state advertisements (LSAs) with other routers. When a router detects a change in topology, it updates its map and recalculates the shortest paths to all destinations.
23. What is the function of BGP?
Ans:
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the protocol used to route data between different autonomous systems on the Internet. It controls how packets are routed over the Internet by sharing reachability and routing data across edge routers. BGP uses network administrators’ defined pathways, rules, and rule sets to determine routing. This ensures optimal data delivery and contributes to the overall stability and efficiency of Internet routing.
24. What are some standard routing protocols?
Ans:
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First): Link-state protocol that uses the Dijkstra algorithm for the shortest path first.
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol): Advanced distance-vector protocol with features of both link-state and distance-vector.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): Path-vector protocol used for routing between autonomous systems on the Internet.
- IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System): Link-state protocol used in large service provider networks.
25. What is a trunk port in a switch?
Ans:
A trunk port on a switch carries traffic for multiple VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks). It tags frames with VLAN identifiers using IEEE 802.1Q or ISL (Inter-Switch Link) encapsulation, allowing switches to manage traffic for multiple VLANs across a single physical link. This capability enhances network efficiency by optimizing bandwidth usage while maintaining network segmentation. Additionally, it simplifies network design by reducing the number of physical connections needed between switches.
26. How does STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) prevent loops in a network?
Ans:
By choosing a root bridge, identifying a single path from each non-root bridge to the root, and obstructing superfluous paths, STP avoids loops. It keeps an eye out for changes in the network’s architecture and dynamically recalculates paths to stay connected while avoiding loops. Through control over data frame forwarding, STP guarantees a network free of loops, improving performance and stability.
27. What is the primary function of HSRP?
Ans:
The Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) serves a crucial role in network infrastructure by facilitating enhanced reliability. Specifically, it enables multiple routers to collaborate, thereby presenting a unified virtual router to hosts within a LAN environment. This redundancy ensures continuous network availability, as one router can seamlessly take over if another fails, minimizing downtime and maintaining network connectivity.
28. What is the function of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), and how does it work?
Ans:
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 network protocol used to discover information about directly connected Cisco devices.
- It allows devices to share information about themselves, such as their operating system version, IP address, and capabilities.
- CDP packets are periodically sent to multicast addresses to advertise these details.
29. What is the difference between access ports and trunk ports?
Ans:
- An access port connects a single device to a switch and belongs to a single VLAN.
- It forwards untagged frames to and from the device.
- A trunk port, on the other hand, carries traffic for multiple VLANs between switches or between a switch and a router trunk ports tag frames with VLAN IDs to ensure that traffic is appropriately segregated.
30. What is the purpose of ACLs (Access Control Lists)?
Ans:
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used to control network traffic and enhance security by defining which packets are allowed or denied to pass through network devices based on criteria such as IP address, protocol type, and port number. ACLs can be applied to routers, switches, and other network devices to filter traffic at various points in the network.
31. What is the mechanism behind Quality of Service (QoS), and how does it operate?
Ans:
Quality of Service (QoS) is a set of technologies that manage network resources to ensure the performance of critical applications. It prioritizes specific traffic types, controls bandwidth allocation, and manages network congestion. Key techniques include traffic classification, traffic shaping, policing, and queuing to optimize packet transmission. By implementing QoS, organizations can enhance user experiences and maintain the reliability of essential services during peak usage times.
32. How do standard and extended ACLs differ?
Ans:
Standard Access Control Lists (ACLs) primarily filter traffic based on source IP addresses, offering a straightforward approach to access control. They are suitable for basic filtering needs. Conversely, extended ACLs provide a more comprehensive filtering capability, as they can consider various criteria such as source and destination IP addresses, protocols (e.g., TCP, UDP, ICMP), and port numbers.
33. What are the steps to configure an ACL on a Cisco router?
Ans:
- Go into the mode of global configuration.
- Use the “access-list” command to define the ACL.
- Indicate which assertions for desired traffic are allowed or denied.
- Utilize the “ip access-group” command to apply the ACL to an interface.
- Use the command “show access-lists” to confirm the ACL configuration.
34. What is the purpose of port security?
Ans:
Port security is a feature used on network switches to restrict the devices that can connect to a specific port. This helps mitigate threats such as MAC address flooding and unauthorized network access. Administrators can configure port security to allow a certain number of devices, define specific MAC addresses, and specify actions (e.g., shutdown, restrict, or protect) when violations occur.
35. What is the function of VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP), and how does it work?
Ans:
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) manages VLAN configuration consistency across a network by propagating VLAN definitions to all switches within a VTP domain. A VTP server maintains the VLAN database and advertises changes to VTP clients, ensuring all switches have the same VLAN configuration. VTP simplifies management, reduces configuration errors, and eases administration, particularly in large networks with multiple switches.
36. What is the difference between inter-VLAN routing and intra-VLAN routing?
Ans:
Inter-VLAN routing refers to the process of routing traffic between different VLANs. It typically involves a Layer 3 device (router or Layer 3 switch) to route packets between VLANs, allowing devices in separate VLANs to communicate. In contrast, intra-VLAN routing deals with traffic within the same VLAN. Since VLANs are broadcast domains, devices within the same VLAN can communicate directly through Layer 2 switching without needing routing.
37. What role does EtherChannel serve?
Ans:
- EtherChannel technology consolidates several physical Ethernet links into a unified logical link, aiming to boost bandwidth and ensure redundancy.
- Its primary objective is to enhance network performance and reliability by combining multiple connections, thereby improving data transfer rates and bolstering fault tolerance.
- In the event of a link failure within the EtherChannel, traffic is seamlessly rerouted across the remaining operational links, guaranteeing uninterrupted connectivity.
38. How does a firewall enhance network security?
Ans:
A firewall enhances network security by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It can block unauthorized access, prevent cyberattacks, filter harmful content, and log security events. Firewalls offer a strong defence against a range of security concerns since they may be set to accept or prohibit traffic based on protocols, port numbers, IP addresses, and application-specific elements.
39. What is the concept of NAT overload, also known as Port Address Translation (PAT)?
Ans:
Port Address Translation (PAT), sometimes referred to as NAT overload, is a networking technique that enables employing a single public IP address to browse the Internet across several devices connected to a private network. It achieves this by assigning unique port numbers to each connection originating from the private network. These port numbers differentiate between the various connections, allowing the NAT router to keep track of which internal device requested each connection.
40. What is a broadcast domain?
Ans:
All other devices receive any broadcast packet sent by a device in a broadcast domain in that logical segment of the network. Routers bound broadcast domains, as routers do not forward broadcast traffic. Within a broadcast domain, devices can directly communicate using broadcast frames. This facilitates efficient communication among devices, while minimizing unnecessary traffic in other network segments.
41. What constitutes a collision domain?
Ans:
- A collision domain denotes a portion of a network where data packets may intersect, potentially causing congestion and necessitating retransmissions.
- Collisions are prevalent in conventional Ethernet hubs and bus setups, where numerous devices utilize a shared communication medium.
- With each port on a switch delineating a distinct collision domain, devices are effectively segregated, diminishing the likelihood of collisions.
42. What is the process of network address translation (NAT)?
Ans:
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a router function used to convert private (non-routable) IP addresses from a local network into either a single public IP address or a range of public IP addresses. This NAT process aids in conserving public IP addresses and provides an additional layer of security by concealing internal network structures from external entities.
43. What are some common wireless networking standards?
Ans:
Several wireless networking standards are commonly utilized, encompassing:
- 802.11b: This standard operates within the 2.4 GHz frequency range and achieves a maximum speed of 11 Mbps.
- 802.11g: Similarly functioning at 2.4 GHz, it provides increased speeds of up to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11n: This standard operates across both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies, offering enhanced speeds of up to 600 Mbps.
- 802.11ac: Functioning specifically within the 5 GHz spectrum, it delivers impressive speeds surpassing 1.3 Gbps.
44. How does WPA2 differ from WEP in wireless security?
Ans:
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) represents a significant advancement in security measures compared to its predecessor, WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). Employing the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption, renowned for its formidable security, WPA2 outshines the RC4 algorithm employed by WEP in terms of robustness and resilience.
45. What is the purpose of a DMZ in network security?
Ans:
In network security, a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) is a physical or logical subnet that separates an internal local area network (LAN) from untrusted external networks (e.g., the Internet). This setup limits the internal network’s exposure to potential attacks while still allowing public access to certain services. By isolating these services, the DMZ enhances security by providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive internal resources.
46. How do VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) work?
Ans:
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create a secure, encrypted connection, or tunnel, over less secure networks like the Internet. They use various protocols, such as IPsec, OpenVPN, and L2TP, to establish and maintain this secure connection. By routing traffic through the VPN server, users can mask their IP addresses and access resources as if they were on a private network. This added layer of security is especially valuable for remote workers and businesses that handle sensitive information.
47. What are the differences between site-to-site and remote-access VPNs?
Ans:
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Connect entire networks, typically between different office locations of the same organization. They allow networks in various geographical locations to share resources securely as if they were on the same local network.
- Remote-Access VPNs: Allow individual users to connect to a private network from a remote location. Employees commonly use this type of VPN to access their organization’s network securely from home or while travelling.
48. Describe the function of a proxy server.
Ans:
Between client devices and other internet servers, a proxy server serves as a middleman. It receives client requests for web resources, forwards these requests to the appropriate servers, and then returns the responses to the clients. Proxy servers can improve security, enhance privacy, cache content for faster access, and control user access to specific resources. They can also hide the client’s IP address from the target server, providing an additional layer of anonymity.
49. What is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)?
Ans:
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a data-carrying technique used in high-performance telecommunications networks. By encapsulating packets from different network protocols, MPLS provides effective and scalable routing and switching while also enhancing data traffic flow speed and control. This technology enables more efficient management of network resources and improves overall network performance, making it ideal for large-scale enterprise applications.
50. How does an IPsec VPN differ from an SSL VPN?
Ans:
- IPsec VPN: Employing the IPsec protocol suite, this VPN secures Internet Protocol (IP) communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet within a communication session. It is commonly utilized for site-to-site VPNs and necessitates client software for remote access.
- SSL VPN: Often accessed via a web browser, it offers simplicity in usability and management without the requirement for specialized client software.
51. What is a WAN (Wide Area Network)?
Ans:
A communications network that spans a substantial geographic area is known as a WAN (Wide Area Network). By connecting numerous smaller networks, such as metropolitan area networks (MANs) or local area networks (LANs), WANs enable resource sharing and communication between nations, continents, and even individual cities. One of the most prominent examples of a WAN is the Internet.
52. What are the differences between a LAN and a WAN?
Ans:
- LAN (Local Area Network): This type of network covers a small geographic area, such as a single building or campus. It offers high data transfer speeds and low latency. LANs are typically owned, managed, and maintained by a single organization.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): This type of network covers a large geographic area, often a city, country, or global area. Compared to LANs, WANs typically have slower data transfer speeds and higher latency. They can be privately owned or leased from telecommunication providers and require more complex management.
53. What is the purpose of a CSU/DSU in a WAN environment?
Ans:
A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) is a device used to connect a digital leased line to a router in a WAN environment. It converts the digital data from the router into a format suitable for transmission over the leased line and vice versa. Essentially, it serves as a modem for digital signals, ensuring proper synchronization and data integrity over the WAN link.
54. What are some standard WAN technologies?
Ans:
Common WAN technologies include:
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- Frame Relay
- ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
- Leased Lines (T1/E1, T3/E3)
- ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
55. How does Frame Relay work?
Ans:
Frame Relay is a WAN technology that provides fast and efficient packet-switched data transmission. It works by establishing a permanent virtual circuit (PVC) between two endpoints. Data is transmitted in variable-sized units called frames, which are relayed through switches in the network. Frame Relay uses a simplified protocol that eliminates much of the overhead found in other packet-switched technologies, resulting in higher performance and lower costs for end users.
56. What is the concept of point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connections?
Ans:
Point-to-point connections involve the direct communication between two endpoints, forming a single path. It’s like a conversation between two people where each message is sent and received directly. Conversely, point-to-multipoint connections allow one sender to communicate with multiple receivers simultaneously. It’s akin to a broadcast, where one speaker addresses many listeners.
57. What is the purpose of SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)?
Ans:
SNMP, or Simple Network Management Protocol, serves the purpose of monitoring and managing network devices and their functions. It allows administrators to collect information about devices on a network, monitor performance, detect and solve network problems, and even configure devices remotely. SNMP operates by sending messages, called “protocol data units” (PDUs), between the management station (the system monitoring the network) and the managed devices (such as routers, switches, and servers).
58. What steps are involved in setting up a basic switch configuration?
Ans:
- Connect the switch to power and the network devices using Ethernet cables.
- Then, use a terminal emulation program to access the switch through its console port.
- Enter the switch’s command-line interface (CLI), configure basic settings such as hostname, IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway, and enable management features like Telnet or SSH.
- Configure VLANs (if needed) to logically segregate network traffic.
59. What steps can be taken to secure a Cisco router?
Ans:
A Cisco router must be secured with various techniques to prevent attacks and unauthorized access. This includes using strong passwords, enabling encryption for remote access protocols like SSH or HTTPS, configuring access control lists (ACLs), disabling unnecessary services, enabling DHCP snooping and port security, implementing VLANs for network segmentation, regularly updating firmware, and monitoring logs for suspicious activity.
60. What is the purpose of a console port on a router?
Ans:
A router’s console port serves as a physical interface for local management and configuration. With a console cable and a terminal emulator (like PuTTY or HyperTerminal) to access the command-line interface (CLI), administrators can connect directly to the router. This direct access is crucial for initial configuration, troubleshooting, and recovery tasks, especially when remote access methods (like SSH or Telnet) are unavailable or disabled.
61. What are the steps to back up and restore a Cisco IOS configuration?
Ans:
- Use commands like “show running-config” to display the current configuration and “copy running-config tftp” to save it to a TFTP server.
- For restoration, retrieve the configuration file from the TFTP server using the “copy tftp running-config” command and confirm the changes with “show running-config.”
- Save the restored configuration to non-volatile memory with “write memory” to ensure it persists after a reboot.
62. What is a Cisco IOS image, and how to upgrade it?
Ans:
The operating system software that powers Cisco switches and routers and offers network and management features is called a Cisco IOS image. It includes features like routing protocols, security mechanisms, and device management tools. Upgrading a Cisco IOS image involves obtaining the new image file from Cisco’s website or a trusted source, transferring it to the device’s flash memory using protocols like TFTP or FTP, and installing the new image using the “boot system” and “reload” commands.
63. Explain the difference between the enable and configure modes in a Cisco device.
Ans:
Enable mode and configure mode are two operational modes in Cisco devices like routers and switches. Enable mode, also known as privileged EXEC mode, grants access to all device commands and configurations, including those that can modify the device’s settings and affect its operation. Configure mode, on the other hand, is a subset of enable mode that focuses specifically on configuring device parameters, such as interface settings, routing protocols, and security policies.
64. What is the purpose of the Cisco three-layer hierarchical model?
Ans:
- The Cisco three-layer hierarchical model is a network design framework that organizes network functionality into three distinct layers: the core layer, the distribution layer, and the access layer.
- The purpose of this model is to provide scalability, flexibility, and efficient traffic management within a network infrastructure.
- The distribution layer controls traffic flow between the core and access layers, implementing policies like access control and Quality of Service (QoS).
65. What is the function of a distribution layer switch?
Ans:
The distribution layer switch plays a critical role in the Cisco three-layer hierarchical model by providing aggregation and distribution of network traffic between the core and access layers. It acts as a boundary between the high-speed core backbone and the lower-speed access layer, facilitating efficient traffic routing, filtering, and policy enforcement. Distribution layer switches typically perform functions such as VLAN trunking, routing between VLANs, Quality of Service (QoS) classification and prioritization, and access control through ACLs.
66. What are some best practices for network design?
Ans:
Best practices for network design include considerations for scalability, reliability, security, and performance. It’s essential to plan for future growth by designing a network that can accommodate increased traffic and new devices without significant redesigns. Mechanisms for redundancy and fault tolerance, such as backup power sources, failover protocols, and redundant communications, aid in ensuring continuous functioning.
67. What role does the network core layer serve?
Ans:
The core layer of a network is crafted to facilitate swift and dependable data transmission among different distribution layers within a vast network infrastructure. Its principal objective is to oversee the efficient routing and switching of data, guaranteeing peak performance and minimal latency. This layer frequently utilizes high-capacity routers and switches to manage the substantial flow of data traffic proficiently.
68. What steps can be taken to troubleshoot a network connectivity issue?
Ans:
- Identify the Problem: Understand the scope and nature of the issue (e.g., specific device, entire network).
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure cables, routers, and switches are correctly connected and powered.
- Ping Tests: Use ping to check connectivity between devices.
- Check IP Configuration: Verify IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateways.
- Review Logs: Analyze logs on network devices to identify issues.
69. What are some standard network troubleshooting tools?
Ans:
- Ping: Tests connectivity between devices.
- Traceroute: Traces the path data takes to a destination.
- Wireshark: Captures and analyzes network packets.
- Nslookup: Queries DNS servers.
- Netstat: Displays network connections and statistics.
70. What are the steps to perform a packet capture on a network?
Ans:
- Install Packet Capture Software: Use tools like Wireshark.
- Select the Network Interface: Choose the network interface to capture traffic.
- Start Capture: Begin the capture process to collect packets.
- Filter Traffic: Use filters to focus on specific traffic types.
- Analyze Captured Packets: Examine the captured packets to identify issues or analyze traffic patterns.
71. What is the purpose of a loopback interface on a router?
Ans:
A loopback interface on a router serves multiple purposes. Primarily, it is a virtual interface that is always up, provided the router is up and running. This makes it extremely useful for network management and troubleshooting. It provides a stable and consistent IP address that can be used for router identification and management and as a stable endpoint for protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
72. What is the concept of redundancy in networking?
Ans:
Redundancy in networking is the practice of providing multiple paths or backup systems to ensure network availability and reliability. This can include redundant hardware (e.g., duplicate routers, switches), redundant links (e.g., multiple connections between network devices), and redundant configurations (e.g., dual-homed connections). Redundancy enhances network resilience, uptime, and reliability, which is crucial for mission-critical applications.
73. What constitutes load balancing, and how is it accomplished?
Ans:
This process optimizes resource utilization, reduces response times, and mitigates the risk of overload. Load balancing is achieved through either hardware, such as load balancers, or software solutions employing load balancing algorithms. These solutions monitor the status and performance of servers or paths and allocate traffic according to predetermined rules or real-time conditions. Standard methods include round-robin, least connections, and hash-based distribution.
74. What is the purpose of a DHCP relay agent?
Ans:
- A DHCP relay agent enables DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) clients to obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server that is not on the same local subnet.
- It forwards DHCP requests from clients to the DHCP server and relays the server’s responses back to the clients.
- This is crucial in large networks, as a centralized DHCP server manages IP address allocation across subnets, simplifying administration and reducing the need for multiple servers.
75. What is a virtual LAN (VLAN)?
Ans:
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical grouping of devices on one or more physical LANs that are configured to communicate as if they are on the same physical LAN, regardless of their actual physical location. VLANs improve network management by segmenting traffic, enhance security by isolating sensitive data, and optimize performance by reducing broadcast domains.
76. What are the steps to configure inter-VLAN routing on a router?
Ans:
- Create VLANs on the switch and as ign ports to the respective VLANs.
- Assign IP addresses to the VLAN interfaces on the router.
- Enable routing on the router.
- Trunk the connection between the router and switch to carry multiple VLAN traffic using 802.1Q encapsulation.
77. What is the difference between routing and switching?
Ans:
Routing and switching serve different purposes in a network. Switching occurs at Layer 2 (Data Link layer) of the OSI model and involves moving data packets within the same network or VLAN based on MAC addresses. Switches create and manage a MAC address table to efficiently direct traffic. Routing, on the other hand, occurs at Layer 3 (Network layer) and involves moving packets between different networks or subnets based on IP addresses.
78. What is the function of a DNS server?
Ans:
A DNS server plays a vital role in the internet ecosystem by translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. It manages client queries, caches responses to expedite future requests, and ensures the reliability of domain resolution through load balancing and redundancy. With DNS servers, accessing websites and online services would be easier, as users would have to remember and input numerical IP addresses instead of convenient domain names.
79. What components are essential in a wireless network?
Ans:
- Access points (APs) facilitate wireless connections, allowing devices to link with a wired network via Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols.
- Wireless Clients are gadgets such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and IoT devices that are engaged in network connectivity.
- Wireless Network Interface Cards (NICs): Hardware enabling devices to join the wireless network.
- Router: Directs data movement between the wireless network and other networks, including the Internet.
80. What is the process behind how Wi-Fi encryption works?
Ans:
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): An older encryption standard, less secure due to vulnerabilities.
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): This rotocol improves security over WEP and uses TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol).
- WPA2: More secure, using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for more robust encryption.
- WPA3: The latest standard, providing enhanced security with Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) for better key exchange and protection against brute-force attacks.
81. What is the purpose of a network access server (NAS)?
Ans:
Users can access a network remotely through the use of a Network Access Server (NAS). It regulates access, maintains connections, and authenticates user credentials. Network Access Points (NAS) enable efficient and safe communication between distant users and network resources. Features like user authorization, firewall protection, and VPN support are frequently included. All things considered, network security and accessibility are greatly enhanced by NAS.
82. What is the process of wireless roaming?
Ans:
- Decision Making: The device decides to switch to a new AP if the current signal is weak or if a more robust AP is found.
- Authentication: The device authenticates with the new AP, often using cached credentials to speed up the process.
- Reassociation: The device reassociates with the new AP, which updates its client table and informs the network of the handoff.
- Data Continuity: Ensures ongoing sessions and data transfers are maintained without interruption.
83. What is a rogue access point, and how to detect it?
Ans:
- Network Scanning: Regularly scan for unauthorized devices using network monitoring tools.
- Wireless intrusion Detection Systems (WIDS): Monitor for suspicious devices and activities.
- Physical Inspection: Regularly check the physical premises for unauthorized hardware.
- Signal Analysis: Analyze the network for unknown signals or unusual traffic patterns.
84. How is network segmentation implemented?
Ans:
In order to perform network segmentation, a network is divided into smaller subnetworks or segments according to user access levels, security constraints, or other criteria. Usually, routers, firewalls, and VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) are used to accomplish this. Segmentation aids in traffic flow management, security breach mitigation, and the isolation of sensitive data. It narrows the range of possible problems, which improves network performance and makes management easier.
85. What is the purpose of a security policy in networking?
Ans:
- Risk Management: Identify and mitigate risks to network security.
- Access Control: Define who can access network resources and under what conditions.
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to legal, regulatory, and organizational requirements.
- Incident Response: Outline procedures for responding to security incidents.
- User Education: Inform users about their responsibilities and best practices for maintaining network security.
86. What is the role of a network administrator?
Ans:
- Network Configuration: Set up and configure network devices such as routers, switches, and APs.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor network performance and security.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose and resolve network issues.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate documentation of network configurations and changes.
- User Support: Provide technical support to users and address connectivity issues.
87. What are the benefits of using network simulation tools like GNS3 or Cisco Packet Tracer?
Ans:
Tools for network simulation, such as GNS3 or Cisco Packet Tracer, have several advantages for both individuals and businesses. The affordable learning environment they offer is one of their biggest benefits. Without the need for pricey physical hardware, users can experiment with different network setups, saving money and resources. Furthermore, without affecting actual network infrastructure, these tools provide a risk-free environment for testing various scenarios and troubleshooting problems.
88. What are several typical network performance indicators?
Ans:
- Bandwidth: Signifying the peak data transfer capacity of a network.
- Throughput: Reflecting the actual rate of successful data transmission.
- Latency: Denoting the duration for data to traverse from its source to its destination.
- Packet Loss: quantifying the percentage of lost packets during transmission.
89. What are the steps to configure a static route on a router?
Ans:
- Access the Router Interface: Log in to the router’s management interface.
- Enter Configuration Mode: Use the appropriate command to enter configuration mode (e.g., configure terminal on Cisco devices).
- Add the Static Route: Use the command to add a static route, specifying the destination network, subnet mask, and next-hop IP address (e.g., IP route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1).
- Save Configuration: Save the configuration to ensure the static route persists after a reboot (e.g., write memory or copy running-config startup-config).
90. What measures can be take to ensure network scalability?
Ans:
- Modular Design: Use a modular approach to add new components easily.
- High-Capacity Devices: Invest in devices that support higher capacity and throughput.
- Virtualization: Use virtualized resources to scale efficiently.
- Cloud Services: Leverage cloud infrastructure for flexible scaling.






